Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
BIg Mac
Caricato da
Anubhav KhannaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIg Mac
Caricato da
Anubhav KhannaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
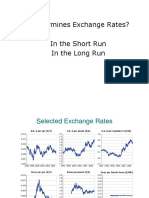
Big Mac Index
Exchange Rate
The price of one currency in terms of another is called an exchange rate. The convention is that the exchange rate is a price of domestic currency per unit of foreign currency.
For eg: Rs. 45.80 per dollar.
So if the exchange rate falls, the domestic currency is worth more.
The Big Max Index
Data for prices of the Big Mac Burger in local currency. Exchange rate of the local currency in terms of the local currency per dollar.
Implied PPP of the dollar, viz. it gives the actual purchasing power of the dollar in terms of that local currency.
Under-valuation or over-valuation of the currency. If the implied PPP is greater than the ER then we say that the local currency is overvalued. Otherwise we say that the local currency is overvalued. For eg: Chiles Peso is undervalued by 2.34%.
BigMac Price Country in Local Currency $2.54 Peso 2.50 A$3.00 Real3.60 1.99 C$2.99 Yuan9.90 Dkr24.75 2.57 HK$10.2 Forint 399 Rupiah14,700 Shekel 13.9 in US dollars $2.54 0.6868 1.6561 1.1502 3.1069 2.0974 1.1947 3.2715 2.5228 1.3792 1.6056 1.6473 2.9374
Actual Exchange Rate 1 USD = 1.00 3.64 1.8115 3.13 1.5613 1.5877 8.2868 7.5653 1.0187 7.7584 248.5 8923.8 4.732
Over(+) / Under(-) Valuation against the dollar, % -73.0769 -16.0916 -51.4377 21.7799 -17.4907 -52.9372 28.7457 -2.8173 -45.7362 -36.8209 -35.1509 15.5959
Purchasing Power Price
United States Argentina Australia Brazil Britain Canada China Denmark Euro area Hong Kong Hungary Indonesia Israel
0.98 1.52 1.52 1.28 1.31 3.90 9.74 0.99 4.21 157 5,787 5.47
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): is a measure of the relative purchasing power of different currencies. It is measured by the price of the same goods in different countries, translated by the FX rate (or exchange rate) of that country's currency against a "base currency". How to read this table: In this case, the goods is the Big Mac. For example, if a BigMac costs 1.90 in Britain and costs $2.43 in US, then the PPP exchange rate would be 1.90/2.43 = 0.7819. If the actual exchange rate is lower (for example, 0.6349 for this case), then the BigMac theory says that you should expect the value of the British Pound to go up until it reaches the PPP exchange rate. The Over/Under valuation against the dollar is calculated as: (PPP - Exchange Rate) ---------------------------------- x 100 Exchange Rate
Key Indicators of Development
Population Gross national income (GNI) $ Billions 2004 $ Per Capita 2004 PPP Gross national Gross domestic product (Per capita % growth 2003-04
(Millions) 2004
$ Billions 2004
$ Per Capita 2004
China
India Switzerland USA Thailand Japan France Germany Brazil Russian
1,296.5
1,079.7 7.4 293.5 62.4 127.8 60.0 82.6 178.7 142.8
1,676.8
674.6 356.1 12,150.9 158.7 4,749.9 1,858.7 2,489.0 552.1 487.3
1,290
620 48,230 41,400 2,540 37,180 30,090 30,120 3,090 3,410
7,170
3,347 261 11,655 500 3,838 1,759 2,310 1,433 1,374
5,530
3,100 35,370 39,710 8,020 30,040 29,320 27,950 8,020 9,620
8.8
5.4 1.3 3.4 5.4 2.5 1.9 1.5 3.9 7.7
World Income (WDR 2005)
Population Gross national income (GNI) PPP Gross national Gross domestic product (Per capita % growth 2003-04
(Millions)
$ Billions 39,833.6
$ Per Capita 6,280
$ Billions 55,584
$ Per Capita 8,760
World
6,345.1
2.9
Low income
2,338.1
1,184.3
510
5,279
2,260
4.4
Middle income High income
3,006.2
6,594.2
2,190
19,483
6,480
6.0
1,000.8
32,064.0
32,040
31,000
30,970
2.8
The Regression Model
Consider model:
the
following
regression
Yi = 1 + 2Xi +ui
where, Y = actual exchange rate X = implied PPP of the dollar Regression
Purchasing Power Parity
PPP states that exchange rates between currencies are in equilibrium when their purchasing power is the same in each of the two countries.
