Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MOM Chapter 01 New-Edited
Caricato da
Mohamad AhmadTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MOM Chapter 01 New-Edited
Caricato da
Mohamad AhmadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter Objectives
Understand the concepts of normal and shear stress
Analyze and design of members subjected on axial load
or shear
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
In-class Activities
1. Check homework, if any
2. Reading Quiz
3. Applications
4. Normal Stress
5. Shear Stress
6. Concept Quiz
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
READING QUIZ
1. What is the normal stress in the bar if P=10
kN and 500mm²?
a) 0.02 kPa
b) 20 Pa
c) 20 kPa
d) 200 N/mm²
e) 20 MPa
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
READING QUIZ (cont)
2. What is the average shear stress in the
internal vertical surface AB (or CD), if
F=20kN, and AAB=ACD=1000mm²?
a) 20 N/mm²
b) 10 N/mm²
c) 10 kPa
d) 200 kN/m²
e) 20 MPa
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
APPLICATIONS
Where does the average normal stress occur?
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
APPLICATIONS (cont)
Will the total shear force over the anchor length be equal to
the total tensile force σtensile A in the bar?
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
APPLICATIONS
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
AVERAGE NORMAL STRESS
Will the total shear force over the anchor length be equal to
the total tensile force σtensile A in the bar?
P
A
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
NORMAL SHEAR STRESS
Fx
zx lim
Fz A0 A
z lim
A0 A Fy
zy lim
A0 A
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
EXAMPLE 1
The bar in Fig. 1–16a has a constant width of 35 mm and a
thickness of 10 mm. Determine the maximum average
normal stress in the bar when it is subjected to the loading
shown.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
EXAMPLE 1 (cont)
Solutions
• By inspection, different sections have different internal forces.
• Graphically, the normal force diagram is as shown.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
EXAMPLE 1 (cont)
Solutions
• By inspection, the largest loading is in region BC,
PBC 30 kN
• Since the cross-sectional area of the bar is constant, the largest
average normal stress is
BC
PBC
30 103
85.7 MPa (Ans)
A 0.035 0.01
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
DESIGN OF SIMPLE CONNECTION
• For normal force requirement
P
A
allow
• For shear force requirement
V
A
allow
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
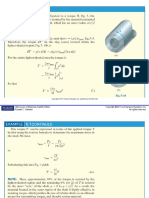
EXAMPLE 2
The rigid bar AB shown in Fig. 1–29a is supported by a steel
rod AC having a diameter of 20 mm and an aluminum block
having a cross sectional area of 1800mm2. The 18-mm-
diameter pins at A and C are subjected to single shear. If the
failure stress for the steel and aluminum 680 MPa is and st fail
70 MPa respectively, and the failure shear stress for each
al fail
pin is 900 MPa , determine the largest load P that can be
fail
applied to the bar. Apply a factor of safety of FS=2.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
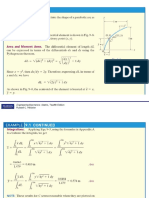
EXAMPLE 2 (cont)
Solutions
• The allowable stresses are
st fail 680
st allow 340 MPa
F .S . 2
al fail 70
al allow 35 MPa
F .S . 2
fail 900
allow 450 MPa
F .S . 2
• There are three unknowns and we apply the equations of equilibrium,
M B 0; P 1.25 FAC 2 0 (1)
M A 0; FB 2 P 0.75 0 (2)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
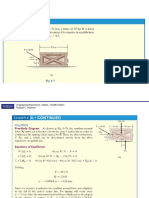
EXAMPLE 2 (cont)
Solutions
• We will now determine each value of P that creates the allowable stress
in the rod, block, and pins, respectively.
• For rod AC, FAC st allow AAC 340106 0.01 2 106.8 kN
106.8 2 171 kN
• Using Eq. 1, P 1.25
• For block B, FB al allow AB 35106 1800106 63.0 kN
63.0 2 168 kN
• Using Eq. 2, P 0.75
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
EXAMPLE 2 (cont)
Solutions
• For pin A or C, V FAC allow A 450106 0.009 2 114.5 kN
114.5 2 183 kN
• Using Eq. 1, P
1.25
• When P reaches its smallest value (168 kN), it develops the allowable
normal stress in the aluminium block. Hence,
P 168 kN (Ans)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
CONCEPT QUIZ
1) The thrust bearing is subjected to the loads
as shown. Determine the order of average
normal stress developed on cross section
through BC and D.
