Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Digital Design: Memory, CPLDs, FPGAs
Caricato da
vikasmumbaiDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Digital Design: Memory, CPLDs, FPGAs
Caricato da
vikasmumbaiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Digital Design: Chapter 10.
Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
10.1 Read-Only Memory
A read-only memory (ROM) is a combinational circuit with n inputs and b outputs. (Fig. 10-1) A ROM stores the truth table of an n-input, b-output combinational logic function. A decoder implemented by ROM (Table 10-1, Fig. 102) ROM is a kind of non-volatile memory. A 4x4 multiplier implemented by ROM. (Table 10-3) Internal structure of A diode ROM. (Fig. 10-5) A ROM using two-dimensional decoding. (Fig. 10-7) Internal structure of a MOS transistor ROM (Fig. 108)
2
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
Commercial ROM types (Table 10-5)
Mask ROM Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM) Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM) Floating gate technology (Fig. 10-10) Programmed by applying a HIGH voltage on the nonfloating gate, and erased by exposing it to ultra-violet light. Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM) Flash ROM
Some standard ROMs (Fig. 10-11)
Output Enable (OE) to control tri-state outputs. Chip-Select (CS) to enable the ROM chip.
Address decoding of ROM applications (Fig. 10-12)
3
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
ROM for low power application (Fig. 10-13) ROM timing (Fig. 10-14)
tAA: Access time from address. tACS: Access time from chip select. tOE: Output Enable time. The propagation delay from OE and CS both asserted until the output drivers have left the Hi-Z state. tOZ: Output-Disable Time tOH: Output-Hold time
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
10.2 Read/Write Memory
RAM (Random Access Memory): most popular read/write memory. The time it takes to read/write a bit of memory is independent of the bits location.
Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) SRAM and DRAM are both volatile. Ferroelectric RAM A kind of non-volatile RAMs.
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
10.3 Static RAM
Basic structure of an SRAM (Fig. 10-19)
Read operation Write operation
Internal structure of an SRAM
RAM cell (Fig. 10-20) A 8x4 SRAM
SRAM timing
Read timing (Fig. 10-22) tAA : Access time from address tACS : Access time from chip select tOE : Output-Enable time tOZ : Output-Disable time tOH : Output-Hold time
6
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
Write timing (Fig. 10-23) tAS: Address setup time before write tAH: Address hold time after write tCSW: Chip-select setup before end of write tWP: Write pulse width tDS: Data setup time before end of write tDH: Data hold time after end of write WE-controlled write versus CS-controlled write (Fig. 10-23)
Standard static RAMs (Fig. 10-24) Asynchronous SRAM and Synchronous SRAM
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
10.4 Dynamic RAM
DRAM structure and operation
A DRAM cell (Fig. 10-31) Write operation Setting the word line to 1. To store a 1, a HIGH voltage is placed on the bit line, which charges the capacitor through the on transistor. To store a 0, a LOW voltage is placed on the bit line, which discharges the capacitor through the on transistor. Read operation The bit line is first precharged to a voltage halfway between HIGH and LOW. The word line is set HIGH so that the precharged bit line is pulled slightly higher or slightly lower. A sense amplifier detects this small change and recovers a 1 or 0 accordingly.
8
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
Reading a DRAM cell destroy the original voltage stored on the capacitor, the DRAM cell must be written back the original data after reading. DRAM refresh (Fig. 10-32) Internal structure of a 64Kx1 DRAM (Fig. 10-33) Multiplexed address inputs RAS_L: Row address strobe to store the higher order bits of the address into the row-address register. CAS_L: Column address strobe to store the lower order bits of the address into the column-address register. Row latches: the latches used to store data input/output from the memory array.
