Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
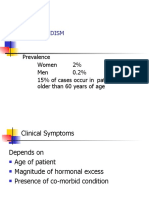
Hyperthyroidism: - 60% Due To Grave's Disease - 40% Due To Miscellaneous Causes
Caricato da
Leitavia D.0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
101 visualizzazioni6 pagineHyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are caused by various conditions that result in excessive or insufficient thyroid hormone levels. The most common causes of hyperthyroidism are Grave's disease and toxic multinodular goiter, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the leading cause of hypothyroidism. Diagnosis involves measuring thyroid hormone levels, and treatments aim to control hormone levels through medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
thyoid
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are caused by various conditions that result in excessive or insufficient thyroid hormone levels. The most common causes of hyperthyroidism are Grave's disease and toxic multinodular goiter, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the leading cause of hypothyroidism. Diagnosis involves measuring thyroid hormone levels, and treatments aim to control hormone levels through medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
101 visualizzazioni6 pagineHyperthyroidism: - 60% Due To Grave's Disease - 40% Due To Miscellaneous Causes
Caricato da
Leitavia D.Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are caused by various conditions that result in excessive or insufficient thyroid hormone levels. The most common causes of hyperthyroidism are Grave's disease and toxic multinodular goiter, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the leading cause of hypothyroidism. Diagnosis involves measuring thyroid hormone levels, and treatments aim to control hormone levels through medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
Hyperthyroidism
• 60% due to Grave’s Disease
• 40% due to miscellaneous causes:
– Thyroiditis, toxic adenomas, TSH-secreting
pituitary tumors, struma ocarii, & hCG-secreting
tumors
• Diagnosis
– Increased T3 and T4
– Decreased TSH
• Except in TSH-secreting tumors
Hypothryoidism Causes
Etiology Clinical Manifestations
Grave’s Disease •TSI binds TSH receptor on •Diffuse nontender goiter
thyroid gland; leads to ↑ T3/T4 with bruit
(diffuse uptake on thyroid scan) •Infiltrative ophthalmopathy
•Associated w/ other (proptosis, extraocular
autoimmune disorders muscle dysfunction)
•Pretibial myxedema
Plummer’s Disease (toxic •Hyperfunctioning areas that •Less severe than Grave’s
multinodular goiter) make ↑ T3/T4 (patchy uptake •Associated w/ life-
on thyroid scan) threatening arrhythmias &
•More common in elderly CHF
Subacute Thyroiditis (de •Inflammation of thyroid •Thyroid gland firm, painful,
Quervain’s thyroiditis) glandspilling of thyroid tender
hormonetransient •Fever
hyperthyroidism •Increased ESR
•Usually preceded by upper •Pain radiating to ears, neck
respiratory infection & arm
Treatment
• Thionamides (PTU & methimazole) to inhibit thyroid hormone
synthesis; PTU also inhibits peripheral conversion of T4 to T3
– Mechanism: Inhibits oxidation & organification of iodine, a required step in
thyroid hormone synthesis
– Both cross the placenta & are contraindicated in pregnancy; PTU is used
during lactation
– Side effects=rash, urticaria, fever, nausea; major effects=agranulocytosis,
thrombocytopenia, acute hepatic necrosis & vasculitis
• β-Blockers (propanolol) to control the adrenergic symptoms
(sweating, tachycardia, tremor)
• Radioactive Iodine to destroy thyroid function
– Side effects=metallic taste, excessive salivation, diarrhea, rash
• Surgery
Signs & Sypmtoms
Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism
Symptoms Hyperactive, irritable Difficulty concentrating, Poor memory
Heat intolerance, sweating Cold intolerance
Palpitations Dyspnea
Fatigue, weakness, Insomnia Fatigue, weakness, lethargy
Diarrhea, polyuria Constipation
Oligomenorrhea, loss of libido Menorrhagia
Weight loss Weight gain, poor appetite
Impaired hearing, hoarse voice (deep voice)
Parasthesias
Tachycardia Bradycardia
Signs
Tremor Delayed Tendon reflex relaxation
Goiter Peripheral edema
Warm, moist skin Dry, coarse skin & Hair loss (Diffuse alopecia)
Proximal muscle weakness Carpal tunnel syndrome
Lid retraction, lid lag Puffy face, hands, & feet (myxedema)
Gynecomastia Diastolic Hypotension
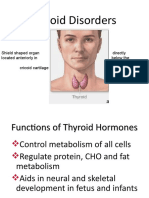
