Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
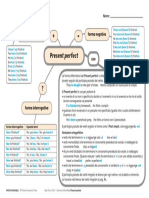
Past Simple
Caricato da
Pabla PicassoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Past Simple
Caricato da
Pabla PicassoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
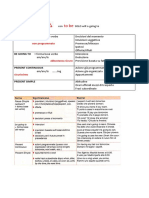
PAST
SIMPLE
Si usa per azioni o situazioni avvenute nel PASSATO ma che sono CONCLUSE
When he was young, he always walked to school.
I lived in Rome for two years, then I went to work in Japan.
ATTENZIONE
Ho visto quel film la settimana scorsa L’azione è passata e il tempo è finito.
I saw that movie last week. > Past Simple.
Ho visto quel film. L’azione è finita, ma il tempo in cui si è svolta non è detto.
I have seen that movie. > Present Perfect
Ho visto quel film questa settimana Il tempo è espresso, ma la settimana non è ancora finita.
I have seen that movie this week. > Present Perfect
TO BE
+ Soggetto + was / were I was on holiday last week
- Soggetto + was / were + NOT He were not on holiday last week
? Was / Were + sogetto. …? Was I on holiday last week?
Verbi regolari e verbi irregolari
I verbi regolari aggiungono -ED per tutte le persone
I verbi irregolari hanno una loro forma specifica per il Past Simple
(regolari) soggetto + verbo base con -ed
+ I worked last night
(irregolari) soggetto + forma del Past Simple
- (regolari e irreg.) soggetto + DID NOT / DIDN’T + verbo base I didn’t work last night
? (regolari e irreg.) DID + soggetto + verbo base Did you work last night?
ATTENZIONE ➞ alcuni verbi regolari modificano l'ortografia:
• se il verbo finisce in -y preceduta da consonante, la y diventa i + ed:
- cry ➞ cried, try ➞ tried
• se il verbo è monosillabico, finisce in consonante preceduto da vocale,
la consonante finale raddoppia:
stop ➞ stopped
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Past SimpleDocumento1 paginaPast SimplePabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Perfect SimpleDocumento4 paginePresent Perfect SimpleAngelica PeruginiNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Perfect Vs Past Simple 2Documento8 paginePresent Perfect Vs Past Simple 2hibaouhadidNessuna valutazione finora
- Tempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoDocumento3 pagineTempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoGabriele1883Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoDocumento3 pagineTempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoStefania StöschNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento4 paginePresent PerfectAlin CesantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Riassunto TempiDocumento2 pagineRiassunto TempiErika ToninelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Tempi Verbali SchemiDocumento7 pagineTempi Verbali SchemiAurora FanaliNessuna valutazione finora
- IngleseDocumento35 pagineIngleseDaniele Bertini100% (2)
- Speak Up - Guida - VerbiDocumento7 pagineSpeak Up - Guida - Verbiscarlet.3lisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Past SimpleDocumento4 paginePast SimpleClaudioNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 VerbiDocumento3 pagine09 Verbiharra3879Nessuna valutazione finora
- PastsimpleDocumento10 paginePastsimpleLaura LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Tabella Tempi VerbaliDocumento5 pagineTabella Tempi VerbaliFrancesca Di GiamberardinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Le Forme Implicite Il Gerundio Semplice e CompostoDocumento4 pagineLe Forme Implicite Il Gerundio Semplice e CompostoewppvwwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento5 paginePresent PerfectRiccardo MonticoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento3 paginePresent Perfecteleonora baroncelliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 07bbbbbbbDocumento5 pagineLesson 07bbbbbbbFrancesco MenichinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoDocumento3 pagineTempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoAndreinaFranceschi67% (6)
- REPORTED or INDIRECT SPEECHDocumento4 pagineREPORTED or INDIRECT SPEECHRebecca LodoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Sintesi APPUNTI INGLESEDocumento5 pagineSintesi APPUNTI INGLESEDanilo MaschiNessuna valutazione finora
- Present ContinuousDocumento1 paginaPresent ContinuousPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Past Simple Vs Present PerfectDocumento3 paginePast Simple Vs Present Perfectsakura.chan190Nessuna valutazione finora
- Appunti Di Grammatica IngleseDocumento16 pagineAppunti Di Grammatica IngleseDaniele MinnoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Test GrammaticaDocumento9 pagineTest GrammaticaAntonella ComesNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple PastDocumento4 pagineSimple PastPianista VirtuosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Simple Past TenseDocumento0 pagineRevision Simple Past TenseeutiuhiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Linkers - ConnettiviDocumento12 pagineLinkers - ConnettiviCristina BahnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Past ContinuousDocumento4 paginePast ContinuousClaudioNessuna valutazione finora
