Ancient Bones And Teeth Found In A Philippine Cave May Rewrite Human History
Islands in Southeast Asia were clearly important in the evolution of early humans, say scientists who have turned up 50,000-year-old remains of what they suspect is a previously unknown human species.
by Christopher Joyce
Apr 10, 2019
3 minutes
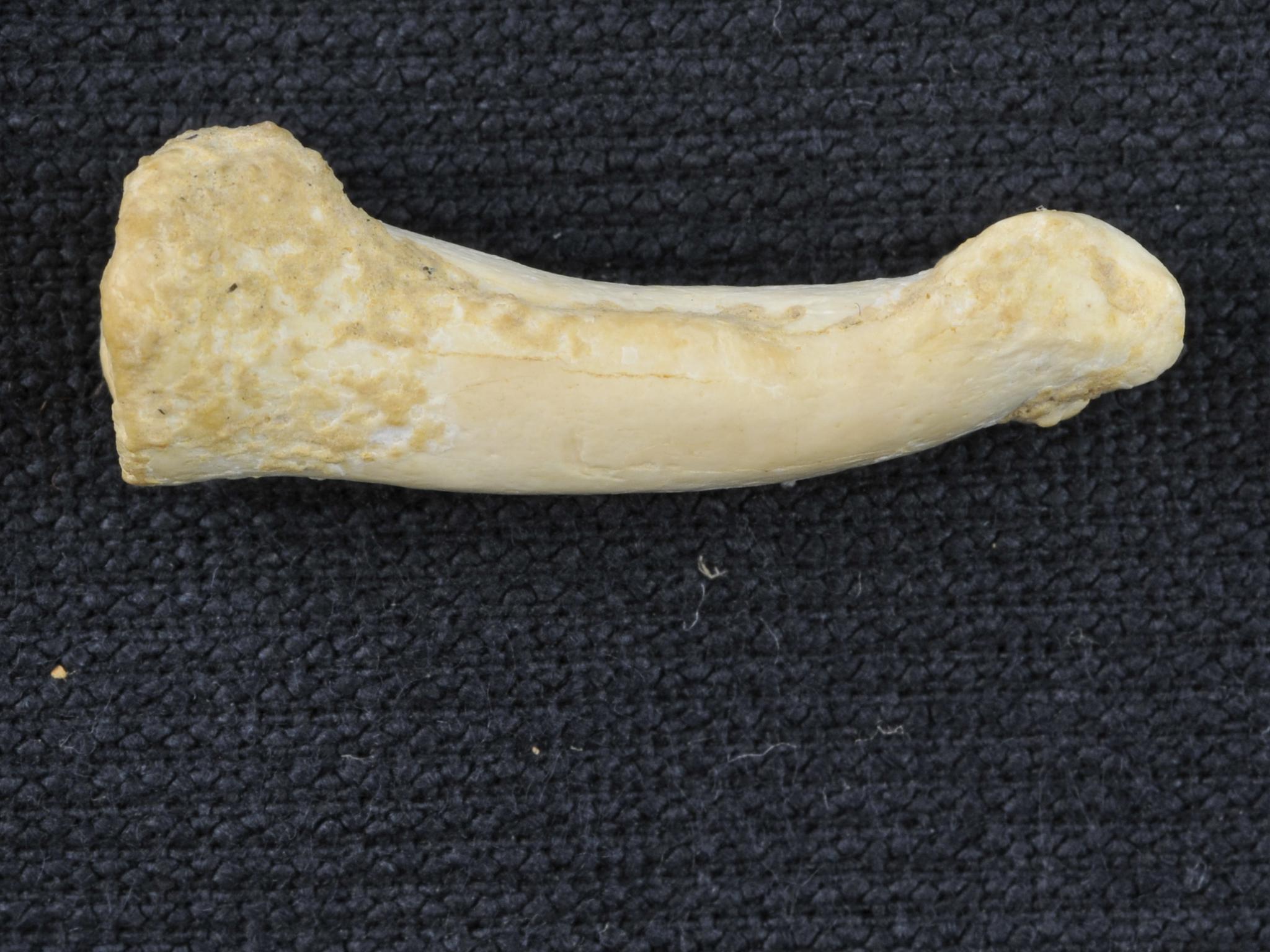
An unusual species of human apparently lived on the island of Luzon in the Philippines as recently as 50,000 years ago. Based on teeth and bones found there, scientists suspect that these early humans probably stood less than 4 feet tall and had several apelike features. Yet, the researchers say, the bones are distinctly human — from a previously undiscovered species.
The first clue was a bone that surfaced in 2007. Archaeologist was digging in a cave on the island of Luzon and found a toe bone. He says it didn't look like
You’re reading a preview, subscribe to read more.
Start your free 30 days