Hypothyroidism
• 95% cases are 1°: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Riedel’s
thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, & surgical destruction
• 2° causes=failure of the pituitary gland
• 3° causes=failure of the hypothalamus
• Diagnosis
– T3/T4/TSH/TRH
• All are helpful to diagnose & distinguish among 1°, 2°, and 3° causes
– Antimicrosomal antibodies to test for Hashitmoto’s Thyroiditis
– Imaging of Pituitary & hypothalamus for tumor
Treatment
• Levothyroxine (T4) replacement
– Levothyroxine is a T4 analog that binds to nuclear
receptors. This leads to ↑ protein synthesis, ↑
metabolic rate,↑ β-receptorsincreased
sensitivity to catecholamines
– Side effects=signs & symptoms of hyperthyroidism
• Use emperic adrenal replacement therapy &
Liothyronine when myxedema coma is involved
– Liothyronine can precipitate heart failure
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reference Ranges PDFDocumento94 pagineReference Ranges PDFdumitrescu sNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid 2Documento16 pagineThyroid 2Haneef SafvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine DisordersDocumento28 pagineEndocrine DisordersRhitzle Ann50% (2)
- Thyroid Disorders: Medical Surgical NursingDocumento20 pagineThyroid Disorders: Medical Surgical Nursingthanuja mathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of The Thyroid Gland Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19eDocumento21 pagineDisorders of The Thyroid Gland Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19ePeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid DiseaseDocumento17 pagineThyroid DiseaseCharlz ZipaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Tyroid DiseasesDocumento40 pagineTyroid DiseasesValentina MilovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Disorders1Documento67 pagineThyroid Disorders1AzeemNessuna valutazione finora
- HyperthyroidismDocumento71 pagineHyperthyroidismAli Murtaza AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Disorder: Aishah Idham Aishah MunirahDocumento47 pagineThyroid Disorder: Aishah Idham Aishah Munirahmunii28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid DisorersDocumento23 pagineThyroid DisorersBryan Lloyd RayatNessuna valutazione finora
- A Presentation On Congenital HyperthyroidismDocumento26 pagineA Presentation On Congenital Hyperthyroidismkriti kaushalNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of The ThyroidDocumento65 pagineDiseases of The ThyroidEdil M JamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid: By: RickyDocumento48 pagineThyroid: By: Rickyricky hutagalungNessuna valutazione finora
- Hipotiroid Dan Tiroiditis 2023Documento53 pagineHipotiroid Dan Tiroiditis 2023ramadhanadlansyah7Nessuna valutazione finora
- HipertiroidDocumento48 pagineHipertiroidIlham KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plenary Week 1 LO No 1Documento25 paginePlenary Week 1 LO No 1Nur Faydotus SalsabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid DisorderDocumento20 pagineThyroid DisorderNadun MethwadaneNessuna valutazione finora
- HypothyroidismDocumento17 pagineHypothyroidismBinbinbabu BinuNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of The Thyroid GlandDocumento10 pagineDiseases of The Thyroid Glandbalkrishna.narshaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroid: SMF Ilmu Penyakit Dalam RSUD Sanjiwani, Gianyar November 2014Documento52 pagineHyperthyroid: SMF Ilmu Penyakit Dalam RSUD Sanjiwani, Gianyar November 2014MedyWedhanggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Pathophysiology: Doc. Mudr. Ing. Rndr. Peter Celec, DRSC., MPHDocumento121 pagineEndocrine Pathophysiology: Doc. Mudr. Ing. Rndr. Peter Celec, DRSC., MPHS ARUNA100% (1)
- Goiter and Malignant Thyroid DiseaseDocumento24 pagineGoiter and Malignant Thyroid Diseaseshaza ewisNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid DisordersDocumento66 pagineThyroid DisordersJOY SANDHYA JOSEPH (RA2123003011002)Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.endocrine (Pt.2)Documento50 pagine2.endocrine (Pt.2)عمر حليم omar haleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Gland Diseases in ChildrenDocumento29 pagineThyroid Gland Diseases in ChildrenadinayNessuna valutazione finora
- ThyroidDocumento96 pagineThyroidNimer Abdelhadi AliNessuna valutazione finora
- HipertiroidDocumento37 pagineHipertiroidTaysqy swftNessuna valutazione finora
