Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Urea Cycle 138
Caricato da
api-267066690 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
483 visualizzazioni14 pagineurea cycle presentation
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentourea cycle presentation
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
483 visualizzazioni14 pagineUrea Cycle 138
Caricato da
api-26706669urea cycle presentation
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 14
Transport of Ammonia
&
Synthesis of Urea
Muhammad Saad Zaheer [ 138 (D) ]
Layout
1. Transport of Ammonia
Sources of Ammonia
Transport and destinations of Ammonia
Disorders related to Ammonia Transport
2. Synthesis of Urea
Site
Urea Cycle
Regulation of Urea Cycle
Urea Cycle Diseases (UCDs)
Transport Of Ammonia
A. Sources of Ammonia
Amino Acid
Transamination by ALT or AST
Forms NH3 *
Oxidative Deamination by Glutamate Dehydrogenase
Forms Aspartate*
* Form the Source of Nitrogen in Kreb Henseleit Urea Pathway
Purine and Pyrimidine catabolism
Intestinal and renal Glutamine Catabolism
Bacterial Urease in the Intestines
B. Transport and Destination of Ammonia
Ammonia is transported in the form of:
• Alanine
[From Muscles to the Liver- “Glucose Alanine Cycle”]
• Glutamine
[From Muscle and Brain to Liver]
[From Liver to Kidneys]
• Urea
[From Liver to Kidneys]
[Little amount to Intestines as well]
C. Disorders
o Ammonia Produced by a variety of body Tissues.
o However its level is mainted at a low level of 5-50
micromoles per Litre.
o However when due to some disorder the amount of
Ammonia is raised in the blood, the situation may end up
in serious neurotoxicity of CNS.
o At Higher levels it may cause coma or Death
Types of Hyperammonemias
i. Acquired Hyperammonemia
• Commonly due to liver disease
• Cirrhosis of liver may result in decreased exposure of
blood to liver and consequently high levels of circulating
ammonia
ii. Hereditary Hyperammonemia
• Urea cycle enzyme disorder (usually recessive and
autosomal)
• Hyperammonemia during 1st few weeks of birth
• Treatment is dec. protein diet and AA binding compounds
which are then excreted from the body. e.g. phenly
butyrate given condenses with Glutamine to be excreted
as acetylglutamine.
Layout
1. Transport of Ammonia
Sources of Ammonia
Transport and destinations of Ammonia
Disorders related to Ammonia Transport
2. Synthesis of Urea
Site
Urea Cycle
Regulation of Urea Cycle
Urea Cycle Diseases (UCDs)
Synthesis of Urea
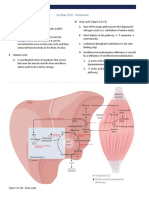
A. Site
Occurs at Liver only
[Why? . . . Because Arginase is present only in
Liver]
B. Urea
From Aspartate From CO2 From Free NH3
C. Reactions
Kreb Hensleit Urea Pathway
2. Carbamoyl Phosphate formation
3. Citrulline Formation
4. Synthesis of Argininosuccinate
5. Cleavage of Argininosuccinate
6. Cleavage of Arginine into Ornithine and Urea
D. Regulation of Urea Synthesis
N-Acetylglutamate is essential activator of Carbamoyl
Phosphate Synthetase I, which is synthesized in a
reaction which is mediated by Arginine.
E. Disorders of Urea Cycle
• Hyperammonemias causing neurologic
disorders (discussed earlier).
• Treated by Hemodialysis and Reduction of
protein intake.
Thanks a lot !
