Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
FYP4 Compressed
Caricato da
Debanjali SahaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
FYP4 Compressed
Caricato da
Debanjali SahaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
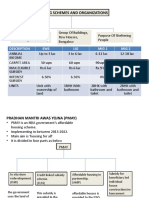
HOUSING
The Fourth Plan led to adoption of the Gadgil In the field of housing, Government has been giving Housing Programmes- Expenditure during 1966-69
formula in 1969. assistance for the benefit of selected sections of the
community and providing accommodation to its employees. Item Plan Funds L.I.C
Total(Rs.
Major Focus: LIC loans, which heretofore supplemented the Plan Crores)
Social Reform provisions, will now be included therein. Subsidised industrial housing 9.29 9.29
Economic Reform Substantial expenditure on housing is made by public sector Low income group housing 8.44 8.44
undertakings, railways, the post and telegraphs and defence. Plantation labour housing 0.17 0.17
Reasons for being Unsuccessful: The major share of the investment on housing comes from
Indo-Pak War of 1971. the private sector. Village housing projects scheme 2.56 2.56
Influx of Refugees from Bangladesh. It is estimated at Rs. 1,400 crores in the Third Plan and Slum Clearance 11.53 11.53
Monsoon failure in 1971,1972 & 1973. expected to rise to Rs. 2,140 crores in the Fourth Plan.
OPEC (Organization of Petrol Exporting Housing Programme:
Land Acquisition and development - 36.0 36.00
Companies) crises. Appropriate layouts made for the growth in villages. Middle income group 1.54 1.54
Basic amenities such as water and sanitation in rural and Rental housing scheme for state
PLAN HOLIDAYS (1966-1969) - -
urban Sector. government employees
Due to miserable failure of the Third Plan the To support the development in housing sector HUDCO was Dock labour housing 0.32 0.32
government was forced to declare "plan holidays" established in 1970. Experimental housing and statistics 0.39 0.39
(from 1966–67, 1967–68, and 1968–69). National Co-orporative Housing Federation of India was Office and residential accommodation 15.75 15.75
Major Highlights of Plan Holidays: founded in 1969 but came into action in 8 th fiveth year plan. total 49.99 36.0 85.99
Reasons for Plan Holidays were War, Lack of Government provides accommodation to its employees.
Resources and Increase in Inflation. Special attention to the growth of small industries in rural
3 annual plans were drawn during this period. areas and small towns. RURAL HOUSING:
Problem of drought during 1966-67. At the end of 1966-67, there were 16 State level co- To get appropriate lay-outs made for the grooving villages.
Priorities was given to agriculture, its allied operative societies and 12,723 primary societies, with a To provide basic amenities such as water and sanitation
activities and industrial sector. total working capital of Rs. 154 crores. During 1966-67, facilities.
Devaluation of Rupee” to increase exports of the these societies built 16,000 independent houses and To stimulate private building and renewal activity.
country. 15,571 tenements Encouragement will have to be given to co-operative
Housing and Urban Development Provision effort.
The twin objectives for fourth five year plan was Item Outlay(Rs. Crores) Special housing schemes in favour of scheduled castes or
“growth with stability” and “progressive states and union territories 188.43 other dis-advantageously placed classes should be
achievement of self-reliance” central sector schemes 48.60 integrated.
Plan in Outlay
office and residential accom. for central govt. employees 30.00 1957 housing projects scheme provides for assistance to
central housing finance corporation 10.00
Item Outlay( Rs.) plantation labour housing 2.00
villagers for construction or improvement of houses, for
Public Sector Plan 15,902 Crores cellular concrete factory in Tamil Nadu 2.60 house sites to landless agricultural workers and for streets
Private Sector Plan 8,980 Crores
dock labour housing 2.50 in selected villages was supported.
experimental housing and research 0.35 Laws conferring proprietary rights to protect the
Urban development, housing and 188 Crores housing statistics 0.35
metropolitan Scheme homesteads of families of landless the agricultural labour ,
town planning 0.50
Housing and Urban development Finance 10 Crores local self-government(training and research) 0.30
large numbers of who belong to scheduled castes and
Corporation total 237.03 backward classes and who live on land belonging to others.