- SC2 2015 HyperthyroidismDocumento38 pagineSC2 2015 HyperthyroidismShafern TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical and Surgical Complications in Pregnancy: Ramon M. Gonzalez, MDDocumento161 pagineMedical and Surgical Complications in Pregnancy: Ramon M. Gonzalez, MDaldeeray01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hypothyroidism (2016)Documento23 pagineHypothyroidism (2016)Moni RethNessuna valutazione finora
- ThyrotoxicosisDocumento42 pagineThyrotoxicosisShaw Khan100% (7)
- The Thyroid GlandDocumento55 pagineThe Thyroid GlandLeonard AcsinteNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Gland DisordersDocumento64 pagineThyroid Gland DisordersFaisal RavifNessuna valutazione finora
- Goitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgeryDocumento59 pagineGoitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgerySandhya guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroidism in Graves' DiseaseDocumento5 pagineHyperthyroidism in Graves' DiseaseRickySaptarshi SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Gland: Dr. Humairah Medina Liza Lubis, M. Ked (PA), SP - PADocumento138 pagineThyroid Gland: Dr. Humairah Medina Liza Lubis, M. Ked (PA), SP - PARizky anandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gangguan Tiroid: - Elisabeth KasihDocumento40 pagineGangguan Tiroid: - Elisabeth KasihFariza AndaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Disease: Sejal Nirban FY1Documento30 pagineThyroid Disease: Sejal Nirban FY1Ahmed AbedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroidism 1Documento34 pagineHyperthyroidism 1mussavir100% (2)
- Thyroid Disease: Dr. Gusti Hariyadi Maulana, MSC, SPPD-KGH Internist-NephrologistDocumento30 pagineThyroid Disease: Dr. Gusti Hariyadi Maulana, MSC, SPPD-KGH Internist-NephrologistNurul HikmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Thyroid DiseasesDocumento25 pagineMain Thyroid DiseasesPurnima ChoudhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Gland and Syndromes Associated With Its DisordersDocumento9 pagineThyroid Gland and Syndromes Associated With Its DisordersNini KikvadzeNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Approach of Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidsm and HyperthyroidsmDocumento73 pagineClinical Approach of Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidsm and HyperthyroidsmdiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroidism: Overview, Symptoms, Causes and DaignosisDocumento11 pagineHyperthyroidism: Overview, Symptoms, Causes and DaignosisSushmitha MaturiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyper and HypothyroidDocumento139 pagineHyper and HypothyroidRaka ZaelaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroidism: Prevalence Women 2% Men 0.2% 15% of Cases Occur in Patients Older Than 60 Years of AgeDocumento54 pagineHyperthyroidism: Prevalence Women 2% Men 0.2% 15% of Cases Occur in Patients Older Than 60 Years of AgeMegan MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine DrugsDocumento20 pagineEndocrine DrugsDuran JustineNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid and ParathyroidDocumento33 pagineThyroid and Parathyroidkhaled alahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Function Tests: Drneha Mahajan MD PathologyDocumento71 pagineThyroid Function Tests: Drneha Mahajan MD PathologyMukesh Kumar ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Disease: Apiradee SriwijitkamolDocumento45 pagineThyroid Disease: Apiradee SriwijitkamolThorsang Chayovan50% (2)
- Slide Kuliah TyroidDocumento57 pagineSlide Kuliah TyroidsuhandinataNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid: By: RickyDocumento116 pagineThyroid: By: Rickyricky hutagalungNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelainan TyroidDocumento20 pagineKelainan TyroidAnnisa Aulia RakhmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes: Generally, What Are They?Documento10 pagineNotes: Generally, What Are They?Yusril MarhaenNessuna valutazione finora
- ThyrotoxicosisDocumento105 pagineThyrotoxicosisAli Murtaza Abbas100% (1)
