Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Erp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005
Caricato da
Priyadarshini SahooDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Erp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005
Caricato da
Priyadarshini SahooCopyright:
Formati disponibili
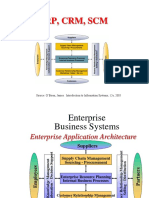
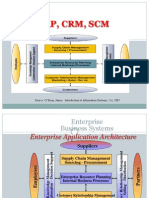
ERP, CRM, SCM
Source: OBrien, James. Introduction to Information Systems, 12e, 2005
Enterprise Business Systems
Enterprise Application Architecture
Suppliers
Supply Chain Management Sourcing - Procurement
Partner Relationship Management Selling Distribution Knowledge Management Collaboration Decision Support
Employees
Enterprise Resource Planning Internal Business Processes
Customer Relationship Management Marketing Sales - Service
Customers
Partners
Enterprise Resource Planning
The Technological Backbone of e-Business
Production Planning Integrated Logistics Sales, Distribution, Customer/ Employee Order Accounting Management Human and Finance Resources
Enterprise Resource Planning The Business Value of ERP
Demand Manufacturing Logistics Planning Planning Planning
Distribution Planning
Order Entry
Purchasing & Accounts Payable
MRP Manufacturing Inventory Distribution Inbound & Production Control & & Accounts Inventory Scheduling Warehousing Receivable Plant Mgmt.
Finance and Accounting Human Resources
Customers
Suppliers
Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise Resource Planning Benefits of ERP
Quality and Efficiency Decreased Costs Decision Support Enterprise Agility
Failures in ERP Do Exist
Enterprise Resource Planning
Causes of ERP Failures
Underestimating the Complexity of Planning, Development, and Training Needed Failure to Involve Affected Employees Trying to do Too Much Too Fast Over Reliance by Company on Claims of Software Companies
CRM: The Business Focus
Supports an Integrated and Collaborative Relationship Between a Business and its Customers
Customer Life Cycle
CRM Functional Solutions
Acquire
Direct Marketing
Enhance
Cross-sell and Up-sell
Retain
Proactive Service
Sales Force Automation
Customer Support
The Internet
CRM Integrated Solution Shared Customer Data Collaborative Service
Partner
Company
Customer
CRM: The Business Focus
CRM Uses IT to Create a CrossFunctional Enterprise System
Marketing and Fulfillment
Fax
Customer Service and Support e-Mail
Web
Sales Cross-Sell Up-Sell
Prospect or Employee
Telephone
Contact and Account Management
Retention and Loyalty Programs
CRM: The Business Focus
Benefits and Challenges of CRM
Identify and Target the Best Customers Customization and Personalization of Products and Services Track Customer Contacts
CRM Failures
50% of Applications Fail to Meet Expectations 20% of the Time CRM Damaged Customer Relationships Lack of Understanding and Preparation is Blamed
CRM: The Business Focus
Gevity HR and Monster.Com: Failures in CRM Implementation
Employees Undercut the System Believing Their Jobs Threatened by CRM On-Line Customer Problem Solutions. Complex Installation Since it Touches So Many Legacy Systems Failures Lead to Loss of Customer Goodwill and Business and Negatively Affects Employees Also
CRM: The Business Focus
Telstra Corporation: The Business Value of CRM
Provides Fixed, Wireless, and eCommerce Services to Customer Base in 19 Countries Offers Voice, Data, Internet, Multimedia and Communications Services Sought CRM Solution to Integrate More than 20 Core Legacy Databases Across the System Benefits Quickly Followed Reduced Training Time
SCM: The Business Network
SCM Software Helps Firms Reengineer and Integrate The Functional SCM Processes
Supply Chain Life Cycle
SCM Functional Processes
Commit Schedule Make Deliver
Strategic Sourcing Forecast and Demand Planning and Procurement Customer Order Fulfillment Service Distribution Network and Warehouse Operations Production Transportation and Shipment Logistics Management
The Internet
SCM Integrated Solution
Supplier
Shared Market Data
Manufacturer
Collaborative Fulfillment
Retailer Customer
SCM: The Business Network Supply Chain Management : a
top strategic objective for many firms The Right Products The Right Place The Right Time In the Proper Quantity At an Acceptable Cost
SCM: The Business Network
Objectives of Supply Chain Management
Business Value Goals
Rapid Demand Fulfillment
Customer Value Goals
Give customers what they want, when and how they want it, at the lowest cost
Collaborative Supply Chain Planning and Execution
Interenterprise Effective Responsiveness and Coordination of Distribution and Manufacturing and Channel Partnerships Accountability to Customers Business Process
