Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture #1: Course Introduction: Hoh in Texas A&M University
Caricato da
HocLieuMoDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture #1: Course Introduction: Hoh in Texas A&M University
Caricato da
HocLieuMoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture #1: Course Introduction
CPSC 608: Advanced Database Systems
Hoh In
Texas A&M University
CPSC 608: L#1 1 Copyright © Hoh In
The Goals of Today
• Understand why do I need to take this Course
• Decide whether I have to continue or drop by
estimating course loading
CPSC 608: L#1 2 Copyright © Hoh In
Contents
• Prologue: CI-DBMS vs DI-DBMS
• The Theme of this Course
• Overview of the Course Structure
• Epilogue and Feedback
CPSC 608: L#1 3 Copyright © Hoh In
Prologue: CI-DBMS vs. DI-DBMS
• What is different?
– File system vs. Database
– DB vs. DBMS
– Central Integrated DBMS vs. Distributed Integrated
DBMS
CPSC 608: L#1 4 Copyright © Hoh In
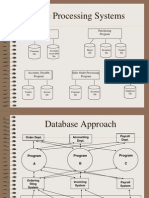
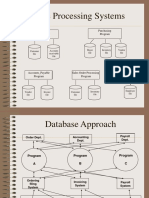
File Processing vs. Database Processing
CPSC 608: L#1 5 Copyright © Hoh In
CI-DBMS vs. DI-DBMS
CPSC 608: L#1 6 Copyright © Hoh In
Example: An Engineering Firm
CPSC 608: L#1 7 Copyright © Hoh In
What are the issues?
• Layers of Transparency
CPSC 608: L#1 8 Copyright © Hoh In
Data Independence
• A fundamental form of transparency in DBMS
• Immunity of user applications to changes in:
– the definition of data
– the organization of data
• Data Independence
– Physical data independence
• Hiding the details of the storage structure from user
applications
– Logical data independence
• Hiding logical structure of the database
CPSC 608: L#1 9 Copyright © Hoh In
Network Transparency
• Called “distribution transparency”
• Feel no difference between CI-DBMS and DI-
DBMS
• Hiding the operational details of the network
• Two types:
– Location transparency
– Naming transparency
CPSC 608: L#1 10 Copyright © Hoh In
Replication Transparency
• Data Replication
– Benefits:
• Performance (increase the locality of reference)
• Availability and Reliability (tolerance of single failure)
– Problems:
• Integrity among duplicated data
– Issues:
• The number of copies of database object
• Distribution of duplicated data
• Replication Transparency
– Hiding the operational details of duplicated data
CPSC 608: L#1 11 Copyright © Hoh In
Fragmentation Transparency
• Break each database relation down into smaller
fragments
– For performance, availability, reliability
– Two types:
• Horizontal fragmentation: divide the tuples (rows)
• Vertical fragmentation: divide the attributes (columns)
• Hiding the operational details of fragmentation
– Support a global query
• Inside the system, it will be translated into several fragment
queries
CPSC 608: L#1 12 Copyright © Hoh In
Transparency Issues
• Who should provide what transparency?
• How do existing systems fare?
CPSC 608: L#1 13 Copyright © Hoh In
Other Issues?
• Reliability
– Through Distributed Transactions
• Performance
• System Expandability
• Complexity
• Cost
• Distributed of Control
• Security
CPSC 608: L#1 14 Copyright © Hoh In
Contents
• Prologue: CI-DBMS vs DI-DBMS
• The Theme of this Course
• Overview of the Course Structure
• Epilogue and Feedback
CPSC 608: L#1 15 Copyright © Hoh In
The Theme of this Course
How to develop ………
the best …….
distributed ……
Database?
CPSC 608: L#1 16 Copyright © Hoh In
Why Database?
• An integrated collection of data elements derived
from an application
– e.g., the data associated with a banking application or
an airline reservation system
– DBMS: a software interface between the user and the
database
• Allows designers to structure their information
• Allows users to query and modify that information
• Helps manage very large amounts of data and many concurrent
operations on the data
CPSC 608: L#1 17 Copyright © Hoh In
Why Distributed?
Sales
Engineering
Accounting
Manufacturing
Shipping/ Payables/
Receiving Inventory Receivables
• Distributed Hardware needs Distributed Software !
Source: OMG Documentation
CPSC 608: L#1 Copyright © Hoh In
Future Networks
Source: OMG Documentation
CPSC 608: L#1 Copyright © Hoh In
Focus on Interoperability
• There will not be consensus on hardware platforms;
• There will not be consensus on operating systems;
• There will not be consensus on network protocols;
• There will not be consensus on application formats.