DRAM timing
RAS-only refresh-cycle timing (Fig. 10-34) Read cycle (Fig. 10-35) Write cycle (Fig. 10-36)
Synchronous DRAM
9
Digital Design: Chapter 10. Memory, CPLDs, and FPGAs
10.5 Complex Programmable Logic Devices 10.6 Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA)
Xilinx XC4000 FPGA family Configurable logic block (CLB) (Fig. 10-44) Configurable interconnect structure (Fig. 10-46) CLB and wiring details (Fig. 10-47)
10
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Advanced Digital Electronics Training SetDocumento2 pagineAdvanced Digital Electronics Training SetosamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Robot Interface Unit PDFDocumento20 pagineRobot Interface Unit PDFRays Pain Sama AkatsukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Trueview 5725Documento45 pagineTrueview 5725Hung Nguyenvan0% (1)
- Mp2-SUPER! - Memory Basics and Memory System Design - v0.3Documento27 pagineMp2-SUPER! - Memory Basics and Memory System Design - v0.3serjaniNessuna valutazione finora
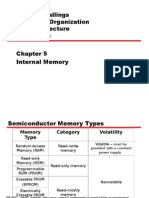
- 5 - Internal MemoryDocumento22 pagine5 - Internal Memoryerdvk100% (1)
- 14 Ram&romDocumento40 pagine14 Ram&rompatilrajucNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory and Programmable LogicDocumento47 pagineMemory and Programmable Logicdewantosatrio50% (2)
- 04-Chap5-Internal MemoryDocumento37 pagine04-Chap5-Internal Memoryabdul shakoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture07-Memory IFDocumento52 pagineLecture07-Memory IFFeyisa BekeleNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.chap3 Automatisme Et Infirmatique IndustrielleDocumento37 pagine3.chap3 Automatisme Et Infirmatique IndustrielleHkbv GjvcNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory - Lec 3Documento74 pagineMemory - Lec 3Danu NimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter9 ROMDocumento22 pagineChapter9 ROMAnupama AnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary MemoriesDocumento25 paginePrimary MemoriesyunangechiNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor and Programmable Logic DeviceDocumento35 pagineSemiconductor and Programmable Logic DeviceTHE PAINKILLERSNessuna valutazione finora
- Inside RAM: Two-Level AddressingDocumento12 pagineInside RAM: Two-Level AddressingdoomachaleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-The Memory SystemDocumento84 pagineChapter 5-The Memory SystemupparasureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Mikroprosessor - W2S1Documento46 pagineSistem Mikroprosessor - W2S1Josep HuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory Fundamentals and InterfacingDocumento50 pagineMemory Fundamentals and InterfacingPREETHINessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable LogicDocumento43 pagineChapter 7 Memory and Programmable LogicShoaib SiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Notes: Memory Technology and System-Level Memory DesignDocumento44 pagineClass Notes: Memory Technology and System-Level Memory DesignHarish ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Computing & Informatics: Short Notes: Microprocessors Intel 8085Documento38 pagineComputing & Informatics: Short Notes: Microprocessors Intel 8085Sayak BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessor Memory Map and I/O DevicesDocumento25 pagineMicroprocessor Memory Map and I/O Devicesnoway snirfyNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory Devices, Circuits, and Subsystem Design: The 8088 and 8086 Microprocessors, Triebel and Singh 1Documento55 pagineMemory Devices, Circuits, and Subsystem Design: The 8088 and 8086 Microprocessors, Triebel and Singh 1Ivan-Jeff AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Programmable Logic DevicesDocumento38 pagineProgrammable Logic DevicesgayathriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Memory and Memory InterfaceDocumento56 pagineChapter 5 Memory and Memory InterfacePetra KalasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory Subsystems OverviewDocumento46 pagineMemory Subsystems OverviewMarliza RosleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Mikroprosessor: Week 4 Session 2Documento44 pagineSistem Mikroprosessor: Week 4 Session 2Dedi BobNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-The Memory SystemDocumento80 pagineChapter 5-The Memory SystemPuneet BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Rabbit - Overview of The Rabbit 4000 Product Line & Dynamic C SoftwareDocumento23 pagineRabbit - Overview of The Rabbit 4000 Product Line & Dynamic C SoftwareAmr ElmestekawiNessuna valutazione finora
- 15-213 Memory Technology March 14, 2000: TopicsDocumento36 pagine15-213 Memory Technology March 14, 2000: TopicsVanu ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8086 InterfaceDocumento26 pagine8086 InterfacelucaslandonNessuna valutazione finora
- 8086 Hardware 2 MEMORY and IO IntefaceDocumento46 pagine8086 Hardware 2 MEMORY and IO IntefaceНемања БорићNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory Types and Classifications GuideDocumento45 pagineMemory Types and Classifications GuideVimoli MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment: Embedded SystemsDocumento6 pagineAssignment: Embedded SystemsSudarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- RAM 2522 DKDocumento40 pagineRAM 2522 DKDon Nipuna PandithasundaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec2 MemDocumento12 pagineLec2 MemparagNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory and Programmable LogicDocumento52 pagineMemory and Programmable LogicMoayid AldeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1Documento30 pagineBab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1haniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V - Memories - VDocumento82 pagineUnit V - Memories - V040-NishanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory: ClassificationsDocumento43 pagineMemory: ClassificationsKumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mc9211unit 5 PDFDocumento89 pagineMc9211unit 5 PDFsanthoshNessuna valutazione finora
- EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques For Digital SystemsDocumento38 pagineEECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques For Digital SystemsNirneya GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 05Documento31 pagineCH 05Ananda Haykel IskandarNessuna valutazione finora
