Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Financial Reporting
Caricato da
ranu dwary amorodito0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
52 visualizzazioni9 pagineWorld markets are becoming increasingly interconnected. As capital markets integrate, companies have more flexibility in where they raise capital. The adoption of global accounting standards has facilitated this trend by making financial information more comparable across borders. This allows resources to be allocated more efficiently and improves decision making by managers, investors and creditors. However, developing high-quality, universally accepted accounting standards while balancing political and practical concerns remains an ongoing challenge.
Descrizione originale:
Menjelasakn ppt tentang finacial reporting dan accounting standard
Titolo originale
Financial reporting ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoWorld markets are becoming increasingly interconnected. As capital markets integrate, companies have more flexibility in where they raise capital. The adoption of global accounting standards has facilitated this trend by making financial information more comparable across borders. This allows resources to be allocated more efficiently and improves decision making by managers, investors and creditors. However, developing high-quality, universally accepted accounting standards while balancing political and practical concerns remains an ongoing challenge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
52 visualizzazioni9 pagineFinancial Reporting
Caricato da
ranu dwary amoroditoWorld markets are becoming increasingly interconnected. As capital markets integrate, companies have more flexibility in where they raise capital. The adoption of global accounting standards has facilitated this trend by making financial information more comparable across borders. This allows resources to be allocated more efficiently and improves decision making by managers, investors and creditors. However, developing high-quality, universally accepted accounting standards while balancing political and practical concerns remains an ongoing challenge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 9
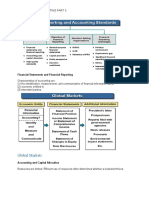
World markets are becoming increasingly
intertwined. With the integration of capital
markets, the automatic linkage between the
location of the company and the location of
the capital market is loosening. As a result,
companies have expanded choices of where
to raise capital, either equity or debt. The
move toward adoption of global accounting
standards has and will continue to facilitate
this trend.
Financial statements and other means of financial
reporting.
Companies most frequently provide;
(1) the statement of financial position
(2) the income statement or statement of comprehensive
income
(3) the statement of cash flows
(4) the statement of changes in equity. Financial reporting
other than financial statements may take various forms.
Examples include the president's letter and supplementary
schedules in the company annual report, prospectuses,
reports filed with government agencies, news releases,
management's forecasts, and descriptions of a company's
social or environmental impact.
Efficient use of scarce resources.
Accounting provides reliable, relevant,
and timely information to managers,
investors, and creditors to allow
resource allocation to the most efficient
enterprises. Accounting also provides
measurements of efficiency
(profitability) and financial soundness.
High-quality standards.
A single, widely accepted set of high-quality
accounting standards is a necessity to ensure
adequate comparability. Investors are increasingly
making investing decisions across international
jurisdictions. As a result, investors need financial
information that is comparable across national
boundaries. But what are high-quality accounting
standards, how should they be developed, and
how should they be enforced is still a much
debated issue.
The objective of general-purpose financial
reporting is to provide financial information about
the reporting entity that is useful to present and
potential equity investors, lenders, and other
creditors in making decisions about providing
resources to the entity. Information that is
decision-useful to investors may also be useful to
other users of financial reporting who are not
investors.
The International Organization of Securities Commissions
(IOSCO) does not set accounting standards but is dedicated to
ensuring that the global markets can operate in an efficient and
effective manner. The International Accounting Standards Board
(IASB) is the leading international accounting standard-setting
organization. Its mission is to develop, in the public interest, a
single set of highquality and understandable International
Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) for general-purpose financial
statements. Standards issued by the IASB have been adopted by
over 149 jurisdictions (similar to countries) worldwide, and all
publicly traded European companies must use IFRS.
IFRS is comprised of
(a) International Financial Reporting Standards
(b) International Accounting Standards
(c) interpretations issued by the IFRS
Interpretations Committee or the former
Standing Interpretations Committee (SIC). In
the absence of a standard or an interpretation,
other accounting literature, including that
contained in the Conceptual Framework for
Financial Reporting and recent pronouncements
of other standard-setting bodies that use a
similar conceptual framework, can be applied.