- I Verbi Idiomatici 1Documento8 pagineI Verbi Idiomatici 1Markkkk1111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento2 paginePresent PerfectRuben PerraNessuna valutazione finora
- PASSATO PROSSIMO e Imperfetto COMPITIDocumento9 paginePASSATO PROSSIMO e Imperfetto COMPITINigar SultanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Past Continuous and Adverbs of MannerDocumento2 paginePast Continuous and Adverbs of MannerSarah RamaginiNessuna valutazione finora
- Il Trapassato ProssimoDocumento2 pagineIl Trapassato ProssimoFederica MascheroniNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Perfect SimpleDocumento3 paginePresent Perfect SimpleClaudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Passato ProssimoDocumento7 paginePassato ProssimoEduardoFMartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Perfect Simple Vs ContinuousDocumento1 paginaPresent Perfect Simple Vs Continuoussakura.chan190Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Five 3 Unit 3 Grammar Present Perfect CompleteDocumento1 paginaHigh Five 3 Unit 3 Grammar Present Perfect CompleteMarMat20% (1)
- TEMPI VERBALIver2011Documento12 pagineTEMPI VERBALIver2011Giulia Marelli100% (1)
- Summer Homework BeginnerDocumento17 pagineSummer Homework BeginnerwillowslandNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Perfect Simple e ContinuousDocumento2 paginePresent Perfect Simple e ContinuousGiovanna ScolloNessuna valutazione finora
- Il Pass Compos - PDFDocumento3 pagineIl Pass Compos - PDFugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Perfect - Passato ProssimoDocumento3 paginePresent Perfect - Passato ProssimoCat 1714Nessuna valutazione finora
- PRESENT SIMPLE e PRESENT CONTINUOUSDocumento2 paginePRESENT SIMPLE e PRESENT CONTINUOUSValeria VerrilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Settimana Inglesistica-1Documento4 pagineSettimana Inglesistica-1teresaNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento3 paginePresent PerfectRiccardo MonticoneNessuna valutazione finora
- I Tempi Verbali Della Grammatica Inglese in Poche RigheDocumento3 pagineI Tempi Verbali Della Grammatica Inglese in Poche RigheAnonymous xfUYiKoDWNessuna valutazione finora
- Tempi VerbaliDocumento4 pagineTempi VerbaliFederico Dal PraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ripasso Di Inglese Per La Terza MediaDocumento5 pagineRipasso Di Inglese Per La Terza MediaAleNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento11 paginePresent PerfectFrancesca PiccirilliNessuna valutazione finora
- ItakDocumento5 pagineItakjoff_grNessuna valutazione finora
- Lezione ItalianoDocumento8 pagineLezione ItalianoLaura De MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nozioni Grammaticali 2.2Documento17 pagineNozioni Grammaticali 2.2Laura D'OsualdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Il Passato ProssimoDocumento3 pagineIl Passato ProssimoMarta RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- English 6Documento6 pagineEnglish 6Marina KrasikovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Appunti PRESENT SIMPLEDocumento4 pagineAppunti PRESENT SIMPLECarlotta MauriziNessuna valutazione finora
- Passato Prossimo - e - ImperfettoDocumento19 paginePassato Prossimo - e - ImperfettoSabrina Pani100% (1)
- Past ContinuousDocumento7 paginePast ContinuousAngelica PeruginiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pillole di Inglese: 1.Avverbi 2.Pronomi Relativi 3.Verbi ModaliDa EverandPillole di Inglese: 1.Avverbi 2.Pronomi Relativi 3.Verbi ModaliValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- FuturoDocumento1 paginaFuturoPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present SimpleDocumento1 paginaPresent SimplePabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present ContinuousDocumento1 paginaPresent ContinuousPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento1 paginaPresent PerfectPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present SimpleDocumento1 paginaPresent SimplePabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present CONTINUOUSDocumento1 paginaPresent CONTINUOUSPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Present PerfectDocumento1 paginaPresent PerfectPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- FuturoDocumento1 paginaFuturoPabla PicassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Appunti Topografia-Idoneità-4°Documento43 pagineAppunti Topografia-Idoneità-4°salvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sine Requie EditabileDocumento1 paginaSine Requie EditabileMitic93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Psicologia Sociale - L'aggressivitàDocumento10 paginePsicologia Sociale - L'aggressivitàMatteoRagneddaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pragmatica Della Comunicazione Umana Processi e Dinamiche Di GruppoDocumento35 paginePragmatica Della Comunicazione Umana Processi e Dinamiche Di GruppoChiara BreciNessuna valutazione finora