Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Design of Wall Footing
Caricato da
Samuel Espartero0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni9 pagineTitolo originale
DESIGN OF WALL FOOTING.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni9 pagineDesign of Wall Footing
Caricato da
Samuel EsparteroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 9
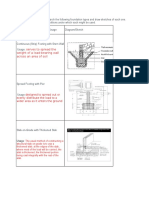
FOOTING
Footings and other foundation units transfer
the loads from the structures to the soil or
rock supporting the structures.
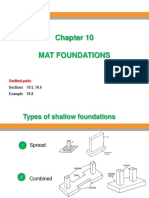
Common types of footings:
1. Wall footing or strip footing is a continuous
strip of concrete that supports a bearing
wall, cantilevering out on each side of the
wall.
2. Spread or square footings
are pads that distribute the
column load in two directions
to an area of soil around the
column.
3. Rectangular footings is used to
support loads on a single column
where sometimes the location is
limited to its property line on one
of the sides.
4. Combined footings are used to support
two heavily loaded columns are so
spaced that normally designed single
footings would run into each other, it
would be rectangular or trapezoidal in
cross section.
5. Cantilever or strap footing which is
really two footings joined by a beam
instead of by a bearing portion of the
footing. Each of the two main parts of
this footing supports a column load.
6. Floating or mat or raft foundation, which is a single
thick mat or slab that supports the entire
structure. This type of foundation is frequently
used with poor soil conditions to equalize
deformations.
7. Pile caps are slabs of reinforced
concrete used to distribute column
loads to group of piles.
Soil Pressure under footing:
The distribution of soil pressure under the footing is a
function of the type of soil and the relative rigidity of
the soil and foundation pad.
For structural design purposes, it is customary to assume
that the soil pressure are linearly distributed uniformly
on the footing.
Column footing must be designed for a 6 strength
conditions:
1. Bearing (compression) from column on top of footing.
2. Dowels into the footing.
3. Strength of soil beneath the footing.
4. Shear strength.
5. Reinforced provided.
6. Development length of bars.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Foundation PDFDocumento3 pagineFoundation PDFhamdan linjee SupaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of ADocumento12 pagineFoundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of Ahabtamu abateNessuna valutazione finora
- FoundationsDocumento36 pagineFoundationsnihaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation Systems - RSW PR 01 - BTech 2 - Pigao, A.R.Documento6 pagineFoundation Systems - RSW PR 01 - BTech 2 - Pigao, A.R.Alainstair Roe Pigao LabausaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation Engineering (PDF) File PDFDocumento44 pagineFoundation Engineering (PDF) File PDFRebwar Ata M.Aldeen100% (1)
- CEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringDocumento36 pagineCEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringRamu KakaNessuna valutazione finora
- FoundationsDocumento32 pagineFoundationsSriLaxmi BulusuNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 4 FoundationDocumento43 pagineCH 4 FoundationEyoatem Teferi100% (1)
- Chapter 3 FoundationDocumento11 pagineChapter 3 FoundationtofshomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-3 FoundationDocumento53 pagineChapter-3 Foundationkader ArefeNessuna valutazione finora
- CMCP Unit 3Documento42 pagineCMCP Unit 3Vishal R100% (1)
- 4.CEE 4101 3 MarchDocumento44 pagine4.CEE 4101 3 MarchPranto KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BCE Lecture 9Documento11 pagineBCE Lecture 9MurgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - Week 1Documento85 pagineLecture - Week 1Asnil PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 LectureDocumento37 pagine4 LecturePranto KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- FoundationDocumento5 pagineFoundationAnna Rose LoboNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Foundation: Shallow FoundationsDocumento12 pagineTypes of Foundation: Shallow FoundationsCaesar DagaasNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Foundation 1Documento14 pagineTypes of Foundation 1Olawale AdebesinNessuna valutazione finora
- Footings: General IntroductionDocumento21 pagineFootings: General IntroductionMd Shafiul Alam FahadNessuna valutazione finora
- Always Try To Do The Best in Your LifeDocumento79 pagineAlways Try To Do The Best in Your LifeNamrata PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity3 2 8foundationtypesDocumento2 pagineActivity3 2 8foundationtypesapi-355856202Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Documento14 pagineTypes of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Rahul Kumawat100% (1)
- Building Technology ArchiDocumento73 pagineBuilding Technology ArchiPathy Amores100% (1)
- Foudation Ass 1Documento1 paginaFoudation Ass 1Jea LagahitNessuna valutazione finora
- FoundationDocumento7 pagineFoundationd81nipatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation and Footing PDFDocumento4 pagineFoundation and Footing PDFHANNAH KIMBERLY AREJOLANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 Lecture NoteDocumento15 pagineChapter-1 Lecture NoteWendimu TolessaNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Element Analysis of Eccentric FootingDocumento92 pagineFinite Element Analysis of Eccentric FootingJunaidAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- "In The Name of Allah, The Most Gracious, & The Most Merciful"Documento37 pagine"In The Name of Allah, The Most Gracious, & The Most Merciful"Uzair SiddiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Chaitanya Mini Project PDFDocumento11 pagineChaitanya Mini Project PDFMàyúr PàwàrNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of FootingsDocumento1 paginaTypes of FootingsmarkensteinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Design System: Submitted By: Hafiz Uzair Naeem Ud Din M. Arch #13Documento8 pagineBuilding Design System: Submitted By: Hafiz Uzair Naeem Ud Din M. Arch #13Uzair SiddiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Foundations AssignmentDocumento8 pagineDesign of Foundations AssignmentLutfan LubaibNessuna valutazione finora