a) C>B>D
b) C>D>B
c) B>C>D
d) D>B>C
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Practicing Oil AnalysisDocumento62 paginePracticing Oil AnalysisCristian SNessuna valutazione finora
- RCD Lecture Note 8 - Eccentrically Loaded Columns PDFDocumento2 pagineRCD Lecture Note 8 - Eccentrically Loaded Columns PDFAugosto FraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Strength of MaterialsDocumento26 pagineIntroduction to Strength of MaterialspamelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences of Classical and Modern Views On GravityDocumento4 pagineDifferences of Classical and Modern Views On GravityJose Miguel Lopez83% (6)
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: Presented By: Shweta Surwase F.Y. M.Sc. (Mental Health Nursing) MIMH, PuneDocumento48 pagineElectroconvulsive Therapy: Presented By: Shweta Surwase F.Y. M.Sc. (Mental Health Nursing) MIMH, PuneShweta KateNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 1-Simplestress PDFDocumento43 pagine1 1-Simplestress PDFAsad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal & Shear Stress - Chapter 1Documento36 pagineNormal & Shear Stress - Chapter 1ezoramajnunNessuna valutazione finora
- Fitness RX For Women - April 2014Documento116 pagineFitness RX For Women - April 2014Ricardo Soares100% (2)
- The BBTT Program REV PDFDocumento40 pagineThe BBTT Program REV PDFBianca Lacramioara Florea100% (3)
- Introduction to Strength of Materials ConceptsDocumento38 pagineIntroduction to Strength of Materials ConceptsAlex JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- LADBS - Swimming PoolsDocumento43 pagineLADBS - Swimming PoolsMichael James100% (1)
- Estimation of The ProjectDocumento89 pagineEstimation of The ProjectNaga PrasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Review MODULE 1 – STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (38 charactersDocumento2 pagineReview MODULE 1 – STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (38 charactersCLAIRENessuna valutazione finora
- Facemasks Manufacturers DirectoryDocumento54 pagineFacemasks Manufacturers DirectoryAlex Kharchuk100% (1)
- Kohler RRT ManualDocumento40 pagineKohler RRT Manualjmh488100% (1)
- Fluent-Intro 16.0 L02 IntroCFD PDFDocumento45 pagineFluent-Intro 16.0 L02 IntroCFD PDFAnonymous 8209ZTNessuna valutazione finora
- Polyester MicrofiberDocumento37 paginePolyester Microfiberpsyish80% (5)
- MOM - Chapter - 08 Combined LoadingDocumento38 pagineMOM - Chapter - 08 Combined LoadingIvan Ng0% (1)
- MOM Chapter 01 New-EditedDocumento20 pagineMOM Chapter 01 New-Editednur yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 01 New-EditedDocumento20 pagineMOM Chapter 01 New-EditedNuur Yusuf Sheikh OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- MechMat Hibbeler Ch01 SlidesDocumento19 pagineMechMat Hibbeler Ch01 SlidesKatrina Ranee RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Stress StrainDocumento71 pagineChapter 1 Stress StrainXander ZanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - StressDocumento14 pagineChapter 1 - StressWissam ZgheibNessuna valutazione finora
- Me - WK 6Documento17 pagineMe - WK 6JAMES CLEARNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter ObjectivesDocumento30 pagineChapter ObjectivesdhaktodesatyajitNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 05 New-EditedDocumento49 pagineMOM Chapter 05 New-Editednur yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 StressDocumento39 pagineChapter 1 StressMaipenrai MemeeNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 02 New-EditedDocumento21 pagineMOM Chapter 02 New-Editednur yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- BS - MOM Week-3 Axial-Load-1Documento27 pagineBS - MOM Week-3 Axial-Load-1basaksenol1Nessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 07 New-EditedDocumento35 pagineMOM Chapter 07 New-Editednur yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- BS - MOM Week-2 StrainDocumento16 pagineBS - MOM Week-2 Strainbasaksenol1Nessuna valutazione finora
- SAB2223 Mechanics of Materials and Structures: Topic 1 Stress and StrainDocumento120 pagineSAB2223 Mechanics of Materials and Structures: Topic 1 Stress and StrainTsalach100% (1)
- Lecture - Combined LoadingsDocumento22 pagineLecture - Combined LoadingsSharvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinic CEMsDocumento23 pagineClinic CEMsJohnaton ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10Documento34 pagineChapter 10Gia BaoNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 02 New-EditedDocumento21 pagineMOM Chapter 02 New-EditedNuur Yusuf Sheikh OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 3-Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocumento22 pagineMOM Chapter 3-Mechanical Properties of MaterialsezoramajnunNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 04 New-EditedDocumento46 pagineMOM Chapter 04 New-Editednur yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Strength of MaterialsDocumento14 pagineIntroduction to Strength of MaterialsJQNessuna valutazione finora
