Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bengkel Peningkatan Maths SPM
Caricato da
Zuraidah MustaffaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bengkel Peningkatan Maths SPM
Caricato da
Zuraidah MustaffaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
JOM SKOR A
a + 90% = 126/140
K1 = 35/40 dan k2=91/100
A 80% = 112/140
K1 = 33/40 dan k2 = 79/100
a- 75% = 105/140
K1 = 30/40 dan k2 =
75/140
SEMUA MANUSIA DILAHIRKAN
DENGAN POTENSI YANG
TINGGI..
KITA YANG MENCORAKKAN
HIDUP KITA.
BERUBAHLAH..
TENTUKAN MASA
DEPAN HIDUP
KITA
jawab soalan mudah dahulu
1. Plans and elevations 12 m
2. graph inequalities 3 m
3. Quadratics equations 4m
4. Area & perimeters 6m
5. Volumes - 4m
6. MATHEMATICAL REASONING -
5M
7. Matrices 6m
8. Graph of functions 12 m
9. Statistics 12m
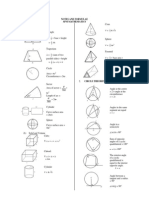
PLANS AND ELEVATIONS
1. Drawing only.
2. Not necessary to label the drawing.
3. Rotation is accepted.
4. Extra lines (added) / not drawn
(missed) [dashed/dotted/solid]
==> no marks given !
4 cm
K
B
D
C
H
G
F
E
A
L
M
J
5 cm
7 cm
2 cm
2 cm
Diagram 15.1
Rajah 15.1
plan
5CM
5CM
2CM
4 cm
K
B
D
C
H
G
F
E
A
L
M
J
5 cm
7 cm
2 cm
2 cm
3 cm
4 cm
1 cm
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
The elevation of the solid as viewed from X.
Elevation as viewed from y
REGION REPRESENTING INEQUALITIES
IN TWO VARIABLES
1. Draw a specific straight line 1 M
2. The region correctly shaded 2 M
INEQUALITIES
> - I>ESAR
< - I<ECIL
INEQUALITIES IN GRAPH OF FUNCTION
PAPER 2 - 2009, 2007, 2005, 2003
Y - KE ATAS GARISAN,
Y - KE BAWAH GARISAN
X - KE KANAN,
X - KE KIRI
GARIS PUTUS-PUTUS UNTUK > ATAU <,
GARIS TERUS UTK DAN
y -x + 5
Y 2x - 2
X > 1
QUADRATIC EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS
1. Write in the general form,
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0.
[ a, b, c ~ constants ( Integer )]
2. Factorise completely
3. Write down the values of unknown
1M
2M
1M
Solve the quadratic equation:
(2y 5)(y + 7) = 4
( )
7
2
2
y
2y
2
+ 14y -5y 35 = 8y -14
2y
2
+ y - 21 = 0
(2y + 7 ) ( y 3 ) = 0
Y = , y = 3
2
7
Circles ; Sector - Perimeter and
Area of shaded region.
Use the correct formulae and substitute
the related values to calculate
i) the perimeter of the diagram,
ii) the area of the shaded region.
6M
Circumference & Area of a circle
~ Circumference : 2tr = td
~ Area : tr
2
u
R
Q
P
O
j
Length of arc
PQR
Area of a
sector OPQR
2
360
r
2
360
r
Given POQ = 60, ROT = 45 and POT = 90. Using =
, calculate
Diberi POQ = 60, ROT = 45 dan POT = 90. Dengan menggunakan = , hitungkan
(a) the perimeter, in cm, of the whole diagram.
perimeter, dalam cm, seluruh rajah itu.
PERIMETER = PO + OT + TS + SQ + QP
cm 3 . 71 @
3
214
@
3
1
71
22
3
1
7 42
21
7
22
2
360
60
7 14
7
22
2
360
30
14 21
=
+ + =
+ + + + =
b) the area, in cm
2
, of the shaded region.
luas, dalam cm
2
, kawasan yang berlorek.
