Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ultra Sound Testing: Opic:-Test Methods and Techniques
Caricato da
Varun Malan0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
17 visualizzazioni23 pagineThis document discusses various ultrasound testing methods and techniques. It describes the pulse echo method, through transmission, and resonance method as the basic ultrasonic methods. It then focuses on the pulse echo testing technique, including the normal beam technique using single, double, and TR probes, as well as the angle beam technique. Immersion testing techniques are also covered. Formulas for velocity correction and calculating skip distances are provided.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
ULTRA SOUND TESTING.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document discusses various ultrasound testing methods and techniques. It describes the pulse echo method, through transmission, and resonance method as the basic ultrasonic methods. It then focuses on the pulse echo testing technique, including the normal beam technique using single, double, and TR probes, as well as the angle beam technique. Immersion testing techniques are also covered. Formulas for velocity correction and calculating skip distances are provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
17 visualizzazioni23 pagineUltra Sound Testing: Opic:-Test Methods and Techniques
Caricato da
Varun MalanThis document discusses various ultrasound testing methods and techniques. It describes the pulse echo method, through transmission, and resonance method as the basic ultrasonic methods. It then focuses on the pulse echo testing technique, including the normal beam technique using single, double, and TR probes, as well as the angle beam technique. Immersion testing techniques are also covered. Formulas for velocity correction and calculating skip distances are provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 23
ULTRA SOUND TESTING
TOPIC:- TEST METHODS AND
TECHNIQUES
Contents
Basic Ultrasonic Methods
Pulse echo method
Through transmission
Resonance method
Pulse echo testing Technique
Normal beam Technique
Applications of contact type Normal beam probes
Using single crystal probes
Using TR probe
Angle beam technique
Immersion testing techniques
Thickness measurement by pulse echo methods
Basic Ultrasonic methods
Ultrasonic waves arriving at an interface between two media are
partially reflected into the medium from which they are incident and
partially transmitted into the other medium.
These are;
Through transmission
Pulse echo method
Resonance method
Pulse Echo Method
Most commonly utilized in UT.
Transmitter and receiver probes are on the same side of the
specimen/job/workpiece.
Defect orientation is cleared
It takes double time of flight to again receive on probe in
comparison to through transmission.
Through Transmission
Two ultrasonic probes are used
One for transmitter probe and another for receiver probe.
Utilises transmitted part of the ultrasonic wave.
Does not give the size and location of defect/discontinuity.
It only shows that defect is present or not.
Presence of defect is shown by reduction of signal amplitude on the
flaw detector screen.
In this method only material is been checked whether it is good or
not.
Used for composite material.
Resonance method
Resonance condition ; it exists when t=λ/2 or in the multiple of
whole number
t- thickness
λ-wavelength
Resonance have variable frequency
Pulse echo and through transmission have fixed frequency.
Pulse echo testing techniques
Normal beam technique
Ultrasonic beam is projected perpendicular to the test specimen.
Technique may use single, double, TR normal beam probes.
Single normal beam probe;- Transducer of the probe acts as both
transmitter and receiver.
Double normal beam probe;- more useful when the specimen shape
is irregular and the back surface is not parallel with the front
surface. One probe transmit and another probe receives the beam
and echo from thee flaws and represent them on the screen . In TR
probe two transducers are in the same case.
Single probe
TR PROBE
Contact Type Testing
Using single crystal probes:
Using TR probes:
Angle beam technique
Single crystal probe
Thickness measurement
Calibration of CRT screen in millimetres using a calibration block.
Thickness of test piece can be read by using single or multiple
backwall echoes.
Smallest wall thickness measured with thee multiple echo method is
3mm.
TR probes
TR probe can measure least thickness 1 mm and results in a very
good near surface resolution.
Calibration for TR probe is made up by step-wedge block.
It has two crystals one is transmitter and another is receiver and
fixed at some angle (2-3 degree)
Laminations check
Velocity Correction
If the calibration block used for the same time base calibration is a
different material than that of the material of the specimen has to be
corrected for the difference in velocity in the calibration block.
