Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Heavy Metals Analysis
Caricato da
ECRDCopyright
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Heavy Metals Analysis
Caricato da
ECRDCopyright:
Harsh K.
Dixit
Envirotech Center for Research & Development
New Delhi
NAAQM Standards
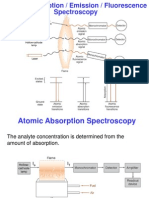
The Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy technique makes use of absorption spectrometry to assess the concentration of an analyte in the sample. Method is based on: Active sampling using PM10 Respirable Dust Sampler & then Sample digestion Analsis by Atomic absorption spectrophotometer
PM10 Sampler Hot plate Analytical Balance Digestion Chamber Polypropylene bottle Glasswares Atomic absorption spectrophotometer
Filter Paper: 8x10 EPM2000 Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) concentrated Nitric Acid (HNO3) concentrated Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4) concentrated Metal Standard Solutions Sodium borohydride Potassium iodide Distilled water
1. Microwave Digestion 2. Hot Plate Digestion
Cut filter paper in small pieces Place these small pieces into a beaker using plastic forceps Cover the filter with extraction solution Place beaker on the hot plate for 30 min. Dont allow sample to dry Remove beaker from hot plate & allow to cool Rinse beaker walls & wash with distilled water Filter the extract and make up to 50 ml.
A light beam containing the corresponding wavelength of the energy required to raise the atoms of the analyte from the ground state to the excited state is directed through the flame or furnace. This wavelength is observed by a monochromator and a detector that measure the amount of light absorbed by the element, hence the number of atoms in the ground state in the flame or furnace. A hollow cathode lamp for the element being determined provides a source of that metals particular absorption wavelength.
I. Flame atomic absorption: for Pb & Ni
II. Graphite furnace atomic absorption: for Low detection limit of Pb & Ni III. Flame-VGA atomic absorption: for As
Choose correct hollow cathod lamp Align the instrument Position the monochromator Select proper monochromator slit width Set the light source current Ignite the flame Regulate the flow of fuel & oxidant Adjust the burner for maximum absorption & stability
Choose correct hollow cathod lamp Place the furnace Align the instrument Position the monochromator Select proper monochromator slit width Set the light source current Switch on chiller Regulate the flow of fuel & oxidant Adjust the burner for maximum absorption & stability Clean graphite tube with a firing
Prepare standard solutions from the stock solutions. Select at least three standards to cover linear range as recommended by method. Aspirate the standards into the flame or inject the standards into the furnace and record the absorbance. Prepare the calibration graph by plotting absorbance and concentration in g/ml.
C = (Ms Mb) x Vs x Fa/V x Ft
Where, C = concentration, g metal/m3 Ms = metal concentration g/mL Mb = blank concentration g/mL Vs = total volume of extraction in mL Fa = total area of exposed filter in cm2 V = Volume of air sampled in m3 Ft = Area of filter taken for digestion in cm2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Atomic Spectroscopy: Principles and ApplicationsDocumento41 pagineAtomic Spectroscopy: Principles and ApplicationsNur Fatin Zahra100% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - Final-1Documento29 pagineMicrosoft PowerPoint - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - Final-1Rht BrdNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrophotometerDocumento22 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrophotometerJawad HafeezNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Wastewater & Gaseous WasteDocumento13 pagineAnalysis of Wastewater & Gaseous WastehammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Tirtha S HGAAS - Experiment Final (ARTIKAN)Documento9 pagineTirtha S HGAAS - Experiment Final (ARTIKAN)Rizka MaharanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabalho 4 (Versão Final)Documento13 pagineTrabalho 4 (Versão Final)ritacostajoanarodrigues754Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absortion Spectroscop yDocumento15 pagineAtomic Absortion Spectroscop yVân Khánh NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Elemental AnalysisDocumento27 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Elemental AnalysisNitiyanandanathan KamalanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization of Crude Oil Properties and TestsDocumento35 pagineCharacterization of Crude Oil Properties and TestsSivakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- III. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)Documento20 pagineIII. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)Chan PhengNessuna valutazione finora
