Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Milk Pasteurization
Caricato da
Sofian NurjamalDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Milk Pasteurization
Caricato da
Sofian NurjamalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MILK PASTEURIZATION
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/29/12
Sofian Nurjamal R ( 15308058)
4/29/12
What is pasteurization??
A process which has an objective to destroy all microorganism in food without decrease the quality of food it self. Sebuah proses yang bertujuan untuk menghancurkan mikroorganisme pada makanan tanpa mengurangi kualitas dari makanan itu sendiri.
4/29/12
Objective of Pasteurization
To destroy pathogenic bacteria and microorganism, and also spoiler microorganism to make a product could last longer in storage Untuk menghancurkan mikroorganisme pathogen dan pembusuk, sehingga produk dapat bertahan lebih lama pada proses penyimpanan(storage)
4/29/12
Holding pasteurization (LTLT)
Called Low Temperature Long Time Pasteurization Founded by Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) that bacteria which cause spoilage and disease will die if heated in temperature 140 F (68,5oC) for 30 minutes To ensure uniform heating the milk is constantly stirred during the process. This pasteurization process use the concept of louis pasteur method, the milk is heated in sterilized tank, then heated in temperature 69-700C for 30 minutes to destroy microorganism in milk product.
4/29/12
Flash Pasteurization (HTST)
Advance of old pasteurization Raw milk is first warmed using the heat of the previously pasteurised milk. It then passes through a hot cylinder at 71.6C for a period of 15 to 17 seconds. The milk is then cooled rapidly in part by transferring its heat to the incoming milk. The temperature may vary due to quality of milk and process management
4/29/12
Scheme of Flash Method (HTST)
Ultra High Temperature Pasteurization (UHT)
4/29/12
The most advance pasteurization method Has 3 alternative
1. 80-820C for 3 second ( www.microbiologyprocedure.com/microbiology-in-dair ) 2. 110-1250C for 0,01-2 second
( http://www.geap.com.au/gpau/cmsdoc.nsf/WebDoc/ndkw7 )
4/29/12
Advantage
This UHT method has advantage compared to conventional pasteurization
Whey protein denaturation Thiamin loss
Direct system (HTST-UHT) 35% Indirect system (LTLT) 65%
0.5 - 0.8% 1.4 - 4.4%
Direct method will destroy ALL microorganism in milk, so milk will last longer and more healthy to be consumed
4/29/12
UHT machine(left) and SHT(right)
Pasteurization vs conventional boiling
4/29/12
Pasteurization is modern and controlled heating, so heat that transferred to milk is more uniform. This method can decrease the percentage of protein denaturization and thiamin loss in milk.UHT is more efficient cause its short time process to reach desired temperature wont destroy a lot of nutrition while milk is processed Conventional boiling is not controlled, so we will unsure the number and the time of heat which transferred to milk, this can cause lot of protein to denaturization and thiamin loss. The nutrition of
4/29/12
Why pasteurization??
If you has a super-power antibody, you wont need pasteurization cause the pathogen microorganism will destroyed with only conventional boiling If you dont has a minimum standard antibody you must use pasteurized milk, cause microorganism in milk will make you sick and you need the very-very sterilized milk such as UHT milk.