Types of PPP
Absolute PPP: The statement that
exchange rates equal relative price levels is referred to absolute PPP. Relative PPP: Relative PPP states that the percentage change in the exchange rate between two currencies over any period equals the difference between the percentage change in the national price levels.
Calculation of PPP
To calculate PPP, one needs to price a representative basket of goods and services across countries.
Problems with PPP
Trade barriers and non-tradables Departure from free competition International differences in price level measurements PPP in the short run and the long run
Purpose of PPP
It is now primarily used to compare living standards across countries. From the perspective of exchange rate determination, PPP is useful as a reminder that monetary policy has no long-run impact on the real exchange rate. These rates are used to translate different currencies into a common currency to measure the purchasing power of per capita income in different countries. To facilitate international comparisons of prices and volumes for GDP and its components. Purchasing power parities as equilibrium exchange rates have long existed in international trade theory.
Big Mac Index:
Assumes that the big mac prices are constant and the dollar exchange rate will adjust to restore PPP Allows economists to make comparisons of exchange rates and relative prices of countries around the globe.
Problems With Big Mac Index
Big Mac is not a tradeable good Its prices vary across locations in a given country Local prices may be distorted by trade barriers on beef, sales taxes etc. Likely to prove to be an imperfect indicator of future exchange rate movements
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Day Trading: Learn How to Create a Six-figure Income (High Win Rate Trading Strategies for Scalping and Swing Trading)Da EverandDay Trading: Learn How to Create a Six-figure Income (High Win Rate Trading Strategies for Scalping and Swing Trading)Nessuna valutazione finora
- July 22, 2010Documento2 pagineJuly 22, 2010Paramjit SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento9 paginePurchasing Power ParityVedang ParabNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento9 paginePurchasing Power Paritymahantesh123Nessuna valutazione finora
- PPP & EXCH RateDocumento12 paginePPP & EXCH RateBahilu Moges MameNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power Parity DissertationDocumento4 paginePurchasing Power Parity DissertationHelpPaperCanada100% (1)
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento22 paginePurchasing Power ParityPrasanjeet DebNessuna valutazione finora
- The Big Mac IndexDocumento11 pagineThe Big Mac IndexMaria OlczykNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Mac IndexDocumento3 pagineBig Mac IndexpjftavaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento3 paginePurchasing Power ParityMrityunjay Kumar GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Parity Conditions: Reading: Chapter 4Documento40 pagineInternational Parity Conditions: Reading: Chapter 4Mahima AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Mac IndexDocumento17 pagineBig Mac IndexLodovico XLeschiNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento11 paginePurchasing Power ParityAbhijitNessuna valutazione finora
- Exchange Rate DeterminationDocumento14 pagineExchange Rate DeterminationSaurabh BihaniNessuna valutazione finora
- International ParityDocumento28 pagineInternational Paritypankajbhatt1993Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2011-12-12 Horizon CommentaryDocumento3 pagine2011-12-12 Horizon CommentarybgeltmakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper On Purchasing Power ParityDocumento7 pagineResearch Paper On Purchasing Power Paritygw131adsNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power Parity & The Big Mac IndexDocumento9 paginePurchasing Power Parity & The Big Mac Indexpriyankshah_bkNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power Parity Master ThesisDocumento6 paginePurchasing Power Parity Master Thesisaprilcharltontulsa100% (2)
- Chapter 5 - Parity ConditionDocumento51 pagineChapter 5 - Parity ConditionAntoine DangNessuna valutazione finora
