Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Definition of Marketing Research: " Systematic Design, Collection, Record, Analysis and Reporting of Data For Aid in Making Business Decisions."
Caricato da
Rahul ShindeDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Definition of Marketing Research: " Systematic Design, Collection, Record, Analysis and Reporting of Data For Aid in Making Business Decisions."
Caricato da
Rahul ShindeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Research Methodology
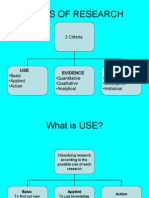
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT Definition of Marketing Research: Systematic design, collection, record, analysis and reporting of data for aid in making business decisions.
F Literally Research means to search again. It connotes scientific investigation wherein the researcher takes another, more careful look at the data to discover all that can be known about the subject of study F If information generated or data collected and analyzed are to be accurate, researcher must have an objective, without engaging in a biased attempt to prove preconceived ideas. F Objective is to facilitate the managerial decision making process for all aspect of business: Finance, Marketing, Personal and so on.
suresh 1
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd
LEVEL 1 ( Strategic )
M a rke ti g S tra te g y n
Segmentation Targeting Positioning
I fo rm a ti n fo r m a rke ti g d e ci o n s n o n si
LEVEL 2 ( Tactical )
M a rke ti g P l n n a
Product Price Promotion Place
suresh
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd
Who constitutes the buyers ?do some people buy and some don t? Why
M a rke t & S a l s R e se a rch e
From which outlet are the product bought ? market share of the respective What are the
What drives a consumer to buy a brand ?
Product Research
Which alternative packaging is most preferred What features / attributes of product is important
suresh
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd
To what extent is sales affected by price? What are the responses to various price levels ?
Pri R e se a rch ce
What pricing policy should be adopted for new product introduction
Which is the most effective advertising mix ? How successful are discounts coupons , lucky d
Promotion(Advertising) Research
What product What advertising theme , appeal , slogan to use ? features should be emphasized
suresh
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd
What type of stores display the product and in what What channels should be used ?
Pl ce ( D i b u ti n ) R e se a rch a stri o
Where and what volumes should the product be stocked ?
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd Four stages of decision making process:
I. Identifying problems or Opportunities: Organization must
determine where it wants to go and how it will get there. E.g.: Develop package for a new brand Increase the amount of repeat purchasing Allocate advertising budget geographically. I. Diagnosing and assessing problems or opportunities: Manager need to gain insights about the underlying factors causing the situation II. Selecting and implementing a course of action: Research is often conducted to obtain specific information that will aid in evaluating the alternatives and in selecting the best course of action
suresh 6
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd
IV.Evaluating the course of action: Objective measurement and the appraisal of extent to which a given activity, project or program has achieved its objective
suresh
Research Methodology
RELEVANCE & SCOPE OF RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT contd Determining when Research should be conducted:
Time Constraint Availability of Data Nature of decision Benefit v / s cost
YES Does the strategic YES t time available Is the information already onmust be made ? before managerial YES decision hand,the decision of considerable decision the or tactical importance ? Is inadequate for making the value of ? research information exceed the cost of c
NO
NO
NO
NO
Research should not be conducted
Conduct Research
suresh
YES
8
Research Methodology
STEPS INVOLVED IN THE RESEARCH PROCESS
Decision making: Process of resolving a problem or choosing among alternative opportunities . Decision making situation ranges from complete certainty to absolute ambiguity
C o m p l te C e rta i ty e n Uncertainty A b so l te A m b i u i u g ty
D e ci o n m a ke r si h a s a l th e l i fo rm a ti n a n d n o e xa ct n a tu re o f b u si e ss p ro b l m . n e R e se a rch m a y not be needed at a l. l
I fo rm a ti n n o a b o u t a l rn a ti s te ve i i co m p l te s n e R e se a rch h a s to be done.