There must be consensus
on interoperability.
Source: OMG Documentation
CPSC 608: L#1 20 Copyright © Hoh In
How to define “The Best”?
• Stakeholder-sensitive
• Domain-sensitive
– Real-time systems vs. Human-life critical systems
• Situation- or Environment-sensitive
• Evolution-sensitive
– Now vs Future
CPSC 608: L#1 21 Copyright © Hoh In
Stakeholder Concern
Customer •
Schedule & Budget estimation
•
Feasibility & Risk assessment
User •
Consistency with requirements and usage
scenarios
Architecture and •
Requirements traceability
•
Support of tradeoff analysis
System Engineer •
Completeness, consistency of architecture
Developer •
Sufficient details for design
•
Reference on selecting/assembling components
Maintainer • Guidance of s/w modification and
architecture evolution
CPSC 608: L#1 22 Copyright © Hoh In
How to Develop?
• Distributed Database Design
• Distributed Query Processing
• Distributed Directory Management
• Distributed Concurrency Control
• Distributed Deadlock Management
• Reliability of Distributed DBMS
• Operating System Support
• Heterogeneous Databases
CPSC 608: L#1 23 Copyright © Hoh In
Contents
• Prologue: CI-DBMS vs. DI-DBMS
• The Theme of this Course
• Overview of the Course Structure
– Part I: Technology Review
– Part II: Distributed and Wireless Database Systems
– Part III: Group Projects
– Exams, Project, Homework Assignments
– BBS and Lab Days
• Epilogue and Feedback
CPSC 608: L#1 24 Copyright © Hoh In
Part I: Technology Review
• Distributed Computing Environment
– Distributed Infrastructure (e.g., .NET, EJB, CORBA)
– XML (e.g., WML for Wireless)
• Basic Database Review (Chapter 1 and 2)
– Relational DBMS, MS Access, Oracle DBMS
• Web Database
– Java, Servlet, Web server, ASP, JSP, SOAP
• Wireless Database
– J2ME, The .NET Compact Framework
CPSC 608: L#1 25 Copyright © Hoh In
Part II: Distributed Database Systems (DDS)
• DB Basic Concepts (Chapter 1,2)
• DDS Architecture (Chapter 4)
• DDS Design (Chapter 5)
• Semantic Data Control (Chapter 6)
• Query Processing:Decomposition,
Localization, Optimization (Chapter 7, 8, 9)
• Transaction Management (Chapter 10)
• Database Interoperability (Chapter 15)
• Database Issues (Chapter 16)
CPSC 608: L#1 26 Copyright © Hoh In
Exams (40 pts)
• Midterm I -- Test for Part I (20 points)
– To test your understanding technology review so that you are
ready to apply this knowledge to build up your distributed
database systems
• Midterm II -- Test for Part II (20 points)
– To test your understanding distributed database theories and
models.
CPSC 608: L#1 27 Copyright © Hoh In
Group Project (30 points)
• Topic: Distributed, Wireless Database Systems
• Deliverables
– Web site (all documents, source codes, useful links, etc)
– Program components; Demo; Documentation (User, Reference,
Installation Manuals)
– Demonstration for all CS/EE/other students, faculty
– Poster and 1-pager advertisement
• Grading Criteria (each - up to 5 points)
– Creativity (Something new), Difficulty, Completeness, Demo, Report,
Code Quality
– Excellent (5 pts); Very Good (4 pts); Good (3); Fair (2); Poor (1)
CPSC 608: L#1 28 Copyright © Hoh In
Homework Assignments (30 points)
• HW#1 (5 pts):
– Internet application (based on Oracle database)
• HW#2 (5 pts):
– Web-based Database application
• HW#3 (20 pts):
– Case Studies: In-depth Paper writing and presentation
• Grading for each HW:
– No return (- 100%);
– Missing capabilities, delayed, poor quality (50%)
– Satisfied (80%)
– Excellent (100%)
CPSC 608: L#1 29 Copyright © Hoh In
Lab Days
• Lab 1: MS Access
• Lab 2: Oracle & SQL
• Lab 3: Web-based Database
• Lab 4: Wireless Database Technologies
• Lab 5: DB Interoperability (.NET, EJB, CORBA)
CPSC 608: L#1 30 Copyright © Hoh In
Grading Ranges
• A: More than and equal to 90
• B: More than and equal to 80 and less than 90
• C: More than and equal to 70 and less than 80
• F: Others.