- ICPEB05 Whatis PPPDocumento4 pagineICPEB05 Whatis PPPvinayaknttfNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power Parity NoteDocumento3 paginePurchasing Power Parity NoteRitaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Big Mac IndexDocumento2 pagineThe Big Mac IndexRahi PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- If PPTSDocumento31 pagineIf PPTSPriti BidasariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento7 paginePurchasing Power ParityShalabh_Hirawa_6551Nessuna valutazione finora
- International BusinessDocumento17 pagineInternational Businessnil_parkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power Parity Literature ReviewDocumento5 paginePurchasing Power Parity Literature Reviewafmzsgbmgwtfoh100% (1)
- The Big Mac TheoryDocumento4 pagineThe Big Mac TheoryGemini_0804Nessuna valutazione finora
- IFM5 Exc Rate Theories Parity ConditionsDocumento42 pagineIFM5 Exc Rate Theories Parity Conditionsashu khetan100% (1)
- Soa University: Name: Gunjan DasDocumento7 pagineSoa University: Name: Gunjan Das87 gunjandasNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation On Foreign Exchange RateDocumento6 pagineDissertation On Foreign Exchange RatePaySomeoneToWriteYourPaperHighPoint100% (1)
- Risk ManagementDocumento18 pagineRisk ManagementelenabaciuNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 INBU 4200 Fall 2010 Parity Models and The Foreign Exchange RateDocumento60 pagine06 INBU 4200 Fall 2010 Parity Models and The Foreign Exchange Ratesomeone08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parity Conditions - Unit IIDocumento13 pagineParity Conditions - Unit IIRk BainsNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Burgernomics: A Big Mac™ Guide To Purchasing Power ParityDocumento2 pagineSummary of Burgernomics: A Big Mac™ Guide To Purchasing Power ParityFreed DragsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Exercises AnswersDocumento5 paginePractice Exercises AnswersShar100% (1)
- PPP & IrpDocumento37 paginePPP & IrpSIDRA ALI MA ECO DEL 2021-23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exchange RatesDocumento34 pagineExchange RatesthebfilesNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2 Interest Rate ParityDocumento30 pagine5.2 Interest Rate ParityRammohanreddy RajidiNessuna valutazione finora
- PPPDocumento4 paginePPPDrMohamed AboulnasrNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento4 paginePurchasing Power Parityakki0rockeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Interest Rate Parity PresentationDocumento31 pagineInterest Rate Parity Presentationviki12334Nessuna valutazione finora
- GDP (Purchasin G Power Parity) and GDP (Official Exchange Rate)Documento11 pagineGDP (Purchasin G Power Parity) and GDP (Official Exchange Rate)Alma KerkettaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Parity ConditionsDocumento35 pagineInternational Parity ConditionsRashique Ul LatifNessuna valutazione finora
- ACCA P4 Investment International.Documento19 pagineACCA P4 Investment International.saeed_r2000422100% (1)
- LO3-4 Chap4Documento17 pagineLO3-4 Chap4Dương Thu HàNessuna valutazione finora
- PPP IRP and Exchange RateDocumento11 paginePPP IRP and Exchange RateMohammed SeidNessuna valutazione finora
- SESSION 1-8 FX ArithmeticsDocumento36 pagineSESSION 1-8 FX ArithmeticsdesaishaishavNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On Unit - Macro Economics and Policy: Foreign Exchange Rate DeterminationDocumento18 pagineAssignment On Unit - Macro Economics and Policy: Foreign Exchange Rate DeterminationPrasanjit BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing Power ParityDocumento8 paginePurchasing Power Paritygazi faisalNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Exchange Rate PHD ThesisDocumento8 pagineReal Exchange Rate PHD ThesisSheila Sinclair100% (2)
- Chapter TwoDocumento9 pagineChapter Twoyassin eshetuNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is GDP Per CapitaDocumento9 pagineWhat Is GDP Per CapitaAnthonySilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplement: Theory and Measurement in The MacroeconomyDocumento10 pagineSupplement: Theory and Measurement in The Macroeconomyeroxo100% (1)
- 4315 Written Project 5 Bond Portfolio PerformanceDocumento9 pagine4315 Written Project 5 Bond Portfolio PerformanceVictor Marcos Hyslop100% (2)
- Topic 2Documento27 pagineTopic 2Jhagantini PalaniveluNessuna valutazione finora
- Determinants of Exchange Rate ThesisDocumento6 pagineDeterminants of Exchange Rate Thesisgloriamoorepeoria100% (1)
- Research Paper Exchange RatesDocumento8 pagineResearch Paper Exchange Ratesfvey0xan100% (1)
