Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Design of Shear Walls
Caricato da
Harold Jackson Mtyana100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
60 visualizzazioni28 pagineDESIGN OF SHEAR WALLS
Titolo originale
DESIGN OF SHEAR WALLS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoDESIGN OF SHEAR WALLS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
60 visualizzazioni28 pagineDesign of Shear Walls
Caricato da
Harold Jackson MtyanaDESIGN OF SHEAR WALLS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 28
Why are buildings with Shear
Walls Preferred in seismic
regions?
•What is shear Wall ????
A shear wall is a wall that is
designed to resist shear, wind force
or the lateral force that causes the
damage to building during
earthquakes.
•RC Building SYSTEMS:
• Three common lateral load resisting systems in
RC Buildings:
Shear Wall in RC buildings:
Vertical plate-like RC Walls
Generally starts at foundation
Goes through full building
height
• Principal attributes:
– Large Strength
– High Stiffness
– Ductility
• Role of Shear Walls:
Smooth transfer of seismic
forces
Vertically oriented wide beams
•Advantages of Shear Walls in
RC buildings:
– Very good earthquake performance,
if properly designed
– In past earthquakes
- Large number of RC frame
buildings damaged or
collapsed
-Shear wall buildings performed
very well
•Advantages of Shear Walls in
RC buildings:
– Easy to construct
- Easily implemented at site
– Effective in
- Reducing construction cost
•Minimizing earthquake damage to
-Structural elements
-Non-Structural elements
E.g., Glass Windows, Building
Contents
•Advantages of Shear Walls in
RC buildings:
– Lesser lateral displacement than
frames
•Architectural Aspects:
Walls must be preferably in
both directions
-In Plan
•Architectural Aspects:
If provided only in one direction, a
proper moment resisting frame must
be provided in the other direction.
•Architectural Aspects:
Shear wall can extend over the full
width of building, or even over partial
width.
•Architectural Aspects:
Wallsshould be throughout the height
– Cannot be interrupted in lower
level
s
•Architectural Aspects:
Walls should be throughout the
height
– Cannot be interrupted in upper
levels.
•Architectural Aspects:
Walls should be along perimeter
of building.
– Improves resistance to twist
•Architectural Aspects:
Openings in walls must
be
– As few as possible
– As small as possible
– As symmetric as possible
•Seismic behavior:
Undesirable Modes of
Failure
•Seismic behavior:
Undesirable Modes of
Failure
•Seismic behavior:
Desirable Mode of
Failure
•Seismic behavior:
Shear demand is more in
lower storeys.
•Seismic Design of RC Walls
Region of Ductile Detailing
•Seismic Design of RC Walls
Possible Geometry of Walls.
•Seismic Design of RC Walls
Primary Reinforcement in Walls.
•Seismic Design of RC Walls
Detailing of Vertical and Horizontal
Bars.
•Seismic Design of RC Walls
Confining Steel in Boundary
Elements.
•Seismic Design of RC Walls
Confining Wall Concrete.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignDa EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction - 5 Shear Wall ...Documento35 pagineConstruction - 5 Shear Wall ...gaurav chaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Types of Structural Systems in Tall BuildingsDocumento3 pagineCommon Types of Structural Systems in Tall BuildingsYati AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Collapse analysis of externally prestressed structuresDa EverandCollapse analysis of externally prestressed structuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear WallDocumento22 pagineShear Wallrenganathank1987100% (1)
- Chapter Two: Lateral Load-Resisting Systems in BuildingsDocumento25 pagineChapter Two: Lateral Load-Resisting Systems in BuildingsDereje bedoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper On Floating ColumnDocumento8 paginePaper On Floating Columnমোঃ হাসান ইমামNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial SheetsDocumento5 pagineTutorial SheetsMr.A.R. VimalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. A. Meher Prasad: Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology MadrasDocumento101 pagineProf. A. Meher Prasad: Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology MadrasEsteban Gabriel Misahuamán CórdovaNessuna valutazione finora
- ETABS Example-RDocumento39 pagineETABS Example-RAnonymous nwByj9LNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Example of A Six Storey Building: Dr. H. J. ShahDocumento51 pagineDesign Example of A Six Storey Building: Dr. H. J. ShahArman MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Design Steps: Er.T.Rangarajan, B.E, M.SC (Struct - Engg), Consulting Structural EngineerDocumento16 pagineSeismic Design Steps: Er.T.Rangarajan, B.E, M.SC (Struct - Engg), Consulting Structural EngineercivilsadiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparision of Is 1893 2002-2016Documento45 pagineComparision of Is 1893 2002-2016dikshith100% (1)