CPSC 608: L#1 31 Copyright © Hoh In
Contents
• Prologue: CI-DBMS vs. DI-DBMS
• The Theme of this Course
• Overview of the Course Structure
• Epilogue and Feedback
CPSC 608: L#1 32 Copyright © Hoh In
Epilogue and Feedback
• I want my class to be:
– Dynamic/Reflective
– Productive
– Useful (in your future career)
– Efficient and Effective
• What do you earn through this class?
CPSC 608: L#1 33 Copyright © Hoh In
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Security Freeze RequestDocumento2 pagineSecurity Freeze RequestClifford FosterNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Lesson 2 Basic Concepts For Construction DatabaseDocumento23 pagineModule 1 Lesson 2 Basic Concepts For Construction DatabaseErza LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Online ShoppingDocumento40 pagineOnline ShoppingJASPER WESSLY77% (31)
- Lesson 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocumento47 pagineLesson 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessGintoki Sakata0% (1)
- Lab3 1worksheetDocumento11 pagineLab3 1worksheetBen Oben100% (1)
- Flexible Workflow in Sales DocumentsDocumento30 pagineFlexible Workflow in Sales DocumentsBalanathan Virupasan100% (2)
- CSE494/598 Principles of Information EngineeringDocumento45 pagineCSE494/598 Principles of Information EngineeringashutoshgindauliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- AMS PresentationDocumento24 pagineAMS PresentationShowkat HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- INFO-6033 - Module 2 - Architecture Design1Documento62 pagineINFO-6033 - Module 2 - Architecture Design1anonmax121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Systems Analysis & Database Management Systems: INFS7007Documento50 pagineSystems Analysis & Database Management Systems: INFS7007Anu SachdevaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Dist Arch (Week 2) Week 3 6Documento65 pagine2 Dist Arch (Week 2) Week 3 6Muhammad Awais ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Three-Tier Architecture: Manuel Corona David NevarezDocumento59 pagineThree-Tier Architecture: Manuel Corona David Nevarezrakesh_cs_jsrNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Management System 1: E-Module inDocumento30 pagineDatabase Management System 1: E-Module inJanah Andrea RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- HWSW Co Design Unit-1notesDocumento195 pagineHWSW Co Design Unit-1notesswapna revuriNessuna valutazione finora
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocumento29 pagineFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Warehouse ArchitectureDocumento63 pagineData Warehouse ArchitectureJasper Andrew Adjarani100% (2)
- Lecture 8Documento24 pagineLecture 8mba20238Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch11 ArchitectureDocumento25 paginech11 ArchitectureSaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dbms Unit-IDocumento80 pagineDbms Unit-ILaxmi Venki100% (4)
- AN6818 Spr2024 Session 2ADocumento42 pagineAN6818 Spr2024 Session 2Atarakhila0721Nessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Computer ApplicationsDocumento28 pagineIntegrated Computer Applicationsnarmada26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Design: Schedule: MW 1:30 PM - 2:45 PM, Tahoe Hall 1026 Instructor: Dr. Sadaf AshtariDocumento31 pagineNetwork Design: Schedule: MW 1:30 PM - 2:45 PM, Tahoe Hall 1026 Instructor: Dr. Sadaf AshtariThông LạiNessuna valutazione finora
- 5-Overiview of Big Data Technologies - HadoopDocumento36 pagine5-Overiview of Big Data Technologies - HadoopWong pi wenNessuna valutazione finora
- DB IntroductionDocumento26 pagineDB IntroductionHamid RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocumento29 pagineChapter 1 IntroductionGachago MainaNessuna valutazione finora
- Redfish Introduction and OverviewDocumento20 pagineRedfish Introduction and Overviewsalist3kNessuna valutazione finora
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocumento35 pagineFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramJan Reinhart PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Management System - Ch02Documento38 pagineDatabase Management System - Ch02Osei BanningNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic3a - DB DesignDocumento20 pagineTopic3a - DB Designmeer hushyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic3b ConceptualDesignDocumento43 pagineTopic3b ConceptualDesignmeer hushyarNessuna valutazione finora
- DbmsDocumento34 pagineDbmsAbhinav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- AMD - Lecture 01Documento47 pagineAMD - Lecture 01My DataNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture2 DbmsDocumento49 pagineLecture2 DbmsUsman AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- IEC 312 - Distributed System SecurityDocumento22 pagineIEC 312 - Distributed System SecurityBhanu NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Database CH 1Documento29 pagineDatabase CH 1mehari kirosNessuna valutazione finora
