Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
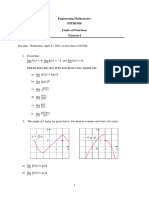
Differentiation
Caricato da
Jibõ Emmä0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
18 visualizzazioni10 pagineMathematics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoMathematics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
18 visualizzazioni10 pagineDifferentiation
Caricato da
Jibõ EmmäMathematics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 10
DIFFERENTIATION
Differentiation is used in business mathematics:
-Determine the maximum and minimum values of particular
functions Eg: Costs, strength, amount of material used in
building, profit and loss.
-When we consider the quantity and supply:
Quantity demanded can be a function of price.
Supply and price or cost and quantity demanded are
some other variables.
- Calculus helps us in finding the arte at which one quantity
changes with respect to the other.
- Product differentiation is economically advantageous to
companies.
Differentiation continues….
1. It provides a reason for consumers as to why
their product is worth investing in as opposed to
all other substitute products.
2. In economics and marketing, product
differentiation is the process of distinguishing a
product or service from others, to make it more
attractive to a particular target market. This
involves differentiating it from competitors’
products as well as firm’s products.
Rules of Differentiation
𝑛 𝑑𝑦
Rule 1: 𝑦 = 𝑥 , 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 = 𝑛𝑥 𝑛−1
𝑑𝑥
Examples
1. Differentiate the following with respect to 𝑥:
(a) 𝑥 𝑛 + 𝑐
(b) 𝑥 𝑛 + 𝑥 𝑚
(c) 𝑥 3
(d) 𝑥 8
1
(e) 𝑥 2
Rule 1 continues….
2. Differentiate the following with respect to 𝑥
(a) 𝑥 −4
(b) 𝑥 3 + 5𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 10
(c) 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐
Rule 2: The Chain / Compound rule
𝑛
𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑢
𝐼𝑓 𝑦 = 𝑢 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 = 𝑥
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑥
Examples
Differentiate the following with respect to 𝑥.
(a) (𝑥 + 3)2
(b) (3𝑥 + 2)4
(c) (𝑥 2 + 3𝑥)2
(d) (1 + 𝑥 2 )
(e) (2𝑥 + 5)−1
1
(f) (3𝑥 − 1) 2
Rule 3: The Product rule
𝐼𝑓 𝑦 = 𝑢𝑣, 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑢 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑣 𝑎𝑟𝑒
𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑢
𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑥 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 =𝑢 +𝑣
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
Examples
Differentiate the following with respect to 𝑥
(a)(5𝑥 + 7)(3𝑥 2 + 5)
(b) 𝑥 2 − 3 𝑥 + 1 2
(c) 𝑥 2 + 1 3 (𝑥 3 + 1)
Rule 3: The Quotient Rule
𝑢
𝐼𝑓 𝑦 = , 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑢 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑣 𝑎𝑟𝑒
𝑣
𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑣
𝑑𝑦 𝑣 𝑑𝑥 − 𝑢 𝑑𝑥
𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑥 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 =
𝑑𝑥 𝑣2
Examples:
Differentiate the following with respect 𝑥:
4𝑥 3 +2
(a) 6
𝑥
(𝑥−3)2
(b)
(𝑥+2)2
𝑥
(c)
(1+𝑥 2 )
INTEGRATION
Integration is defined as the mixing or people
together that were formerly separated.
Differentiation calculates the slope the curve.
Integration calculates the area under the curve.
It is the reverse of differentiation. Integration means
summation(s) and it represented by the symbol: ∫
Integration formula:
𝑛 𝑥 𝑛+1
න 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑛+1
+𝑐
𝑐 is the constant of integration.