- Thyroid and Parathyroid Disorders - Umar ZeinDocumento39 pagineThyroid and Parathyroid Disorders - Umar ZeinZahrah El FaradisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mayuri Thyroid MTDocumento24 pagineMayuri Thyroid MTmayuri zanwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroiddisorders PDFDocumento51 pagineThyroiddisorders PDFIslam ShoukryNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Disorders AtfDocumento48 pagineThyroid Disorders AtfRana Ahsan JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MhpeDocumento52 pagineThyroid Diseases: Peter S. Aznar, MD, FPSP, MhpeDeomicah SolanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid GlandDocumento59 pagineThyroid Glandbessan alfqeatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Perfect Thyroid Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Managing And Healing Thyroid Symptoms For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesDa EverandThe Perfect Thyroid Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Managing And Healing Thyroid Symptoms For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Function Test 12-2-09Documento69 pagineThyroid Function Test 12-2-09Romaysaamohamed AlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SeminarDocumento58 pagineEndocrine SeminarShahirah ShuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrinology LastDocumento44 pagineEndocrinology Lastlestrange1984100% (1)
- Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Himachal Pradesh "A Hospital Based Study"Documento32 paginePrevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Himachal Pradesh "A Hospital Based Study"dalip kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Function: Clinical Chemistry IiiDocumento20 pagineThyroid Function: Clinical Chemistry IiiJannica Dominique ClarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Hipertiroidism - EnglezaDocumento13 pagineHipertiroidism - Englezaalexya2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kasus Sistem Endokrin 1Documento3 pagineKasus Sistem Endokrin 1lilik kartiniNessuna valutazione finora
- PathoDocumento54 paginePathojohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid ReportDocumento105 pagineThyroid ReportAARVNessuna valutazione finora
- Kanski Clinical Ophthalmology Chapter 3 ORBITDocumento43 pagineKanski Clinical Ophthalmology Chapter 3 ORBITSekar Ayu WulandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Metabolism UwksDocumento54 pagineThyroid Metabolism UwksDaniel VictorNessuna valutazione finora
- ThyrotoxicosisDocumento15 pagineThyrotoxicosischrysandre100% (1)
- Endocrine Sample ExamDocumento9 pagineEndocrine Sample Examteabagman100% (2)
- Thyroid and Parathyroid Disorders: by Dr. Magdi Awad Sasi 2013Documento65 pagineThyroid and Parathyroid Disorders: by Dr. Magdi Awad Sasi 2013Eidi IdhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Grave's Disease EDITEDDocumento39 pagineGrave's Disease EDITEDLadipo Temitope AyodejiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroidism: NCM 116 Lec Mrs. Ma Jesseca P. MonsantoDocumento6 pagineHyperthyroidism: NCM 116 Lec Mrs. Ma Jesseca P. MonsantoMarcel Quario OrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amiodarone & Thyroid Disease JCEM 2010Documento8 pagineAmiodarone & Thyroid Disease JCEM 2010IffatNaeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Disorders: Khalid Al-Shali MBBS, MSC, FRCP (C), Facp Assistant Professor, Department of MedicineDocumento53 pagineThyroid Disorders: Khalid Al-Shali MBBS, MSC, FRCP (C), Facp Assistant Professor, Department of MedicineRahmi Rahma Andini100% (1)
- Get Your Life Back Thyroid Health MANUAL PDF 1 by Kim Wolinski FINALDocumento52 pagineGet Your Life Back Thyroid Health MANUAL PDF 1 by Kim Wolinski FINALKrn Glez100% (8)
- Endocrine System DisordersDocumento74 pagineEndocrine System DisordersFaith Levi Alecha AlferezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthroposophy Autoimmune - Diseases PDFDocumento30 pagineAnthroposophy Autoimmune - Diseases PDFpenfo100% (1)
- Q. What Is The Difference Between Myxedema and Hypothyroidism?Documento4 pagineQ. What Is The Difference Between Myxedema and Hypothyroidism?Wan Razin Wan HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Elecsys Reference RangesDocumento95 pagineElecsys Reference Rangescandy jmzNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Function TestDocumento21 pagineThyroid Function TestPat JacintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbal Formulation Considerations For Autoimmune DisordersDocumento26 pagineHerbal Formulation Considerations For Autoimmune Disordershitesh mendirattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endemic and Sporadic GoiterDocumento13 pagineEndemic and Sporadic GoiterBtwo SoelNessuna valutazione finora