Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Flow Process Analysis
Caricato da
Adama QuayeDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Flow Process Analysis
Caricato da
Adama QuayeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
Process-Flow
Analysis
2
Outline
Systems Thinking
The Process View of Business
Flowchart Analysis
Materials-Flow Analysis
Using Process-Flow Analysis
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
3
Systems Thinking
Definition of a system
Application of systems thinking to
businesses
Role of cross functional teams in
systems analysis
4
Flowchart Analysis
Targets process elements for change
Steps in process flow chart analysis
5
Targets process elements for
change
Raw materials
Product (output) design
Job design
Processing steps used
Management control information
Equipment or tools
Suppliers
6
Steps in process flow chart
analysis
O Select a process
O Form a team or individual as the project leader
O Decide on the objectives of the analysis
O Define customers and suppliers
O Describe the existing transformation process
O Develop improved process design
O Gain management approval of the improved
design
O Implement the new process design
7
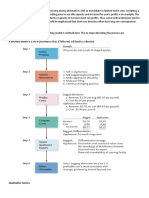
Materials-Flow Analysis
Objectives of MFA
Key concepts and tools:
EThroughput time
EAssembly drawing (Figure 7.2)
EAssembly (Gozinto) chart (Figure 7.3)
ERouting sheet (Figure 7.4)
EFlow Process Chart (Figure 7.5)
8
Assembly Drawing for a Tricycle (Figure 7.2)
9
Symbols for Flow-Process Chart
Operation (a task or work activity)
Inspection (an inspection of the product for
quantity or quality)
Transportation (a movement of material from
one point to another)
Storage (an inventory or storage of materials
awaiting the next operation)
Delay (a delay in the sequence of operations)
10
Questions to Ask in FPA
What does the customer need?, operations are necessary? Can some
operations be eliminated, combined, or simplified?.
Who is performing the job? Can the operation be redesigned to use less
skill or less labor? Can operations be combined to enrich jobs? .
Where is each operation conducted? Can layout be improved? .
When is each operation performed? Is there excessive delay or
storage? Are some operations creating bottlenecks? ..
How is the operation done? Can better methods, procedures, or
equipment be used? .
11
Information Flow Analysis
Types of information flow:
EInformation is the product of operation
EInformation is used for management control
Symbols used in information flow analysis
(Figure 7.9)
12
Symbols for Information Processing Flow Chart
Origin of record (used to identify an operation that involves the addition
of significant data to a blank form)
Subsequent writing (a step in which significant data is added to an existing
record)
Handling operations (any nonproductive step, such as sorting, stapling, or
folding)
Move (a step in which the record is transported from one person, department,
or work place to another)
Inspection (used when the step involves examination of the quality or
clearness of a record)
Delay, file, and destroy (identifies a point or time at which the record is
inactive
13
Sociotechnical Approach to PFA
Task 1: Def i ne scope of t he
process-flow study and general
problems
Task 1: Defi ne scope of the
process-flow study and general
problems
Task 1: Define scope of the
pr oc es s - f l ow s t udy and
general problems
Task 1: Define scope of the
pr oc es s - f l ow s t udy and
general problems
Task 1: Defi ne scope of the
process-flow study and general
problems
Task 1: Define scope of the
pr oc es s - f l ow s t udy and
general problems
Task 1: Define scope of the
pr oc es s - f l ow s t udy and
general problems
Task 1
Report
Task 1
Report
Task 1
Report
14
Business Process Reengineering
(BPR)
BPR defined (Hammer and Champy)
BPR Philosophy
Principles of BPR
15
BPR Philosophy
Does the reengineering consultant see
the glass as half full or half empty?
Neither.
Its the wrong size of glass!