4/29/12
Milk born disease
Mycobacterium bovis is consumed in the milk and passes from human intestine to the blood, from which it spreads to most organs. Brucellosis, a blood-disease is caused by Gramnegative rod, Brucella abortus. When transmitted to man through cow milk, the bacterium infect the blood-rich organs. Q fever, caused by rickettsia, Cxiella burnetii is also a milk borne disease. Other important disorders associated with milk are primary a typical pneumonia, toxoplasmosis,
4/29/12
reference
http://www.microbiologyprocedure.com/microbiology-in-dairy/ultrapasteurization (03-10-2010 21.37 WIB)
http://www.microbiologyprocedure.com/microbiology-in-dairy/holding-method-p (03-10-2010 : 21.37 WIB)
http://www.microbiologyprocedure.com/microbiology-in-dairy/flash-method-past (03-10-2010 : 21.42 WIB)
http://id.shvoong.com/exact-sciences/1799738-prinsip-pasteurisasi-dan-sterilisasi
/ (03-10-2010 : 21.43 WIB)
http://www.geap.com.au/gpau/cmsdoc.nsf/WebDoc/ndkw747c3b (03-102010 : 21.48) http://www.answers.com/topic/pasteurization (03-10-2010 : 22.15)
http://www.microbiologyprocedure.com/microbiology-in-dairy/milk-borne-disease (03-10-2010 : 22.27)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Retail Banking Black BookDocumento95 pagineRetail Banking Black Bookomprakash shindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermented Milk ProductsDocumento7 pagineFermented Milk ProductsSunil BishnoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions and Standards - Processing Steps - Shelf-Life - Fermented Dairy ProductsDocumento30 pagineDefinitions and Standards - Processing Steps - Shelf-Life - Fermented Dairy ProductsfafaoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersDocumento8 pagineTop Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersBassignotNessuna valutazione finora
- HomogenisationDocumento32 pagineHomogenisationdrsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Print Adh Lam Slit - May 6 2010Documento22 pagineFinal - Print Adh Lam Slit - May 6 2010cassilda_carvalho@hotmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Fat Rich Dairy Products Technology 1Documento243 pagineFat Rich Dairy Products Technology 1sakshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Dairy ProductsDa EverandAdvances in Dairy ProductsFrancesco ContoNessuna valutazione finora
- Coconut Water: Global Trends, Sciences, Processing and Packaging TechnologyDocumento34 pagineCoconut Water: Global Trends, Sciences, Processing and Packaging TechnologyĐivềphía Mặt Trời100% (1)
- Hydraulic Mining ExcavatorDocumento8 pagineHydraulic Mining Excavatorasditia_07100% (1)
- Exotic DVM 11 3 CompleteDocumento12 pagineExotic DVM 11 3 CompleteLuc CardNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of HACCP Implementation in Milk Processing PDocumento6 pagineStudy of HACCP Implementation in Milk Processing PHamada H. ShaatNessuna valutazione finora
- Milk PowderDocumento28 pagineMilk PowderJinggazoomNessuna valutazione finora
- ESL Milk Production - 2014 - 4 - Expertenwissen - ESLDocumento6 pagineESL Milk Production - 2014 - 4 - Expertenwissen - ESLsyalcinkayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdocuments - in Apv Dairy Technology 01 2003Documento127 pagineFdocuments - in Apv Dairy Technology 01 2003Elif UsluNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Management of Critical Contro PDFDocumento5 pagineEffective Management of Critical Contro PDFĐivềphía Mặt TrờiNessuna valutazione finora
- Westfalia Separator - Separators For The Diary IndustryDocumento44 pagineWestfalia Separator - Separators For The Diary Industryserbian_freemanNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Dairy ProductsDocumento22 pagineList of Dairy ProductsAnonymous rGMvFoT3ks100% (1)
- Albanian Flour Mill Course Trial ResutlsDocumento9 pagineAlbanian Flour Mill Course Trial ResutlsqeremiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dried Dairy IngredientsDocumento60 pagineDried Dairy IngredientsJulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin C Retention - White Paper RevisionDocumento12 pagineVitamin C Retention - White Paper RevisionLeonardo SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cilinary Set UpDocumento32 pagineCilinary Set UpOla Kareem100% (1)
- Pasteurization IDocumento33 paginePasteurization IMohammad Ashraf Paul100% (1)
- Dairy Aseptic SystemsDocumento231 pagineDairy Aseptic SystemsVineet MakkerNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013.10.23 COP For Milk Producers Oct 2013Documento139 pagine2013.10.23 COP For Milk Producers Oct 2013FLed NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Oatly Environmental Metric SystemDocumento46 pagineOatly Environmental Metric Systemmehvesdila.durmazNessuna valutazione finora
