Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ecg 3
Caricato da
api-3757039100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
83 visualizzazioni18 pagineBy the end of lesson 3 the student will: Be able to identify sinus rhythms: NSR, sinus bradycardia, Sinus Tachycardia and Sinus Arrhythmia. Understand re-entry circle, and its electrophysiological implication on supra-ventricular arrhythmas formation. Be able to diagnose Atrial Fibrillation and flutter. Understand the difference and clinical implication of wide vs. Narrow complex atria.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
ECG-3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoBy the end of lesson 3 the student will: Be able to identify sinus rhythms: NSR, sinus bradycardia, Sinus Tachycardia and Sinus Arrhythmia. Understand re-entry circle, and its electrophysiological implication on supra-ventricular arrhythmas formation. Be able to diagnose Atrial Fibrillation and flutter. Understand the difference and clinical implication of wide vs. Narrow complex atria.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
83 visualizzazioni18 pagineEcg 3
Caricato da
api-3757039By the end of lesson 3 the student will: Be able to identify sinus rhythms: NSR, sinus bradycardia, Sinus Tachycardia and Sinus Arrhythmia. Understand re-entry circle, and its electrophysiological implication on supra-ventricular arrhythmas formation. Be able to diagnose Atrial Fibrillation and flutter. Understand the difference and clinical implication of wide vs. Narrow complex atria.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 18
E.C.G.
Course – III
Atrial rhythms
Dr. Michael Kassirer
”Dept. Internal Medicine ”D
Tel-Aviv Medical center
Objective
By the end of lesson 3 the student will:
Be able to identify sinus rhythms: NSR, Sinus
bradycardia, Sinus tachycardia and sinus
arrhythmia.
Understand re-entry circle, and its electro-
physiological implication on supra-ventricular
arrhythmias formation.
Be able to diagnose atrial fibrillation and flutter.
Understand the difference and clinical implication
of wide vs. narrow complex tachycardia.
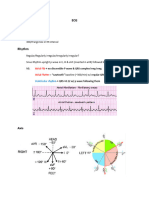
Normal Sinus Rhythm
))NSR
Each P is followed by QRS
Each QRS is preceded by P wave.
P wave –form and PR interval are constant
HR = 60-80 (limits: 50-100)
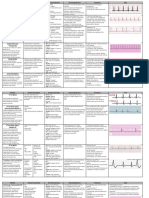
Sinus Bradycardia
Each P is followed by QRS
Each QRS is preceded by P wave.
HR < 50 bpm
Reasons for Sinus
Bradycardia
Hypothermia
Drugs: β blockers, Ca Blockers,
Digoxin etc.
Hypothyroidism
↑ Vagal activation - ↑ I.C.P,
Glaucoma
Inf. Wall MI
Sinus Tachycardia
Each P is followed by QRS
Each QRS is preceded by P wave.
HR > 100 bpm
Reasons for Sinus
Tachycardia
↑ Sympathetic activation:
High output state – Exercise,
Pregnancy, Thyrotoxicosis, Fever.
Compensatory – Anemia,
Hypovolemia, H.F
Stress – hypoxia, Pain, Anxiety
Sinus Arrhythmia
Normal variant – esp. in young
↑ HR in Inspiration, ↓ HR on
Expiration
Tachycardia
3 or more complexes at rate > 100
bpm
Impulse propagation (re-entry)
Impulse formation – enhanced
automaticity
- triggered
activity
)Atrial Fibrillation )A.Fib
Chronic Vs. Paroxysmal
Disorganized atrial activity (rate:350-
600)
Irregular irregularity rhythm
Reasons for Atrial
Fibrillation
Normal Heart (Uncommon) –
Following surgery, Alcohol
intoxication,
Triggered by hypoxia, metabolic,
homodynamic derangement.
thyrotoxicosis
Persistent AF = Cardiovascular
disease (esp. mitral disease, RHD,
Enlarged LA)
Re-entry
S.V.T = AVNRT
SupraVentricular Tachycardia
S.V.T = AVNRT
Multifocal Atrial
Tachycardia
Tachycardia – irregular rhythm
Changing P shape and PR interval
Typical with Rt. Heart strain –
COPD, P.E.
