Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Neuro Linguistic Programming PPT 1 9
Caricato da
NirupsplanetDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Neuro Linguistic Programming PPT 1 9
Caricato da
NirupsplanetCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Neuro-Linguistic Programming
Lesson Plan
Introduction The Way we Learn Learner Style Preferences Discussion Total Time - 1hr
WISDeM
Neuro-Linguistic Programming
When did it start? ---- What is it?
Neuro-Linguistic Programming comes from the disciplines that influenced the early development of its field, beginning as an exploration of the relationship between neurology, linguistics, and observable patterns (programs) of behaviour. John Grinder, a Professor at UC Santa Cruz and Richard Bandler, a graduate student, developed NLP in the mid-1970s. Definition 1: The reception, via our nervous system, of instances received and processed by the five senses (sight - iconic, hearing echoic, touch haptic, taste gustatory, and smell olfactory), the resultant use of language and nonverbal communication system through which neural representation are coded, ordered, and given meaning using our ability to organise our communication and neurological systems to achieve specific desired goals and results. Definition 2: The Study of the Structure of Subjective Experience and what can be calculated from it.
(Pasztor, 1998; Sadowski & Stanney, 1999; Slater, Usoh, & Steed, 1994).
William A.Janvier & Claude Ghaoui, Liverpool John Moores University, UK.
Mch-04
WISDeM
Communication Preference
William A.Janvier & Claude Ghaoui, Liverpool John Moores University, UK.
Mch-04
The Way We Learn
WISDeM
William A.Janvier & Claude Ghaoui, Liverpool John Moores University, UK.
Mch-04
WISDeM
Learner Profile - Communication Preference
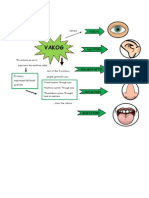
Sensual Memory
60% Iconic
NLP
Visual
LP
SEE
30% Echoic
Auditory
HEAR
10% Haptic
Kinaesthetic
(tactile-haptic instances)
FEEL
(emotional)
NLP = Neuro-Linguistic Programming LP = Language Patterns
William A.Janvier & Claude Ghaoui, Liverpool John Moores University, UK.
Mch-04
Learner Profile VARK (Neil
Fleming 1987)
Learning Style Preferences
Visual oriented students
Learn via their eyes, in charts, graphs, flow charts, and symbolic representation
Auditory oriented students
Learn via their ears
Read/Write oriented students
Learn via the written/printed word
Kinaesthetic oriented students
Learn by doing simulated or real
Learners Learning Style Preference is firmly established before joining Higher Education and may be not be interpreted correctly by tutors.
Multi-modality
Learn by multi-sensory input
Learner Profile MBTI
(Myers-Briggs 1948)
Type Indicator Preference Types
Interpersonal Com m unication Inform ation Processing Inform ation Evaluation Decision Style (E) Extroversion (S) Sensing (T) Thinking (J) Judgem ent (I) Introversion (N) Intuition (F) Feeling (P) Perception
16 Styles:
ESTJ - ESTP - ESFJ - ESFP - ENTJ - ENTP - ENFJ - ENFP ISTJ - ISTP - ISFJ - ISFP - INTJ - INTP - INFJ - INFP
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Neuro-Linguistic Programming NEWDocumento8 pagineNeuro-Linguistic Programming NEWMafe MafeildusNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Workshop NCDocumento19 pagineNLP Workshop NCshrinidhik@gmailcomNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP PresentationDocumento26 pagineNLP PresentationShaju Naduvil67% (3)
- NLP Chicago Bta 2011Documento32 pagineNLP Chicago Bta 2011Jeisson Esteban Hernandez GuachavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Using NLP On YourselfDocumento11 pagineUsing NLP On Yourselfmitovedi4608Nessuna valutazione finora
- En NLP Trainers TrainingDocumento10 pagineEn NLP Trainers TrainingTRAINERHARPREETNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Metaphor (Transcript)Documento3 pagineCreating Metaphor (Transcript)Jhunar John TauyNessuna valutazione finora
- Meta-NLP Curriculum PDFDocumento4 pagineMeta-NLP Curriculum PDFGalal NadimNessuna valutazione finora
- Vakog: Primary Representational SystemDocumento1 paginaVakog: Primary Representational SystemRocio GoymilNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Practitioner CourseDocumento2 pagineNLP Practitioner Coursefdaniels999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nlpmasters Program - NLP Practitioner Certification - 5.1.2012Documento8 pagineNlpmasters Program - NLP Practitioner Certification - 5.1.2012Sherry WongNessuna valutazione finora
- NLPDocumento4 pagineNLPAlmaz RizviNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Master PracDocumento183 pagineNLP Master PracJeisyn Murphy100% (2)
- Communication NLP PDFDocumento2 pagineCommunication NLP PDFLaurenNessuna valutazione finora