B u si e ss n p ro b l m i e s u n cl a r e R e se a rch m a y b e a w a ste o f ti e , h o w e ve r m ca n b e a ttra cti ve fo r d e ci o n si m a ke rs
suresh 9
Research Methodology
STEPS INVOLVED IN THE RESEARCH PROCESS contd
Problem discovery and definition
Problem discovery
Selection of exploratory research technique
Secondary (historical data)
Pilot study
Experience survey
Case study
Problem definition (statement of research objective)
Planning the research design
Selection of basic research method
Survey
Experiment
Secondary data study
Observation
suresh
10
Research Methodology
STEPS INVOLVED IN THE RESEARCH PROCESS contd
Sampling
Selection of sample design
Probability sampling
Nonprobability sampling
Data gathering
Collection of data (fieldwork)
Editing and coding data
Data processing and analysis Data
processing and analysis
Drawing conclusion and preparing report
Interpretation of findings
Report
suresh
11
Research Methodology
Problem discovery Problem definition (statement of research objectiv
The formulation of a problem is often more essential than its solution - Albert Einstein
Introduce new product Design a test market to assess the likely acceptance of the n
General statement
Adopt pricing strategy Assess new product for a the potential levels of demand associated with various p
Develop package for a new product Evaluate effectiveness of alternate package design
Allocate advertising budget geographically level of market penetration in the respect Determine current
suresh
Specifically identified
12
Research Methodology
RESEARCH DESIGN
Research Design
Q u a l ta ti i ve R e se a rch
Focus of research not on numbers but on words and observations
Determines the extent
Q u a n ti ti ta ve R e se a rch
of some phenomena in form of numbers
Exploratory Research
Conducted during initial stage of research process Clarifies the thought about research problem Eg. What are the10 most
Descriptive Research
Describes characteristics a population Determines the answers to
Causal Research
Identifies cause-andeffect relationship among variables. Eg: Influence of price, packaging, advertising on sales. Exploratory and Descriptive research normally precede Causal research Eg. Will buyer purchase TV if a variable/feature
important variable consumers use to decide while buying TV? ( ABSOLUTE AMBIGUITY )
who, what, when, where and how kind of questions Helps in segment and target the market. Eg. What are the ratings given to variables? Who gave the ratings? Where (which zone/state) rating was given? ( UNCERTAINTY )
incorporated in it? ( COMPLETE CERTAINTY )
* Degree of uncertainty of a research problem determines the research methodology suresh
13
Research Methodology
Selection of exploratory research technique
Secondary (historical data)
Data gathered and recorded by someone else prior to the current needs of the researcher. Secondary data are usually historical. q Objective for Secondary data: F Fact Finding: Eg. Sales, Market share of a product. Population, age, gender (Census data) F Model Building: Specifying relationship between two or more variables. research Eg. Used to estimate growth, inflation for financial
Used to calculate market potential (population X per capita income)
suresh 14
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Secondary (historical data)
contd
q Classification of Secondary data: F Internal and Proprietary data: E.g.. Purchase/sales volume of products for a Shopping Mall F Books and Periodicals: E.g.. Journal of Marketing research, Business week, Financial Analyst journal F Government Sources: E.g.. Census Data (No. of members in family, gender, age etc). Economic data series like GDP, balance of Payment F Regional Publications: E.g.. Publications generated by different banks Metro political planning agencies of the city provides about population, economies, transportation F
suresh 15
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Secondary (historical data)
contd
q Classification of Secondary data: F Media Sources: E.g.. TV channel viewership data F Market Share data: Retail sales volume data based on product movement. F Consumer attitude and public opinion research: Syndicated service for report findings from attitude research and opinion poll
F Stock Market sources: E.g.. Reports provided by BSE, NSE, moneycontrol.com,
F suresh 16
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
Pilot study generates primary data usually for qualitative analysis. It serve as a guide for the larger study. Include focus group interviews, projective techniques and depth interviews q Focus Group Interview (FGD):
suresh
17
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
contd
F Moderator (interviewer) and 6-10 participants. F Participants meet at a central location. F Moderator introduces the topic and encourages the group members to discuss. F Often used for concept and refinement . (E.g.. New name or attribute for a product) F Videoconferenced focus group allows managers to send messages to moderator F Quickly analyzed and less expensive, however small discussion group will rarely be representative sample. F
suresh 18
q Focus Group Interview (FGD):
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
contd
q Projective Techniques: Questioning that enable to project belief and feeling of a person onto a third party, which otherwise is not expressed. Objective is to discover an individuals attitude, motivation.
q
Word Association: Frequently used in testing potential brand names.
q q
Sentence Completion: Respondents are required to complete a number of partial statements. E.g.:
I.
19 High salary will help me purchasing suresh ___________________
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
q
contd
Third-Person Techniques: F Respondents are asked why a third person (e.g. a neighbor) does what he does or thinks what he thinks about a brand, company or a concept. (Providing a mask is a basic idea) Thematic Apperception Test (TAT): Consist of pictures or cartoon in which the Research topic is centre of attention
suresh
20
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
contd
I.