Pre-excitation syndrome
))WPW
AVN bypass tract
Paroxysmal
tachycardia
Typical ECG
pattern:
Shrt PR (<
0.12)
Delta wave
Wide QRS
2° ST-T
changes
Pre-excitation syndrome
))WPW
Premature atrial contraction
))PACs / APBs
Normal Heart (Uncommon) –
Following surgery, Alcohol
intoxication,
Triggered by hypoxia, metabolic,
homodynamic derangement.
thyrotoxicosis
Persistent AF = Cardiovascular
disease (esp. mitral disease, RHD,
Enlarged LA)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- EKG Arrhythmia Identification and Treatment GuideDocumento28 pagineEKG Arrhythmia Identification and Treatment GuideJason LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrhythmia: PalpitationDocumento36 pagineArrhythmia: PalpitationHala BahaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supraventricular ArrhythmiasDocumento56 pagineSupraventricular ArrhythmiasGading AuroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiology - ArrhythmiaDocumento18 pagineCardiology - Arrhythmiadrfabianomarins100% (1)
- Supplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Documento14 pagineSupplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Andrea Love PalomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventricular Arrhythmias-Classification, Etiology, ECG, Clinical Characteristics, TreatmentDocumento3 pagineVentricular Arrhythmias-Classification, Etiology, ECG, Clinical Characteristics, TreatmentSoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac DysrythmiasDocumento190 pagineCardiac DysrythmiasKoRnflakes100% (4)
- Cardiology-5 DysrhythmiaDocumento16 pagineCardiology-5 DysrhythmiaMahmoud RamadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Arrythmias in The ED Menbeu Edited From AnaDocumento106 pagineCardiac Arrythmias in The ED Menbeu Edited From AnaTemesgen Geleta100% (1)
- DR Mohamed A. Fathi Cardiology Specialist and Tutor GMCHRCDocumento76 pagineDR Mohamed A. Fathi Cardiology Specialist and Tutor GMCHRCMohamed Ahmed FathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By: Melissa PeartDocumento20 paginePresented By: Melissa PeartMelissa Monique Peart-YatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ngaji Arrythmia Cordis 3Documento122 pagineNgaji Arrythmia Cordis 3Dhita Dwi NandaNessuna valutazione finora
- KRIZELDocumento13 pagineKRIZELKrizel Adina TanNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Findings in Marathon Runner with AIVRDocumento24 pagineECG Findings in Marathon Runner with AIVRmohamedsmnNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnomalites of ECGDocumento81 pagineAbnomalites of ECGgrreddy8364320Nessuna valutazione finora
- New ACLS Protocol Handout 4352 63Documento19 pagineNew ACLS Protocol Handout 4352 63starshine70006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction System: Rhythm Identification and TreatmentDocumento12 pagineConduction System: Rhythm Identification and Treatmenthops23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arrhythmia A ADocumento42 pagineArrhythmia A AMohd Faizal KasnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitals: Department of Paediatrics Nepalese Army Institute of Health SciencesDocumento20 pagineVitals: Department of Paediatrics Nepalese Army Institute of Health SciencesDrakensberg EspaNessuna valutazione finora
- Peri Operative Arryhthmias: Dr. Juzny Alkatiri, SPPD, SPJPDocumento102 paginePeri Operative Arryhthmias: Dr. Juzny Alkatiri, SPPD, SPJPAstari Pratiwi NuhrintamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of ECGDocumento11 paginePrinciples of ECGDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07Documento60 pagineECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07ampogison08Nessuna valutazione finora
- The ElectrocardiogramDocumento2 pagineThe ElectrocardiogramOh DehNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs used to treat cardiac arrhythmiasDocumento74 pagineDrugs used to treat cardiac arrhythmiasGunel Sadiqova100% (1)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4Documento3 pagineCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4ktfosterfd2096% (96)
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsDocumento125 pagineNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsAyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Week 1Documento15 paginePathophysiology Week 1Dan HoNessuna valutazione finora