SCHOOL OF PLANNING
FIRST FIVE YEAR PLAN (1969-74) AYUSH GUPTA AND PARUL SURAIA AND ARCHITECTURE,
NEW DELHI
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FYP1 CompressedDocumento2 pagineFYP1 CompressedDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1011Documento1 paginaChap 1011Shivani SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing Finance in India: Development, Growth and Policy ImplicationsDocumento11 pagineHousing Finance in India: Development, Growth and Policy ImplicationsAmit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Philippine Housing Industry RoadMapDocumento4 pagineThe Philippine Housing Industry RoadMapMargaret Sarte de GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Five Year Plans: (First To Sixth)Documento7 pagineFive Year Plans: (First To Sixth)Anshika SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing Policy in India PDFDocumento26 pagineHousing Policy in India PDFabhishek yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4,5 PDFDocumento21 pagineLecture 4,5 PDFgitansh tyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- IjserDocumento32 pagineIjserKingshuk MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing and Urban and Rural Planning: Major Consideration in 3 Five Year PlanDocumento1 paginaHousing and Urban and Rural Planning: Major Consideration in 3 Five Year PlanDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Nagar Federation, Solapur: DPR No.1Documento35 pagineRay Nagar Federation, Solapur: DPR No.1Milind WadekarNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Year PlansDocumento8 pagine5 Year Planspavithra.aNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-Viii 8.1. Housing & Urban Development Corporation (HUDCO) Limited Urban DevelopmentDocumento13 pagineChapter-Viii 8.1. Housing & Urban Development Corporation (HUDCO) Limited Urban DevelopmentJayjeet BhattacharjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- "Five Year Plans of India": WelcomeDocumento26 pagine"Five Year Plans of India": WelcomeankurNessuna valutazione finora
- Muralidhar Rao, Silver Jubilee CollegeDocumento14 pagineMuralidhar Rao, Silver Jubilee CollegeAppan Kandala VasudevacharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing Policies - IndiaDocumento32 pagineHousing Policies - IndiaAjyant SuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures Necessary and Implemented During The Tenth Plan PeriodDocumento1 paginaMeasures Necessary and Implemented During The Tenth Plan PeriodDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- NHA AttyPagunsanDocumento83 pagineNHA AttyPagunsanJesus Villaflor Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- HousingDocumento28 pagineHousingReshmi Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- Public Hearing On DisplacementsDocumento56 paginePublic Hearing On Displacementsf20221782Nessuna valutazione finora
- Udha 1992Documento13 pagineUdha 1992Gen Lamsis AlmoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Evs 2Documento15 pagineEvs 2Devagya GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing - Five Year PlanDocumento3 pagineHousing - Five Year PlantejaswiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Estate Dec 2020Documento8 pagineReal Estate Dec 2020asefsdffNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing & Urban Development Corporation LTD: IPO FlashDocumento4 pagineHousing & Urban Development Corporation LTD: IPO FlashSachinShingoteNessuna valutazione finora
- 3150 - 49 - 479 - Housing MODULE 4Documento20 pagine3150 - 49 - 479 - Housing MODULE 4amlaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECONOMICS PROJECT (Final Draft)Documento18 pagineECONOMICS PROJECT (Final Draft)Vasudha Dattakumar GuravNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - III Urban Land Market and Urban Planning in IndiaDocumento24 pagineChapter - III Urban Land Market and Urban Planning in IndiaSARVESH NANDGIRIKARNessuna valutazione finora
