Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ap Abortion
Caricato da
Kartikeya Arya0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
25 visualizzazioni11 pagineread
Titolo originale
ap_abortion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoread
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
25 visualizzazioni11 pagineAp Abortion
Caricato da
Kartikeya Aryaread
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 11
Abortion
Prof. Kumar Neeraj Sachdev
6168-F
Department of Humanities and Social Sciences
Moral Dilemmas
• World Poverty
• Euthanasia
• Abortion
• Case Studies
Abortion - Questions
• Do women have the right to abort
unwanted pregnancies?
• Is the state entitled to make deliberate
abortion illegal?
• Should some abortions be permitted
and others not?
Abortion
• An abortion occurs when the pregnancy is
ended so that it does not result in the birth
of a child. Sometimes this is called
'termination of pregnancy‘.
• There is a difference between Spontaneous
Abortion (or Miscarriage, that is presently
used in Medical Language) and Induced
Abortion (or Abortion)
Arguments against Abortion
• Sanctity of Life especially Human Life
• Sentience Criterion
– Sentience is the capacity to have experiences
especially pleasurable and painful experiences
• Potential Personhood
Arguments for Abortion
• That abortion should be permitted
because the prohibition of abortion leads
to highly undesirable consequences;
• That women have a moral right to
choose abortion; and
• That fetuses are not yet persons that
thus do not yet have a substantial right to
life.
Abortion in India
• The Indian Penal Code, which was enacted in 1860 and was
written in accordance with British law at the time of its
creation, declared induced abortion as illegal. Induced
abortion was defined as purposely "causing miscarriage.“
• Abortion practitioners would either be imprisoned for up to
three years, fined, or both; women undergoing abortions
could be imprisoned for up to seven years and also be
charged an additional fine. The only exception was when
abortion was induced in order to save the life of the
woman.
• Despite the fact that this passage in the penal code was
changed in Great Britain in 1967, India did not change it
until 1971.
• The Indian abortion law falls under the Medical Termination of
Pregnancy (MTP) Act, which was enacted by the Indian
Parliament in the year 1971 with the intention of reducing the
incidence of illegal abortion. The MTP Act came into effect
from 1 April 1972 and was amended in the years 1975 and
2002.
• Pregnancies not exceeding 12 weeks may be terminated based
on a single opinion formed in good faith. In case of pregnancies
exceeding 12 weeks but less than 20 weeks, termination needs
opinion of two doctors. The Medical Termination of Pregnancy
(MTP) Act of India clearly states the conditions under which a
pregnancy can be ended or aborted, the persons who are
qualified to conduct the abortion and the place of
implementation.
• Some of these qualifications are as follows:
• Women whose physical and/or mental health were
endangered by pregnancy
• Women facing the birth of a potentially handicapped or
malformed child
• Rape
• Pregnancies in unmarried girls under the age of
eighteen with the consent of a guardian
• Pregnancies in "lunatics" with the consent of a
guardian
• Pregnancies that are a result of failure in sterilization
Concluding Remark
Arguments for and against abortion
suggest that a decision for abortion,
it at all unavoidable, should be
cautiously arrived at, that is to say,
should be based upon rationally
considered judgment in a particular
situation.
Thank You.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BusDocumento164 pagineBuskkkkkkkkkkkkkkkerNessuna valutazione finora
- FCFF 3 STDocumento3 pagineFCFF 3 STKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Technological Disruption On Workforce Challenges of Indian Banks - Identification, Assessment & MitigationDocumento142 pagineImpact of Technological Disruption On Workforce Challenges of Indian Banks - Identification, Assessment & MitigationKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultimate Guide To Co Living Ebook OutsiteDocumento21 pagineUltimate Guide To Co Living Ebook OutsiteIsrael Leal100% (1)
- QP Paper 2Documento20 pagineQP Paper 2Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiitjee: JEE (Advanced) - 2017Documento17 pagineFiitjee: JEE (Advanced) - 2017Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- QP Paper 1 PDFDocumento22 pagineQP Paper 1 PDFKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iit Jee 2010 Paper 1Documento33 pagineIit Jee 2010 Paper 1Umang MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkene Alkyne PDFDocumento45 pagineAlkene Alkyne PDFKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper 1 GR 1 Theory FOR WEB PDFDocumento8 pagineSample Paper 1 GR 1 Theory FOR WEB PDFJoelClarinSilorio0% (2)
- Document PDF 183 2Documento34 pagineDocument PDF 183 2Mayank SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- PaperDocumento14 paginePaperSayan Kumar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
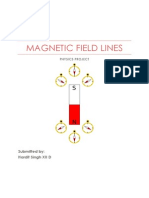
- Physics Project Class 12Documento7 paginePhysics Project Class 12Keith Payne60% (20)