Formula;-
Thickness of specimen=indicated thickness*(longitudinal velocity in
specimen/longitudinal velocity in calibration block)
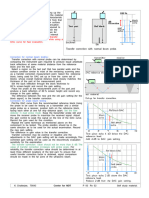
Angle beam technique
The angle beam technique is used to transmit ultrasonic waves into a
test specimen at a predetermined angle to the test surface. According to
the angle selected , the wave modes produced in the test specimen may
be mixed longitudinal and transverse , transverse only or surface waves
mode.
Transverse waves at various angle of refraction between 35 degree to
80 degree are used to locate defects
Common terminology;-
• Half skip distance(HSD)
• Full skip distance(FSD)
• Half skip beam path(
• Full skip beam path
Continued…
• FORMULA;-
• HSD= t*tanθ
• FSD=2*HSD
• H S BEAM PATH= t/cosθ
• FSBPL=2*HSBP
ANGLE PROBE
Immersion Testing
Immersion testing techniques is mainly used in in the laboratory for
automatic work for large installations.
It has advantage of uniform couplant conditions obtained ,
longitudinal and transverse waves can be generated with the same
probe simply by changing the incident angle.
In the rough surface area we can perform immersion testing
successfully.
Best is dipped all things in couplant.
When the couplant layer is sufficient enough to separate the entry
surface and initial pulse then it is called to be immersion testing .
When layer is in microns than it can be ignored and called contact
testing.
THANK YOU
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Industrial radiography A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandIndustrial radiography A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- P 14 Cover Sheets 10 07Documento4 pagineP 14 Cover Sheets 10 07carlos100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFDocumento26 pagineUltrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFKarthicWaitingNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Ultrasonic Thickness MeasurementDocumento18 pagineIntroduction To Ultrasonic Thickness MeasurementNail Widya Satya100% (1)
- Pana USDocumento52 paginePana USflorin100% (1)
- Inspection Technologies Brochure English 5Documento19 pagineInspection Technologies Brochure English 5Agus WiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Testing Training (UT) : Level-IIDocumento8 pagineUltrasonic Testing Training (UT) : Level-IIAn IkhrandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Thickness Gaging: by Tom NelliganDocumento4 pagineUltrasonic Thickness Gaging: by Tom NelliganCarlos BustamanteNessuna valutazione finora
- The Eddy Current Inspection Method Pt4Documento4 pagineThe Eddy Current Inspection Method Pt4vrapciudorianNessuna valutazione finora
- M022 Jsa For Magnetic Penetration TestDocumento4 pagineM022 Jsa For Magnetic Penetration TestYahafis MaulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- (ASME Sec V Article 4 & 5) : UT - Ultrasonic TestingDocumento31 pagine(ASME Sec V Article 4 & 5) : UT - Ultrasonic Testingvijay vickyNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiography Part 2 - TWIDocumento8 pagineRadiography Part 2 - TWIKolusu SivakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Flaw Evaluation in Ultrasonic Testing Using Microprocessor Assisted MethodsDocumento4 pagineQuick Flaw Evaluation in Ultrasonic Testing Using Microprocessor Assisted MethodsGustavo Shaw0% (1)
- Interpretation of Weld RadiographsDocumento14 pagineInterpretation of Weld RadiographsJuliogNessuna valutazione finora
- Weld Scanning ProcedureDocumento5 pagineWeld Scanning ProcedureLutfi IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 243 Standard Practice For Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Examination of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes.Documento7 pagine243 Standard Practice For Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Examination of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes.Ali MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus For Radiographic Testing-Level Ii I. Theory: 40 Hours-40x60 2400 Min. I. Practical:40 HoursDocumento9 pagineSyllabus For Radiographic Testing-Level Ii I. Theory: 40 Hours-40x60 2400 Min. I. Practical:40 HoursSathia SeelanNessuna valutazione finora
- DMS 2 Thickness Gauge TrainingDocumento34 pagineDMS 2 Thickness Gauge TrainingcarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- B-Scan Buggy Demo ProcedureDocumento12 pagineB-Scan Buggy Demo ProcedureJuan Ricardo Villanueva ReañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel NDT Ultrasonic - Level II PowerpointDocumento285 pagineSteel NDT Ultrasonic - Level II PowerpointAhmad ToufailyNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocumento22 pagineLiquid Penetrant TestingNishant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CINDE Course Calendar - Feb 3, 2016Documento32 pagineCINDE Course Calendar - Feb 3, 2016PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Linearity of Equipment GainDocumento4 pagineLinearity of Equipment GainReezman MalkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Echo To Echo (Holloway NDT Article)Documento4 pagineEcho To Echo (Holloway NDT Article)pjhollowNessuna valutazione finora