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) Mission: Pmay (U)Documento19 paginePradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) Mission: Pmay (U)KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing AgenciesDocumento12 pagineHousing AgenciesPriyankaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zonal Plan P-II North Delhi - Reports - PDFDocumento31 pagineZonal Plan P-II North Delhi - Reports - PDFPragati SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines Jnnurm Bsup IhsdpDocumento26 pagineGuidelines Jnnurm Bsup Ihsdptaniachopra50% (2)
- List of Priority Programs and Projects in The 2017-2022 Public Investment Programs (PIP) Chapter 12: Building Safe and Secure CommunitiesDocumento3 pagineList of Priority Programs and Projects in The 2017-2022 Public Investment Programs (PIP) Chapter 12: Building Safe and Secure CommunitiesRenBrandt TangonanNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing in Five Year PlansDocumento20 pagineHousing in Five Year PlansLavanya Jothi Venkatachalam100% (2)
- 1V Housing Finance Schemes in India An AnalysisDocumento50 pagine1V Housing Finance Schemes in India An AnalysisKishan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Module6 Urban Design StudioDocumento28 pagineModule6 Urban Design StudioJeric Gonzales MadronioNessuna valutazione finora
- Government of India: Guidelines ForDocumento53 pagineGovernment of India: Guidelines ForNishant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SBM GuidelineDocumento53 pagineSBM GuidelineTesfaye Teferi ShoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Challenges To Opportunities - India - August 2018 PDFDocumento22 pagineChallenges To Opportunities - India - August 2018 PDFViren BhuptaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Policy Note 2016 - 17 EnglishDocumento30 paginePolicy Note 2016 - 17 EnglishsantoshspavNessuna valutazione finora
- Town Planning: Submitted: Ankita Mahajan 4-BDocumento9 pagineTown Planning: Submitted: Ankita Mahajan 4-BSahil HarjaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 18HFA Guidelines March2016-EnglishDocumento62 pagine18HFA Guidelines March2016-EnglishSonali NathNessuna valutazione finora
- Manila: Socialized Housing, Land Use and Climate ChangeDocumento46 pagineManila: Socialized Housing, Land Use and Climate ChangeKaren Balisacan Segundo RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1&2Documento4 pagineWeek 1&2Sebastian CincoNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing & Community PlanningDocumento29 pagineHousing & Community PlanningRaj SekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Gist September 2017Documento13 pagineGist September 2017Abhijai RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing and Urban Development Corporation LTD IPO NoteDocumento15 pagineHousing and Urban Development Corporation LTD IPO NoteSrikant SuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing Schemes and Organizations: Description EWS LIG Mig 1 Mig 2Documento18 pagineHousing Schemes and Organizations: Description EWS LIG Mig 1 Mig 2Pratik ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- PPPs in Affordable Housing UpdatedDocumento97 paginePPPs in Affordable Housing UpdatedKoneti SiddharthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Public-Private Partnership IN Slum Upgrading and Housing For The PoorDocumento20 paginePublic-Private Partnership IN Slum Upgrading and Housing For The PoorNusrat Jahan MituNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing ChandigarhDocumento28 pagineHousing ChandigarhAnas KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Show Img PDFDocumento7 pagineShow Img PDFSatyam BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- China's Strategies For DevelopmentDocumento1 paginaChina's Strategies For DevelopmentVaishnavi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Hfa GuidelinesDocumento62 pagineHfa GuidelinesthesreejitNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By-Grish (018) Kaustubh (023) Pooja (024) Parul (039) Shubham (054) Guided By-Prof. ShrutiDocumento70 pagineSubmitted By-Grish (018) Kaustubh (023) Pooja (024) Parul (039) Shubham (054) Guided By-Prof. ShrutiparulNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 3Documento4 pagineChap 3Sandeep AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chief Minister Jan Awas Yojana 2015 RajasthanDocumento64 pagineChief Minister Jan Awas Yojana 2015 RajasthanSWARNADEEP MANDALNessuna valutazione finora