SCM: The Business Network
Objective of SCM Efficiently Manages this Process by:
Forecasting Demand Controlling Inventory Enhancing Business Relationships Receiving Feedback and Status of Every Link of the Chain
SCM: The Business Network
Benefits and Challenges of SCM
Lack of Proper Planning Knowledge, Tools, and Guidelines Inaccurate Demand Forecasts Lack of Adequate Collaboration Software Itself Immature
Enterprise Application Integration
EAI Software Connects Major eBusiness Applications Like CRM and ERP
Front-Office CRM Applications Customer Service Field Service Product Configuration Sales Order Entry Enterprise Application Integration EAI Back-Office ERP Applications Distribution Manufacturing Scheduling Finance
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ERP and CRMDocumento17 pagineERP and CRMSrinibas JenaNessuna valutazione finora
- ErpcrmDocumento18 pagineErpcrmravideva84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Erp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Documento17 pagineErp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Gangadhar MamadapurNessuna valutazione finora
- Erp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Documento17 pagineErp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005tazeem khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Erp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Documento17 pagineErp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Gangadhar MamadapurNessuna valutazione finora
- ERP - ECRM and ESCMDocumento39 pagineERP - ECRM and ESCMAbhishek TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Enterprise Business SystemsDocumento27 pagineChapter 8 Enterprise Business SystemsParvez AliNessuna valutazione finora
- ErpcrmscmDocumento31 pagineErpcrmscmYogesh BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts and ImplementationDocumento30 pagineConcepts and Implementationsantu15038847420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 - Enterprise Applications - Thien Nguyen - V2Documento43 pagineLecture 6 - Enterprise Applications - Thien Nguyen - V2Huong Nguyen Thi XuanNessuna valutazione finora
- ERP Implementation FundamentalsDocumento35 pagineERP Implementation FundamentalsVibhas MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nterprise Esources Lanning: Customer Relationship ManagementDocumento44 pagineNterprise Esources Lanning: Customer Relationship ManagementSupriyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mba, BM 303Documento25 pagineMba, BM 303Naveen SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy Enterprise Applications - Part 02Documento16 pagineAchieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy Enterprise Applications - Part 02Rashmi RathnayakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Selling 2Documento41 pagineCross Selling 2SenthilNathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reporters: Rosario, Vanessa A. Poyaoan, Kimberly CDocumento32 pagineReporters: Rosario, Vanessa A. Poyaoan, Kimberly CNiebla Sanchez Jay-ArNessuna valutazione finora
- BGS Customer Relationship Management: History and Development of CRMDocumento17 pagineBGS Customer Relationship Management: History and Development of CRMFahad Bin SohailNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocumento39 pagineMcgraw-Hill/Irwin Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinArslan SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- ECS402 - Fundamental of MIS - CRMDocumento15 pagineECS402 - Fundamental of MIS - CRMnarumisensei12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of Implementing A CRM System in Cellular Telecom ServicesDocumento29 pagineBenefits of Implementing A CRM System in Cellular Telecom ServicesNimisha WalechaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 08Documento44 pagineChap 08Dhivya ThilagavathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 008Documento25 pagineChap 008Ashfaqur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Beyond ERP: Dept. of Information Systems SVKM's NMIMS University 1Documento21 pagineBeyond ERP: Dept. of Information Systems SVKM's NMIMS University 1devesh_mendiratta_61Nessuna valutazione finora
- ch12 MIS2017Documento22 paginech12 MIS2017MBFINessuna valutazione finora
- Mba Customer Relationship ManagementDocumento18 pagineMba Customer Relationship ManagementAbhiShek ParaSharNessuna valutazione finora