Respondent to tell what's happening in the picture and what the people might do next
suresh
21
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
contd
I. I
Or respondent to construct a story looking at series of pictures with continuity
suresh
22
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Pilot study
contd
F Interview is extensive, unstructured and undisguised (not direct questions). F Most of the questions are open ended F Respondent is free to respond the way he/she likes F Interpretation of such data is highly subjective F F
q Depth interview:
suresh
23
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Experience survey
F Issues and ideas are discussed with those having experience in subject on which Research is being done. F Interview is done with small no. of knowledgeable people. F The purpose is to help formulate the problem and clarify the concept. F Exploratory information from an Experience survey is not expected to be conclusive.
suresh
24
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f e xp l ra to ry re se a rch te ch n i u e e o o q
Case study
F Purpose is to obtain information from one or a few situation that are similar to researchers problem situation. F F
suresh
25
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f d e scri ti / e o p ve ca u sa l re se a rch
Survey
Defined as a method of gathering primary data based on communication with representative sample. Most surveys are descriptive but they can be also be designed to provide causal explanation
Ways to carry out a Survey: F Door-to-Door Personal Interview: Personal interview conducted at the respondents home or the place of business F Mall Intercept Personal Interview: Personal interview conducted in shopping malls F Telephone Interviews: Contacting respondents by telephone to gather responses to survey questions. F Mail Survey: A self-administered questionnaire sent through the mail to respondent.
suresh 26
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f d e scri ti / e o p ve ca u sa l re se a rch
S u rve y
Speed of data collection
Door to Door PI
Mall Intercept PI Telephone Interview
Mail Survey
Interview Survey
Moderate
Fast
Very Fast
Slow
Instantaneous
Respondent cooperation Excellent Moderate to Low Good Moderate Varies
Questionnaire length Long Moderate to long Moderate Varies Moderate
Possibility of respondent misunderstanding Low Low Average High High
Degree of interviewer influence on ans. High High Moderate
None
None
Cost Highest Moderate to high Low to moderate
Lowest
Low
suresh
27
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f d e scri ti / e o p ve ca u sa l re se a rch
S u rve y C l ssi ca ti n o f S u rve y o n Te m p o ra l B a si a fi o s
C ro ss S e cti n a lS tu d i s o e D a ta co l e cte d a t a l si g l p o i t i ti e . n e n n m V a ri u s se g m e n ts o f o p o p u l ti n a re sa m p l d . a o e R e l ti n sh i a m o n g a o p va ri b l s a re i ve sti a te d a e n g b y cro ss ta b u l ti n a o ( Profiling ). E g . A d H o c stu d i s, e U sa g e
Lo n g i d i a lS tu d i s tu n e R e sp o n d e n ts a re q u e sti n e d a t d i re n t o ffe m o m e n ts i ti e n m S i i a r g ro u p o f p e o p l m l e a re exp e cte d to b e i n e a ch sa m p l . e D o n e u su a l y th ro u g h l a panel E g . C o n su m e r p a n e l stu d y ,
suresh 28
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f d e scri ti / e o p ve ca u sa l re se a rch
O b se rva ti n o Business Researchers can observe people, objects, events or other phenomena by assigning the task to human observer or by using machines designed for specific observation tasks.
suresh
29
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f d e scri ti / e o p ve ca u sa l re se a rch
O b se rva ti n o
H u m a n b e h a vi r o r a cti n o o
S e l cti n o f p ro d u cts fro m a sh e l e o f
Ve rb a lb e h a vi r o
C o m m u n i ti n o f a n e m p l ye e w i su b o rd i a te s a n d b ca o o th n
E xp re ssi b e h a vi r ve o
Fa ci lexp re ssi n , to n e o f vo i w h i e se e i g d e m o o f a co n su m a o ce l n
Te m p o ra lp a tte rn s
Ti e ta ke n to co m p l te a ta sk m e
Ph ysi lp a tte rn s ca
Fo o tfa l co rd e d i a sh o p p i g m a l o n w e e ke n d lre n n l
Ve rb a la n d p e cto ra lre co rd
N u m b e r o f i l stra ti n s i a te xt b o o k lu o n suresh 30
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f d e scri ti / e o p ve ca u sa l re se a rch
O b se rva ti n o
q Mechanical Observation: F Television Monitoring: Eg. PeopleMeter used to obtain ratings of television program. F Monitoring website traffic: Recording no. of people visiting a particular website F Measuring physiological reactions: Eg:
Eye tracking monitor: Measures unconscious eye movement, used in recording the pattern of a hoarding or print ad being noticed Voice Pitch analysis: Measures emotional reaction as reflected in physiological changes in persons voice
suresh 31
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f sa m p l d e si n e o e g
Sampling: The process of using a small number of items or part of a large population to make conclusion about the whole population.