Challenges include
(1) IFRS in a political environment
(2) the expectations gap
(3) financial reporting issues related to key
performance measures widely used by management,
forward-looking information needed by investors and
creditors, sufficient information on a company's soft
assets (intangibles), and real-time financial
information, including fair values
(4) ethics in accounting
(5) international convergence
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- International Financial Statement Analysis WorkbookDa EverandInternational Financial Statement Analysis WorkbookNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Reporting and Accounting Standards: Learning ObjectivesDocumento13 pagineFinancial Reporting and Accounting Standards: Learning ObjectivesHanif MusyaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Secrets of Accounting and Financial ManagementDa EverandThe Secrets of Accounting and Financial ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- CFAS MODULE and AssDocumento87 pagineCFAS MODULE and AsshellokittysaranghaeNessuna valutazione finora
- International Financial Statement AnalysisDa EverandInternational Financial Statement AnalysisValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- CFAS MODULE and AssDocumento87 pagineCFAS MODULE and AsshellokittysaranghaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Reporting under IFRS: A Topic Based ApproachDa EverandFinancial Reporting under IFRS: A Topic Based ApproachNessuna valutazione finora
- Cfas Material 1Documento22 pagineCfas Material 1Maybeline BonifacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Acfm Ch-Two 2022Documento46 pagineAcfm Ch-Two 2022mihiretche0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - Development of Financial Reporting Framework and Standard Setting Body PDFDocumento6 pagineModule 1 - Development of Financial Reporting Framework and Standard Setting Body PDFAubrey CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cfas Module and AssDocumento86 pagineCfas Module and AsshellokittysaranghaeNessuna valutazione finora
- CFAS MODULE and Ass PDFDocumento86 pagineCFAS MODULE and Ass PDFhellokittysaranghaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cfas Material 1 PDFDocumento6 pagineCfas Material 1 PDFErmelyn GayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting QuizDocumento14 pagineAccounting QuizMarthen YoparyNessuna valutazione finora
- Compiled By: Anwar A. (MSC)Documento14 pagineCompiled By: Anwar A. (MSC)AN AdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL ACCOUNTINGDocumento15 pagineChapter-1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL ACCOUNTINGWoldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Accounting IFRS 3rd Edition-43-62Documento20 pagineIntermediate Accounting IFRS 3rd Edition-43-62dindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ias MergedDocumento157 pagineIas MergedAnalou LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Akuntansi KeuanganDocumento8 pagineTugas Akuntansi KeuanganꧾꧾNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Work PSA AssignmentDocumento17 pagineFinal Work PSA AssignmentEbenezer BentilNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Intermediate Accounting CH 123Documento5 pagineAssignment Intermediate Accounting CH 123NELVA QABLINANessuna valutazione finora
- F1 - Financial Reporting - M1 - Summary - NotesDocumento22 pagineF1 - Financial Reporting - M1 - Summary - NotesSyaznee IdrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - Development of Financial Reporting Framework and Standard-Setting BodiesDocumento8 pagineModule 1 - Development of Financial Reporting Framework and Standard-Setting BodiesAndrealyn DitanNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Reporting and Accounting Standards Power Point)Documento33 pagineFinancial Reporting and Accounting Standards Power Point)Astrid NainggolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ifrs & PFRSDocumento74 pagineIfrs & PFRSRey ArellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermidiate FA I ChapterDocumento12 pagineIntermidiate FA I Chapteryiberta69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Accounting Standards, Ind AS and IFRS - Taxguru - inDocumento13 pagineOverview of Accounting Standards, Ind AS and IFRS - Taxguru - inPurohit Raju1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amity Law School Analysis and Financial Reporting Analysis Reporting of Financial Statements (International)Documento11 pagineAmity Law School Analysis and Financial Reporting Analysis Reporting of Financial Statements (International)namrataNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - Ankit Singh BBA (P) 2Documento19 pagineAssignment - Ankit Singh BBA (P) 2Rahul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- IFRSDocumento14 pagineIFRSNishchay Dhingra100% (1)