- DDocumento3 pagineDLucille Samson ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Dp9 Anchorage Zone Detailing PDFDocumento18 pagine9 Dp9 Anchorage Zone Detailing PDFkesharinareshNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Stress: Definition - Concentric and Eccentric Loading - Shearing Stress: Definition - Bearing Stress: Definition - Stress On An Oblique Plane - Design ConsiderationsDocumento29 pagineNormal Stress: Definition - Concentric and Eccentric Loading - Shearing Stress: Definition - Bearing Stress: Definition - Stress On An Oblique Plane - Design ConsiderationsEsra'a SmadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Loadings Chapter 8Documento28 pagineCombined Loadings Chapter 8ezoramajnunNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning Civil Engineering Department Dr. Eng. Mustafa Maher Al-TayebDocumento17 pagineFaculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning Civil Engineering Department Dr. Eng. Mustafa Maher Al-TayebHazem AlmasryNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of Metals: StrainDocumento27 pagineMechanical Properties of Metals: Strainrr pandianNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 07Documento35 pagineChapter 07Hassan SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce at Phinma Coc: Axially Loaded Compression MemberDocumento3 pagineCe at Phinma Coc: Axially Loaded Compression MemberNala FertuNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Stresses and Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocumento73 pagineSimple Stresses and Thin-Walled Pressure Vesselsaileen eustaquioNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1Documento5 pagine1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1onenoteforlocadNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 Simple StressesDocumento4 pagineAssignment 1 Simple StressesYoloerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - Axial Stress and Strain - 3Documento26 pagineLecture 1 - Axial Stress and Strain - 3Alvin DeliroNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Course OverviewDocumento20 pagineMechanics of Deformable Bodies Course OverviewJullian Paul GregorioNessuna valutazione finora
- C E D C A E: Chapter 2: StrainDocumento19 pagineC E D C A E: Chapter 2: Strainhend mahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Materials Course OverviewDocumento19 pagineMechanics of Materials Course OverviewSahar Batool QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocumento5 pagineTutorial 1 PDFthehungengineerNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocumento5 pagineTutorial 1 PDFthehungengineerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Bearing and Punching Stress, StrainDocumento16 pagineLecture 2 Bearing and Punching Stress, StrainDennisVigoNessuna valutazione finora
- STRESS AND STRAIN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMAL DESIGNDocumento3 pagineSTRESS AND STRAIN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMAL DESIGNYasser ZubaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 213 - (Spring, 2024) - Chapter # 2Documento16 pagineME 213 - (Spring, 2024) - Chapter # 2omaruhu822Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 Mechanics of Materials Opening and Chap 1Documento66 pagine2023 Mechanics of Materials Opening and Chap 1彭莉棋Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of Metals: StrainDocumento26 pagineMechanical Properties of Metals: StrainAd Man GeTigNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Series 1 November 23 2020 PDFDocumento19 pagineModule 1 Series 1 November 23 2020 PDFjb12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Axial LoadingDocumento33 pagineChapter 4 - Axial LoadingMaipenrai Memee100% (1)
- Combined LoadingDocumento22 pagineCombined LoadingSang Ka KalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2-Axially Loaded MembersDocumento35 pagineChapter 2-Axially Loaded MembersMUHAMMAD HAFIZ KAMAL MOHAMAD KAMALNessuna valutazione finora
- Tegangan Geser Rata-Rata: Oleh: Fitri Hardiyanti Mochamad Yusuf SantosoDocumento23 pagineTegangan Geser Rata-Rata: Oleh: Fitri Hardiyanti Mochamad Yusuf SantosoAndi RahmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Beer Chapter 1Documento90 pagineBeer Chapter 1amarilis100% (2)
- Bolted Joints and Bolt Preload OverviewDocumento14 pagineBolted Joints and Bolt Preload OverviewKishore MylavarapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Planning Civil Engineering Department Petra Christian UniversityDocumento59 pagineFaculty of Civil Engineering and Planning Civil Engineering Department Petra Christian Universitykenny lieNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM2E Chap1bDocumento33 pagineMOM2E Chap1bpoom2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ice CH4 2019-2020 PDFDocumento28 pagineIce CH4 2019-2020 PDFMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Hibbeler ch02 ExDocumento9 pagineHibbeler ch02 ExMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Hibbeler ch05 ExDocumento44 pagineHibbeler ch05 ExMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 01 