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Fast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentDa EverandFast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Screenshot 2021-05-25 at 1.47.14 PMDocumento7 pagineScreenshot 2021-05-25 at 1.47.14 PMAynaz ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ammonia and Urea CycleDocumento17 pagineAmmonia and Urea CycleAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of Aminoacids 2Documento68 pagineMetabolism of Aminoacids 2Mi PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle and Disorders - RM - F2014Documento18 pagineUrea Cycle and Disorders - RM - F2014Leon WarrenNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Katabolisme Asam Amino-1Documento19 pagineB. Katabolisme Asam Amino-1M Sifal MaulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aminoacid MetabolismDocumento22 pagineAminoacid MetabolismFazal Akbar KhaliliNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea CycleDocumento24 pagineUrea CycleReath Gatkuoth DuothNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 3rdDocumento16 pagineClass 3rdJude Chisom Jnr NwaugoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Transport of Ammonia DR MAx Efui Annani-AkollorDocumento32 pagine3 Transport of Ammonia DR MAx Efui Annani-AkollorMax Annani-akollorNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein and Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento32 pagineProtein and Amino Acid MetabolismVirag0% (1)
- Inborn Errors of Urea SynthesisDocumento14 pagineInborn Errors of Urea SynthesisDaryl Jacob Bigay100% (1)
- Print - Chapter 14. Ammonia and UreaDocumento9 paginePrint - Chapter 14. Ammonia and UreabelaginaNessuna valutazione finora
- Protien and Urea CycleDocumento33 pagineProtien and Urea CycleTAUQEER Ali shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle: Dr. Amro Yousef Al-AmlehDocumento45 pagineUrea Cycle: Dr. Amro Yousef Al-AmlehDr. Amro YousefNessuna valutazione finora
- UreaDocumento16 pagineUreaMuhammad AmjadNessuna valutazione finora
- METABOLISME ASAM AMINO Protein BiologiDocumento31 pagineMETABOLISME ASAM AMINO Protein BiologiAxzchiuu :vNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOSINTESIS PROTlanjutanDocumento31 pagineBIOSINTESIS PROTlanjutanAprilikkaearlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea CycleDocumento39 pagineUrea Cycledrismailkm20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle & HyperammoniaDocumento6 pagineUrea Cycle & HyperammoniaSal TlsNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle and Its DefectsDocumento48 pagineUrea Cycle and Its DefectsStevia NdoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein 3Documento39 pagineProtein 3امجد حسين جواد كاظمNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Team Urea Cycle (1st Edition)Documento6 pagineBiochemistry Team Urea Cycle (1st Edition)Yangnuu TitusNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle LehningerDocumento34 pagineUrea Cycle LehningerMohamadJamaludinNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle3Documento14 pagineUrea Cycle3Akinrotimi OluwadunsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein, Nitrogen Katabolisme Dan Siklus UreaDocumento35 pagineProtein, Nitrogen Katabolisme Dan Siklus UreaAnonymous QCMhA4wNgBNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid CatabolismDocumento19 pagineAmino Acid Catabolismwmdpr4x64fNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid Catabolism-Part-1: Biochemistry For Medics - Lecture Notes Professor (DR.) Namrata ChhabraDocumento43 pagineAmino Acid Catabolism-Part-1: Biochemistry For Medics - Lecture Notes Professor (DR.) Namrata Chhabrashree devNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle and Protein MetabolismDocumento39 pagineUrea Cycle and Protein Metabolismikramullahkhan211Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle 2Documento21 pagineUrea Cycle 2Akinrotimi OluwadunsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Properties of ProteinsDocumento46 paginePhysical Properties of ProteinsTasneem AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Metabolism Dental and Physiotherapy Part 1Documento17 pagineProtein Metabolism Dental and Physiotherapy Part 1Nada Atef KoraitemNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins and Amino Acids Metabolism: Tahun Ajar 2016/2017Documento47 pagineProteins and Amino Acids Metabolism: Tahun Ajar 2016/2017Aswar AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea CycleDocumento3 pagineUrea CycleSundaralingam RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Ammonia IntoxicationDocumento31 pagineAmmonia IntoxicationClare DucutNessuna valutazione finora
- UrineDocumento41 pagineUrineWahab KhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento15 pagineAmino Acid MetabolismMayur KaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Inborn ErrorsDocumento16 pagineInborn ErrorsSophia PerdidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction Amino Acid Matabolism and CatabolismDocumento45 pagineIntroduction Amino Acid Matabolism and CatabolismAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'd100% (1)
- Amino Acid Metabolism II. Urea CycleDocumento39 pagineAmino Acid Metabolism II. Urea Cycleputri jessicaNessuna valutazione finora
- BP U9d Protein MetabolismDocumento80 pagineBP U9d Protein MetabolismChristian Angelo AgbunagNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Lecture PPT 7Documento16 pagineBiochemistry Lecture PPT 7Chiranjeevi JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Item - 11, Protein MetabolismDocumento12 pagineItem - 11, Protein MetabolismSheikh FahadNessuna valutazione finora