S a m p ln g i
Pro b a b i i l ty
N o n Pro b a b i i l ty
Te ch n i u e i w h i e ve ry q n ch m e m b e r o f th e p o p u l ti n a o h a s a kn o w n , n o n ze ro p ro b a b i i o f se l cti n . l ty e o Typ e s: S i p l ra n d o m m e S yste m a ti c S tra ti e d fi C l ste r u
Te ch n i u e i w h i u n i q n ch ts o f sa m p l a re se l cte d o n e e th e b a si o f p e rso n a l s j d g m e n t o r co n ve n i n ce . u e Typ e s: Q u o ta J d g m e n t/ p u rp o si u ve C o n ve n i n ce e S n o w b a l l
suresh 32
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f sa m p l d e si n e o e g
Pro b a b i i l ty
Simple random: Each possible sample has an equal probability of being included in the sample. Each member of sample is assigned a number and sample unit is selected by random method. Eg. Random digit dialing for Telephone interviews or random selection of respondents from census data. Systematic : Elements are selected from population at a uniform interval that is measured in time or order. Eg. Mall Intercept PI conducted every Wednesday in Bigbazaaror 2 houses skipped after every door to door interview.
suresh
33
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f sa m p l d e si n e o e g
Pro b a b i i l ty
Stratified : Population divided into relatively homogeneous group, called strata. From each stratum, a specified no. of elements corresponding to the proportion of that stratum in the population is selected by simple random sampling. Eg. Out of an entire population of 50,000 of an area, if people from age group 20-24 yrs are 10,000, then after a sample of, say 200 is achieved by simple random sampling, the number people between that age group will be more or less 40. Cluster : Population is divided into groups or cluster. Eg. Survey to be conducted in North and West.
* In Stratified , each group has small variation within itself but wide variation between groups . There is considerable variation within each group but the groups are similar to each other . suresh
34
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f sa m p l d e si n e o e g
N o n Pro b a b i i l ty
Quota : Various subgroup in a population are represented by sample to the exact extent that the researcher desires . Eg. Out of an entire population of 50,000 of an area, if people from age group 20-24 yrs are 10,000, then a Quota of 40 people should be achieved in that age group if the sample size is selected as 200. Purpose is to ensure various subgroups in a population are represented by the sample. Quota sampling have a tendency to include people who are easily found within the Quota (unlike Stratified in which strata are formed and people are selected by simple random sampling)
suresh 35
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f sa m p l d e si n e o e g
N o n Pro b a b i i l ty
Judgment / purposive : Experienced researcher selects the sample based on his/her judgment about some characteristics required of the sample member. Eg. For a telecom company study, the proportion of people to be studied for a sample of 1000 are: 1.600 (60%) those who presently use companys sim card 2.250 (25%) those who have never used companys sim card 3.150 (15%) those who switched after using companys sim card The above proportion of sample may be less than fully representative of population 1.
suresh
36
Research Methodology
S e l cti n o f sa m p l d e si n e o e g
N o n Pro b a b i i l ty
Convenience : Refers to sampling by obtaining people who are most conveniently available. Eg. News reporters present reviews of a movie from people coming out of theatre, who are presumed to reflect public opinion Snowball : Sampling procedure in which initial respondents are selected by probability method and additional respondents are obtained from information provided by the initial respondents.
suresh
37
Research Methodology
Typ e s o f q u e sti n o
Open - ended and Closed - ended : What do u like about Surf detergent: 1.Cleaning power 2.Fragrance 3.Dissolve easily 4.Any other (please specify)______________ Dichotomous Questions : Two alternatives given to choose Are you a user of Surf detergent? 1.Yes 2.No
suresh
38
Research Methodology
Typ e s o f q u e sti n o
Multiple Choice : Usually an extension of Dichotomous What do u like about Surf detergent: 1.Cleaning power 2.Fragrance 3.Dissolve easily 4.Any other (please specify)______________ Scaling questions ( rating / ranking ): Rating: Rate the following detergent brands on a scale of 1-10
Brand A Brand B Brand C 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 7 8 8
suresh
9 9 9
10 10 10
39
Research Methodology
Types of question
Scaling questions ( rating / ranking ): Ranking: Rank the following brand on their ability to clean clothes: (1=best, 2=next best etc.)