- Formwork/Shuttering: CMR College of Engineering and TechnologyDocumento47 pagineFormwork/Shuttering: CMR College of Engineering and TechnologyGlistering DharNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Behaviour of Irregular StructureDocumento24 pagineSeismic Behaviour of Irregular StructureLalit ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Bridge DesignDocumento67 pagineIntroduction To Bridge DesignSukrit GhoraiNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 - Chapter 6 PDFDocumento39 pagine16 - Chapter 6 PDFDipankar NathNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of RCC ColumnsDocumento14 pagineDesign of RCC Columnsprashmce100% (1)
- Construction JointDocumento1 paginaConstruction JointNumair Ahmad FarjanNessuna valutazione finora
- RCCDocumento16 pagineRCCSyed Sirajul HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of (G+100) Storied Building by Using SoftwareDocumento3 pagineAnalysis and Design of (G+100) Storied Building by Using SoftwareInternational Journal of Innovations in Engineering and ScienceNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Queries:: A Few General Queries On SAP2000/ETABS/SAFEDocumento48 pagineList of Queries:: A Few General Queries On SAP2000/ETABS/SAFERohan Polekar100% (1)
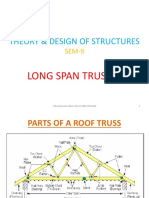
- Long Span TrussesDocumento26 pagineLong Span TrussesAshish Gokawar100% (1)
- Detailing of RCC Slabs PresentantionsDocumento31 pagineDetailing of RCC Slabs PresentantionsMligo ClemenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn Raft-RC Raft Foundation Analysis Design and Drawing SoftwareDocumento108 pagineLearn Raft-RC Raft Foundation Analysis Design and Drawing SoftwareRahul Kumar100% (2)
- Short RCC Column Performances in Different ConditionsDocumento16 pagineShort RCC Column Performances in Different ConditionssjmorabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Ii - Design ConceptsDocumento85 pagineUnit Ii - Design ConceptsAguero AgueroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch.5 Structural Design of Foundations: Q P L BDocumento8 pagineCh.5 Structural Design of Foundations: Q P L BHusam A. Al-HaidriNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of RCC Structure (CE6G) - Design of Slab and BeamDocumento32 pagineDesign of RCC Structure (CE6G) - Design of Slab and BeamSharath WankdothNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Combined FootingsDocumento19 pagineDesign of Combined FootingsRajib BasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Comb Foot MCNDocumento22 pagineComb Foot MCNmohanty_anantakumar6332Nessuna valutazione finora
- Staad - Pro-V8i (Advanced) - Video TrainingDocumento4 pagineStaad - Pro-V8i (Advanced) - Video TrainingSmartlearning TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Overhead RCC Rectangular WaterDocumento4 pagineDesign of Overhead RCC Rectangular WaterAhmed AwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Sloping Slab - Analysis and Design of Sloping SlabDocumento5 pagineSloping Slab - Analysis and Design of Sloping SlabAbuturab SharikmaslatNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Element Analysis of Skew Curved RC Box Girder BridgeDocumento8 pagineFinite Element Analysis of Skew Curved RC Box Girder BridgeTran Tien DungNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforcement Detailing of RCC SlabsDocumento6 pagineReinforcement Detailing of RCC SlabsGani AnosaNessuna valutazione finora
- (LECT-21,22) Prestressed Concrete SlabsDocumento22 pagine(LECT-21,22) Prestressed Concrete SlabsSushil MundelNessuna valutazione finora
- DOS Tall Building FinalDocumento50 pagineDOS Tall Building Finalsoham trivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Composite BridgeDocumento10 pagineDesign of Composite BridgeHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 - Structural WallsDocumento37 pagine8 - Structural Wallskenny lie100% (1)
- DesigningConcreteStructures RCDC TRNC03788Documento58 pagineDesigningConcreteStructures RCDC TRNC03788Rifky NetriadyNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Calculate Lap Length in Column Beam and Slab - Lapping ZoneDocumento10 pagineHow To Calculate Lap Length in Column Beam and Slab - Lapping ZoneQamar JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- RCC Foundation-Unit 3Documento18 pagineRCC Foundation-Unit 3ayeshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Bridges NicholsonDocumento94 pagineSimple Bridges Nicholsonfarhaad shaikNessuna valutazione finora
- R C C Beam DesignDocumento6 pagineR C C Beam DesignBehroozNessuna valutazione finora