- Financial Reporting Case 3Documento3 pagineFinancial Reporting Case 3HUPGUIDAN, GAUDENCIANessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of IFRS-Issues and ChallengesDocumento12 pagineIntroduction of IFRS-Issues and ChallengesAbhisshek GautamNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Seminar 4Documento20 pagineFinal Seminar 4Sumit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- AkDocumento7 pagineAkDavid BakcyumNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 1 FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDSsDocumento6 pagineMODULE 1 FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDSsVivo V27Nessuna valutazione finora
- W1 Module 2 The Environment For Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 2Documento5 pagineW1 Module 2 The Environment For Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 2leare ruazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Financial Reporting and Accounting Standards - Intermediate Accounting - IFRS Edition, 2nd EditionDocumento41 pagineChapter 1 - Financial Reporting and Accounting Standards - Intermediate Accounting - IFRS Edition, 2nd EditionWihl Mathew ZalatarNessuna valutazione finora
- Conceptual FrameworksDocumento169 pagineConceptual FrameworksAllana MierNessuna valutazione finora
- Diff Betn Us Gaap - IfrsDocumento9 pagineDiff Betn Us Gaap - IfrsVimal SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento79 pagineChapter 1alemu desta100% (1)
- CH 1Documento97 pagineCH 1Anteneh YitbarekNessuna valutazione finora
- E - Content On IFRSDocumento20 pagineE - Content On IFRSPranit Satyavan NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting For ManagersDocumento235 pagineAccounting For Managerssajaggrover100% (2)
- Fa I Chapter 1Documento10 pagineFa I Chapter 1Tewanay BesufikadNessuna valutazione finora
- IM - Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards 2Documento88 pagineIM - Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards 2Shekainah BNessuna valutazione finora
- IM - Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards PDFDocumento88 pagineIM - Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards PDFJocel VictoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Accounting IssuesDocumento29 pagineInternational Accounting IssuesHetal GadhviNessuna valutazione finora
- SEC Concept Release: International Accounting Standards: Securities and Exchange CommissionDocumento50 pagineSEC Concept Release: International Accounting Standards: Securities and Exchange CommissionSreeramulu Satish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial ReportingDocumento10 pagineFinancial Reportingrafiulbiz12Nessuna valutazione finora
- CFAS Assessment Activities 1Documento5 pagineCFAS Assessment Activities 1King SigueNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash Flow and Company Valuation Analysis: Practical Approach To Ina PLC, The Biggest Croatian Oil CompanyDocumento20 pagineCash Flow and Company Valuation Analysis: Practical Approach To Ina PLC, The Biggest Croatian Oil CompanyKaka AwaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Accounting and Reporting 02Documento6 pagineFinancial Accounting and Reporting 02Nuah SilvestreNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Accounting and Reporting 02Documento6 pagineFinancial Accounting and Reporting 02Nuah SilvestreNessuna valutazione finora
- Background of IfrsDocumento2 pagineBackground of IfrsShelze Consulting100% (1)
- Intermediat Accounting PPT FA IDocumento76 pagineIntermediat Accounting PPT FA ITarekegn DemiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Acctg 3 NotesDocumento6 pagineIntermediate Acctg 3 NotesCindy The GoddessNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Lecture - Ch. 1Documento15 pagine1st Lecture - Ch. 1otaku25488Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1Documento11 pagineLesson 1shadowlord468Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cfas 1Documento10 pagineCfas 1Bea charmillecapiliNessuna valutazione finora
