Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Caricato da
Ibrahim AlturaikiDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Caricato da
Ibrahim AlturaikiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Click to edit Master subtitle style
5/5/12
C-reactive protein (CRP)
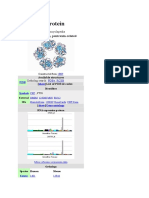
In acute phase protein, one of the pentraxin
proteins in serum, and is comprised of five amino acid polypeptide subunits that are all the same and arranged in the a disk conformation without covalent bonds..
Human CRP is composed of five identical
polypeptide units non-covalently arranged as a cyclic pentamer.
5/5/12
5/5/12
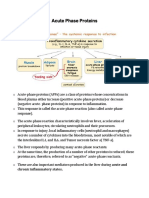
Acute phase proteins:
are plasma proteins synthesized by the liver, that increase in concentration during inflammation.
Pentraxin:
are a family of acute phase plasma proteins comprised of five identical globular subunits.
5/5/12
IL-6 promotes the synthesis and release of C-
reactive protein (CRP) by the liver.
Although present in normal individuals in only
trace (low) amounts in the plasma.
Inflammation induced by bacteria infection,
necrosis of tissue, trauma, or malignant tumors , may cause a striking increase in the serum concentration to levels of up to 2000 times the reference range within 48 hours of the inducing condition.(levels of CRP rapidly increase within 2 hours of acute insult, reaching a peak at 48 hours)..
5/5/12 CRP rises up to 50,000-fold in acute
CRP declines with a relatively short half-life of
18 hours.
Once the condition that induced its elevation
has resolved, the CRP concentration returns to normal within a short time.
5/5/12
CRP levels signify the extent of the disease
activity.
CRP has the greater sensitivity of any
nonspecific test used in screening for organic disease.
It is much more reliable than is the
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Measuring CRP level is a screen for infectious
and inflammatory diseases.
5/5/12
CRP readily binds to phosphocholine (a
molecule expressed on some microbes) and acts as an opsonin (physiological role) as Acute phase proteins that:
CRP in one of a set of serum proteins known
1/ inhibit the spread of infectious organisms. 2/ act on the hypothalamus to increase body temperature and produce fever, an effective means of inhibiting microbial growth.
CRP enhancing uptake of microorganisms by 5/5/12
microphages and neutrophils.
The physiological role of CRP is to bind to
phosphocholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells (and some types of bacteria) in order to activate the complement system. to foreign and damaged cells and enhances phagocytosis by macrophages (opsonin mediated phagocytosis), which express a receptor for CRP.
It is thought to assist in complement binding
It is also believed to play another important
role in innate immunity, as an early defense 5/5/12 system against infections
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Acute Phase Proteins 1Documento10 pagineAcute Phase Proteins 1Abdurahman DarahemNessuna valutazione finora
- Minireview: C-Reactive ProteinDocumento4 pagineMinireview: C-Reactive ProteinpriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: Reaction, Is The Rate at WhichDocumento37 pagineErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: Reaction, Is The Rate at WhichAsmita PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumoniae, Was The First Acute-Phase Protein To Be Described and Is An ExquisitelyDocumento11 paginePneumoniae, Was The First Acute-Phase Protein To Be Described and Is An ExquisitelyLabontu IustinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Phase Reactants: by Dr. Sarah Firdous Moderator Dr. Ch. NavaneethaDocumento75 pagineAcute Phase Reactants: by Dr. Sarah Firdous Moderator Dr. Ch. NavaneethaNoorul AinNessuna valutazione finora
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocumento13 pagineWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistslidawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP LabDocumento13 pagineCRP Labngurah_wardanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Minireview: C-Reactive ProteinDocumento4 pagineMinireview: C-Reactive ProteinFernando Amblódegui GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Chapter 5Documento57 pagineIs Chapter 5aemancarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ProposalDocumento8 pagineProject ProposalArnab ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S2213434415000195 MainDocumento6 pagine1 s2.0 S2213434415000195 MainElisaNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP Who PDFDocumento4 pagineCRP Who PDFEllya Latifah IlyasNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0006291X07024345 MainDocumento6 pagine1 s2.0 S0006291X07024345 MainErsin KARATAŞNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Inflammatory SyndromeDocumento6 pagineExploring Inflammatory SyndromeEmi ValcovNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 BSMT 3A Act. 5.2Documento7 pagineGroup 1 BSMT 3A Act. 5.2Gennelyn Ross Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Therapeutic Apheresis - Use of Human Serum Albumin, Fresh Frozen Plasma and Cryosupernatant Plasma in Therapeutic Plasma ExchangeDocumento11 pagineTherapeutic Apheresis - Use of Human Serum Albumin, Fresh Frozen Plasma and Cryosupernatant Plasma in Therapeutic Plasma ExchangePritha BhuwapaksophonNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Phase Reactants - UpToDateDocumento15 pagineAcute Phase Reactants - UpToDateKarito FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP TestDocumento2 pagineCRP Testces8bautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rol Cut Biblio 1-7Documento14 pagineRol Cut Biblio 1-7chandanNessuna valutazione finora