- ERP SYstemsDocumento48 pagineERP SYstemsviggyscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing A CRM Implementation: A People, Process, and Technology ApproachDocumento36 pagineManaging A CRM Implementation: A People, Process, and Technology ApproachSaket MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM Implementation: Presented byDocumento21 pagineCRM Implementation: Presented bykamaljit09dmNessuna valutazione finora
- c8. Business Across Enterprise.gDocumento43 paginec8. Business Across Enterprise.gMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 08Documento53 pagineChap 08JD AsharNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM ComponentsDocumento16 pagineCRM ComponentsAnonymous n1d0jN4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocumento21 pagineCustomer Relationship ManagementSneha Giji SajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Relationship Management: Acknowledgements To Euan Wilson (Staffordshire University)Documento18 pagineCustomer Relationship Management: Acknowledgements To Euan Wilson (Staffordshire University)Neha BhograNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Cross Functional Enterprise SystemsDocumento24 pagineChapter 5 Cross Functional Enterprise SystemsshalvenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Enterprise Business SystemsDocumento6 pagineChapter 8 Enterprise Business SystemsErfan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM - DefinedDocumento26 pagineCRM - Definedssnil1970Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mis Assignment.Documento13 pagineMis Assignment.Sena TeferaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Business SystemsDocumento52 pagineEnterprise Business SystemsYasir Hasnain100% (1)
- 2015-BA7301 (1) - Unit 5 (New)Documento114 pagine2015-BA7301 (1) - Unit 5 (New)Latha Dona VenkatesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Business Systems: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocumento47 pagineEnterprise Business Systems: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinAhmed Mostafa ElmowafyNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 ERP Sales CRM and Knowledge ManagementDocumento25 pagineCH 7 ERP Sales CRM and Knowledge ManagementshathaNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM StrategyDocumento40 pagineCRM StrategyLotox Miarta100% (2)
- E-Business Materi 7 (CRM)Documento17 pagineE-Business Materi 7 (CRM)Amat DamuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Realtions ManagementDocumento30 pagineCustomer Realtions ManagementDeck MaganaNessuna valutazione finora
- Serve Your Customers Better With Microsoft Dynamics CRMDocumento24 pagineServe Your Customers Better With Microsoft Dynamics CRMnileshpatwardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CRMDocumento21 pagineCRMVivek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Documento25 pagineCustomer Relationship Management (CRM)Surgeo PashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5Documento37 pagineModule 5zkharuri7220Nessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Relationship: Management (CRM)Documento59 pagineCustomer Relationship: Management (CRM)soma shivangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Customer Relationship Management System: By-Atul ChaudharyDocumento39 paginePresentation On Customer Relationship Management System: By-Atul Chaudharysalmanali123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Information Technology in Management: A Competitive ImperativeDocumento30 pagineInformation Technology in Management: A Competitive Imperativesjkushwaha21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Documento31 pagineCustomer Relationship Management (CRM)Swagatika MahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM in Ecommerce - FinalDocumento18 pagineCRM in Ecommerce - FinalSharik KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical CRM - 1Documento29 pagineAnalytical CRM - 1thisisrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento20 pagineChapter 2arunkorathNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi 9 CRM & SCMDocumento29 pagineMateri 9 CRM & SCMNeo Achmad SukarnoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Real-Time Contact Center: Strategies, Tactics, and Technologies for Building a Profitable Service and Sales OperationDa EverandThe Real-Time Contact Center: Strategies, Tactics, and Technologies for Building a Profitable Service and Sales OperationNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM in Real Time: Empowering Customer RelationshipsDa EverandCRM in Real Time: Empowering Customer RelationshipsNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM Database Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandCRM Database Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- NISM Equity Derivatives Study Notes-Feb-2013Documento26 pagineNISM Equity Derivatives Study Notes-Feb-2013Priyadarshini Sahoo100% (1)