- Change Your Business With NLP: Powerful Tools To Improve Your Organisation's Performance and Get ResultsDocumento28 pagineChange Your Business With NLP: Powerful Tools To Improve Your Organisation's Performance and Get ResultsCapstone Publishing100% (3)
- Notes 1 NLP FoundationsDocumento13 pagineNotes 1 NLP FoundationsR Selva Raja100% (1)
- Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)Documento11 pagineNeuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)Pudz AzahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Manjunath VS NmitDocumento48 pagineManjunath VS NmitRekha AranhaNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Master Practitioner Course PDFDocumento4 pagineNLP Master Practitioner Course PDFfdaniels99933% (3)
- Communications in Action NLPDocumento23 pagineCommunications in Action NLPSam100% (1)
- A Z of NLP PDFDocumento9 pagineA Z of NLP PDFViseshNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Implications in TeachingDocumento12 pagineNLP Implications in TeachingPapa ChakNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP PresuppositionsDocumento6 pagineNLP PresuppositionsV Ranga Nathan100% (1)
- FAQ On NLPDocumento2 pagineFAQ On NLPV Ranga NathanNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Business Practitioner-OverviewDocumento11 pagineNLP Business Practitioner-OverviewabobeedoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is NLP?Documento18 pagineWhat Is NLP?ViseshNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Module 8 Meta ProgramsDocumento16 pagineNLP Module 8 Meta ProgramsKaushal Fernando100% (7)
- Sample NLP Practitioner ManualDocumento17 pagineSample NLP Practitioner ManualAnonymous kbmKQLe0J0% (1)
- Behaviour DescriptionsDocumento202 pagineBehaviour Descriptionslyndon_baker_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hermann Brain Dominance InstrumentDocumento63 pagineHermann Brain Dominance InstrumentSomrita SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP CommunicationDocumento4 pagineNLP CommunicationTheera Piroonratana100% (1)
- Generative NLP Robert Dilts PDFDocumento11 pagineGenerative NLP Robert Dilts PDFCristina LorinczNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Practitioner Workbook Business NLP Training - UkDocumento68 pagineNLP Practitioner Workbook Business NLP Training - UkAnonymous 46g46KxZp100% (3)
- Licensed NLP Practitioner UK September 2015-ManchesterDocumento22 pagineLicensed NLP Practitioner UK September 2015-Manchesterbetty cosgrave100% (2)
- LANLP Manual PDFDocumento130 pagineLANLP Manual PDFDany DnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Meta-Nlp: Accelerated NLP Practitioner TrainingDocumento51 pagineMeta-Nlp: Accelerated NLP Practitioner TrainingMichiel PaulusNessuna valutazione finora
- Res EvidenceBasedStudy PsychotherapyDocumento9 pagineRes EvidenceBasedStudy PsychotherapyJuan Carlos SanzNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP For MANAGEMENTDocumento34 pagineNLP For MANAGEMENTVisesh100% (1)
- NLP For TeflDocumento29 pagineNLP For TeflRodrigo VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Principles of NLP (Ebook)Documento5 pagineThe Principles of NLP (Ebook)Peter MachNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP AdvancedDocumento10 pagineNLP AdvancedBhandari NivaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Day NLPDocumento1 pagina1 Day NLPViseshNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Practitioner & Master Practitioner Certification: (Neuro-Linguistic Programming)Documento6 pagineNLP Practitioner & Master Practitioner Certification: (Neuro-Linguistic Programming)PreetiBhambhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP For Testers: - A Brief IntroductionDocumento9 pagineNLP For Testers: - A Brief IntroductionezpynaNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Practitioner Brochure PDFDocumento5 pagineNLP Practitioner Brochure PDFNuman TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Modelling UndisclosedDocumento15 pagineNLP Modelling UndisclosedMarco Gallico0% (1)
- NLP CourseDocumento2 pagineNLP CourseRonaldo MofuNessuna valutazione finora
- NLP Trainers Training 2019 PDFDocumento4 pagineNLP Trainers Training 2019 PDFSHASHANKNessuna valutazione finora
- Ericksonian TherapyDocumento2 pagineEricksonian Therapyosher260% (1)
- Effective Communication SkillsDocumento42 pagineEffective Communication SkillsAfolabi Kilaso100% (1)
- Transderivational Search: TDS in Human Communication and ProcessingDocumento3 pagineTransderivational Search: TDS in Human Communication and ProcessingZorica TrailovicNessuna valutazione finora
- The Framework of Neuro Linguistic ProgrammingDocumento1 paginaThe Framework of Neuro Linguistic ProgrammingionplesaNessuna valutazione finora
- NlpworkshopDocumento78 pagineNlpworkshopSam100% (1)
- NLP Cheat SheetDocumento5 pagineNLP Cheat SheetstreakerstreetNessuna valutazione finora