- IMMUNOSEROLOGY PT 4Documento10 pagineIMMUNOSEROLOGY PT 4Cheryl Ann De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Landmark 2332Documento14 pagineLandmark 2332Visioning SolitudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Biomarkers inDocumento32 pagineLaboratory Biomarkers inXTraw ViewNessuna valutazione finora
- Who NMH NHD Epg 14.7 EngDocumento4 pagineWho NMH NHD Epg 14.7 EngJohnDoeNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP - TestDocumento5 pagineCRP - TestMohammed R.HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevated Phospholipase D Levels Cause Rapamycin Resistance in DU145 CellsDocumento7 pagineElevated Phospholipase D Levels Cause Rapamycin Resistance in DU145 Cellsapi-252167632Nessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Anti-Peptide Polyclonal Antibodies Raised Against Immunogenic Sequences of Protein Encoded by Fj194940.1 GeneDocumento9 pagineDevelopment of Anti-Peptide Polyclonal Antibodies Raised Against Immunogenic Sequences of Protein Encoded by Fj194940.1 GeneijsidonlineinfoNessuna valutazione finora
- ESR in OrthopaedicsDocumento4 pagineESR in Orthopaedicsdoos1Nessuna valutazione finora
- PRP in DermatologyDocumento36 paginePRP in DermatologySuryakant HayatnagarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- High CholesterolDocumento7 pagineHigh CholesterolAlphaRaj MekapoguNessuna valutazione finora
- Wang 2015Documento14 pagineWang 2015Manuel Esquivel OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomarkers in SepsisDocumento33 pagineBiomarkers in SepsisAnjana KsNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute-Phase Proteins: Cem Gabay, Irving KushnerDocumento6 pagineAcute-Phase Proteins: Cem Gabay, Irving KushnerDharmender ChanghtaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 BRDocumento11 pagine2017 BRCony GSNessuna valutazione finora
- PKD BiochemistryDocumento7 paginePKD BiochemistryHyun Jae WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Procalcitonin: Reference RangeDocumento3 pagineProcalcitonin: Reference RangeRahmiati LaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Maedica 15 513Documento4 pagineMaedica 15 513Nasrin SharifiNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of Protein and MRNA Expression of The MTORC1 RepressorDocumento6 pagineRegulation of Protein and MRNA Expression of The MTORC1 RepressorIsa AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Khatri 2020Documento10 pagineKhatri 2020Sukma's Wahyulii TiyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 2. InnataDocumento15 pagineTaller 2. InnataMaría Alejandra Mancera GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Proteins and InflammationDocumento13 pagineBlood Proteins and InflammationValentina SuescunNessuna valutazione finora
- High Catalytic Activity of Human Cytochrome P450 Co-Expressed With Human NADPH-Cytochrome P450 Reductase in Escherichia Coli (1998)Documento11 pagineHigh Catalytic Activity of Human Cytochrome P450 Co-Expressed With Human NADPH-Cytochrome P450 Reductase in Escherichia Coli (1998)Nimra Naveed ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion - 2012 - McLeod - Plasma and Plasma Derivatives in Therapeutic PlasmapheresisDocumento7 pagineTransfusion - 2012 - McLeod - Plasma and Plasma Derivatives in Therapeutic PlasmapheresisMohd Anas SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Whole Blood and PBMC Assays ForDocumento5 pagineComparison of Whole Blood and PBMC Assays ForFani LonelygirlNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Extracellular Secretion Mechanisms in E. Coli Strains BL21 (DE3) and Nissle 1917Documento10 pagineComparing Extracellular Secretion Mechanisms in E. Coli Strains BL21 (DE3) and Nissle 1917vikramreddy041302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research Epstein-Barr Virus Encoded Latent MembraneDocumento9 pagineResearch Epstein-Barr Virus Encoded Latent MembraneMiss AmyNessuna valutazione finora
- C Reactive ProteinDocumento24 pagineC Reactive ProteinMohammed FareedNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP - TestDocumento5 pagineCRP - TestAhmed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Heidi LuckDocumento17 pagineHeidi LuckAfif FaiziNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Enzymology-4th LevelDocumento29 pagineClinical Enzymology-4th Leveltony maxxNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Article: Involvement of Prohibitin Upregulation in Abrin-Triggered ApoptosisDocumento11 pagineResearch Article: Involvement of Prohibitin Upregulation in Abrin-Triggered ApoptosisAndri Praja SatriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Out PDFDocumento16 pagineOut PDFyostiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Department Faculty of Medicine Helwan UniversityDocumento4 pagineBiochemistry Department Faculty of Medicine Helwan UniversityAbdelrahman KhaledNessuna valutazione finora