New-EditedDocumento19 pagineMOM Chapter 01 New-EditedMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Hibbeler Apa ExDocumento17 pagineHibbeler Apa ExMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Hibbeler ch04 ExDocumento38 pagineHibbeler ch04 ExMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Hibbeler ch01 ExDocumento35 pagineHibbeler ch01 ExMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 09Documento32 pagineCH 09Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 01 New-EditedDocumento19 pagineMOM Chapter 01 New-EditedMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 08Documento21 pagineCH 08Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 11Documento14 pagineCH 11Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 3Documento9 pagineExp 3Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10Documento26 pagineCH 10Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 08Documento21 pagineCH 08Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento16 pagineCH 03Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- TH PP CH1 2019-2020Documento10 pagineTH PP CH1 2019-2020Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 01Documento4 pagineCH 01Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- MOM Chapter 02 New-EditedDocumento18 pagineMOM Chapter 02 New-EditedMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Template - Strength ReportDocumento3 pagineTemplate - Strength ReportMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- TH PP CH1 2019-2020Documento10 pagineTH PP CH1 2019-2020Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- TH PP CH7 2019-2020Documento33 pagineTH PP CH7 2019-2020Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No 5 Full Load CI EngineDocumento3 pagineExperiment No 5 Full Load CI EngineMohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- TH PP CH6 2019-2020Documento37 pagineTH PP CH6 2019-2020Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- TH PP CH4 2018-2019Documento16 pagineTH PP CH4 2018-2019Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- TH PP CH6 2019-2020Documento37 pagineTH PP CH6 2019-2020Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPERIMENT NO 3 Willan's LineDocumento3 pagineEXPERIMENT NO 3 Willan's LineMohamad Ahmad100% (1)
- Solution SamanualDocumento375 pagineSolution SamanualCeazer SdNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPERIMENT NO 3 Willan's LineDocumento3 pagineEXPERIMENT NO 3 Willan's LineMohamad Ahmad100% (1)
- Normalized Carbon Steel 230M07Documento12 pagineNormalized Carbon Steel 230M07Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Statepfofileofvidarbha PDFDocumento53 pagineStatepfofileofvidarbha PDFAditiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mil STD 785BDocumento90 pagineMil STD 785BLaura Encinas EscobarNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer PackagesDocumento72 pagineComputer PackagesBildad JoashNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories and philosophies that shaped early childhood educationDocumento3 pagineTheories and philosophies that shaped early childhood educationJamille Aira PascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive Communication, Assignment 2Documento3 paginePurposive Communication, Assignment 2Myles Ninon LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chevrolet 2005 Uplander Electrical Wiring DiagramDocumento62 pagineChevrolet 2005 Uplander Electrical Wiring Diagramromain.richertNessuna valutazione finora
- FOOD PRESERVATION CHART FOR CANNING LOW-ACID & ACID FOODSDocumento2 pagineFOOD PRESERVATION CHART FOR CANNING LOW-ACID & ACID FOODSjhNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts Catalogue: Nova L5-L6Documento69 pagineParts Catalogue: Nova L5-L6juanjoserodriguezalzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ashrae Handbook 2000 CHDocumento32 pagineAshrae Handbook 2000 CHKazuto NakazatoNessuna valutazione finora
- KS1 A Good Bubbling CauldronDocumento11 pagineKS1 A Good Bubbling CauldronViktoriia PolushkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tots FaqDocumento12 pagineTots FaqkbsnNessuna valutazione finora
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas PressureDocumento1 paginaPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas Pressurelelon ongNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento9 pagineChapter 4Aung KhantNessuna valutazione finora
- SSCM Roads and Bridges - Annex III Technical Specifications 105 C1 PDFDocumento254 pagineSSCM Roads and Bridges - Annex III Technical Specifications 105 C1 PDFSite Engineer.2p2100% (1)
- Drag LinesDocumento31 pagineDrag LinesJonas GondimNessuna valutazione finora
- Abb 60 PVS-TLDocumento4 pagineAbb 60 PVS-TLNelson Jesus Calva HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Financial Analysis of Tri Van Drum AirportDocumento81 pagineA Study On Financial Analysis of Tri Van Drum AirportN.MUTHUKUMARAN100% (1)
- JSA - MergeDocumento11 pagineJSA - MergeIzzuddin MustapaNessuna valutazione finora
- BX 560GDocumento20 pagineBX 560Gmacanipharoldf6220Nessuna valutazione finora