- Europe EEMEA CIP Pest Management Dairy Suppliers 2015 PDFDocumento92 pagineEurope EEMEA CIP Pest Management Dairy Suppliers 2015 PDFkunal shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Technology For Production of Soluble Tea PowderDocumento8 pagineProcess Technology For Production of Soluble Tea PowderLuisa Fernanda Quiceno Giraldo100% (1)
- FDA Guide To Aseptic ProcessingDocumento22 pagineFDA Guide To Aseptic ProcessingĐivềphía Mặt Trời100% (1)
- Susu SKM Dan EvaporatedDocumento10 pagineSusu SKM Dan EvaporatedVitriMurzzeen100% (1)
- Milk Production ProcessDocumento11 pagineMilk Production ProcessMahdiyeh MosaviradNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Edyta Margas Dry Material Handling - An Overview of The EHEDG Guidelines and Hygienic PracticesDocumento41 pagine3 Edyta Margas Dry Material Handling - An Overview of The EHEDG Guidelines and Hygienic PracticesИван ЧечушковNessuna valutazione finora
- Particles Fibres Pulp WhitepaperDocumento11 pagineParticles Fibres Pulp WhitepaperGorack ShirsathNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerging Dairy Processing Technologies: Opportunities for the Dairy IndustryDa EverandEmerging Dairy Processing Technologies: Opportunities for the Dairy IndustryNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps of PasteurizationDocumento2 pagineSteps of PasteurizationMichel AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Various Methods of PasteurizationDocumento3 pagineVarious Methods of PasteurizationSumit Sharma PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting Milk Flavor Problems - Dairy Cattle Nutrition - Penn State ExtensionDocumento7 pagineTroubleshooting Milk Flavor Problems - Dairy Cattle Nutrition - Penn State ExtensionCostaEdvaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 UHT ProcessingDocumento6 pagine8 UHT ProcessingOsman Aita100% (1)
- FDA Recommended Pasteurization TimeDocumento2 pagineFDA Recommended Pasteurization TimeMarquel Audreyan0% (1)
- APV Membrane Systems For Multi Dairy ApplicationsDocumento43 pagineAPV Membrane Systems For Multi Dairy ApplicationsRavi Chandran RNessuna valutazione finora
- China GB4789.40 2010 Food Microbiological Examination Enterobacter Sakazakii PDFDocumento13 pagineChina GB4789.40 2010 Food Microbiological Examination Enterobacter Sakazakii PDFmmoradi55Nessuna valutazione finora
- 000 Startup & AgendaDocumento4 pagine000 Startup & AgendaHoàng Minh ÁiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide To Clean in Place (CIP)Documento6 pagineA Guide To Clean in Place (CIP)Dominic TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Defect in Evaporated and Condensed MilkDocumento4 pagineDefect in Evaporated and Condensed MilkSai NalkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetra Therm Aseptic Visco SSHEDocumento4 pagineTetra Therm Aseptic Visco SSHEsudheendracvkNessuna valutazione finora
- Course - CHEESE TECHNOLOGYDocumento5 pagineCourse - CHEESE TECHNOLOGYAmit Kr GodaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Milk Production PlantDocumento3 pagineMilk Production PlantMie DtsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review in Reuse of Water in Dairy Companies Possible SolutionsDocumento21 pagineA Review in Reuse of Water in Dairy Companies Possible SolutionsWendyNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilization of BranDocumento14 pagineStabilization of BranayshaambadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Inplant Training Report-Coke2009Documento80 pagineInplant Training Report-Coke2009patkiprashantNessuna valutazione finora
- Dairy Lessons Learned Publication FINALDocumento187 pagineDairy Lessons Learned Publication FINALsubhendujenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling of Milk and Milk Products For Different TestsDocumento3 pagineSampling of Milk and Milk Products For Different TestsSusheel TalrejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Organisms in Milk 280Documento11 pagineMicro Organisms in Milk 280kirti1111Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.milk Processing - NDDocumento13 pagine2.milk Processing - NDAbhithNessuna valutazione finora
- Milk Microbiology: Viable Count Method Dye Reduction Test Direct Microscopic CountDocumento14 pagineMilk Microbiology: Viable Count Method Dye Reduction Test Direct Microscopic CountDayledaniel SorvetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Ambient Yoghurt WPDocumento18 pagineUnderstanding Ambient Yoghurt WPHoàng Nguyễn VănNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.CPGSymposium GEADocumento21 pagine10.CPGSymposium GEAAhmet MetinNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Fill Versus Aseptic Versus Preservatives Hot Fill Versus Aseptic Versus PreservativesDocumento26 pagineHot Fill Versus Aseptic Versus Preservatives Hot Fill Versus Aseptic Versus PreservativesLa Hoài NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Dairy Tech TestDocumento6 pagineDairy Tech Testqamar uz zamanNessuna valutazione finora