- MemoryDocumento60 pagineMemoryDev PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- ARM Instruction Set for Data Transfer and Memory Mapped I/O (Part 2Documento13 pagineARM Instruction Set for Data Transfer and Memory Mapped I/O (Part 2Sagar BhokareNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory and Programmable Logic: CSA051 - Digital Systems 數位系統導論Documento33 pagineMemory and Programmable Logic: CSA051 - Digital Systems 數位系統導論J RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch04 The Memory SystemDocumento45 pagineCh04 The Memory SystemAlok SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The Memory System: Fundamental ConceptsDocumento115 pagineThe Memory System: Fundamental ConceptsRajdeep ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Fundamentals Course OverviewDocumento86 pagineComputer Fundamentals Course OverviewpratibhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Memory ElementDocumento87 pagineChapter 4 Memory ElementWann FarieraNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 554 Computer Architecture Main Memory Spring 2013Documento35 pagineECE 554 Computer Architecture Main Memory Spring 2013Emmanuel KishoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory Design and Layout OptimizationDocumento21 pagineMemory Design and Layout OptimizationmohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- BY: For:: Ahmad Khairi HalisDocumento19 pagineBY: For:: Ahmad Khairi HalisKhairi B HalisNessuna valutazione finora
- MT 1Documento90 pagineMT 1pummykidNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 5Documento26 pagineCH 5DraxZebNessuna valutazione finora
- DDR Memory Types and Specifications GuideDocumento26 pagineDDR Memory Types and Specifications GuideAlpynNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 - Internal MemoryDocumento63 pagine05 - Internal MemoryKashif AmjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessor 1Documento73 pagineMicroprocessor 1Rishi KeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Random Access MemoryDocumento20 pagineDynamic Random Access MemoryNahum QuirosNessuna valutazione finora
- Week3 Microcontroller and Assembly LanguageDocumento27 pagineWeek3 Microcontroller and Assembly LanguageFelipe TeixeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Engine / TurboGrafx-16 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #16Da EverandPC Engine / TurboGrafx-16 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Da EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Nessuna valutazione finora
- NES Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #1Da EverandNES Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #1Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Time Delay CalculationsDocumento16 pagineTime Delay Calculationsraghuramu23456100% (1)
- HP ENVY BrochureDocumento11 pagineHP ENVY BrochureWhite WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Hitachi H SeriesDocumento3 pagineHitachi H SeriesIsaac SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessor OperationDocumento6 pagineMicroprocessor Operationrooopes5Nessuna valutazione finora
- xc3000 Logic Cell Array FamilyDocumento8 paginexc3000 Logic Cell Array FamilyRemo NamNessuna valutazione finora
- GS. System RequirementsDocumento2 pagineGS. System RequirementsFrancis CayananNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008-10 HUB The Computer Paper ToDocumento40 pagine2008-10 HUB The Computer Paper TothecomputerpaperNessuna valutazione finora
- SC50 020 Primary APIDocumento22 pagineSC50 020 Primary APIkishan1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Third GenerationDocumento23 pagineThird Generationapi-265824751Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clock Domain Crossing BasicsDocumento9 pagineClock Domain Crossing BasicsRapolu SushmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Principles and Application by Leach & Malvino ExportDocumento69 pagineDigital Principles and Application by Leach & Malvino ExportOfficial KillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventaris Lab Komputer Desain Grafis Dan KppiDocumento11 pagineInventaris Lab Komputer Desain Grafis Dan KppiIsmail MarzukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gigabyte Technology Gigabyte Technology Gigabyte Technology: GA-G31M-S2C GA-G31M-S2C GA-G31M-S2CDocumento33 pagineGigabyte Technology Gigabyte Technology Gigabyte Technology: GA-G31M-S2C GA-G31M-S2C GA-G31M-S2CWilvert ChumaceroNessuna valutazione finora
- Reverse Carry Propagate Full Adder Design and Performance Comparision With Error Tolerant AdderDocumento29 pagineReverse Carry Propagate Full Adder Design and Performance Comparision With Error Tolerant AdderZEBA THAHASEEN SNessuna valutazione finora
- PIA-1 - The Peripheral Interface Adapter (PIA) - MC6820Documento14 paginePIA-1 - The Peripheral Interface Adapter (PIA) - MC6820samy_hackerNessuna valutazione finora
- 8086 CH 2 ArchitecureDocumento14 pagine8086 CH 2 ArchitecureSANJEEV NARANGNessuna valutazione finora
- UART Controller With FIFO Buffer Function Based On APB BusDocumento4 pagineUART Controller With FIFO Buffer Function Based On APB Bus16. Gunawan Budi PrakosoNessuna valutazione finora
- C: T.E. S: Tcs Q B T - I: (Academic Year 2018-19 Odd Sem)Documento3 pagineC: T.E. S: Tcs Q B T - I: (Academic Year 2018-19 Odd Sem)jayabaNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectricDocumento37 pagineElectricRohit PentapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ladder Logic Fundamentals and Programming ExamplesDocumento6 pagineLadder Logic Fundamentals and Programming ExamplesAhmedsadatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.8inch Touch Screen User Manual Arduino-En V1.00.2017.03.22Documento21 pagine2.8inch Touch Screen User Manual Arduino-En V1.00.2017.03.22aleolaiz4762Nessuna valutazione finora
- Altus Quark 2400 - ALNETDocumento3 pagineAltus Quark 2400 - ALNETzjjuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Load SheddingDocumento4 pagineAutomatic Load SheddingNkechi JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic and Logical Circuits Practical Lec 2Documento7 pagineElectronic and Logical Circuits Practical Lec 2malik Al kadahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ab 1769-Ascii PDFDocumento2 pagineAb 1769-Ascii PDFAnonymous uAnAv5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sicam Sat 1703 Acp - RtuDocumento12 pagineSicam Sat 1703 Acp - RtutduskoNessuna valutazione finora
- PNMS+ Back To Back (Point To Multi Point) ConnectionDocumento1 paginaPNMS+ Back To Back (Point To Multi Point) ConnectionAhmed IsmailNessuna valutazione finora