- IFRS A Briefing For Boards of DirectorsDocumento60 pagineIFRS A Briefing For Boards of DirectorsJose Martin Castillo PatiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- FT Problem Set 01 DepreciationDocumento2 pagineFT Problem Set 01 DepreciationshaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Marathon Notes Session 1 Pranav PopatDocumento71 pagineCost Marathon Notes Session 1 Pranav PopatRohit bhulNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson .-Lesson 4: Supplier, Value, and Supply Chain-01Documento15 pagineLesson .-Lesson 4: Supplier, Value, and Supply Chain-016jbfth7k4nNessuna valutazione finora
- Greens2020TraderTaxGuide PDFDocumento132 pagineGreens2020TraderTaxGuide PDFvej100% (2)
- Intermediate Accouting Sample ProblemsDocumento24 pagineIntermediate Accouting Sample ProblemstrishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study DK Goel Accountancy Class 12 - Volume 1 Chapter 3Documento6 pagineStudy DK Goel Accountancy Class 12 - Volume 1 Chapter 3kamalpanjwani07Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.certificate, AcknowledgementDocumento5 pagine2.certificate, AcknowledgementTarun BamolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pas 23-Borrowing CostsDocumento10 paginePas 23-Borrowing CostsRey Jr Alipis0% (1)
- Merchant BankingDocumento93 pagineMerchant BankingSaadhana MuthuNessuna valutazione finora
- BDO Easy Investment PlanDocumento12 pagineBDO Easy Investment Planannair_redNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi Basic GKInvestDocumento85 pagineMateri Basic GKInvestEdy NuryantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Panera Bread Report 2010Documento7 paginePanera Bread Report 2010Akshita ShrivastavNessuna valutazione finora
- Stock Screener PDFDocumento4 pagineStock Screener PDFchintanghadiyaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Arens Aas17 PPT 21Documento38 pagineArens Aas17 PPT 21Huong LienNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost of CapitalDocumento16 pagineCost of Capitalsarvan kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Member-Managed LLC Operating Agreement Template TemplateDocumento5 pagineMember-Managed LLC Operating Agreement Template TemplateNicolas RotundoNessuna valutazione finora
- Perusahaan ManufakturDocumento26 paginePerusahaan ManufakturMuhammad Mahesa PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- uNIT V-IFMDocumento28 pagineuNIT V-IFMgangaananthNessuna valutazione finora
- Afar Hedging Ja With AnswersDocumento3 pagineAfar Hedging Ja With AnswersShigure KousakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spotify Technology S.A.: United States Securities and Exchange CommissionDocumento48 pagineSpotify Technology S.A.: United States Securities and Exchange CommissionSunday AyomideNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Management BookDocumento21 pagineFinancial Management BookiqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Techinical AnalysisDocumento14 pagineTechinical AnalysisCamille BagadiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus 7 Weeks ABMF2013 Fundamental of FinanceDocumento6 pagineSyllabus 7 Weeks ABMF2013 Fundamental of FinanceKanchelskiTehNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabozzi Bmas8 PPT Ch01Documento22 pagineFabozzi Bmas8 PPT Ch01Leslie RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Vice President Security Lending in NYC NY NJ Resume Fernando RiveraDocumento3 pagineVice President Security Lending in NYC NY NJ Resume Fernando Riverafernandorivera1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Company Analysis and Stock ValuationDocumento57 pagineFinal - Company Analysis and Stock ValuationSaad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CMSA Approval of Swala Oil and Gas (Tanzania) Plc's ProspectusDocumento1 paginaCMSA Approval of Swala Oil and Gas (Tanzania) Plc's ProspectusMuhidin Issa MichuziNessuna valutazione finora
- (Cfas) M1&2 Final NotesDocumento5 pagine(Cfas) M1&2 Final NotesMa. Alessandra BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Question FMDocumento4 pagineImportant Question FMHardeep KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital MGTDocumento26 pagineWorking Capital MGTIrum KhanNessuna valutazione finora