- Big Picture Economics: How to Navigate the New Global EconomyDa EverandBig Picture Economics: How to Navigate the New Global EconomyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Macedonian KavalDocumento1 paginaMacedonian Kavalmikiszekely1362Nessuna valutazione finora
- NumerologieDocumento22 pagineNumerologieJared Powell100% (1)
- FlazasulfuronDocumento2 pagineFlazasulfuronFenologiaVinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Book 1Documento1 paginaBook 1PES SAFETYNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of The IEEE Color BooksDocumento6 pagineAn Overview of The IEEE Color BooksOhm666Nessuna valutazione finora
- Truong Quang Tuong ITITIU20130 Lab 2 CDocumento6 pagineTruong Quang Tuong ITITIU20130 Lab 2 CTrương Quang TườngNessuna valutazione finora
- Our Lady of Fatima University: College of Business & AccountancyDocumento17 pagineOur Lady of Fatima University: College of Business & AccountancyCLARIN GERALDNessuna valutazione finora
- Pezzol Catalog 21 - INTERNATIONALDocumento74 paginePezzol Catalog 21 - INTERNATIONALAhmed CapoNessuna valutazione finora
- TamasDocumento180 pagineTamaslike 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- API 571 Quick ReviewDocumento32 pagineAPI 571 Quick ReviewMahmoud Hagag100% (1)
- Stock+List 6ct8.3g2 Esn#30549237 Cpl#2218 GeneradorDocumento34 pagineStock+List 6ct8.3g2 Esn#30549237 Cpl#2218 GeneradorAlexis SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Silo Dryers: Mepu - Farmer S First Choice Mepu To Suit Every UserDocumento2 pagineSilo Dryers: Mepu - Farmer S First Choice Mepu To Suit Every UserTahir Güçlü100% (1)
- 1.toyotamarklogo Standard Jan 2021 eDocumento43 pagine1.toyotamarklogo Standard Jan 2021 eMercadeo TosakaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Practical Approach To Classical YogaDocumento39 pagineA Practical Approach To Classical Yogaabhilasha_yadav_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Despiesse de Las Guallas D6H SERIE 3ZF06342Documento4 pagineDespiesse de Las Guallas D6H SERIE 3ZF06342David manjarresNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansi/Isa - 75.08.04-2001 (R2013) Face-to-Face Dimensions For Buttweld-End Globe-Style Control Valves (Class 4500)Documento16 pagineAnsi/Isa - 75.08.04-2001 (R2013) Face-to-Face Dimensions For Buttweld-End Globe-Style Control Valves (Class 4500)Horas CanmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.1 ANSYS CompositePrepPostDocumento2 pagine12.1 ANSYS CompositePrepPostLakmal ArandaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 4Documento44 pagineBiology Unit 4Mohammad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternatives To Shifting Cultivation-248Documento9 pagineAlternatives To Shifting Cultivation-248Chandrashekhar KhobragadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulatory Framework For Water Dams in QuebecDocumento2 pagineRegulatory Framework For Water Dams in QuebecRaveeNessuna valutazione finora
- Shadow UAV HandbookDocumento57 pagineShadow UAV HandbookGasMaskBob100% (2)
- Know Thyself - Jnana Yoga - Par - Omraam Mikhael AivanhovDocumento314 pagineKnow Thyself - Jnana Yoga - Par - Omraam Mikhael AivanhovPedro Ribeiro100% (5)
- Motion of A Simple Pendulum in A FluidDocumento16 pagineMotion of A Simple Pendulum in A FluidGokul JeevaNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP MonsoonDocumento2 pagineDLP MonsoonjennifertariaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALDocumento70 pagine06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALSan AngadiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6RA80 Quick Commissioning Without TachoDocumento7 pagine6RA80 Quick Commissioning Without TachoBaldev SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Geology and Mineralization of The Maggie Creek DistrictDocumento28 pagineGeology and Mineralization of The Maggie Creek DistrictRockstone Research Ltd.Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2006 - Dong Et Al - Bulk and Dispersed Aqueous Phase Behavior of PhytantriolDocumento7 pagine2006 - Dong Et Al - Bulk and Dispersed Aqueous Phase Behavior of PhytantriolHe ZeeNessuna valutazione finora
- M.E Construction Engineering ManagementDocumento43 pagineM.E Construction Engineering ManagementLeilani JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pocket Book AGDocumento67 paginePocket Book AGsudiraharjaNessuna valutazione finora