- Directorate of Distance Education, Davv, Indore: Admit Card JUN 2016Documento1 paginaDirectorate of Distance Education, Davv, Indore: Admit Card JUN 2016Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- QP Paper 1Documento22 pagineQP Paper 1Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- 16008715 (1)Documento2 pagine16008715 (1)Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper KVPY XII Final Paper - 01!11!2015 - FinalDocumento52 paginePaper KVPY XII Final Paper - 01!11!2015 - FinalKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Equilibrium Study NotesDocumento28 pagineChemical Equilibrium Study NotesKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl HalideDocumento71 pagineAlkyl HalideKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problems Nov 30 2010Documento5 paginePractice Problems Nov 30 2010Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Conic Section DPP 1-12-13thDocumento63 pagineConic Section DPP 1-12-13thKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper KVPY XII Final Paper - 01!11!2015 - FinalDocumento52 paginePaper KVPY XII Final Paper - 01!11!2015 - FinalKartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problems Nov 27 2000Documento6 paginePractice Problems Nov 27 2000Kartikeya AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Critique3m CabusDocumento4 pagineCritique3m Cabusapi-273469220Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of LabourDocumento18 pagineMechanism of LabournamithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1B Chapter 22Documento22 pagineGroup 1B Chapter 22Melody DoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teenage Pregnancies in CaliforniaDocumento5 pagineTeenage Pregnancies in CaliforniaAnnold ochiezyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pilates Reformer 1Documento143 paginePilates Reformer 1Suat Barut100% (6)
- Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) For Sub-Centres: DraftDocumento60 pagineIndian Public Health Standards (IPHS) For Sub-Centres: DraftRekha ChakrabartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Capstone OutlineDocumento3 pagineCapstone Outlineapi-395468231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research Project ReportDocumento42 pagineResearch Project ReportmutsapoNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Item ObstetricsDocumento4 pagine100 Item ObstetricsEmir Mukhtar Malcampo KamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Malaria Infection Prevalence and Risk Factors in Pregnant Women at Kampala International University HospitalDocumento13 pagineMalaria Infection Prevalence and Risk Factors in Pregnant Women at Kampala International University HospitalKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNessuna valutazione finora
- IUCD Manual EnglishDocumento194 pagineIUCD Manual EnglishHarshaWakodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- HS1207 01 ICA Individual Assignment Instructions 2021 - 1001 ModDocumento6 pagineHS1207 01 ICA Individual Assignment Instructions 2021 - 1001 ModMelissa Chen100% (1)
- Lactating Adenoma A Case ReportDocumento3 pagineLactating Adenoma A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- CopperDocumento110 pagineCopperVirra Mayang ArumNessuna valutazione finora
- Fhap Family Summary: Group MembersDocumento5 pagineFhap Family Summary: Group MembersJacob JrNessuna valutazione finora
- School-Life Balance The Aftermath of Teenage Pregnancy PhenomenonDocumento15 pagineSchool-Life Balance The Aftermath of Teenage Pregnancy PhenomenonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- UserManual ANM Process PDFDocumento44 pagineUserManual ANM Process PDFGafoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Prenatal Development (Child Psychology)Documento37 paginePrenatal Development (Child Psychology)Yel BaldemorNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Biography of Our Beloved Prophet MuhammadDocumento3 pagineA Brief Biography of Our Beloved Prophet MuhammadAntonina MukhametshinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter To Governor With SignaturesDocumento7 pagineLetter To Governor With SignaturesAdrian Mojica50% (2)
- Case Write-Up Obstetrics & Gynaecology Posting SESSION 2021/2022Documento25 pagineCase Write-Up Obstetrics & Gynaecology Posting SESSION 2021/2022Luqman MalekNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.hospital RHC Stgs - Federal Government of Somalia PDFDocumento200 pagine3.hospital RHC Stgs - Federal Government of Somalia PDFFaisal mohammed AbdullahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio On M104 Clinical Management and High Risk PregnanciesDocumento31 paginePortfolio On M104 Clinical Management and High Risk PregnanciesKIMBERLY JANE OTAGAN DALAGANNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay RandomsDocumento28 pagineEssay RandomslorochimonsterNessuna valutazione finora
- The High Risk New BornDocumento23 pagineThe High Risk New Bornchhaiden100% (4)
- Clinical Autogenic Training in PregnancyDocumento2 pagineClinical Autogenic Training in PregnancyIvana PetrovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation-Severe Acute MalnutritionDocumento29 pagineCase Presentation-Severe Acute Malnutritionroutc076Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm NotesDocumento28 pagineMidterm NotesGen FranchesKyle Cortez ErigbuagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Indonesia Health Profile 2013 - V2 Untuk WebDocumento386 pagineIndonesia Health Profile 2013 - V2 Untuk WebMuhammadZendyDrivamaSuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Through The Life Cycle 5Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento45 pagineNutrition Through The Life Cycle 5Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFnhanselinak9wr16100% (9)