- G S Earth WireDocumento10 pagineG S Earth WiresaratNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspection Report Bifab Ut On Duplex Stainless Steel Piping PDFDocumento11 pagineInspection Report Bifab Ut On Duplex Stainless Steel Piping PDFquiron2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Thickness GaugeDocumento5 pagineUltrasonic Thickness GaugecarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Inspection 2Documento21 pagineUltrasonic Inspection 2pktienNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Testing 2Documento19 pagineUltrasonic Testing 2Vijayakumar ChandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For The Preparation and Grading of NDTDocumento4 pagineGuidelines For The Preparation and Grading of NDTL...nNessuna valutazione finora
- ATTAR Student Handbook LatestDocumento13 pagineATTAR Student Handbook LatestRahul PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix 1 Part 1b Ultrasonic AUT & MEPAUT 4th Edition February 2016Documento17 pagineAppendix 1 Part 1b Ultrasonic AUT & MEPAUT 4th Edition February 2016Brandon EricksonNessuna valutazione finora
- P4a-MT-103, Rev.3Documento67 pagineP4a-MT-103, Rev.3Hatem RagabNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Equipment Catalog 2015Documento67 pagine2015 Equipment Catalog 2015karthikeyan1992Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Temperature Ultrasonic TestingDocumento3 pagineHigh Temperature Ultrasonic TestingCarlos Bustamante100% (1)
- Srut GWDocumento2 pagineSrut GWNour MasmoudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion MappingDocumento17 pagineCorrosion MappingJuliog100% (1)
- Inspection Trends (January 2013 Vol. 16 No. 1)Documento28 pagineInspection Trends (January 2013 Vol. 16 No. 1)Patrick DominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- RT ProcedureDocumento10 pagineRT ProcedureSandeep SundriyalNessuna valutazione finora
- NDT of CompositeDocumento24 pagineNDT of CompositePavana KumaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.PCN Paut and TofdDocumento9 pagine3.PCN Paut and TofdRIGHT SAFETY JOBSNessuna valutazione finora
- NDT Basic PresentationDocumento207 pagineNDT Basic PresentationIvan AgurtoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rms Auto Ut Corrosion Mapping PDFDocumento6 pagineRms Auto Ut Corrosion Mapping PDFSangeeth Kavil PNessuna valutazione finora
- U.T ProcedureDocumento10 pagineU.T ProceduretreyX67Nessuna valutazione finora
- MPT Training CoursesDocumento156 pagineMPT Training CoursesShyam Sundar GayenNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfer CorrectionDocumento1 paginaTransfer CorrectionkattabommanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Power Corporation Weld Ut: Flaw Location Calculations (For Ut-Ii Training Programme)Documento1 paginaNuclear Power Corporation Weld Ut: Flaw Location Calculations (For Ut-Ii Training Programme)Yogi YuganNessuna valutazione finora
- NDT ISO IEC 17025 Application DocumentDocumento41 pagineNDT ISO IEC 17025 Application DocumentVicky SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- DMA For Austenitic Weld InspectionDocumento17 pagineDMA For Austenitic Weld InspectionRupam BaruahNessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Wave Presentation NDT Global 1Documento41 pagineGuided Wave Presentation NDT Global 1Ahmed LepdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonidos Manual PDFDocumento78 pagineUltrasonidos Manual PDFJose Luis Gonzalez Perez100% (1)
- Interpretation of EN 1712 Acceptance CriteriaDocumento4 pagineInterpretation of EN 1712 Acceptance CriteriaYuzi VengamNessuna valutazione finora
- L - 02 - Calibration of The Testing SystemDocumento60 pagineL - 02 - Calibration of The Testing SystemSanjaya PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultra Sound Testing: Opic:-Test Methods and TechniquesDocumento23 pagineUltra Sound Testing: Opic:-Test Methods and TechniquesVarun MalanNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Lesson5 08 12Documento27 pagineUT Lesson5 08 12Gulfam HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 PDF Ultrasonic TestingDocumento61 pagineModule 4 PDF Ultrasonic Testingjesna mohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Testing-Section 4Documento146 pagineUT Testing-Section 4Charlie Chong100% (1)