- CHNSO Analyzer Tech and ApplicationsDocumento85 pagineCHNSO Analyzer Tech and ApplicationsAya Shaaban ElHussaini ShaabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods For Measurement OF BENZENE, Benzopyrene Toluene & Xylene (BTX) in AirDocumento65 pagineMethods For Measurement OF BENZENE, Benzopyrene Toluene & Xylene (BTX) in AirECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Tutorial 2Documento9 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Tutorial 2MSKNessuna valutazione finora
- Principal of AASDocumento77 paginePrincipal of AASabpizz100% (1)
- CHM 5175: Part 2.3: Absorption SpectrosDocumento83 pagineCHM 5175: Part 2.3: Absorption Spectrostieuca08Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHM260 Experiment 4Documento11 pagineCHM260 Experiment 4Muhammad Azri Haziq57% (7)
- Instrumen Pengukur Parameter Fisika/Kimia OseanografiDocumento30 pagineInstrumen Pengukur Parameter Fisika/Kimia OseanografiI Faode HayawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi - 2 - Atomic AbsorptionDocumento51 pagineMateri - 2 - Atomic AbsorptionSalwa KamiliaNessuna valutazione finora
- GCMS Lecture On 14 Oct 2023Documento57 pagineGCMS Lecture On 14 Oct 2023Shaivya BajpayeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento30 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosRashed BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Techniques for Elemental AnalysisDocumento30 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy Techniques for Elemental AnalysisAris TaoemesaNessuna valutazione finora
- ASAP2060 UiTM TrainingDocumento60 pagineASAP2060 UiTM TrainingMuhammad Rahimi100% (1)
- Gas Chromatography ExplainedDocumento51 pagineGas Chromatography ExplainedKasun WekasingheNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 BSE Fire Lab NotesDocumento7 pagine2022 BSE Fire Lab NotesTsz Sang IpNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy NotesDocumento5 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy Notesaryan86yaNessuna valutazione finora
- L4B PDFDocumento34 pagineL4B PDFbrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Astmd 5765Documento2 pagineAstmd 5765erlinda rhohmatul lailiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrophotometerDocumento8 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectrophotometersaurabh_acmasNessuna valutazione finora
- Methodology For Analysis of Metals by Atomic Absorption Spectrometer PrincipleDocumento3 pagineMethodology For Analysis of Metals by Atomic Absorption Spectrometer PrinciplesrinivasnaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Aoac 2006.03 PDFDocumento11 pagineAoac 2006.03 PDFjesusNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Members: Suhaidah Binti Nazori UK21425 Mohd Faizuddin Bin Abu Hasan UK21455 Siti Fasihah Binti Rameli UK21478Documento27 pagineGroup Members: Suhaidah Binti Nazori UK21425 Mohd Faizuddin Bin Abu Hasan UK21455 Siti Fasihah Binti Rameli UK21478ah_16036566Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Options For BioChar Adsorption and Surface Area Characterization of Biochar Materials PPT 2012Documento26 pagineAnalytical Options For BioChar Adsorption and Surface Area Characterization of Biochar Materials PPT 2012Jean Carlos Gonzalez HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 10 (Chemistry)Documento10 pagineExperiment 10 (Chemistry)nikenantha100% (1)
- Atomic Absorption & EmissionDocumento80 pagineAtomic Absorption & EmissionAkshay Patil100% (1)
- Atomic Absorption & EmissionDocumento80 pagineAtomic Absorption & Emissionindustrial technoNessuna valutazione finora
- c127.1 Expt 6 & 11 ReportDocumento52 paginec127.1 Expt 6 & 11 ReportKarina NarcisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Lesson 3 QC2 LECDocumento95 pagineModule 1 Lesson 3 QC2 LECKrisel AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cod Procedure For HACH DR 2800Documento8 pagineCod Procedure For HACH DR 2800Berliana Cahya NingtiasNessuna valutazione finora
- D4208 (Total Chlorine in Coal by The Oxygen Bomb CombustionIon V)Documento3 pagineD4208 (Total Chlorine in Coal by The Oxygen Bomb CombustionIon V)Ale Hurtado MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- AttachmentDocumento33 pagineAttachmentKrupali AtodariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento41 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosTasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report - Determination of Accelerants in Fire Debris Using Solid Phase MicroextractionDocumento6 pagineLab Report - Determination of Accelerants in Fire Debris Using Solid Phase MicroextractionNur Atiqah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) EXPLAINEDDocumento119 pagineATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) EXPLAINEDWangsa DodolNessuna valutazione finora