- Yojana September-2017 PDFDocumento19 pagineYojana September-2017 PDFps3225Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mundashi Mwango ZambiaDocumento16 pagineMundashi Mwango ZambiaelvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Affecting Housing Shortage in IndiaDocumento10 pagineFactors Affecting Housing Shortage in IndiaDivisha JindalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Geography of Post-War France: A Social and Economic ApproachDa EverandThe Geography of Post-War France: A Social and Economic ApproachNessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure 15 - Tool For Water Treatment Plant DesignDocumento3 pagineAnnexure 15 - Tool For Water Treatment Plant DesignMicheal Jackson100% (2)
- Finance Assignment 2 PDFDocumento32 pagineFinance Assignment 2 PDFDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revit Architecture: WB437-1466946523 Debanjali SahaDocumento1 paginaRevit Architecture: WB437-1466946523 Debanjali SahaDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cottage Block - Ground Floor Plan Cottage Block - First Floor Plan Villa Unit Block - Ground Floor PlanDocumento1 paginaCottage Block - Ground Floor Plan Cottage Block - First Floor Plan Villa Unit Block - Ground Floor PlanDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th FYP PanelDocumento2 pagine12th FYP PanelDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pannel Sheet 11 FypDocumento2 paginePannel Sheet 11 FypDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures Necessary and Implemented During The Tenth Plan PeriodDocumento1 paginaMeasures Necessary and Implemented During The Tenth Plan PeriodDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fifth Five Year Plan (1974 - 1979) - Removal of Poverty and Attainment of Self-RelianceDocumento1 paginaFifth Five Year Plan (1974 - 1979) - Removal of Poverty and Attainment of Self-RelianceDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Background:: Aim of Eighth Five Year PlanDocumento2 pagineBackground:: Aim of Eighth Five Year PlanDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing Urban Development Water Supply and Civic Amenities: Ninth Plan - StrategiesDocumento3 pagineHousing Urban Development Water Supply and Civic Amenities: Ninth Plan - StrategiesDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rolling Plan 6 Five Year Plan: Legend/Notes/ InferencesDocumento2 pagineRolling Plan 6 Five Year Plan: Legend/Notes/ InferencesDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fyp-2 Comp.Documento2 pagineFyp-2 Comp.Debanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing and Urban and Rural Planning: Major Consideration in 3 Five Year PlanDocumento1 paginaHousing and Urban and Rural Planning: Major Consideration in 3 Five Year PlanDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamil Nadu - DaphneDocumento25 pagineTamil Nadu - DaphneDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- West Bengal - DebanjaliDocumento28 pagineWest Bengal - DebanjaliDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Achieving Sustainable Development Goals On Water and Sanitation PDFDocumento1 paginaAchieving Sustainable Development Goals On Water and Sanitation PDFDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Art NoveauDocumento33 pagineArt NoveauDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Private Financing For Infrastructure and Sustainable Growth PDFDocumento1 paginaPrivate Financing For Infrastructure and Sustainable Growth PDFDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- West Bengal - DebanjaliDocumento28 pagineWest Bengal - DebanjaliDebanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Cost Techniques in ConstructionDocumento41 pagineLow Cost Techniques in ConstructionDebanjali Saha100% (1)
- 11 04 07Documento88 pagine11 04 07Debanjali SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- HPSSC Clerk Accountant Cum Clerk PostDocumento1 paginaHPSSC Clerk Accountant Cum Clerk Post11458Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Assignment 1Documento9 pagineComputer Assignment 1Lyming GameNessuna valutazione finora