- ClinicalEnzymology 4thLevelPharmacyStudentsDrMIKotbElSayedDocumento29 pagineClinicalEnzymology 4thLevelPharmacyStudentsDrMIKotbElSayedAnusha SebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- BCH421 CA - 2021 Revised-1Documento5 pagineBCH421 CA - 2021 Revised-1idriscognitoleadsNessuna valutazione finora
- Prolactin Increase Frecuency of T Helper FolicularDocumento15 pagineProlactin Increase Frecuency of T Helper Folicularauroragamez2015Nessuna valutazione finora
- Romiplastion Purification Fayaz2016Documento5 pagineRomiplastion Purification Fayaz2016venkynmNessuna valutazione finora
- Latex AggluDocumento3 pagineLatex AggluAbigrael TangcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein TherapeuticsDocumento14 pagineProtein TherapeuticsSumanth Kumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bed MakingDocumento8 pagineBed MakingV_RN100% (1)
- Elementary School Student Handbook 2016 2017Documento113 pagineElementary School Student Handbook 2016 2017Raniel Alemania LacuarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Western Mindanao State University: Activity IvDocumento6 pagineWestern Mindanao State University: Activity IvRoshin TejeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Domestic Violence Literature Review ExampleDocumento5 pagineDomestic Violence Literature Review Examplefvdra0st100% (1)
- NIRMA (RCP) - Background InvestigationsDocumento3 pagineNIRMA (RCP) - Background InvestigationskevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Spark by John Ratey - Chapter 1 PDFDocumento25 pagineSpark by John Ratey - Chapter 1 PDFRobert CazoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicle Bill Dec28Documento2 pagineMedicle Bill Dec28pises97155Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module B - Lesson 5Documento17 pagineModule B - Lesson 5Melanie CortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Project Analysis On ShampooDocumento12 pagineChemistry Project Analysis On ShampoomrlkranadonNessuna valutazione finora
- Serum Ionic Calcium Levels and Hypocalcemia in DenDocumento5 pagineSerum Ionic Calcium Levels and Hypocalcemia in DenJoko Purnomo HNessuna valutazione finora
- Methodological Advances in Differential Psychology: William Revelle David M. Condon Joshua WiltDocumento28 pagineMethodological Advances in Differential Psychology: William Revelle David M. Condon Joshua WiltDaniela RiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation Importance of StudyDocumento5 pagineDissertation Importance of StudyPaperWritersSingapore100% (1)
- Edgar N. Rapisora, Petitioner, vs. Civil Service Commission, Respondent.Documento2 pagineEdgar N. Rapisora, Petitioner, vs. Civil Service Commission, Respondent.JhunMirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- STS - MODULE1 - Answer SheetsDocumento8 pagineSTS - MODULE1 - Answer SheetsRamil VillacarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Jenis Barang Nama Matkes SAT Harga Sat Bekal LaboratDocumento570 pagineJenis Barang Nama Matkes SAT Harga Sat Bekal LaboratANNISA RAHMATINANessuna valutazione finora
- Online Under Graduate Ayurveda/Siddha/Unani/Homoeopathy SeatsDocumento3 pagineOnline Under Graduate Ayurveda/Siddha/Unani/Homoeopathy SeatsNT- Dhany sirNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Certificate For Cause of DeathDocumento1 paginaMedical Certificate For Cause of DeathTikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study AriannaDocumento7 pagineCase Study Ariannaapi-582257412Nessuna valutazione finora
- Van de Ven Andrew H., Walker Gordon. The Dynamics of Interorganizational Coordination, - Administrative Science Quaterly, 1984, 598 - 621Documento25 pagineVan de Ven Andrew H., Walker Gordon. The Dynamics of Interorganizational Coordination, - Administrative Science Quaterly, 1984, 598 - 621afftsaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.introduction About The Study A) Feasibility StudyDocumento19 pagine1.introduction About The Study A) Feasibility StudyDiscov Singh100% (8)
- Biomedical Admissions Test (Bmat) : Section 1Documento14 pagineBiomedical Admissions Test (Bmat) : Section 1zozo 55Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bazooka Monthly Current Affairs August 2023 CompressedDocumento134 pagineBazooka Monthly Current Affairs August 2023 CompressedarjunNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Insulin Versus Premixed Insulin For The Treatment of T2DmDocumento98 pagineBasal Insulin Versus Premixed Insulin For The Treatment of T2DmMaya SwariNessuna valutazione finora
- GDocumento1 paginaGAlexandra CROITORUNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS BenzolDocumento11 pagineMSDS Benzolasnandy100% (2)
- KPPS Dan Linmas PadaasihDocumento14 pagineKPPS Dan Linmas PadaasihabdulhalimmuhlisNessuna valutazione finora
- CP - 679A Hoja de SeguridadDocumento3 pagineCP - 679A Hoja de SeguridadErik RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet Section 1 - Product & Company IdentificationDocumento8 pagineSafety Data Sheet Section 1 - Product & Company IdentificationBoyet BaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- VEINDOCANOL English PresentationDocumento9 pagineVEINDOCANOL English PresentationSOLOSCOPE MEDICALNessuna valutazione finora
- Stigma Masyarakat Terhadap Gangguan Jiwa: Literature ReviewDocumento10 pagineStigma Masyarakat Terhadap Gangguan Jiwa: Literature ReviewBenni SuryaNessuna valutazione finora