16
Principles of BPR
Organize around outcomes
Have the people who do the work, process
their own information
Put the decision point where work is
performed and build control into the
process
Eliminate unnecessary steps in the
process
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Law of NationsDocumento667 pagineThe Law of NationsJo Jo100% (1)
- Measuring Performance in OperationsDocumento35 pagineMeasuring Performance in OperationsMaxine SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Mee2008 VusDocumento42 pagineDesign Mee2008 VusRajesh RJNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Legal Compliance in StaffingDocumento21 pagineStrategic Legal Compliance in StaffingChitty clsNessuna valutazione finora
- FAST (Functional Analysis System Technique)Documento11 pagineFAST (Functional Analysis System Technique)abilash_nivas100% (1)
- F5 TcpdumpDocumento14 pagineF5 TcpdumpNETRICH IT SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Analysis and HR PlanningDocumento32 pagineJob Analysis and HR Planningtony_njNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Job AnalysisDocumento31 pagine3 Job AnalysisFaisal MalekNessuna valutazione finora
- CaseStudy - White ManufacturingDocumento2 pagineCaseStudy - White Manufacturingsatnam paddaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch20 Introducing New Market OfferingsDocumento2 pagineCh20 Introducing New Market OfferingsRina Fordan BilogNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic and Operational Planning: Ip Ceit Inictel-UniDocumento34 pagineStrategic and Operational Planning: Ip Ceit Inictel-UniHugo Alonzo RamírezNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Studies TrainingDocumento28 pagineTime Studies TrainingAhmed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross 1988Documento11 pagineCross 1988deltanueveNessuna valutazione finora
- BPMDocumento100 pagineBPManandNessuna valutazione finora
- 0perationsmanagement 1Documento29 pagine0perationsmanagement 1naufalmamet100% (1)
- OM CH 12 Heizer Inventory MGTDocumento49 pagineOM CH 12 Heizer Inventory MGTSyeda AqsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pay Equity: Internal and External ConsiderationsDocumento9 paginePay Equity: Internal and External ConsiderationsOnline AccessNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Process - Analysis - Practice - Problem - SolutionsDocumento7 pagine4 Process - Analysis - Practice - Problem - SolutionsHEMANT KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Heizer Om12 Ch06 FinalDocumento73 pagineHeizer Om12 Ch06 FinalBahri Karam KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Organisational Structure GuideDocumento35 pagineOrganisational Structure GuideShardulNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean Six Sigma Mid-Term Ass Final 1.0Documento21 pagineLean Six Sigma Mid-Term Ass Final 1.0era nominNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Guide to Operations Management: Concepts and Case NotesDa EverandEssential Guide to Operations Management: Concepts and Case NotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Compensation: Third Canadian Edition Milkovich, Newman, ColeDocumento28 pagineCompensation: Third Canadian Edition Milkovich, Newman, ColeNeha AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing and Operations ManagementDocumento52 pagineManufacturing and Operations ManagementRohit DhawareNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluating Work: Job EvaluationDocumento46 pagineEvaluating Work: Job EvaluationshirinaserkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tactical Decision MakingDocumento2 pagineTactical Decision MakingMay AugustusNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Process SelectionDocumento18 pagineChapter 4 Process Selectionmohammed mohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Management EssentialsDocumento43 paginePerformance Management EssentialsMarida SinagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Job AnalysisDocumento17 pagineChapter 4 Job AnalysisAbir AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM Chapter 7Documento9 pagineTQM Chapter 7Jesse John A. CorpuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Consulting and Reengineering: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Documento29 pagineOperations Consulting and Reengineering: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004gudunNessuna valutazione finora
- Database LifecycleDocumento45 pagineDatabase LifecyclePooja Prateek JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Internal AlignmentDocumento24 paginePresentation On Internal AlignmentAman KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - : Product Design & Process SelectionDocumento15 pagineChapter 3 - : Product Design & Process SelectionAmal MechanicNessuna valutazione finora
- CS3 App Dev CompetencyDocumento10 pagineCS3 App Dev CompetencyPKNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - BaDocumento10 pagineUnit 1 - Baprem nathNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Accounting EssayDocumento8 pagineManagerial Accounting EssayPatrick PetitNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Management: Network DiagramsDocumento21 pagineProject Management: Network Diagramsvenkatesh@2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Function Analysis System Technique: Lesson 09Documento11 pagineFunction Analysis System Technique: Lesson 09arun100% (1)
- Lecture - 1 - Foundation of Information Systems in BusinessDocumento39 pagineLecture - 1 - Foundation of Information Systems in BusinesschalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Defining and Measuring ProductivityDocumento4 pagineDefining and Measuring ProductivityFadhil HerdiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Performance of Responsibility CentersDocumento30 pagineMeasuring Performance of Responsibility CentersRajat SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Outsourcing Strategies For Capital ProductivityDocumento9 pagineOutsourcing Strategies For Capital ProductivitySunnyVermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance AppraisalDocumento81 paginePerformance AppraisalIkhlaasKaushalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 02 Operations ManagementDocumento3 pagineLesson 02 Operations ManagementmohmodNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Processes Conversion (Ex. Iron To Steel) Fabrication (Ex.Documento9 pagineTypes of Processes Conversion (Ex. Iron To Steel) Fabrication (Ex.ashishgiri67% (3)