- Chater Three 3-1-Introduction:: 3-2-1-1-Profile MethodDocumento7 pagineChater Three 3-1-Introduction:: 3-2-1-1-Profile MethodMohammed DawoodNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - AAS Part 2Documento40 pagine2 - AAS Part 2Jun MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling of Air: Pranay Krishnan MSC Evs Part Ii Roll No: 14Documento44 pagineSampling of Air: Pranay Krishnan MSC Evs Part Ii Roll No: 14Pranay Krishnan100% (1)
- SCH 2304 Aas Practical 3 & 4Documento4 pagineSCH 2304 Aas Practical 3 & 4Korir DennisNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 4-Emission Air Pollution (L7)Documento37 pagineWeek 4-Emission Air Pollution (L7)Devendraa MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 8 and 10 - Basic Principles of Atomic Absorption and Atomic Emission SpectrosDocumento129 pagineCH 8 and 10 - Basic Principles of Atomic Absorption and Atomic Emission SpectrosfaisalNessuna valutazione finora
- D6721-Standard Test Method For Determination of Chlorine in Coal by Oxidative Hydrolysis MicrocoulometryDocumento4 pagineD6721-Standard Test Method For Determination of Chlorine in Coal by Oxidative Hydrolysis MicrocoulometryAyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento28 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosvvrckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Engineering Lab Techniques: Suleman SikandarDocumento5 pagineEnvironmental Engineering Lab Techniques: Suleman SikandarSikandar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.7.2018 Guidelines For Manual SamplingDocumento46 pagine9.7.2018 Guidelines For Manual SamplingmswNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Copper by AASDocumento18 pagineDetermination of Copper by AASWan ShamNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption and Atomic Emission (Flame Photometry) SpectrometryDocumento52 pagineAtomic Absorption and Atomic Emission (Flame Photometry) Spectrometry.aju12.Nessuna valutazione finora
- AAS LecturesDocumento22 pagineAAS LecturesarnomasvosveNessuna valutazione finora
- Flame PhotometerDocumento5 pagineFlame PhotometerسيليناNessuna valutazione finora
- Monitoring Toxic Gases in the Atmosphere for Hygiene and Pollution Control: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesDa EverandMonitoring Toxic Gases in the Atmosphere for Hygiene and Pollution Control: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (17)
- E Learning Levels of DevelopmentDocumento1 paginaE Learning Levels of DevelopmentECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- NH3Documento8 pagineNH3ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Development Phases of E Learning ModuleDocumento1 paginaDevelopment Phases of E Learning ModuleECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Benzo (A) PyreneDocumento14 pagineAnalysis of Benzo (A) PyreneECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of NOx in Ambient AirDocumento12 pagineAnalysis of NOx in Ambient AirECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- O3Documento15 pagineO3ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of SO2 in Ambient AirDocumento20 pagineAnalysis of SO2 in Ambient AirECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Prest. Managing Urban Air Quality, 17.3Documento17 paginePrest. Managing Urban Air Quality, 17.3ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Air MONDocumento33 pagineAir MONECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple EarthDocumento5 pagineSimple EarthECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Benzene: Harsh K. DixitDocumento10 pagineAnalysis of Benzene: Harsh K. DixitECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Apm550 MFCDocumento11 pagineApm550 MFCECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- PM10 MeasmntDocumento10 paginePM10 MeasmntECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Prest WM Abridged) Envirotech 17.3Documento20 paginePrest WM Abridged) Envirotech 17.3ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Particulate Sampler IonDocumento1 paginaParticulate Sampler IonECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- CO AnalyzerDocumento8 pagineCO AnalyzerECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Met One BAM-1020Documento10 pagineMet One BAM-1020ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- WM271 2010Documento7 pagineWM271 2010ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Heavy Metals AnalysisDocumento14 pagineHeavy Metals AnalysisECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Polln & MetDocumento15 pagineAir Polln & MetECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- OzoneDocumento11 pagineOzoneECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of NOx in Ambient AirDocumento12 pagineAnalysis of NOx in Ambient AirECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Abhijit PathakDocumento66 pagineAbhijit PathakECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- GasesDocumento12 pagineGasesECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- BTEXDocumento7 pagineBTEXECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Pm2.5 Epa Cfr50Documento102 paginePm2.5 Epa Cfr50ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- NH3Documento8 pagineNH3ECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Benzo (A) PyreneDocumento14 pagineAnalysis of Benzo (A) PyreneECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of SO2 in Ambient AirDocumento20 pagineAnalysis of SO2 in Ambient AirECRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Ice Plant Design GuideDocumento4 pagineMini Ice Plant Design GuideDidy RobotIncorporatedNessuna valutazione finora
- MSc Analytical Chemistry SyllabusDocumento66 pagineMSc Analytical Chemistry SyllabusJNessuna valutazione finora
- 2423L3Documento8 pagine2423L3Ruben SyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lutensol XL Types: Technical InformationDocumento8 pagineLutensol XL Types: Technical InformationeduardoaffreNessuna valutazione finora
- Rs and Their Applications: Propagation of Gaussian Beams & Optical ResonatorsDocumento14 pagineRs and Their Applications: Propagation of Gaussian Beams & Optical ResonatorsShakir KhattakNessuna valutazione finora
- Talk 5-3-1 CST Euc 2012Documento175 pagineTalk 5-3-1 CST Euc 2012Anonymous 3GE9cFCNessuna valutazione finora
- Is: 8887:2018Documento13 pagineIs: 8887:2018Indira Banerjee100% (7)
- Exam Style Answers 8 Asal Physics CBDocumento2 pagineExam Style Answers 8 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank On Atomic Structure-2Documento7 pagineQuestion Bank On Atomic Structure-2Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivation of The Boltzmann Distribution LawDocumento10 pagineDerivation of The Boltzmann Distribution Lawlmcristina5Nessuna valutazione finora
- !doctype H P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Documento4 pagine!doctype H P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)jenisatrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic Chemistry For The JEE Mains and Advanced by K Rama RaoDocumento937 pagineInorganic Chemistry For The JEE Mains and Advanced by K Rama RaoAlan100% (1)
- 9701 s10 Ms 21Documento8 pagine9701 s10 Ms 21Hubbak Khan100% (1)
- Hydrometallurgy: Gui Liu, Zhongwei Zhao, Ahmad Ghahreman TDocumento20 pagineHydrometallurgy: Gui Liu, Zhongwei Zhao, Ahmad Ghahreman TShivansh MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kim ReformerDocumento2 pagineKim ReformeralejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- HED 60hz 2015Documento11 pagineHED 60hz 2015Waltero AscanioNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento4 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentSiva ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 - Physical Science PDFDocumento10 pagineModule 4 - Physical Science PDFDarry Blancia100% (1)
- DiffusionDocumento2 pagineDiffusionAnkita SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- S9 - End-Of-Unit 8 TestDocumento2 pagineS9 - End-Of-Unit 8 TestShahana Ahth100% (2)
- (ThermodynamicsDocumento10 pagine(ThermodynamicsAhmed58seribegawanNessuna valutazione finora
- BismuthDocumento20 pagineBismuthjosevitorromualdoNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Experimental Techniques: Chromatography, Separation & PurificationDocumento4 pagineIGCSE Experimental Techniques: Chromatography, Separation & PurificationFabian Obame0% (1)
- Sherubtse College Faculty of Mathematics and Computer ScienceDocumento9 pagineSherubtse College Faculty of Mathematics and Computer ScienceSampa Nima YoezerNessuna valutazione finora
- Potentiometry: Cell Reference Indicator JunctionDocumento12 paginePotentiometry: Cell Reference Indicator JunctionPrathi100% (1)
- Degrees of Freedom Analysis for Process UnitsDocumento7 pagineDegrees of Freedom Analysis for Process UnitsAhmed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials and Manufacturing ProcessesDocumento6 pagineMaterials and Manufacturing ProcessesNaresh Kumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramics International: SciencedirectDocumento9 pagineCeramics International: Sciencedirect18-021Nurul Syifa RidzkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Slime PDFDocumento2 pagineSlime PDFSwati AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- J Diamond 2005 09 007Documento4 pagineJ Diamond 2005 09 007Yohanes Fredy KartikoNessuna valutazione finora