- Substitute FrameDocumento22 pagineSubstitute FrameRAJA SEKHARNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Aspects of PSCDocumento73 paginePractical Aspects of PSCNagpur-Civil MRIDCNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Examples On Seismic Evaluation-V1.0Documento45 pagineSolved Examples On Seismic Evaluation-V1.0sanket100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5 Structural AnalysisDocumento76 pagineCHAPTER 5 Structural AnalysisDavid MurphyNessuna valutazione finora
- Highway Survey and Alignment LocationDocumento79 pagineHighway Survey and Alignment LocationAbdullahi Abdi HashiNessuna valutazione finora
- View Topic - Design Corner Eccentric Footing On Both SideDocumento5 pagineView Topic - Design Corner Eccentric Footing On Both SidejayadushNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2 Presentation PDFDocumento40 pagineDay 2 Presentation PDFradhi_rads89Nessuna valutazione finora
- CE6686 - Design of RCC and Composite StructuresDocumento12 pagineCE6686 - Design of RCC and Composite StructuresSabarinath MuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of RCC Building As Per Indian Standard by ETABSDocumento49 pagineDesign of RCC Building As Per Indian Standard by ETABSYOGESH BANGNessuna valutazione finora
- IV. N S: Umerical TudyDocumento1 paginaIV. N S: Umerical TudyKNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure Details FOR Foundation: Practical Architectural Training-Fun Begins (For Interns and Freshers)Documento37 pagineStructure Details FOR Foundation: Practical Architectural Training-Fun Begins (For Interns and Freshers)Divya Varshney100% (1)
- Design of Steel Strs - 8th Sem VTU NotesDocumento12 pagineDesign of Steel Strs - 8th Sem VTU NotesHarish T S GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect - 2 - Earthquake - Resistant - Systems - Part 2Documento13 pagineLect - 2 - Earthquake - Resistant - Systems - Part 2jana ShmaysemNessuna valutazione finora
- Pawar A D Associate Professor: Apawar@nicmar - Ac.inDocumento70 paginePawar A D Associate Professor: Apawar@nicmar - Ac.inAboalmaaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewDocumento47 pagineLecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Design StepsDocumento16 pagineSeismic Design StepsGopal MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4-Code Based Design of Reinforced Concrete High Rise Buildings-1Documento67 pagineLecture 4-Code Based Design of Reinforced Concrete High Rise Buildings-1Harold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewDocumento47 pagineLecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Wall DesignDocumento22 pagineShear Wall DesignHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edge Distance Spacing and Bearing in Bolted Connections - Lewis - 1996 PDFDocumento53 pagineEdge Distance Spacing and Bearing in Bolted Connections - Lewis - 1996 PDFArun MaskNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2-Earthquake Waves and Their Effects On StructuresDocumento29 pagineLecture 2-Earthquake Waves and Their Effects On StructuresHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - Tension MembersDocumento40 pagineLecture 3 - Tension MembersHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Etabs Tutorials 01Documento70 pagineEtabs Tutorials 01Harold Jackson Mtyana100% (1)
- Lecture 1-INTRODUCTION TO HIGH RISE BUILDINGS PDFDocumento63 pagineLecture 1-INTRODUCTION TO HIGH RISE BUILDINGS PDFHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (1)
- Box Culvert PresentationDocumento40 pagineBox Culvert Presentationdaleema80% (5)
- Earthquake Waves and Their Effects On BuildingsDocumento35 pagineEarthquake Waves and Their Effects On BuildingsHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt5 160919183424Documento93 pagineChapt5 160919183424FayyazAhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Plate Girder ExampleDocumento18 pagineDesign of A Plate Girder ExampleHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Stub For Transmission Line TowersDocumento26 pagineDesign of Stub For Transmission Line Towersdebjyoti_das_685% (13)
- Data Sheet - ThroughboltDocumento2 pagineData Sheet - ThroughboltHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardinal Series: TrendingDocumento17 pagineCardinal Series: TrendingHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pds Staadpro LTR 0617 HR FDocumento2 paginePds Staadpro LTR 0617 HR FMassa SebatianNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial STAAD.X TowerDocumento54 pagineTutorial STAAD.X TowerJuan Eduardo PFNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Wall DesignDocumento22 pagineShear Wall DesignHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (1)
- BRIDGE HydraulicsDocumento44 pagineBRIDGE HydraulicsHarold Jackson Mtyana0% (1)
- Autocad Civil 3D User InterfaceDocumento25 pagineAutocad Civil 3D User InterfaceHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (1)
- Concrete Columns Aci Manual en PDFDocumento204 pagineConcrete Columns Aci Manual en PDFjgvidalNessuna valutazione finora