- 9a. Metabolisme Asam AminoDocumento62 pagine9a. Metabolisme Asam AminohimawarumNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter X - Mechanism of Protein MetabolismDocumento30 pagineChapter X - Mechanism of Protein MetabolismAngelo AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Pathology BS-MLT 5Th SemesterDocumento36 pagineChemical Pathology BS-MLT 5Th SemesterMuhammad AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- (Krebs-Henseleit Cycle) : Urea FormationDocumento15 pagine(Krebs-Henseleit Cycle) : Urea Formationعلي عبيد العتابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer B: A Deficiency in Carbamoyl Phos-: Metabolic BiochemistryDocumento25 pagineAnswer B: A Deficiency in Carbamoyl Phos-: Metabolic BiochemistryHoanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Metabolism of Proteins & Amino AcidsDocumento79 pagine3 Metabolism of Proteins & Amino AcidsYashfa YasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Section XVII - Ammonia: Figure 2.5.20Documento3 pagineSection XVII - Ammonia: Figure 2.5.20Katharine NervaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea CycleDocumento6 pagineUrea CycleMegan GohNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolisme Protein: Oleh: Gusliani Eka Putri, M.SiDocumento65 pagineMetabolisme Protein: Oleh: Gusliani Eka Putri, M.Sipuskesmas patamuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein MetaboilisamDocumento18 pagineProtein MetaboilisamSumit PandyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento15 pagineAmino Acid Metabolismshanto.tn98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mls 218 Protein-MetDocumento45 pagineMls 218 Protein-MetZainabNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions On Amino Acid Urea CycleDocumento17 pagineQuestions On Amino Acid Urea Cyclejmenchaca8080Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urea CycleDocumento4 pagineUrea CycleKunal DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Turn OverDocumento29 pagineProtein Turn Overabdullah zaheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid CatabolismDocumento7 pagineAmino Acid CatabolismAhmed Ali Mohammed AlbashirNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea Cycle 1Documento25 pagineUrea Cycle 1Tanvi ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- 91931-Article Text-260086-1-10-20131218Documento8 pagine91931-Article Text-260086-1-10-20131218Liana OpriţăNessuna valutazione finora
- Challenges Faced by Families of Autistic Children-153Documento5 pagineChallenges Faced by Families of Autistic Children-153Zahoor Ahmad100% (1)
- Gynecological NursingDocumento329 pagineGynecological Nursingsharon ocharaNessuna valutazione finora
- ForrestDocumento4 pagineForrestAbulHasan Idrus IstarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanisms of Ageing and Development: SciencedirectDocumento8 pagineMechanisms of Ageing and Development: SciencedirectAgustin LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs-1.ppt 0Documento22 pagineDrugs-1.ppt 0Esraa BahaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Detox Smoothies PDFDocumento20 pagineCellular Detox Smoothies PDFRuth Engelthaler100% (3)
- Fix Daftar PustakaDocumento6 pagineFix Daftar Pustakaeka saptaning windu fitriNessuna valutazione finora
- FitnessDocumento3 pagineFitnessapi-301417711Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 The Circulatory System of MammalsDocumento30 pagineChapter 6 The Circulatory System of MammalsRethenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Barneys Farm SeedsDocumento46 pagineBarneys Farm SeedsPedro MarquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Acidosis FinalDocumento29 pagineMetabolic Acidosis FinalTera SurbaktiNessuna valutazione finora
- 24.18.00 - Chikungunya2 DR RAGADocumento48 pagine24.18.00 - Chikungunya2 DR RAGAjcvh24Nessuna valutazione finora
- GMAT Reading Comprehension PracticeDocumento84 pagineGMAT Reading Comprehension PracticeDâu Tây100% (4)
- Genetic Engineering PDFDocumento50 pagineGenetic Engineering PDFBrian Rey L. AbingNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasmodium Infection (Malaria) : Medical ParasitologyDocumento7 paginePlasmodium Infection (Malaria) : Medical ParasitologyBalisi Manuel FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Practice Sheet - 105 Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Biomentors Classes Online, Mumbai Date - 27 September 2018Documento6 pagineDaily Practice Sheet - 105 Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Biomentors Classes Online, Mumbai Date - 27 September 2018Sushree DeepaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactive ArthritisDocumento8 pagineReactive ArthritisamereNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5 - Facial Pain and TMJ DiseaseDocumento6 pagineLecture 5 - Facial Pain and TMJ DiseaseJeff ChadwickNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategies For Feeding The Preterm Infant: ReviewDocumento10 pagineStrategies For Feeding The Preterm Infant: ReviewSanjuy GzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflammation. Etiology. Vascular Changes. Cellular Events in Inflammation. Acute Inflammation. Morphologic PatternsDocumento57 pagineInflammation. Etiology. Vascular Changes. Cellular Events in Inflammation. Acute Inflammation. Morphologic PatternsZauzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Africa South of The SaharaDocumento40 pagineChapter 7 Africa South of The Saharafuck ypouNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal ChikungunyaDocumento4 pagineJurnal ChikungunyaFitri Nadia SilvaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health DirectoryDocumento88 pagineMental Health DirectoryAbhijit DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary of Commonly Used Dental Terms: 14212 Ambaum Boulevard Southwest Suite #101, Burien, WA 98166Documento10 pagineGlossary of Commonly Used Dental Terms: 14212 Ambaum Boulevard Southwest Suite #101, Burien, WA 98166Mayra RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Toshiba Xario XG User ManualDocumento25 pagineToshiba Xario XG User ManualSalah AnamNessuna valutazione finora
- SyncytiumDocumento87 pagineSyncytiumjustin sNessuna valutazione finora
- DSE-03-U2 - Behavior & HealthDocumento23 pagineDSE-03-U2 - Behavior & HealthIndrashis MandalNessuna valutazione finora