Brand A Brand B Brand C ____ ____ ____
suresh
40
Research Methodology
Scales used in questionnaire
Scales
Nominal Number are only used as labels Eg. 1.Bank Account No. 2.No. of element in each category Permissible operation: 1. Mode 2. No. of element in each category Test of Significance: Chi Square
Ordinal Scale Variable have meaningful orders Eg. 1.Ranking of products Permissible operation: 1. Mode 2. Median 3. Percentile Test of Significance: 1. Non parametric statistical test 2. Sign test
Interval Variables used to compute statistical measures (avg, std deviation) Eg. 1.Rating given to attributes of
Ratio All arithmetic operations are possible on a ratios scale. Eg. 1.Age 2. Income
3. Weight products Permissible operation: Permissible operation: 1. Mode 1. Mode 2. Median 2. Median 3. Mean 3. Mean 4. Std deviation 4. Std deviation Test of Significance: Test of Significance: All 1. z-test 2. t-test 3. F-test suresh 41
Research Methodology
CASE
Background
Rockledge Corporation shows its presence in various sectors: Steel, Telecom, Banking, and Automobile. The company has decided to diversify its portfolio by getting in Consumer durable sector, beginning with manufacturing of TV.
Need
Entering in TV industry
suresh
42
Research Methodology
C A SE
Research Objective
Identifying preference and potential demand among various age and income group. Finding media sources used before buying TV Determining appropriate price levels for sizes of TV intended to launch: 21inches and 29 inches. Analyzing competition on various parameters Identifying aspiration for buying TV
suresh
43
Research Methodology
C A SE
Research Design
Descriptive
Sources of Data
Primary
suresh
44
Research Methodology
C A SE
Data Collection
Research approach: Survey Research Research instrument: Questionnaire, to collect primary data Sampling plan: Sampling unit (Target Population): I Male and Female . I Above 27 years I . I. Household income not lesser than 2,00,000 I I Rs. I . Owning TV at home V V .Location: Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai and Bangalore
suresh 45
Research Methodology
C A SE
Data Collection
contd
Sampling plan: Sample size : 3500 (700 in each Metro)
Age Group:
28 to 39 yrs - 1250
40 to 51 yrs - 1250 58 yrs and above - 1000
Income Group:
2,00,000 R s to 4,00,000 Rs- 750
4,10,000 Rs to 6,00,000 Rs - 1250 6,10,000 and above - 1500
suresh
46
Research Methodology
C A SE
Data Collection
contd
Sampling plan: 2,00,000 4,00,000
28 39 yrs 40 51 yrs 250 250 R s Rs 4,10,000 Rs 6,00,000 Rs 500 500 250
1250
6,10,000 and above 500 500 500
1500
Sub Total
1250 1250 1000 3500
58 yrs and above 250 Sub Total
750
Sampling procedure: Non Probability (Judgment/purposive) Contact Method: Door to door personal interview
suresh
47
Research Methodology
C A SE
Data Analysis
Identifying potential demand among various age group.
Definitely buy 28 39 yrs 388 40 51 yrs 150 58 yrs and above Sub Total
170 708
Probably buy
225 300 120 645
May or may not buy
275 288 190 753
Probably Definitely Sub Total not buy not buy
163 425 400 988 200 88 120 408 1250 1250 1000 3500
Using Chi Square concept, at 5% significance level, there is a significant difference among proportion and thus age group and purchase intention are dependent.
suresh 48
Research Methodology
C A SE
D a ta A n a l s ysi
I e n ti n g p o te n ti ld e m a n d a m o n g va ri u s i co m e g ro u p . d fyi a o n
Definitely buy
2,00,000 4,00,000 Rs 4,10,000 6,00,000 Rs 6,10,000 5,00,000 Rs 143 350 195 688
Probably buy
248 225 225 698
May or may not buy
165 338 495 998
Probably Definitely Sub Total not buy not buy
143 175 360 678 53 163 225 440 750 1250 1500 3500
Sub Total
Using Chi Square concept, at 5% significance level, there is a significant difference among proportion and thus income group and purchase intention are dependent.