Examples
1. Integrate the following with respect to 𝑥:
(a) 𝑥 5 𝑑𝑥
(b) (2𝑥 + 3) 𝑑𝑥
(c) 𝑥𝑎(+ 𝑏) 𝑑𝑥
1
(d) 𝑥𝑑 𝑥
3
2. Integrate the following with respect to 𝑥:
(a) (3𝑥 + 2)3 𝑑𝑥
(b) (2𝑥 + 3)5 𝑑𝑥
(c) 3𝑥 − 4 −2 𝑑𝑥
1
(d) 2𝑥 + 3 𝑑𝑥2
(e) (𝑥 3𝑥 2 + 2)4 𝑑𝑥
Examples continue…….
3. Integrate the following with respect to 𝑥:
3 3
(a) 1 𝑥 𝑑𝑥
5
(b) 3 (3𝑥 3 +2)𝑑𝑥
4
(c) 0 (2𝑥 3 +2)𝑑𝑥
3 2
(d) 1 (𝑥 +3)𝑑𝑥
4. Find the area enclosed by the curve
𝑦 = 𝑥 2 𝑥 − 2 , the 𝑥-axis and the lines
𝑥 = 0 and 𝑥 = 2.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Designing The Franchise SystemDocumento11 pagineDesigning The Franchise SystemAi Lyn100% (2)
- Mang InasalDocumento74 pagineMang InasalAnne Flores86% (7)
- Pepsi AssignmentDocumento14 paginePepsi AssignmentMuhammad Osama AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Transportation Research Part A: Megersa AbateDocumento12 pagineTransportation Research Part A: Megersa AbateZen ZeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Calculus: Quarter 4 - Module 5Documento12 pagineBasic Calculus: Quarter 4 - Module 5John Carlo RafaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Director Manager Enterprise Sales in Houston TX Resume Steven HartleyDocumento4 pagineDirector Manager Enterprise Sales in Houston TX Resume Steven HartleyStevenHartleyNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM DellDocumento10 pagineCRM DellSaurabh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Livable Streets Downtown PlanDocumento44 pagineLivable Streets Downtown PlanwakeactiveNessuna valutazione finora
- PLASTIC Material DervitiveDocumento7 paginePLASTIC Material DervitiveAshraf AlsalmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 5 Add Math - Chapter 3Documento27 pagineForm 5 Add Math - Chapter 3surya vishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- 02rules of DifferentiationDocumento16 pagine02rules of DifferentiationAtta SoomroNessuna valutazione finora
- ChristianDocumento7 pagineChristianJohnny JanulgueNessuna valutazione finora
- Relations and Functions Power Point-1Documento102 pagineRelations and Functions Power Point-1fmukuka12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ceit DEDocumento69 pagineCeit DEClint MosenabreNessuna valutazione finora
- Ste Calculus 10 q2 w1Documento4 pagineSte Calculus 10 q2 w1Payn RocasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Derivative of A FunctionDocumento3 pagineLesson 3 Derivative of A FunctionJunior LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Senior High School Grade Basic CalculusDocumento32 pagineWhole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Senior High School Grade Basic CalculusKayrell AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- SLG 2.1.2 Definition of Functions and Operations On Functions (Session 2 of 3)Documento6 pagineSLG 2.1.2 Definition of Functions and Operations On Functions (Session 2 of 3)jvvuvuuv lopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Differentiation: 1. Constant Function RuleDocumento18 pagineRules of Differentiation: 1. Constant Function RuleZhiYar NamiqNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK6Documento11 pagineWEEK6Crius DiomedesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 10. Hhigher Order Derivatives and Chain RuleDocumento9 pagineLecture 10. Hhigher Order Derivatives and Chain RuleLuisa Jane De LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- M2-Exam 3Documento16 pagineM2-Exam 3youngturtlevibesNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3-DCM202113 - Functions (Part 3)Documento12 pagineWeek 3-DCM202113 - Functions (Part 3)Daniela Malapascua DayaganonNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiderivatives of Algebraic Functions: Basic Calculus Grade 12 Quarter 4 May, 2021Documento3 pagineAntiderivatives of Algebraic Functions: Basic Calculus Grade 12 Quarter 4 May, 2021Kazandra Cassidy GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chain RuleDocumento11 pagineChain RuleJhiela Mae MacaraigNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.0 Introduction of Derivative: DX Dy DX DFDocumento40 pagine3.0 Introduction of Derivative: DX Dy DX DFGoh Siak PengNessuna valutazione finora