AREA 0F THE SHADED REGION :
3 . 205 @
3
616
@
3
1
205
3
2
25 231
14
7
22
360
15
21
7
22
360
60
=
=
=
cm
2
2
2
Solid Geometry ;
~ Volume
Use the correct formulae and substitute
the related values to calculate the volume
of the composite solid.
4M
VOLUMES OF THE SOLIDS :
cm 1400
770 630
10 7
7
22
2
1
10 3 ) 28 14 (
2
1
=
+ =
+ + =
2
3
Mathematical Reasoning.
1. A Statement. 1M
2. A Quantifier.
1M
3. Operations involving Not or
No, And and Or,.
4. Implication: The converse
5. Argument.
6. Deduction and Induction.
1M
1M
1M
2M
MATHEMATICAL REASONING PAPER 2 ONLY.
1. STATEMENT / PERNYATAAN AYAT YANG MAKSUDNYA
JELAS BENAR ATAU PALSU.
2. PENGKUANTITI
ALL / SEMUA --- UNTUK SEMUA KES
SOME --- BENAR BAGI BEBERAPA KES SAHAJA.
3. OPERASI - a. Not / bukan mengubah maksud
pernyataan b. menggabung (compound) 2
pernyataan dgn :
p q P and q P or q
Benar / true Benar / true Benar / true Benar / true
Palsu / false Benar / true Palsu / false Benar / true
Benar / true Palsu / false Palsu / false Benar / true
Palsu / false Palsu / false Palsu / false Palsu / false
4.IMPLIKASI / IMPLICATION
Jika P, maka Q / If p, then q
a. Satu implikasi sahaja :
Antecedent : m > n
Consequent : m n > 0
Implication : If m > n, then m - n > 0.
Converse : If m n > 0, then m > n.
b. 2 implikasi -- p if and only if q
Implication 1 : If p, then q
Implication 2 : If q, then p.
5. HUJAH / ARGUMENTS TIGA BENTUK
P1 : ALL A IS B P1 : IF P, THEN Q P1 : IF P, THEN Q
P2 : C IS B P2 : P P2 : ~ P
CONCLUSION: C IS A CONCLUSION : Q CONCLUSION : ~ Q
6. MAKING DECISION / MEMBUAT KESIMPULAN
INDUCTION / ARUHAN
From several cases formula
DEDUKSI / DEDUCTION - SPM 2008
Formula use in several cases
TEOREM IBNU HAITHAM
c
a
b
a, b, c
3, 4, 5
5, 12, 13
6, 8, 10
7, 24, 25
8, 15, 17
9, 12, 15
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
x
144
121
100
81
64
49
36
25
16
9
4
1
2
x
1728
1331
1000
729
512
343
216
125
64
27
8
1
3
x
1
3
1
2
10. a. 8
3
= 512 and 8 =
X
X
= 3 if and only if y = 27
3
. y b
3 , 27 : 2
27 , 3 : 1
3
3
= =
= =
y then Ify I
theny y If I
c. Premise 1: If P Q = P, then P Q
Premise 2: ..
conclusions : P Q P
c
=
P Q
.
c
2. Solving the matrix equation :
If M =
=
a b
d
x
y
p
q
=
x
y
p
q
M
1
4M
MATRICES
1. Using the identity matrix - concept of inverse
matrix
AB = I = BA to find the constant.
2M/3M
(
d c
b a
1
A
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
d c
b a
A
|
|
.
|
\
|
a c
b d
bc ad
A
1
1
CERITA ADA DUIT BAYAR CUKAI
ada duit, bayar cukai,
Jadi : songsangannya
1 per ada duit tolak bayar cukai,
Duit ada, tolak bayar tolak cukai
Invrse matrices
,
maka
Jika tiada songsangan , maka ad bc = 0
|
|
.
|
\
|
3 1
1 2
|
|
.
|
\
|
2 1
3 n
m
8 It is given that the inverse matrix of
(a) Find the values of m and of n.