suresh 49
Research Methodology
C A SE
D a ta A n a l s ysi
Fi d i g m e d i so u rce s u se d b e fo re b u yi g T V n n a n
Hoardings TV Advertisement Friends Relatives Colleagues Manufacturer / dealer brochure Newspaper Internet Dealer sales staff
suresh
50
Research Methodology
C A SE
D a ta A n a l s ysi
D e te rm i i g a p p ro p ri te p ri l ve l fo r 2 1 i ch e s n n a ce e s n
TV is cheap but of acceptable quality
TV is expensive but will possibly buy
suresh
51
Research Methodology
C A SE
D a ta A n a l s ysi
A n a l n g co m p e ti o n o n va ri u s p a ra m e te rs yzi ti o
Sony
Price Brand Image Latest Model Features Latest Technology Offers/Schemes
LG
Samsung
Videocon
suresh
52
Research Methodology
C A SE
D a ta A n a l s ysi
Analyzing competition on various parameters.contd
R a ti g g i n to B ra n d s fo r a ttri u te La te st M o d e l : n ve b
Sony
Respondent 1 Respondent 2 Respondent 3 Respondent 4 Respondent 5 3 3 5 2 5 . . . . . . . 4 2
LG
4 2 5 2 2 . . . . . . . 3 3
Samsung
2 3 4 4 3 . . . . . . . 2 1
Videocon
2 1 2 5 3 . . . . . . . 3 1
. . . . . . . Respondent 3499 Respondent 3500
suresh
53
Research Methodology
C A SE
D a ta A n a l s ysi
A n a l n g co m p e ti o n o n va ri u s p a ra m e te rs. co n td yzi ti o
Testing data by Anova at 5% significance level, there is a significant difference in rating given to brands for Latest Model. No significant difference shown on Further analysis of Sony and Samsung on mean rating given for latest Technology at 5% significance, using 2 sample hypothesis concept
suresh
54
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Research MethodologyDocumento36 pagineResearch Methodologyepo_tian100% (1)
- What Is Research MethodologyDocumento16 pagineWhat Is Research Methodologysanu8182% (22)
- Research MethodologyDocumento32 pagineResearch MethodologyMuhammad Mahadi100% (23)
- Research MethodologyDocumento55 pagineResearch Methodologyezzo_gattusoNessuna valutazione finora
- Research MethodologyDocumento25 pagineResearch MethodologyMohamed Imran Predhanekar100% (6)
- Types of Research MethodologyDocumento6 pagineTypes of Research MethodologysahejuNessuna valutazione finora
- Research MethodologyDocumento3 pagineResearch Methodologyakshay akkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing A Research Proposal: Christian Akrong Hesse (PHD)Documento28 pagineWriting A Research Proposal: Christian Akrong Hesse (PHD)Right Karl-Maccoy Hattoh100% (2)
- Introduction To Research Methodology 2Documento101 pagineIntroduction To Research Methodology 2Ahmad Taimoor Ranjha100% (1)
- ResearchMethodology - Types of ResearchDocumento16 pagineResearchMethodology - Types of ResearchPinkAlert100% (3)
- Research Design: Dr. Vipul PatelDocumento19 pagineResearch Design: Dr. Vipul PatelTejan ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Research MethodologyDocumento108 pagineResearch MethodologyRahul Mandal100% (9)
- Research Methods and DesignsDocumento36 pagineResearch Methods and DesignsGr8 zaibiNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Data CollectionDocumento27 pagineMethods of Data Collectionnaveenyadav2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Training in Research Methods Soft Skills Enhancement For Postgraduate StudentsDocumento16 pagineTraining in Research Methods Soft Skills Enhancement For Postgraduate StudentsVirginia VirgieNessuna valutazione finora
- Research ProblemDocumento30 pagineResearch ProblemSajib Chakraborty100% (1)
- Chapter 4 RESEARCH PROBLEMDocumento25 pagineChapter 4 RESEARCH PROBLEMMelody PardilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methods Exam 1 Study GuideDocumento54 pagineResearch Methods Exam 1 Study GuideLaura100% (28)
- Data Collection Methods Chapter 5Documento17 pagineData Collection Methods Chapter 5bookwormjoeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines To Research ProposalDocumento8 pagineGuidelines To Research ProposalhayrekopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methodology Notes by DR KalailakshmiDocumento110 pagineResearch Methodology Notes by DR KalailakshmiArvind Thankappan75% (4)
- Types of Research MethodDocumento4 pagineTypes of Research MethodNataliavnNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methodology: Lecture 6: Methods of Data CollectionDocumento49 pagineResearch Methodology: Lecture 6: Methods of Data CollectionRobertSingkoh100% (3)
- Research MethodologyDocumento135 pagineResearch MethodologyDyaji Charles Bala100% (1)