- RC SlabDocumento12 pagineRC SlabGenny Aubrey CarcedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ar 373 BT 3 ReviewerDocumento11 pagineAr 373 BT 3 ReviewerMelvin AlarillaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsDocumento10 pagine1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Shakib Sir URP - FoundationDocumento48 pagineShakib Sir URP - FoundationHome Tutor Provider KhulnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5.1 Foundation (Part 1)Documento53 pagineChapter 5.1 Foundation (Part 1)Issack Mattew100% (1)
- 2.0 Cegeotech2 Lec m1 (Intro)Documento19 pagine2.0 Cegeotech2 Lec m1 (Intro)Mineski Prince GarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pile FoundationDocumento7 paginePile Foundationcabaas hassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforced Cement Reinforced Cement Reinforced Cement Reinforced Cement Concrete Floors Concrete Floors Concrete Floors Concrete FloorsDocumento6 pagineReinforced Cement Reinforced Cement Reinforced Cement Reinforced Cement Concrete Floors Concrete Floors Concrete Floors Concrete FloorslakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Construction TechnologyDocumento18 pagineBuilding Construction Technologycha purNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Chapter 3 Part 1 Foundations.Documento40 pagine3 Chapter 3 Part 1 Foundations.Enanye AragawNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil Fondation by Civil1st SemDocumento22 pagineBasic Civil Fondation by Civil1st Semking RHNessuna valutazione finora
- Mat Foundations: Omitted PartsDocumento55 pagineMat Foundations: Omitted PartsipmawanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 FE - Foundation TypesDocumento15 pagine2 FE - Foundation TypesYang ZhengNessuna valutazione finora
- FoundationDocumento17 pagineFoundationIshita DhingraNessuna valutazione finora
- BCM Assignment Group 8Documento18 pagineBCM Assignment Group 8Ashrutha HarshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Foundation: Why A Foundation Is ProvidedDocumento12 pagineTypes of Foundation: Why A Foundation Is ProvidedMin Min IINessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil FondationDocumento22 pagineBasic Civil FondationGokul KannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil Fondation by Civil1st SemDocumento22 pagineBasic Civil Fondation by Civil1st SemNita NabanitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil Fondation by Civil1st SemDocumento22 pagineBasic Civil Fondation by Civil1st SemAyaz ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-22 FoundationDocumento20 pagineChapter-22 Foundationdesubie bireNessuna valutazione finora
- Geotechnical Engneering: What Is Foudation?Documento7 pagineGeotechnical Engneering: What Is Foudation?starr awanNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Foundation 1Documento11 pagineTypes of Foundation 1Saad SohailNessuna valutazione finora
- Pad and Strip FoundationsDocumento19 paginePad and Strip FoundationsSyafiq_Richman_9904Nessuna valutazione finora
- BCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021Documento21 pagineBCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021hyperloop707 designNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionDa EverandStrength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionNessuna valutazione finora
- Wallfooting Sample Design (A Brief Approach)Documento11 pagineWallfooting Sample Design (A Brief Approach)Samuel Espartero100% (1)
- Administrative Policies and Procedures: Scdot Bridge Design ManualDocumento50 pagineAdministrative Policies and Procedures: Scdot Bridge Design ManualSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- PHILIPPINE WOOD and TIMBER DESIGN (Problems With Solutions)Documento12 paginePHILIPPINE WOOD and TIMBER DESIGN (Problems With Solutions)Samuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge Replacement Project Development Process: Scdot Bridge Design ManualDocumento50 pagineBridge Replacement Project Development Process: Scdot Bridge Design ManualSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination of Bridge Replacement Projects: Scdot Bridge Design ManualDocumento20 pagineCoordination of Bridge Replacement Projects: Scdot Bridge Design ManualSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- PERMEABILITYDocumento28 paginePERMEABILITYSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- SLOPEDocumento16 pagineSLOPESamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Filtration, Reinforced Wall and DrainageDocumento15 pagineFiltration, Reinforced Wall and DrainageSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Geogrids, Reinforced WallDocumento37 pagineGeogrids, Reinforced WallSamuel Espartero0% (1)
- Roads and PavementsDocumento20 pagineRoads and PavementsSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Design of A 3-Storey BuildingDocumento10 pagineSeismic Design of A 3-Storey BuildingSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Design Tabulated Stress ResultDocumento7 pagineSeismic Design Tabulated Stress ResultSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Compaction EquipmentDocumento63 pagineCompaction EquipmentSamuel Espartero50% (2)
- Design of Rectangular FootingDocumento5 pagineDesign of Rectangular FootingSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Elective On Structural Analysis by Portal MethodDocumento5 pagineTechnical Elective On Structural Analysis by Portal MethodSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge Presentation 1Documento13 pagineGe Presentation 1Samuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Footing: Common Types of FootingsDocumento9 pagineFooting: Common Types of FootingsSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Atterberg Limits, A Presentation ApproachDocumento7 pagineAtterberg Limits, A Presentation ApproachSamuel EsparteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Equipment GuideDocumento17 pagineConstruction Equipment GuideSamuel Espartero100% (3)