A =
IS
|
|
.
|
\
|
3 1
1 2
1
A
1 ) 1 ( ) 3 ( 2
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
2 1
1 3
7
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
2 1
1 3
a
b
c
d
m , n = 1
7
1
=
7 2 = q p
7 3 = + q p
Using matrix method , calculate the values of p and of q
|
|
.
|
\
|
3 1
1 2
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
7
7
|
|
.
|
\
|
q
p
|
|
.
|
\
|
q
p
7
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
2 1
1 3
|
|
.
|
\
|
7
7
7
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
) 7 ( 2 ) 7 ( 1
) 7 ( 1 ) 7 ( 3
7
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
21
14
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
2
p = 2, q = -3
THE STRAIGHT LINE
(Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides that
are parallel)
(Trapezium : A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel line)
(Two parallel lines)
* Find/Calculate
i) the gradient of a straight line,
y
2
y
1
x
2
x
1
m =
or m =
y intercept
x intercept
2M
ii) the equation of a straight line, y = mx + c.
[ Using the formulae : y
1
= mx
1
+ c
or y y
1
= m(x x
1
)]
2M
iii) x-intercept or y-intercept.
[ y = 0 to obtain xintercept or vice-versa!] 1M
Garis lurus QR ialah selari dengan paksi-y dan garis PQ ialah selari dengan garis RS.
Persamaan garis lurus PQ ialah 2x + y = 10.
a. Nyatakan persamaan garis lurus RQ.
QR // paksi-y, maka persamaannya ialah x= 5
b. Cari persamaan garis lurus RS dan seterusnya, nyatakan pintasan-y bagi garis
lurus itu.
RS // PQ, maka kecerunan RS = kecerunan PQ
maka m = -2
Guna m = -2 dan R( 5,14), ganti dalam y=mx + c
Maka 14 = -2(5) + c
14 + 10 = c
C = 24 , maka persamaan RS ialah y = - 2x + 24. dan pintasan-y = 24
10 2
10 2
+ =
= +
x y
y x
LINES AND PLANES IN 3D
IDENTIFY THE ANGLE BETWEEN :
1. LINE AND PLANE
BY : BOLD THE LINE AND SHADE THE PLANE
IDENTIFY THE ANGLE USING SAME ALPHABETS
INTERSECTION POINT
2. TWO PLANES - IDENTIFY THE ANGLE USING SAME ALPHABETS
-INTERSECTION LINE
3. IDENTIFY THE NORMAL LINE TO FORM THE RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLE
4. DONT FORGET --- SOH CAH TOA
MARKING : - NAME THE ANGLE ---- 1M
USE TRIGONOMETRY TO CALCULATE THE ANGLE - 1M,
STATE THE VALUE OF THE ANGLE --- 1M
Kenal pastikan dan hitungkan sudut di antara satah OJM dengan tapak JKLM.
1. ABJAD YANG SAMA IALAH JM
2. SUDUT MESTI DARI O, O PULA SEGARIS / SESATAH DENGAN M
3. O PULA TERGAK DI ATAS L
4. MAKA SUDUTNYA IALAH
OML Z
1. Coefficient of the unknown to be
eliminated must be the same. 1M
2. Write in linear equation of one unknown
1M
3. Find the values of the unknowns 2M
SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS
[ By elimination ]
3
. 5w + 4x = 1 ----
(1)
2w 5x = 7 ----
(2)
Boleh selesaikan guna kaedah penghapusan, penggantian atau matriks.
(1) x 2 2( 5w + 4x = 1) ------------ 10w + 8x = 2 --------- (3)
(2) x 5 5(2w 5x = 7) ------------ 10w 25x = 35 --------- (4)
(3) (4) 10w 10w + 8x (-25x) = 2- 35
33x = -33
x = -1
Ganti x = -1 dalam (2)
2w -5(-1) = 7
2w = 7 5
2w = 2
w = 1
PROBABILITY
The probability of event A,
( )
( )
( )
n A
P A
n S
=
The probability of the complement of event A, ( A' )
) ( 1 ) ' ( A P A P =
List the sample space and the events.