- An in Plant Training ReportDocumento24 pagineAn in Plant Training ReportPrince KehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dairy Lab Mannual CompleteDocumento40 pagineDairy Lab Mannual CompleteZarakhankhan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing A Lactose Crystallization Process Based On Dynamic Metastable LimitDocumento13 pagineDesigning A Lactose Crystallization Process Based On Dynamic Metastable LimitGian VillafverteNessuna valutazione finora
- IFF DuPont NB Profiles PDFDocumento2 pagineIFF DuPont NB Profiles PDFSetu ShroffNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypobaric Storage in Food Industry: Advances in Application and TheoryDa EverandHypobaric Storage in Food Industry: Advances in Application and TheoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Jan 25th 6 TicketsDocumento2 pagineJan 25th 6 TicketsMohan Raj VeerasamiNessuna valutazione finora
- S4 HANALicensing Model External V19Documento28 pagineS4 HANALicensing Model External V19Edir JuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Communications 05sept2023Documento14 pagineImportance of Communications 05sept2023Sajib BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (R)Documento23 pagineChemistry Investigatory Project (R)BhagyashreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pioneer vsx-1020-k 1025-k SM PDFDocumento132 paginePioneer vsx-1020-k 1025-k SM PDFluisclaudio31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Protein Plant Based Food Sector Report 2Documento199 pagineSmart Protein Plant Based Food Sector Report 2campeon00magnatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Focus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesDocumento35 pagineFocus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesAlexis De Jesus FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityDocumento16 pagine2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityportsmouthheraldNessuna valutazione finora
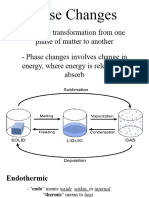
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveDocumento19 pagineGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveJolo Allexice R. PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Antibodies PropertiesDocumento3 pagineNotes On Antibodies PropertiesBidur Acharya100% (1)
- Csu Cep Professional Dispositions 1Documento6 pagineCsu Cep Professional Dispositions 1api-502440235Nessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Geoelectric Method For GroundwaterDocumento11 pagineApplication of Geoelectric Method For GroundwaterMunther DhahirNessuna valutazione finora
- NABARD R&D Seminar FormatDocumento7 pagineNABARD R&D Seminar FormatAnupam G. RatheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Back Propagation Neural NetworkDocumento10 pagineBack Propagation Neural NetworkAhmad Bisyrul HafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Beckers World of The Cell 9th Edition Hardin Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Beckers World of The Cell 9th Edition Hardin Solutions Manual PDFgebbielean1237100% (12)
- Draft PDFDocumento166 pagineDraft PDFashwaq000111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Upes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsDocumento7 pagineUpes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsSuvedhya ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bajaj Vs Hero HondaDocumento63 pagineBajaj Vs Hero HondaHansini Premi100% (1)
- C4 Vectors - Vector Lines PDFDocumento33 pagineC4 Vectors - Vector Lines PDFMohsin NaveedNessuna valutazione finora
- EAC Inquiry SDCDocumento9 pagineEAC Inquiry SDCThe Sustainable Development Commission (UK, 2000-2011)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Binge Eating Disorder ANNADocumento12 pagineBinge Eating Disorder ANNAloloasbNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Prescription Drug Marketing in India-OPPIDocumento23 pagineGuidelines For Prescription Drug Marketing in India-OPPINeelesh Bhandari100% (2)
- Эквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Documento7 pagineЭквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Алексей ЯмаNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Concepts in Elbow Fracture Dislocation: Adam C Watts, Jagwant Singh, Michael Elvey and Zaid HamoodiDocumento8 pagineCurrent Concepts in Elbow Fracture Dislocation: Adam C Watts, Jagwant Singh, Michael Elvey and Zaid HamoodiJoão Artur BonadimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPDocumento13 pagineGrade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPManongdo AllanNessuna valutazione finora
- All Day Breakfast: .Served With Cappuccino or Espresso or Lime Juice or TeaDocumento7 pagineAll Day Breakfast: .Served With Cappuccino or Espresso or Lime Juice or TeaBryan KuoKyNessuna valutazione finora