- Loading To Box CulvertsDocumento20 pagineLoading To Box CulvertsHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5 Lateral BucklingDocumento33 pagineLecture 5 Lateral BucklingHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No.7 - Bridge BearingsDocumento39 pagineLecture No.7 - Bridge BearingsHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (2)
- Lecture No.3 - Bridge-SuperstructureDocumento29 pagineLecture No.3 - Bridge-SuperstructureHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No.3 - Bridge-SuperstructureDocumento29 pagineLecture No.3 - Bridge-SuperstructureHarold Jackson MtyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical FibreDocumento17 pagineOptical Fibreshah alomNessuna valutazione finora
- Solartech Solar Pumping Inverter: Technical DataDocumento1 paginaSolartech Solar Pumping Inverter: Technical Dataadolfo escobarNessuna valutazione finora
- Recovery of Spent CatalystDocumento4 pagineRecovery of Spent CatalystUtsav PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specification of Stay InsulatorDocumento11 pagineTechnical Specification of Stay Insulatorraj_stuff006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inlet DuctDocumento14 pagineInlet DuctAhmad ArmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Api Tubing Casing Id CalculatorDocumento45 pagineApi Tubing Casing Id CalculatorRyan LlanetaNessuna valutazione finora
- AMZ PresenceDocumento6 pagineAMZ Presencemarginwalker77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stator Earth Fault in 200MW Generator-A Case StudyDocumento5 pagineStator Earth Fault in 200MW Generator-A Case StudylrpatraNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Oracle Application Framework (OAF) Training Guide - EO, VO, Page, Query Region, LOV, PPRDocumento73 pagine3-Oracle Application Framework (OAF) Training Guide - EO, VO, Page, Query Region, LOV, PPRPreethi KishoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Cks 180 Ton MIGAS BaruDocumento46 pagineCks 180 Ton MIGAS BaruHario PramuditoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kiln Performance - Efficiency FormulasDocumento12 pagineKiln Performance - Efficiency FormulasMohamed ZayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Igor Programming PDFDocumento33 pagineIntroduction To Igor Programming PDFpaulklyuyevNessuna valutazione finora
- Road Geometry & Transition CurveDocumento8 pagineRoad Geometry & Transition CurveNann Kay Thari KyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Users Manual For Oslo, Bremen and Turboaire.: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsDocumento40 pagineUsers Manual For Oslo, Bremen and Turboaire.: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructionsbuttler25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis For Crane HookDocumento6 pagineDesign and Analysis For Crane Hookmukeshsonava076314Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump: LPH 55312, LPH 55316, LPH 55320Documento12 pagineLiquid Ring Vacuum Pump: LPH 55312, LPH 55316, LPH 55320Edu CordonNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrographic Survey: Ecg 305: Chapter 7Documento24 pagineHydrographic Survey: Ecg 305: Chapter 7Ahmad ZahirNessuna valutazione finora
- Banana ChipsDocumento5 pagineBanana Chipsbikram limbuNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.0L EngineDocumento347 pagine4.0L EngineCapssa Oscar100% (2)
- Adaptive Antenna Systems: Widrow, E. GoodeDocumento17 pagineAdaptive Antenna Systems: Widrow, E. GoodeKhal ZeratulNessuna valutazione finora
- Backup BatteryDocumento4 pagineBackup Batteryzabiruddin786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bioreactor Design: Mata Kuliah: Pengantar Teknologi BioprosesDocumento33 pagineBioreactor Design: Mata Kuliah: Pengantar Teknologi BioprosesyassinharanNessuna valutazione finora
- TGE 5, TGE 5-Ex, TGM 5, TGM 5-Ex, TGU 5, TGU 5-Ex: Transmitter For Angular PositionDocumento10 pagineTGE 5, TGE 5-Ex, TGM 5, TGM 5-Ex, TGU 5, TGU 5-Ex: Transmitter For Angular Positionvinodk335Nessuna valutazione finora
- NE5521Documento9 pagineNE5521Carlos TibussiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ohlins Tool Manual 2017Documento46 pagineOhlins Tool Manual 2017Pier o.f.r.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gapura Company Profile - 17mar17Documento43 pagineGapura Company Profile - 17mar17als izmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Neutron ScatteringDocumento191 pagineIntro To Neutron ScatteringEleni MitsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Craftsman 82141 User ManualDocumento36 pagineCraftsman 82141 User ManualJoe100% (1)
- WPH02 01 Que 20160120Documento24 pagineWPH02 01 Que 20160120Omar HashemNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT8 02SC Challenge Sol21Documento24 pagineMIT8 02SC Challenge Sol21Gabriel TeodoroNessuna valutazione finora