- ENMATH11E - LECTURE 4 - FactoringDocumento10 pagineENMATH11E - LECTURE 4 - FactoringG7 SJ-01 Cabataña, MichailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied1 Unit5 2011ECDocumento44 pagineApplied1 Unit5 2011ECTadesse100% (1)
- 2 3ProductandQuotientRulesDocumento3 pagine2 3ProductandQuotientRulesJudielyn SamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions Bank - Integration Using SubstitutionDocumento9 pagineQuestions Bank - Integration Using SubstitutionwafaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Mary Grace E. Butac: Lesson PlanDocumento5 paginePrepared By: Mary Grace E. Butac: Lesson PlanNornie MicsNessuna valutazione finora
- GM1. Intro To FunctionsDocumento5 pagineGM1. Intro To FunctionsGabriel Benedict DacanayNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Arithmetic and FunctionsDocumento5 pagineReview Arithmetic and FunctionsAdrianus RioNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Calculus & Techniques of Differentiation: DerivativesDocumento12 pagineDifferential Calculus & Techniques of Differentiation: Derivativeslaila qistinaNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH161 Exam 2-V1Documento4 pagineMATH161 Exam 2-V1Roba El GhorNessuna valutazione finora
- MP01 Genmath Week01 Functions GreenDocumento53 pagineMP01 Genmath Week01 Functions Greenfelix florentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- GM M11GM-Ia-3 Q1Documento6 pagineGM M11GM-Ia-3 Q1Ernesto Cabuyadao100% (1)
- Handout 1 Gen MathDocumento3 pagineHandout 1 Gen MathOliric NabcihNessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP TASK Chapter 1 & 2 - XXX VersionDocumento2 pagineGROUP TASK Chapter 1 & 2 - XXX Versionsilent spritsNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial4 - Limits of FunctionsDocumento2 pagineTutorial4 - Limits of Functionscameroncrow30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Relations and Functions Q-1Documento27 pagineRelations and Functions Q-1Alex HalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential CalculusDocumento51 pagineDifferential CalculusCheenee RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacal 8Documento16 pagineBacal 8MAEZEL ASHLEY FREDELUCESNessuna valutazione finora
- GenMath Module 3 Week 3Documento16 pagineGenMath Module 3 Week 3Immanuel CañecaNessuna valutazione finora
- MTH123, Practice Questions FUPREDocumento4 pagineMTH123, Practice Questions FUPRETina OsimenNessuna valutazione finora
- Susie CoursepackDocumento404 pagineSusie CoursepackChiOfGreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocumento8 pagineAlgebraic ExpressionssethNessuna valutazione finora
- General: Quarter 1 - Week 1Documento19 pagineGeneral: Quarter 1 - Week 1Jakim LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With SolutionDocumento128 pagineClass XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With Solutionanushkabisht2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- General: Quarter 1 - Week 1Documento18 pagineGeneral: Quarter 1 - Week 1ARNEL GONZALESNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 TEST 2 SOLUTION INTEGRATION (PURE MATHEMATICS) ShareDocumento7 pagine2022 TEST 2 SOLUTION INTEGRATION (PURE MATHEMATICS) SharenomoszengNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions 1.1 Functions As Mathematical ModelsDocumento13 pagineFunctions 1.1 Functions As Mathematical Modelsarajara16Nessuna valutazione finora
- QUPM Sample Test 2Documento14 pagineQUPM Sample Test 2reemkhaled1103Nessuna valutazione finora
- Part II: Contains Short Answer Problems. Write The Most Simplified Answer On The Space Provided. (2 PT Each)Documento2 paginePart II: Contains Short Answer Problems. Write The Most Simplified Answer On The Space Provided. (2 PT Each)Zerihun IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Concepts and Activities: Page - 1Documento5 pagineLearning Concepts and Activities: Page - 1RexTheKingNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Calculus: Quarter 3 - Module 5 Rules of DifferentiationDocumento28 pagineBasic Calculus: Quarter 3 - Module 5 Rules of DifferentiationHarold BunaosNessuna valutazione finora