- Accelerated Idioventricular RhythmDocumento5 pagineAccelerated Idioventricular RhythmMed AmineNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop Pit IV THN 2017Documento57 pagineWorkshop Pit IV THN 2017anettepardedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Download ebook Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology And Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine Pdf full chapter pdfDocumento67 pagineDownload ebook Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology And Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine Pdf full chapter pdfmartha.delancey633100% (17)
- Heart Dysrhythmias Cheat Sheet PDFDocumento5 pagineHeart Dysrhythmias Cheat Sheet PDFbarbaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsDocumento76 pagine8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Width of The QRS Complex: - Wide VT, SVT With Aberrant Conduction - Narrrow SVTDocumento11 pagineWidth of The QRS Complex: - Wide VT, SVT With Aberrant Conduction - Narrrow SVTWidelmark FarrelNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG - NotesDocumento33 pagineECG - NotesNaveen ChandanNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Arrhythmia Classification GuideDocumento6 pagineECG Arrhythmia Classification GuideEzzat SalemNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG SummaryDocumento11 pagineECG Summaryjackfruit5887Nessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Interpretation GuideDocumento11 pagineECG Interpretation GuideJonathan DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - PPT DR Erika Maharani SPJPDocumento42 pagine2 - PPT DR Erika Maharani SPJPAmry YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases: Kursk State Medical UniversityDocumento88 pagineDepartment of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases: Kursk State Medical UniversityHendraDarmawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aritmii EngDocumento90 pagineAritmii EngAnna HaritonencoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021-Lecture 4-Cardiac Cell and PhysiologyDocumento24 pagine2021-Lecture 4-Cardiac Cell and PhysiologyMajd HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFDocumento3 pagineCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFlml100% (1)
- ECG Master Class-1Documento132 pagineECG Master Class-1Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Arrhythmia Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDocumento13 pagineArrhythmia Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentHarmeet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3aatrialrhythms 110624075109 Phpapp02Documento35 pagine3aatrialrhythms 110624075109 Phpapp02Win Ichda AlfahleviNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypotension & Shock Case GuideDocumento61 pagineHypotension & Shock Case GuidetantosatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrhythmias GeneralDocumento131 pagineArrhythmias GeneralAnonymous IRl5fn6Nessuna valutazione finora
- ECG INTERPRETATION GUIDEDocumento54 pagineECG INTERPRETATION GUIDEnovylatifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Atrial FibrillationDocumento2 pagineAtrial Fibrillationdragtoss2Nessuna valutazione finora
- DYSRHYTHMIASDocumento9 pagineDYSRHYTHMIASgudobenNessuna valutazione finora
- A Normal Adult 12Documento8 pagineA Normal Adult 12el adikkzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocumento60 pagineCardiac ArrhythmiasMelissa Monique Peart-YatesNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Flutter, AFDocumento80 pagineA. Flutter, AFclaimstudent3515Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtDa EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Guide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyDa EverandGuide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyRuth WillisNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideDa EverandUnderstanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Examine The Heart and Blood VesselsDocumento62 pagineHow To Examine The Heart and Blood Vesselsapi-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary HTNDocumento59 paginePulmonary HTNapi-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg 5Documento16 pagineEcg 5api-3757039100% (1)
- Ecg 2Documento29 pagineEcg 2api-3757039100% (1)
- Ecg 7Documento9 pagineEcg 7api-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg 6Documento17 pagineEcg 6api-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg 1Documento43 pagineEcg 1api-3757039100% (2)
- Ecg 4Documento18 pagineEcg 4api-3757039100% (3)
- Ecg 8Documento14 pagineEcg 8api-3757039100% (1)