- Situation AnalysisDocumento18 pagineSituation Analysisfaisal_fiazzNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Data CollectionDocumento7 pagineChapter 1 - Data CollectionRay AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Research MethodologyDocumento48 pagineResearch Methodologyashwath44100% (8)
- Research MethodologyDocumento93 pagineResearch MethodologyJaya Mishra100% (3)
- Chap3 Developing Research ProposalDocumento37 pagineChap3 Developing Research Proposalketema simeNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix - A Academic Tools To Write Research Proposal For M.Phil. /Ph.D. / UG & PG ProjectDocumento8 pagineAppendix - A Academic Tools To Write Research Proposal For M.Phil. /Ph.D. / UG & PG ProjectROHIT RANENessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 Formulating The Research DesignDocumento39 pagineLecture 6 Formulating The Research DesignHamdan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Data Collection & QuestionnaireDocumento19 pagineMethods of Data Collection & QuestionnairePraveen Nair100% (2)
- Types of Research DesignDocumento18 pagineTypes of Research DesignAshish Patel100% (5)
- Types of Research & Research ProcessDocumento32 pagineTypes of Research & Research Processitishaagrawal41Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Assessment For Introduction To Research Methods (RMCR3101)Documento4 pagineFinal Assessment For Introduction To Research Methods (RMCR3101)Maddah HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocumento20 pagineHow To Write A Research ProposalFeyzar Al Fariq DjakajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research - ProposalDocumento29 pagineResearch - ProposalAfzaal Ashraf KhiladiNessuna valutazione finora
- Res. MethodDocumento333 pagineRes. MethodNidhi Agrawal100% (1)
- How To Write A Statement ProblemDocumento5 pagineHow To Write A Statement ProblemPrincess Kaye Mangaya100% (1)
- Admision Research Proposal TemplateDocumento4 pagineAdmision Research Proposal TemplaterahulprabhakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling Qualitative ResearchDocumento11 pagineSampling Qualitative ResearchJoyce Anne Valladolid100% (4)
- Research MethodologyDocumento353 pagineResearch MethodologyJohny86% (59)
- Experimental ResearchDocumento14 pagineExperimental ResearchFirdaus Aziz100% (1)
- Types of ResearchDocumento19 pagineTypes of Researchapi-3731537100% (11)
- Research - ProposalDocumento31 pagineResearch - ProposalEmmanuel Selase AsamoahNessuna valutazione finora
- Research MethodDocumento67 pagineResearch MethodMuhammad Ahsan100% (1)
- Method and Technique of Data Collection: Primary and Secondary DataDocumento44 pagineMethod and Technique of Data Collection: Primary and Secondary DataSuruchi Kaprwan100% (2)
- Dissertation ChecklistDocumento7 pagineDissertation Checklistlwanga67Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research Design and Types of ResearchDocumento53 pagineResearch Design and Types of Researchjoshipooja100% (5)
- Research MethodologyDocumento203 pagineResearch Methodologyrohit vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps in Research ProcessDocumento37 pagineSteps in Research ProcessVipeen Thackarey100% (1)
- Being Investigated and Promotes Confidence in The Overall Quality of Your Analysis andDocumento5 pagineBeing Investigated and Promotes Confidence in The Overall Quality of Your Analysis andZara MoosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methodology Module 1Documento49 pagineResearch Methodology Module 1Sakshi JogiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bus 115 Study Guide 1Documento6 pagineBus 115 Study Guide 1NatfleezyNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Research MethodologyDocumento53 pagineIntroduction To Research MethodologyamitsanuroyNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Research in BusinessDocumento24 pagineRole of Research in BusinessVajid KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Research: Dheeraj Chadha B.Tech (Chemical & Bio Engineering) MBA (HR & Marketing)Documento66 pagineMarketing Research: Dheeraj Chadha B.Tech (Chemical & Bio Engineering) MBA (HR & Marketing)Hemant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methodology and Quantitative TechniquesDocumento102 pagineResearch Methodology and Quantitative TechniquesAnshu MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Discussion On KFADocumento38 pagineGroup Discussion On KFARahul ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sachin Iyer Drunken Driving v.1Documento8 pagineSachin Iyer Drunken Driving v.1Rahul ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- ShikshaDocumento3 pagineShikshaRahul ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Taxation 2011 - MMMDocumento21 pagineTaxation 2011 - MMMRahul ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Coca Cola Marketing PlanDocumento10 pagineCoca Cola Marketing PlanLove juiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 2 - Mode - Report - Interactive Workbook - Unit 1 - Market Research - Vocabulary - ML368 - MyEnglishLabDocumento1 paginaExercise 2 - Mode - Report - Interactive Workbook - Unit 1 - Market Research - Vocabulary - ML368 - MyEnglishLabK60 ĐỖ LÊ TÚ LINHNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Statistics and Probability g11 Quarter 4 Module 1 Test of HypothesisDocumento36 pagine1 Statistics and Probability g11 Quarter 4 Module 1 Test of HypothesisISKA COMMISSIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Testing SyllabusDocumento4 pagineManual Testing SyllabusBaranishankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistik Ayun RuthDocumento4 pagineStatistik Ayun RuthPuskesmas BulikNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of Higher Quality Level of The Software ProcessDocumento9 pagineBenefits of Higher Quality Level of The Software ProcessMert ErkolNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation Tool For Quantitative Research Final DefenseDocumento2 pagineEvaluation Tool For Quantitative Research Final DefenseJayr Osorio100% (3)
- Group 1 Research No. 1 I. Title: Learning Syles of Sophomore Students of PupDocumento4 pagineGroup 1 Research No. 1 I. Title: Learning Syles of Sophomore Students of PupAe RaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cve 172Documento4 pagineCve 172Jesimie OriasNessuna valutazione finora
- A Systematic Review of The Quality of Iv Fluid Therapy in Veterinary MedicineDocumento8 pagineA Systematic Review of The Quality of Iv Fluid Therapy in Veterinary MedicineNicol RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Phân Tích Định LượngDocumento30 paginePhân Tích Định LượngVõ Thị ThưNessuna valutazione finora
- Xlstat 14Documento3 pagineXlstat 14Ehsan QadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental DesignDocumento56 pagineExperimental DesignG100% (5)
- C 5 ADocumento127 pagineC 5 AminhchauNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold Storage Project PDFDocumento10 pagineCold Storage Project PDFRajat Sahni0% (1)
- Ielts Resource Pack Test 2 Reading Answers KeyDocumento1 paginaIelts Resource Pack Test 2 Reading Answers KeyAunaunZaa'Nessuna valutazione finora
- Personality TestDocumento8 paginePersonality TestnieotyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Appropriate Statistics For Ordinal Level DataDocumento33 pagineAppropriate Statistics For Ordinal Level DataJohn PriorNessuna valutazione finora
- Jamestown Steel Company Manufactures and Assembles... : Step-By-StepDocumento4 pagineJamestown Steel Company Manufactures and Assembles... : Step-By-Stepmesba HoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- The Electoral Legislation of Somalia 195 PDFDocumento221 pagineThe Electoral Legislation of Somalia 195 PDFmuktar7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample and Sampling ProcessDocumento37 pagineSample and Sampling ProcessNavpreet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Form Beep Test Recording SheetDocumento3 pagineForm Beep Test Recording SheetAlitNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Na Chapter 3Documento9 pagineLast Na Chapter 3Florante De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Test 10 KeyDocumento10 pagineSample Test 10 KeyAli Zain ParharNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Quality and Testing (CSC 4133) : Common Interview QuestionsDocumento46 pagineSoftware Quality and Testing (CSC 4133) : Common Interview QuestionsrohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper of MBADocumento32 pagineResearch Paper of MBAop bolte broNessuna valutazione finora
- RM Module-3Documento82 pagineRM Module-3mahanth gowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes #1Documento30 pagineNotes #1Sharon Rose MedezNessuna valutazione finora
- Association Between Safety Leading Indicators and Safety Climate Levels - 000Documento11 pagineAssociation Between Safety Leading Indicators and Safety Climate Levels - 000Fernanda RibeiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Madayag Laarni Grace F. Worksheet No. 9Documento2 pagineMadayag Laarni Grace F. Worksheet No. 9Laarni Grace Madayag100% (2)