- Factoring WorkbookDocumento11 pagineFactoring WorkbookElaine zhuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 FT Math 02 Calculus 2Documento3 pagine1 FT Math 02 Calculus 2John Mark FilosofoNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied I Work SheetDocumento3 pagineApplied I Work SheetwabdushukurNessuna valutazione finora
- Module1.1 - AntiDifferentiation Concepts - FormulasDocumento3 pagineModule1.1 - AntiDifferentiation Concepts - FormulasJ KimNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4 Inverse of A FunctionDocumento19 pagine2.4 Inverse of A FunctionNot.DXcr GaMeRNessuna valutazione finora
- Em 1202 Midterm Exam March 18 2023 Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineEm 1202 Midterm Exam March 18 2023 Answer KeyDela Cruz MelvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Ques Bank 11th CommerceDocumento2 pagineAnnual Ques Bank 11th Commercealokkulkarni14Nessuna valutazione finora
- D. Factorising Linear and Quadratic ExpressionsDocumento13 pagineD. Factorising Linear and Quadratic ExpressionsRaihan RafaNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High SchoolDocumento18 pagineLESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High Schooltrisha paclebNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-3 NyproDocumento14 pagine4-3 NyproFitria Nur RamadhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales & Distribution Management: Assignment OnDocumento9 pagineSales & Distribution Management: Assignment OnSOMYA RANJAN NANDANessuna valutazione finora
- Bus115 Tma Summer 2019Documento4 pagineBus115 Tma Summer 2019Amethyst OnlineNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-How To Convert A Commodity Into BrandDocumento17 pagine01-How To Convert A Commodity Into BrandNavanidhi KishoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Client and Assignment InformationDocumento2 pagineModule 4 Client and Assignment Informationapi-317274650Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Beer Cafe FOFO - Business Model - JodhpurDocumento1 paginaThe Beer Cafe FOFO - Business Model - JodhpurTarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On QUBEEDocumento22 paginePresentation On QUBEEinvissiblesoulNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion Ch01Documento16 pagineDiscussion Ch01An A Meisly80% (5)
- Brekka: Extending The Mode-of-Operation Approach Beyond The Self-Service Supermarket ContextDocumento29 pagineBrekka: Extending The Mode-of-Operation Approach Beyond The Self-Service Supermarket ContextNew England Law ReviewNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Planning and DevelopmentDocumento48 pagineProduct Planning and Developmenthari kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ABM AssignmentDocumento7 pagineABM AssignmentSoma BanikNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocumento1 paginaBlue Ocean StrategyMireille KirstenNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumption, Savings and InvestmentDocumento26 pagineConsumption, Savings and InvestmentProfessor Tarun DasNessuna valutazione finora
- KisikisiDocumento7 pagineKisikisijalunasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Business ResearchDocumento39 pagineIntroduction To Business Researchpopat vishalNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento5 pagineDocumentAshwin JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyundai SantroDocumento20 pagineHyundai SantroKamlesh Kumar KhiyataniNessuna valutazione finora
- Resto TeracafeDocumento10 pagineResto Teracafeeko purwantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Agritourism Workbook FINAL PDFDocumento41 pagineAgritourism Workbook FINAL PDFntv2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- ColgateDocumento17 pagineColgateSyed QaiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Imc Tools SurfDocumento6 pagineImc Tools SurfSyed Azfar HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bose Marketing Project PDFDocumento28 pagineBose Marketing Project PDFhi2joeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Service DistributionDocumento36 pagineService Distributionumesh kumar sahuNessuna valutazione finora