- Name - : Quiz 2Documento3 pagineName - : Quiz 2api-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz # 3: NameDocumento4 pagineQuiz # 3: Nameapi-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skin and LimbsDocumento13 pagineSkin and Limbsapi-3757039Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABG InterpertationDocumento14 pagineABG Interpertationapi-3757039100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease:: Pathology & TreatmentDocumento17 pagineCoronary Artery Disease:: Pathology & TreatmentJohn FisherNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical Care 5: Clinical Pharmacy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento80 paginePharmaceutical Care 5: Clinical Pharmacy Coronary Artery DiseaseJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus SEM IIDocumento6 pagineSyllabus SEM IITrisha khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Format Mcu Baru (Master File)Documento9 pagineFormat Mcu Baru (Master File)Indah PratiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Study ReportDocumento4 pagineClinical Study ReportMarius AdrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Compendium On The Pathophysiology and Treatment of HypertensionDocumento11 pagineCompendium On The Pathophysiology and Treatment of HypertensionKamar OperasiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is CardiomyopathyDocumento8 pagineWhat Is CardiomyopathysakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- PalpitationsDocumento3 paginePalpitationsJessica Febrina WuisanNessuna valutazione finora
- CREO Objetivos ACOGDocumento48 pagineCREO Objetivos ACOGMiguel Gómez100% (1)
- Approach To Cyanotic Heart Disease Christopher Cheung Santokh Dhillon PDFDocumento13 pagineApproach To Cyanotic Heart Disease Christopher Cheung Santokh Dhillon PDFsuckeydluffyNessuna valutazione finora
- Uttam Maheshwari Ji Gau Ke Chamatkari AushadhiDocumento2 pagineUttam Maheshwari Ji Gau Ke Chamatkari Aushadhiसुमित भारत भूषण वर्मा83% (6)
- ESO EMS Index 2018Documento16 pagineESO EMS Index 2018epraetorianNessuna valutazione finora
- Ubat Darah TiggiDocumento30 pagineUbat Darah TiggiAnys Isyah Mohd RozaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood TransfusionDocumento41 pagineBlood TransfusionajNessuna valutazione finora
- Livia Sagita Ruslim Cardio StemiDocumento34 pagineLivia Sagita Ruslim Cardio StemiAnthony ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporary PacemakerDocumento35 pagineTemporary Pacemakerromeorobin07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocumento41 pagineAssessment of Cardiovascular Systembicariato100% (7)
- Stroke and Subarachnoid HaemorrhageDocumento69 pagineStroke and Subarachnoid HaemorrhagePrincewill SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM122n - HealthTeaching-Plan - OR-NARCE-VARELADocumento5 pagineNCM122n - HealthTeaching-Plan - OR-NARCE-VARELAAlmera Rose NarceNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Navas Kizhakkayil: SUBJECT: Application To Doctor VacancyDocumento3 pagineDr. Navas Kizhakkayil: SUBJECT: Application To Doctor VacancyNasih TrNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Case Presentation OnDocumento95 pagineChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Case Presentation OnJunery Bagunas100% (2)
- Propofol Drug StudyDocumento3 paginePropofol Drug Studygersalia.christiennikkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Effectiveness of Statin Therapy in Ischemic Post Stroke PatientsDocumento6 pagineEffectiveness of Statin Therapy in Ischemic Post Stroke Patientsvhania baniNessuna valutazione finora
- ACFrOgAVR-VCxUN6jt54IUYM FZawDPsgPgb0m2mudgtuZ6j2yfKS5yAJ8-VrVvbJU2ZY2tI1V1i4SFxy2nItnUuhy5qbd45WoegyEo1w2oLHgxslm9Fqsl htLGiFYDocumento6 pagineACFrOgAVR-VCxUN6jt54IUYM FZawDPsgPgb0m2mudgtuZ6j2yfKS5yAJ8-VrVvbJU2ZY2tI1V1i4SFxy2nItnUuhy5qbd45WoegyEo1w2oLHgxslm9Fqsl htLGiFYAneesh MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial OrgansDocumento184 pagineArtificial OrganshemavathyrajasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Virchow's Triad and ThrombosisDocumento53 pagineVirchow's Triad and ThrombosishjjhNessuna valutazione finora
- History of CPB: Edith Early Star V CPPTDocumento24 pagineHistory of CPB: Edith Early Star V CPPTManglarapu SuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment of Retinal Vascular Occlusion After COVID-19 VaccinationDocumento10 pagineRisk Assessment of Retinal Vascular Occlusion After COVID-19 VaccinationJuan PeNessuna valutazione finora
- Care For Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocumento15 pagineCare For Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsJesse Kate GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Manouver VagalDocumento8 pagineManouver VagalAnna Andany100% (1)