- Itec411 - Network Design: Chapter 1 - Identifying Your Customer'S Needs and GoalsDocumento34 pagineItec411 - Network Design: Chapter 1 - Identifying Your Customer'S Needs and GoalsNatenael BerhanuNessuna valutazione finora
- DBMS Unit 1Documento37 pagineDBMS Unit 1Soham MahajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit01 DBMSDocumento34 pagineUnit01 DBMSayushishi0#Nessuna valutazione finora
- Software Design: Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB 0131 650 5899 Mfelici@inf - Ed.ac - UkDocumento20 pagineSoftware Design: Massimo Felici Room 1402, JCMB, KB 0131 650 5899 Mfelici@inf - Ed.ac - Ukapi-26462544Nessuna valutazione finora
- Application Layer: Schedule: MW 1:30 PM - 2:45 PM, Tahoe Hall 1026 Instructor: Dr. Sadaf AshtariDocumento52 pagineApplication Layer: Schedule: MW 1:30 PM - 2:45 PM, Tahoe Hall 1026 Instructor: Dr. Sadaf AshtariThông LạiNessuna valutazione finora
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocumento35 pagineFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramSweety RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- SEN3006-Software Architecture: Asst. Prof. Serkan AyvazDocumento406 pagineSEN3006-Software Architecture: Asst. Prof. Serkan AyvazdrogoNessuna valutazione finora
- I and C Architecture DesignDocumento65 pagineI and C Architecture DesignMvHHNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I - Introduction To DatabaseDocumento31 pagineUnit I - Introduction To DatabaseGaurav Patni100% (1)
- Database 2Documento60 pagineDatabase 2homeworktask0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Database Systems - PPTX (Repaired)Documento238 pagineFundamentals of Database Systems - PPTX (Repaired)Capt. NuhaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Management SystemsDocumento306 pagineDatabase Management SystemsSarvesh BossNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Systems Development LifecycleDocumento48 pagineDatabase Systems Development LifecyclePaylaşım KanalıNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson3 1Documento30 pagineLesson3 1PriyanshuNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Orientation - Session I: Introduction and FundamentalsDocumento41 pagineService Orientation - Session I: Introduction and FundamentalsSunil SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing Relational Database Products-2Documento43 pagineIntroducing Relational Database Products-2Dastan AkatovNessuna valutazione finora
- ©silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan 1. 1 Database System ConceptsDocumento44 pagine©silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan 1. 1 Database System ConceptsGampa SatheeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Management SystemsDocumento34 pagineDatabase Management SystemsRam Prasad Reddy SadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computational GridsDocumento40 pagineComputational GridsdaiurqzNessuna valutazione finora
- 23 - 11. Architecture DesignDocumento32 pagine23 - 11. Architecture DesignGialap DuongNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Database - PPT Compatibility ModeDocumento30 pagine9 Database - PPT Compatibility ModeBagus FatkhurroziNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1Documento36 pagineWeek 1Mohammed FoysalNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Design & ManagementDocumento45 pagineDatabase Design & ManagementyohoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1Documento57 pagineChap 1Maria ChaudhryNessuna valutazione finora
- Architecture Definition: - A "Software Architecture" Is The Structure (Or Structures) of A System, Which CompriseDocumento25 pagineArchitecture Definition: - A "Software Architecture" Is The Structure (Or Structures) of A System, Which CompriseRachelle JacosalemNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 06Documento25 pagineCH 06Ainun NadjibNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Underlying Principles of Distributed - SystemDocumento27 pagine6 Underlying Principles of Distributed - Systemselvajoe821Nessuna valutazione finora
- Application Design: Key Principles For Data-Intensive App SystemsDa EverandApplication Design: Key Principles For Data-Intensive App SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Quick Guides: Part 2 - Oracle Database DesignDa EverandOracle Quick Guides: Part 2 - Oracle Database DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- TLTKDocumento1 paginaTLTKtranthiluuNessuna valutazione finora