- DOE Report XinliShaDocumento16 pagineDOE Report XinliShaXinli ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mba A Study of Human Resource Planning at Gei Industrial Systems Ltd. BhopalDocumento56 pagineMba A Study of Human Resource Planning at Gei Industrial Systems Ltd. BhopalNAVEEN ROYNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizational StructureDocumento26 pagineOrganizational StructureSahanaa AJNessuna valutazione finora
- TQC MCQsDocumento34 pagineTQC MCQsAbdullah PaktinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 02 - Public Affairs ManagementDocumento7 pagineChapter 02 - Public Affairs ManagementThao TrungNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Review & Capital Budgeting ProcessesDocumento8 pagineProject Review & Capital Budgeting Processesamitsingla19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1Documento17 pagineModule 1buviaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 2Documento3 pagineAssignment No 2Adeel AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- GE MatrixDocumento6 pagineGE MatrixManish JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain ManagementDocumento64 pagineOperations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain ManagementAbdullah S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter OverviewDocumento57 pagineChapter OverviewWajiha SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - The Analysis and Design of WorkDocumento12 pagineChapter 4 - The Analysis and Design of WorkProbo SutejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management-Chapter 1 & 2Documento10 pagineStrategic Management-Chapter 1 & 2rumelrashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Compensation Management NotesDocumento19 pagineCompensation Management Notesgulludada2005100% (1)
- Vice President Part 3Documento22 pagineVice President Part 3morgan mugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Process-Flow Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocumento26 pagineProcess-Flow Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinVanessa Aulia PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Golden AltarDocumento3 pagineThe Golden AltarAdama QuayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 4Documento3 pagineProject 4Adama QuayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Engineering TechnologyDocumento10 pagineQuality Engineering TechnologyAdama QuayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 4Documento3 pagineProject 4Adama QuayeNessuna valutazione finora
- H Value1Documento12 pagineH Value1Sahyog KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer LiteracyDocumento5 pagineComputer LiteracyMazaasach MazaNessuna valutazione finora
- AJD275Documento5 pagineAJD275mhmmd14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ias Public Administration Mains Test 1 Vision IasDocumento2 pagineIas Public Administration Mains Test 1 Vision IasM Darshan UrsNessuna valutazione finora
- LTSpiceModelTutorial 2Documento2 pagineLTSpiceModelTutorial 2Hermawan Rahmat HidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Plan On Vodafone vs. Pakistani OperatorsDocumento47 pagineMarket Plan On Vodafone vs. Pakistani OperatorswebscanzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyberoam Quick Start Guide-50i-500iDocumento8 pagineCyberoam Quick Start Guide-50i-500iPaul Anim AmpaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Piston SkirtDocumento2 paginePiston SkirtAmmar OmranNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 V2 2250 PR Pid 000001 - 1 - PDFDocumento1 pagina4 V2 2250 PR Pid 000001 - 1 - PDFdavidNessuna valutazione finora
- C - TurretDocumento25 pagineC - TurretNathan BukoskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Estimator by VladarDocumento10 pagineTraining Estimator by VladarMohamad SyukhairiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitin FicoDocumento3 pagineNitin Ficoapi-3806547100% (1)
- Commercial Grade Dedication GuidanceDocumento64 pagineCommercial Grade Dedication Guidancealien686Nessuna valutazione finora
- Note-145 Biostat Prof. Abdullah Al-Shiha PDFDocumento157 pagineNote-145 Biostat Prof. Abdullah Al-Shiha PDFAdel Dib Al-jubeh100% (2)
- Semiconductor Devices Are Electronic Components That Exploit The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialsDocumento3 pagineSemiconductor Devices Are Electronic Components That Exploit The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialsNuwan SameeraNessuna valutazione finora
- MiVoice Office 400 Products BR enDocumento12 pagineMiVoice Office 400 Products BR enWalter MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Embraer Spec E175-E2Documento1 paginaEmbraer Spec E175-E2Ward DepoorterNessuna valutazione finora
- ExcelDocumento258 pagineExcelsusi herawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ReportDocumento10 pagineProject ReportKaljayee singhNessuna valutazione finora
- RS124 ManualDocumento13 pagineRS124 ManualSoakaosNessuna valutazione finora
- Pasundan United FC - Anggaran Dasar Dan Rumah Tangga Pasundan United FCDocumento1.231 paginePasundan United FC - Anggaran Dasar Dan Rumah Tangga Pasundan United FCdondo lambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintain Safe Systems with Maintenance Free EarthingDocumento12 pagineMaintain Safe Systems with Maintenance Free EarthingRavi Shankar ChakravortyNessuna valutazione finora
- MD 5 SumDocumento47 pagineMD 5 SumBabay Si TagamaNessuna valutazione finora
- C# Abstract Classes and Interfaces ExplainedDocumento20 pagineC# Abstract Classes and Interfaces ExplainedshubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Terra Point White PaperDocumento10 pagineTerra Point White Paperobi SalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Amu Resume by KKMDocumento2 pagineAmu Resume by KKMapi-457874888Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1800 Series Inverted Bucket Steam TrapsDocumento2 pagine1800 Series Inverted Bucket Steam TrapsIoana PopescuNessuna valutazione finora
- The DC Blocking Filter - J de Freitas Jan 2007Documento7 pagineThe DC Blocking Filter - J de Freitas Jan 2007Hiếu Trung HoàngNessuna valutazione finora