The probability of combined events
~ or ( addition )
~ and ( multiplication ) 2M
A combined event, A or B,
~ P(A B) = P(A) + P(B)
A combined event, A and B,
~ P(A B) = P(A) P(B)
PROBABILITY
2 3 4 5 6
A.LIST THE SAMPLE SPACE
(WITHOUT REPLACEMENT)
S = { (2,3), (2,4) , (2,5), (2,6), (3,2),
(3,4) , (3,5), (3,6), (4,2), (4,3) , (4,5),
(4,6), (5,2), (5,3) , (5,4), (5,6), (6,2),
(6,3) , (6,4), (6,5)}
B. i. Probabilty of code begin with number 4 :
Code begin with 4 = {(4,2), (4,3) , (4,5), (4,6) }
P (code begin with 4)
16
4
=
4
1
=
B. ii. Probabilty of code consist of two odd
numbers or 2 even numbers :
Code consist of 2 even numbers or 2 odd
numbers are = {(2,4),(2,6),(4,2), (4,6), (6,2), (6,4),
(3,5), (5,3) }
P (odd or even numbers)
16
8
=
2
1
=
GRAPHS OF FUNCTIONS
a. Completed the table / calculate the values of y.
2M
b. (i) Both axes drawn in the correct direction and
uniform scale, 1M
(ii) All the points plotted correctly, 2M
(iii) Draw the graphs of function
~ quadratic/cubic/reciprocal. 1M - 2M
c. Find the values of x or y from the graph drawn
1M/2M
d. (i) Write down/state the linear equation,
y = mx + c 1M
(ii) Draw the straight line, y = mx + c 1M
(iii) Find the intersection point and state the
value of x coordinate 1M
x
y
Describe, in full :
ROTATION
Rotation 1M
State the angle in degrees
& *direction of rotations 1M
(clockwise or anti clockwise)
Centre of rotations 1M
(Coordinates or the point in the diagram given)
TRANSFORMATIONS
ENLARGEMENT
Enlargement 1M
Scale factor k 1M
[ k : integer ! ]
Centre of enlargement 1M
(Coordinates or the point in the diagram given)
Area of Image =
(Scale Factor) x
2
area of object
=
2
area of object x k
Using the formula to find
3M
TRANSLATIONS
h
k
Translation
2M
Reflections 1M
state the axis of reflection
(In the line .) 1M
[Equation of the straight line or the line
that join two points]
REFLECTIONS
Examples:
A rotation of 90
o
anticlockwise
about point (6,2) 3M
An enlargement with scale factor 3
centered at point H 3M
A reflection in the line y = 2 2M
2
3
Translation
2M
STATISTICS
a) Complete the table given 4M
c) (i) Both axes drawn in the correct direction and
uniform scale, 1M
(ii) Plot the points and draw
~ a histogram / a frequency polygon / an ogive 2M
b) Calculate the estimated mean 4M
d)(i) From the ogive, find
~ 3
rd
quartile, 1
st
quartile,
interquartile range , median 1M
(ii) State the information from the ogive /
histogram / frequency polygon 1M
EARTH AS A SPHERE
1 Finding the latitude or longitude,
Location of a place
2M
2 Find the distance
(a) Shortest distance (a great circle)
*difference in latitude 60
*difference in longitude (equator) 60
(b) Along a parallel of latitude
difference in longitude 60 cos of latitude
2M / 3M
Z substended =
Z substended =
2M
or
Distance
60
Distance
60 cos of latitud
3 Calculate the
(a) average speed,
(b) time taken for the flight.
2M/3M
Speed
Time
Distance
EARTH AS A SPHERE
akhir kata :
1,2,3
Harap semua suka
C,b, a
Semoga semua skor a!
kalau hendak, seribu
daya!
semoga berjaya!