- NLPU 100 Background of NLPDocumento5 pagineNLPU 100 Background of NLPJeremy GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocumento19 pagineTeaching Listening and SpeakingPio MelAncolico Jr.100% (1)
- Unit 3: Teaching ListeningDocumento31 pagineUnit 3: Teaching ListeningrighteousnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocumento23 pagineTeaching Listening and Speakingkyla quilicol100% (1)
- Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocumento23 pagineTeaching Listening and SpeakingMa. Andrea MacatangayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Link Between Neurology and Language TeachingDocumento4 pagineThe Link Between Neurology and Language TeachingMelanie PalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics 11 02566Documento13 pagineElectronics 11 02566卓七越Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 Information ExchangeDocumento15 pagine2010 Information ExchangeAnastasia RotareanuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Anti-PaladinDocumento9 pagineThe Anti-PaladinBobbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Quotation - 1Documento4 pagineQuotation - 1haszirul ameerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Intel 8086 / 8088/ 80186 / 80286 / 80386 / 80486 Jump InstructionsDocumento3 pagineThe Intel 8086 / 8088/ 80186 / 80286 / 80386 / 80486 Jump InstructionsalexiouconNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Skill - Time ManagementDocumento18 pagineCommunication Skill - Time ManagementChấn NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- An Enhanced Radio Network Planning Methodology For GSM-R CommunicationsDocumento4 pagineAn Enhanced Radio Network Planning Methodology For GSM-R CommunicationsNuno CotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tax Havens IMF PDFDocumento59 pagineTax Havens IMF PDFClassic PhyXNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 10. Value Proposition.Documento69 pagineSession 10. Value Proposition.Bibhu R. TuladharNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Frank K. Reilly & Keith C. BrownDocumento113 pagineInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Frank K. Reilly & Keith C. BrownWhy you want to knowNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference GuideDocumento88 pagineReference GuideAnonymous Qm0zbNk100% (1)
- DG Oil SpecificationDocumento10 pagineDG Oil SpecificationafsalmohmdNessuna valutazione finora
- Collecting, Analyzing, & Feeding Back DiagnosticDocumento12 pagineCollecting, Analyzing, & Feeding Back DiagnosticCaroline Mariae TuquibNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing Principles and Practices-IDocumento8 pagineAuditing Principles and Practices-IMoti BekeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Final SEC Judgment As To Defendant Michael Brauser 3.6.20Documento14 pagineFinal SEC Judgment As To Defendant Michael Brauser 3.6.20Teri BuhlNessuna valutazione finora
- BV DoshiDocumento6 pagineBV DoshiNimNessuna valutazione finora
- Flight Data Recorder Rule ChangeDocumento7 pagineFlight Data Recorder Rule ChangeIgnacio ZupaNessuna valutazione finora
- Docket - CDB Batu GajahDocumento1 paginaDocket - CDB Batu Gajahfatin rabiatul adawiyahNessuna valutazione finora
- BSRM Ultima BrochureDocumento2 pagineBSRM Ultima BrochuresaifuzzamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pen Pal Lesson Plan 3Documento3 paginePen Pal Lesson Plan 3api-664582820Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dependent ClauseDocumento28 pagineDependent ClauseAndi Febryan RamadhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis ListDocumento1 paginaDiagnosis ListSenyorita KHayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stratum CorneumDocumento4 pagineStratum CorneumMuh Firdaus Ar-RappanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Acceptable Use Policy 08 19 13 Tia HadleyDocumento2 pagineAcceptable Use Policy 08 19 13 Tia Hadleyapi-238178689Nessuna valutazione finora
- National Insurance Mediclaim Claim FormDocumento4 pagineNational Insurance Mediclaim Claim FormIhjaz VarikkodanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Transport Network SwitchingDocumento16 pagineOptical Transport Network SwitchingNdambuki DicksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Anarchy One-Sheet Sell SheetDocumento2 pagineFinal - Anarchy One-Sheet Sell SheetMaddanie WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicating Value - PatamilkaDocumento12 pagineCommunicating Value - PatamilkaNeha ArumallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eje Delantero Fxl14 (1) .6Documento2 pagineEje Delantero Fxl14 (1) .6Lenny VirgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Our Story Needs No Filter by Nagarkar SudeepDocumento153 pagineOur Story Needs No Filter by Nagarkar SudeepKavya SunderNessuna valutazione finora