- Contact and InformationDocumento4 pagineContact and InformationTauhid hassan SakibNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Suffragists ORIGINAL DOCUMENTSDocumento3 pagineAnti-Suffragists ORIGINAL DOCUMENTSZzFlxskNessuna valutazione finora
- (試題) 102-2 嚴震生 非洲政治 期中考 - 看板 NTU-Exam - 批踢踢實業坊 PDFDocumento1 pagina(試題) 102-2 嚴震生 非洲政治 期中考 - 看板 NTU-Exam - 批踢踢實業坊 PDF林裕翔Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pacto de Sangre Readings-1Documento32 paginePacto de Sangre Readings-1Rianne BagcatinNessuna valutazione finora
- BTE MathuraDocumento103 pagineBTE MathuraPramodNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample: Extracurricular Activities and Student Essay ofDocumento2 pagineSample: Extracurricular Activities and Student Essay ofapi-250025057Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Noli Me Tangere and El FilibusterismoDocumento11 pagineComparison of Noli Me Tangere and El FilibusterismoJessa Mae SusonNessuna valutazione finora
- Generation GapDocumento17 pagineGeneration Gapfarwanadeem0611Nessuna valutazione finora
- Caobisco 16022018090629 Caobisco 29062017163536 2018 Statistics ExtractDocumento4 pagineCaobisco 16022018090629 Caobisco 29062017163536 2018 Statistics ExtractMilica BarjaktarevicNessuna valutazione finora
- VERMIN Paul HarveyDocumento1 paginaVERMIN Paul HarveyfreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Andrés Bonifacio: Bonifacio Spanish Name SurnameDocumento6 pagineAndrés Bonifacio: Bonifacio Spanish Name SurnameBert DayritNessuna valutazione finora
- Polgov ManuscriptDocumento3 paginePolgov ManuscriptIris May PatronNessuna valutazione finora
- The New York Times 2017-08-09Documento50 pagineThe New York Times 2017-08-09stefanoNessuna valutazione finora
- GO MS 122 Transgers & Postings - Additional InstructionsDocumento3 pagineGO MS 122 Transgers & Postings - Additional InstructionsUPENDRANessuna valutazione finora
- A'De (RSTRDVDDVGVCV %) ) DFTTF Svu+ Z - Zdecj: 1lwlvkhyhqvvfruhvfulswv /-3 Vfrxsdjdlqvw&KludjDocumento12 pagineA'De (RSTRDVDDVGVCV %) ) DFTTF Svu+ Z - Zdecj: 1lwlvkhyhqvvfruhvfulswv /-3 Vfrxsdjdlqvw&KludjHema and syedNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Ebook PDF Analytics and Decision Support in Health Care Operations Management 3rd Edition PDFDocumento41 pagineFull Download Ebook PDF Analytics and Decision Support in Health Care Operations Management 3rd Edition PDFsam.smith964100% (35)
- Jadwal Host SIH FH UB - 15 April 2021 S.D. 28 Mei 2021Documento54 pagineJadwal Host SIH FH UB - 15 April 2021 S.D. 28 Mei 2021Fahmi Arief HidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Indonesia - WikipediaDocumento39 pagineIndonesia - WikipediaNashrllahNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rise of BJP in IndiaDocumento2 pagineThe Rise of BJP in Indiasandrasree2023Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motion For Early Resolution Court of AppealsDocumento4 pagineMotion For Early Resolution Court of AppealsManlapaz Law Office100% (1)
- Chapter 6Documento3 pagineChapter 6Len Abo AshesNessuna valutazione finora
- Turcomp: Engineering Services Sdn. Bhd. (243046-P)Documento1 paginaTurcomp: Engineering Services Sdn. Bhd. (243046-P)Mohd NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Queen VictoriaDocumento4 pagineQueen VictoriaNaomi0% (1)
- Selected Candidates For The Post of UDC (BS-11), Open Merit QuotaDocumento5 pagineSelected Candidates For The Post of UDC (BS-11), Open Merit QuotaAZAM WAQASNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rise and Fall of The Left and The Maoist Movements in PakistanDocumento16 pagineThe Rise and Fall of The Left and The Maoist Movements in Pakistannikesh moreNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4 W1 Trends, Networks - KSA-LeaPDocumento5 pagineQ4 W1 Trends, Networks - KSA-LeaPMary Jane CalandriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sbi Foundation GrantDocumento2 pagineSbi Foundation GrantVivek Singh100% (1)
- UPS PMI For Q4 2023 10.30.2023Documento17 pagineUPS PMI For Q4 2023 10.30.2023Jayson PacomaNessuna valutazione finora