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mathematics: Problem Solving in MathematicsDocumento17 pagineMathematics: Problem Solving in MathematicsRedzuan SaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Add MathsDocumento40 pagineAdd MathsJoseph TingNessuna valutazione finora
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematics SPM 2011.powerpointDocumento55 pagineMathematics SPM 2011.powerpointuzai88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes and Formulae MathematicsDocumento9 pagineNotes and Formulae MathematicsNurAinKhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDa EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramah Maths 2011Documento9 pagineCeramah Maths 2011soon siew leeNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDa EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNessuna valutazione finora
- Matematik K1 Modul Kecemerlangan SMKAM2 2023Documento21 pagineMatematik K1 Modul Kecemerlangan SMKAM2 2023Faisal Zharif FZNessuna valutazione finora
- Iit Jee 2005 MatDocumento7 pagineIit Jee 2005 MatLokesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionDa EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Documento133 pagineAnalytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Edward RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Analysis and Probability: Solutions to ProblemsDa EverandReal Analysis and Probability: Solutions to ProblemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Technique MM 2Documento34 pagineAnswer Technique MM 2Lä HäNäNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers and Solutions: WC! Ibc! - Icei lAC! Iec! lAC! - lAC! - IBC!Documento74 pagineAnswers and Solutions: WC! Ibc! - Icei lAC! Iec! lAC! - lAC! - IBC!Jay-Ann SampsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Asymptotes: If An Asymptote Is Neither Parallel To X-AxisDocumento6 pagineAsymptotes: If An Asymptote Is Neither Parallel To X-AxisMaster RaghuNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Maths FormulaeDocumento10 pagineBasic Maths FormulaeAns DevNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: End of Year Exam RevisionDocumento15 pagineMathematics: End of Year Exam Revisionapi-354037574Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Some Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in MathematicsDocumento12 pagineSome Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in Mathematicsparchure123100% (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringDa EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocumento9 pagineFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocumento9 pagineNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometrySharmini RajagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDa EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- TMM - Chapter 2Documento18 pagineTMM - Chapter 2Ahmed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial SPM 2014 Melaka P1 & P2 PDFDocumento65 pagineTrial SPM 2014 Melaka P1 & P2 PDFrusleenaosman790% (1)
- Tables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesDa EverandTables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3Documento39 pagineApplied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3bigbangmelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDa EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Form 4: - Chapter 5: The Straight Line - Subtopic 5.4: Equation of A Straight LineDocumento53 pagineMathematics Form 4: - Chapter 5: The Straight Line - Subtopic 5.4: Equation of A Straight Linechia poh hooiNessuna valutazione finora
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Da EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Documento13 pagineMaths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Apex InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Solutions Manual For StudentsDocumento106 pagineSolutions Manual For StudentsEddie HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ipmat Indore 2021 Official Paper 02760aa991f7bDocumento23 pagineIpmat Indore 2021 Official Paper 02760aa991f7bSamir Shiva ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 1a Chapter IDocumento68 pagineMath 1a Chapter IDimple DizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional FiguresDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional FiguresNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Paper 1Documento7 pagineTrial Paper 1MuhandiramalageNessuna valutazione finora
- UCE Book 4Documento134 pagineUCE Book 4Ssonko Martin100% (1)
- 15aimo 2Documento10 pagine15aimo 2Hoàng LongNessuna valutazione finora