- QueryDocumento104 pagineQueryBinary Mass MascotNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 DesignDocumento66 pagine3 DesignJosita AedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Outline: Background Distributed DBMS ArchitectureDocumento23 pagineOutline: Background Distributed DBMS ArchitectureHocLieuMoNessuna valutazione finora
- Semantic Data ControlDocumento12 pagineSemantic Data Controlfatima_akramNessuna valutazione finora
- English For Philology (NguyenThiBichThuy)Documento102 pagineEnglish For Philology (NguyenThiBichThuy)HocLieuMo100% (1)
- © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocumento30 pagine© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedHocLieuMo100% (2)
- Distirbuted DataBase TransactionDocumento135 pagineDistirbuted DataBase Transactiongouse5815100% (1)
- Giao Trinh Toan Dai Hoc Su Pham TP - HCMDocumento163 pagineGiao Trinh Toan Dai Hoc Su Pham TP - HCMPham Huu DanhNessuna valutazione finora
- L P Trì Nh Hà M: Đ Ạ IH Ọ CB Á Ch Khoa Khoa Công Ngh Ệ Thông TinDocumento50 pagineL P Trì Nh Hà M: Đ Ạ IH Ọ CB Á Ch Khoa Khoa Công Ngh Ệ Thông TinHocLieuMoNessuna valutazione finora
- TH Iet Keung Dung ChatDocumento5 pagineTH Iet Keung Dung ChatHocLieuMoNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiprotocol Service10Documento8 pagineMultiprotocol Service10HocLieuMo100% (2)
- Gismt 05Documento1 paginaGismt 05HocLieuMoNessuna valutazione finora
- JDBC Introduction To JDBC: 1. Java - Sql. 2. Javax - Sql.Documento7 pagineJDBC Introduction To JDBC: 1. Java - Sql. 2. Javax - Sql.mrcopy xeroxNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring Framework - Notes PreparedDocumento4 pagineSpring Framework - Notes PreparedchavsNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Mining Analysis On EB Bill SystemDocumento4 pagineData Mining Analysis On EB Bill SystemBlm TbpNessuna valutazione finora
- Ext Dir ComandDocumento6 pagineExt Dir Comand006024Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course Registration System Development: OnlineDocumento45 pagineCourse Registration System Development: OnlineSukhmeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Identityserver4 Readthedocs Io en LatestDocumento238 pagineIdentityserver4 Readthedocs Io en Latestprasadz101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Devoxx Dagger2.ForExport PDFDocumento291 pagineDevoxx Dagger2.ForExport PDFIonut NegruNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is AllDebrid - How To Install and Setup All Debrid Pin On KodiDocumento7 pagineWhat Is AllDebrid - How To Install and Setup All Debrid Pin On Kodifsrom3100% (1)
- HTTP Response 500 Is Returned When Doing Connection TestDocumento2 pagineHTTP Response 500 Is Returned When Doing Connection TestFarai ZiweniNessuna valutazione finora
- Consolidated Queries ResponseDocumento201 pagineConsolidated Queries ResponseRuchir Chaturvedi100% (1)
- Os Lab ManualDocumento107 pagineOs Lab ManualYuva PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- OBR Troubleshooting GuideDocumento153 pagineOBR Troubleshooting GuideNowshathNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of A Web-Based Decision Support System For Choosing Higher Education StudiesDocumento16 pagineAnalysis and Design of A Web-Based Decision Support System For Choosing Higher Education StudiesCristian ColicoNessuna valutazione finora
- MeshCentral2UserGuide 0.2.9Documento67 pagineMeshCentral2UserGuide 0.2.9RIOTECNessuna valutazione finora
- A1 ReportDocumento15 pagineA1 Reportapi-377875723Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dim As New: Oledbconnection OledbconnectionDocumento3 pagineDim As New: Oledbconnection Oledbconnectionnarender sNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To ITBMDocumento25 pagineIntroduction To ITBMlulughoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Integration PDFDocumento43 pagineManual Integration PDFnetelsrt1298Nessuna valutazione finora
- HW 425322 1samplDocumento8 pagineHW 425322 1samplbhis PuneNessuna valutazione finora
- Asritha Pulipaka ResumeDocumento9 pagineAsritha Pulipaka Resumeanandanakshaykumar2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures 5th Edition by Barringer and IrelandDocumento41 pagineTest Bank For Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures 5th Edition by Barringer and IrelandBoqorka America0% (1)
- PHP FormDocumento11 paginePHP FormImanNessuna valutazione finora
- CompactGuardLogix Controller Safety Tag MappingDocumento2 pagineCompactGuardLogix Controller Safety Tag Mappingali_paçalNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet IP 11 EDocumento50 pagineWorksheet IP 11 EashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Processes: HistoryDocumento23 pagineOperating Processes: HistoryFadel MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Asug82651 - Sap S4hana Licensing CloudDocumento36 pagineAsug82651 - Sap S4hana Licensing CloudSAP ShoreNessuna valutazione finora