- Derivative Question and AnswerDocumento15 pagineDerivative Question and AnswerPriyadarshini Sahoo65% (23)
- Mutual Funds: Presentation OnDocumento52 pagineMutual Funds: Presentation OnSurendra SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Erp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Documento17 pagineErp, CRM, SCM: Source: O'Brien, James. Introduction To Information Systems, 12e, 2005Priyadarshini SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- M & ADocumento9 pagineM & APriyadarshini SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Inversion in Conditional SentencesDocumento2 pagineInversion in Conditional SentencesAgnieszka M. ZłotkowskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Nimal SandaratneDocumento12 pagineDr. Nimal SandaratneDamith ChandimalNessuna valutazione finora
- 504 Loan Refinancing ProgramDocumento5 pagine504 Loan Refinancing ProgramPropertywizzNessuna valutazione finora
- Adidas Case StudyDocumento5 pagineAdidas Case StudyToSeeTobeSeenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Origin and Development of English NovelDocumento16 pagineThe Origin and Development of English NovelFaisal JahangeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Gabbard - Et - Al - The Many Faces of Narcissism 2016-World - Psychiatry PDFDocumento2 pagineGabbard - Et - Al - The Many Faces of Narcissism 2016-World - Psychiatry PDFatelierimkellerNessuna valutazione finora
- CV - Parisi - UChileDocumento5 pagineCV - Parisi - UChileFen_udechileNessuna valutazione finora
- Iraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Documento29 pagineIraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Beatriz RosenburgNessuna valutazione finora
- I See Your GarbageDocumento20 pagineI See Your GarbageelisaNessuna valutazione finora
- DESIGNATIONDocumento16 pagineDESIGNATIONSan Roque ES (R IV-A - Quezon)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Role of A ManagerDocumento8 pagineRole of A ManagerMandyIrestenNessuna valutazione finora
- Knitting TimelineDocumento22 pagineKnitting TimelineDamon Salvatore100% (1)
- XZNMDocumento26 pagineXZNMKinza ZebNessuna valutazione finora
- WN On LTC Rules 2023 SBDocumento4 pagineWN On LTC Rules 2023 SBpankajpandey1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporary Worl Module 1-Act.1 (EAC) Bea Adeline O. ManlangitDocumento1 paginaContemporary Worl Module 1-Act.1 (EAC) Bea Adeline O. ManlangitGab RabagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Consti 2: Case Digests - Regado: Home Building & Loan Assn. V BlaisdellDocumento6 pagineConsti 2: Case Digests - Regado: Home Building & Loan Assn. V BlaisdellAleezah Gertrude RegadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Facilitators of Globalization PresentationDocumento3 pagineFacilitators of Globalization PresentationCleon Roxann WebbeNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Grading Science 6 Worksheet 16 Code: S6Mtiii-J-5Documento3 pagineSecond Grading Science 6 Worksheet 16 Code: S6Mtiii-J-5Catherine Lagario RenanteNessuna valutazione finora
- The Body of The Atman in The Katha UpanishadDocumento4 pagineThe Body of The Atman in The Katha UpanishadmikikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Democratic EducationDocumento11 pagineDemocratic Educationpluto zalatimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Study in USADocumento4 pagineWhy Study in USALowlyLutfurNessuna valutazione finora
- Rong Sun ComplaintDocumento22 pagineRong Sun ComplaintErin LaviolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Occult Final DraftDocumento142 pagineOccult Final DraftAlquimista AncestralNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento3 pagineAssignment 1Bahle DlaminiNessuna valutazione finora
- Linking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationDocumento2 pagineLinking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationAlexa GandioncoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aradau Security Materiality SDDocumento22 pagineAradau Security Materiality SDTalleres NómadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sally Tour: TOUR ITINRARY With QuoteDocumento2 pagineSally Tour: TOUR ITINRARY With QuoteGuillermo Gundayao Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vayutel Case StudyDocumento10 pagineVayutel Case StudyRenault RoorkeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Hassan I SabbahDocumento9 pagineHassan I SabbahfawzarNessuna valutazione finora
- Martin, BrianDocumento3 pagineMartin, Brianapi-3727889Nessuna valutazione finora