- Straight Lines HSNDocumento18 pagineStraight Lines HSNapi-298592212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Year 10 wk27 Maths: Plotting ST Line Graphs Shading InequalitiesDocumento26 pagineYear 10 wk27 Maths: Plotting ST Line Graphs Shading InequalitiesBrivimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of DerivativesDocumento33 pagineApplications of DerivativesRiddhima MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 10 Formula IcseDocumento9 pagineClass 10 Formula IcseAdarsh Dongare100% (4)
- Analytical Geometry: y y M X XDocumento10 pagineAnalytical Geometry: y y M X XKomanduri Murali SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Iit Jee 2004 MathDocumento7 pagineIit Jee 2004 MathLokesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Stage 3 Revision Sheet HigherDocumento9 pagineStage 3 Revision Sheet Highercozzy'mozzy..dozzy.;Nessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Calculus-I: Note: 1. If K ( 0) Is The Curvature of A Curve at P, Then The RadiusDocumento28 pagineDifferential Calculus-I: Note: 1. If K ( 0) Is The Curvature of A Curve at P, Then The RadiustechzonesNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 15 Kinetics of Particles Impulse and MomentumDocumento24 pagineCH 15 Kinetics of Particles Impulse and MomentumKhaled ObeidatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Jan P1 QPDocumento28 pagine2009 Jan P1 QPNafi Ul KaysarNessuna valutazione finora
- ME320 Professor John M. Cimbala: Recall Our Fluid Statics EquationDocumento9 pagineME320 Professor John M. Cimbala: Recall Our Fluid Statics EquationSudesh PowarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science DelusionDocumento150 pagineScience Delusiondimitrescu anaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel To HP Inclined To HP One Small Side Inclined To VP: Surface SurfaceDocumento4 pagineParallel To HP Inclined To HP One Small Side Inclined To VP: Surface Surfaceajeng.saraswatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Math MajorDocumento26 pagineMath MajorMuffy Fernandez100% (1)
- Introduction To General Relativity Corrections 5 - Schwarzschild MetricDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To General Relativity Corrections 5 - Schwarzschild MetricAnonymous NNElumNessuna valutazione finora
- Saldanha (2017) Space After Deleuze PDFDocumento233 pagineSaldanha (2017) Space After Deleuze PDFcwaranedNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotational Concept (Konsep Rotasi)Documento6 pagineRotational Concept (Konsep Rotasi)bat.laughNessuna valutazione finora
- Floor Plan DrawingsDocumento6 pagineFloor Plan DrawingsMae_Sheryn_Lip_1795Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Integrals and Integral Theorems: R, R R RDocumento23 pagineVector Integrals and Integral Theorems: R, R R RRoy VeseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test 7: VectorsDocumento2 pagineCore Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test 7: VectorslaurenNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 2 Moment of Inertia PDFDocumento14 pagine08 2 Moment of Inertia PDFReddyvari VenugopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Order in Crystals1Documento35 pagineInternal Order in Crystals1Kripa KattelNessuna valutazione finora
- S Aces: For Early Childhood EducationDocumento20 pagineS Aces: For Early Childhood EducationEmilija AntevskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec02 Curves Surfaces 2 PDFDocumento110 pagineLec02 Curves Surfaces 2 PDFBilkis Jamal FerdosiNessuna valutazione finora
- K (XL: andDocumento3 pagineK (XL: andEpic WinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Geometric Objects and TransformationsDocumento43 pagineChapter 3 Geometric Objects and TransformationsKay KhineNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.sheet Metal ModelingDocumento8 pagine8.sheet Metal Modelingpiero perezpNessuna valutazione finora
- SQP 22201 Applied Mathematics PDFDocumento6 pagineSQP 22201 Applied Mathematics PDFNilesh Avhad0% (1)
- ArchiCAD Canopy GuideDocumento15 pagineArchiCAD Canopy GuideFellow9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solid WorksDocumento65 pagineSolid WorkssumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus PDFDocumento101 pagineCalculus PDFNovember100% (1)
- Tevian Dray, Corinne A Manogue - The Geometry of The Octonions-World Scientific Publishing Company (2015)Documento229 pagineTevian Dray, Corinne A Manogue - The Geometry of The Octonions-World Scientific Publishing Company (2015)Miguel Angel Hanco Choque100% (2)
- 4 THDocumento2 pagine4 THYohannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Curvilinear (Two-Dimensional) Motion: ME 231: DynamicsDocumento20 pagineCurvilinear (Two-Dimensional) Motion: ME 231: DynamicsRenthel CuetoNessuna valutazione finora
- (Sergei Ovchinnikov) Functional Analysis (B-Ok - Xyz) (001-050) PDFDocumento50 pagine(Sergei Ovchinnikov) Functional Analysis (B-Ok - Xyz) (001-050) PDFOswaldo VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet Books SJSNDocumento21 pagineSheet Books SJSNArya GuptaNessuna valutazione finora