- Test TechniquesDocumento15 pagineTest TechniquesAdarsh ChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Ultrasonictesting and AE TestingDocumento10 pagineModule 4 Ultrasonictesting and AE Testingujwalroy119Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4bDocumento33 pagineChapter 4bAhmed shabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dawn of The DhammaDocumento65 pagineDawn of The Dhammaarkaprava paulNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Design by Anil ValiaDocumento10 pagineLight Design by Anil ValiaMili Jain0% (1)
- How Plants SurviveDocumento16 pagineHow Plants SurviveGilbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 My Hobbies Lesson 1 Getting StartedDocumento14 pagineUnit 1 My Hobbies Lesson 1 Getting StartedhienNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023Documento45 pagineFundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023saiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Have Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Documento25 pagineHave Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Aditya ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus (2020) : NTA UGC-NET Computer Science and ApplicationsDocumento24 pagineSyllabus (2020) : NTA UGC-NET Computer Science and ApplicationsDiksha NagpalNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Automatic License Plate Recognition System in Mobile-Based PlatformDocumento6 pagineA Review of Automatic License Plate Recognition System in Mobile-Based PlatformadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG STUDY (Erythromycin)Documento3 pagineDRUG STUDY (Erythromycin)Avianna CalliopeNessuna valutazione finora
- JamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateDocumento23 pagineJamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateSunkilr Sönny100% (4)
- Pre-Qin Philosophers and ThinkersDocumento22 paginePre-Qin Philosophers and ThinkersHelder JorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dispersion Relation of Electromagnetic WavesDocumento2 pagineDispersion Relation of Electromagnetic WavesFidel SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of Light Electric VehicleDocumento14 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Light Electric VehicleAshish NegiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Talents: Phrasal Verbs: TurnDocumento5 pagineUnit 2 Talents: Phrasal Verbs: TurnwhysignupagainNessuna valutazione finora
- Centiloquium of PtolemyDocumento37 pagineCentiloquium of PtolemyNatasa Karalic Koprivica100% (9)
- GE Elec 7 UNIT-3 NoDocumento22 pagineGE Elec 7 UNIT-3 NoLyleNessuna valutazione finora
- Support of Roof and Side in Belowground Coal MinesDocumento5 pagineSupport of Roof and Side in Belowground Coal MinesNavdeep MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 01 Geography The Earth in The Solar SystemDocumento10 pagineChapter - 01 Geography The Earth in The Solar SystemKarsin ManochaNessuna valutazione finora
- 热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远Documento7 pagine热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远小黄包Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics 8th Canadian Edition Andrew AbelDocumento16 pagineTest Bank For Macroeconomics 8th Canadian Edition Andrew AbelstebinrothNessuna valutazione finora
- Edwards SVV HandoutDocumento2 pagineEdwards SVV HandoutossinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmology Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocumento9 pagineCosmology Questions and Answers - SanfoundryGopinathan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Vivekananda'S Conception of Normative Ethics and Resolution Ethical Problems in BusinessDocumento8 pagineVivekananda'S Conception of Normative Ethics and Resolution Ethical Problems in BusinessYajat BhargavNessuna valutazione finora
- Library SectionsDocumento4 pagineLibrary SectionsGello Sotnuiq100% (4)
- Applications Description: General Purpose NPN Transistor ArrayDocumento5 pagineApplications Description: General Purpose NPN Transistor ArraynudufoqiNessuna valutazione finora
- 33kV BS7835 LSZH 3core Armoured Power CableDocumento2 pagine33kV BS7835 LSZH 3core Armoured Power Cablelafarge lafargeNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test BankDocumento27 paginePractical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test Bankdavidhallwopkseimgc100% (28)
- Debug and AssemblerDocumento9 pagineDebug and AssemblerManoj GurralaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sc10 - Worksheet On Atoms and IonsDocumento6 pagineSc10 - Worksheet On Atoms and IonsAnmol AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary Scheme of Work Form 2Documento163 pagineSecondary Scheme of Work Form 2Fariha RismanNessuna valutazione finora