Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture 22 - Thermo-II OCT 14
Caricato da
zabidullah0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
26 visualizzazioni12 pagineTitolo originale
Lecture 22_Thermo-II OCT 14.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
26 visualizzazioni12 pagineLecture 22 - Thermo-II OCT 14
Caricato da
zabidullahCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 12
CHAPTER 10
VAPOR AND COMBINED
POWER CYCLES
LECTURE # 22
Energy and Exergy Analyses of a Combined
Gas Turbine-Vapor Power Plant
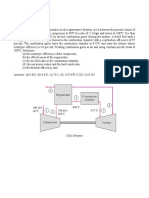
A combined gas turbine–vapor power plant has a net power output of 45 MW.
Air enters the compressor of the gas turbine at 100 kPa, 300 K, and is
compressed to 1200 kPa. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 84%.
The condition at the inlet to the turbine is 1200 kPa, 1400 K. Air expands
through the turbine, which has an isentropic efficiency of 88%, to a pressure of
100 kPa. The air then passes through the interconnecting heat recovery steam
generator and is finally discharged at 400 K. Steam enters the turbine of the
vapor power cycle at 8 MPa, 400 ℃, and expands to the condenser pressure of
8 kPa. Water enters the pump as saturated liquid at 8 kPa. The turbine and
pump of the vapor cycle have isentropic efficiencies of 90 and 80%,
respectively.
(a) Determine the mass flow rates of the air and the steam, each in kg/s; the
net power developed by the gas turbine and vapor power cycle, each in MW;
and the thermal efficiency.
(b) Develop a full accounting of the net rate of exergy increase as the air
passes through the gas turbine combustor.
Discuss.
Let T0 = 300 K, p0 = 100 kPa.
For Mid-term Exam
• Short conceptual questions
• Learn / Memorize the commonly used formulae
• Detailed Numerical Problems (properties tables will be
provided)
• Approach to numerical problems
• Assumptions
• Schematic
• T-s / P-v etc diagrams
• Data
• To find
• Formulae / relations
Exams Preparation Tips
• Study the lectures slides
• Read the relevant sections of textbook (for further
clarification)
• Answer conceptual questions (end of chapter exercises)
• Be prepared to solve unseen questions (focus on
concepts)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFDocumento1 pagina1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFsuby100% (1)
- MPD 2012 - Sheet 3 - Binary and Combined CyclesDocumento3 pagineMPD 2012 - Sheet 3 - Binary and Combined CyclesPeter Raouf100% (1)
- Final Exam ENGI 2800 - Engineering Thermodynamics IDocumento2 pagineFinal Exam ENGI 2800 - Engineering Thermodynamics Iياسر سعيد عبادي البحريNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign - Engg. ThermodynamicsDocumento8 pagineAssign - Engg. ThermodynamicsSagarZopeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Application of Thermodynamics To Flow ProcessesDocumento27 pagine1 - Application of Thermodynamics To Flow ProcessesEllen Jane Ramos100% (1)
- Power Plant Engg Assignment-1Documento2 paginePower Plant Engg Assignment-1keyredin selmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermo of MechDocumento2 pagineThermo of MecheyobNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleDocumento24 pagineAssignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleMatthias100% (1)
- Gas Turbines Tutorial Part 1 of 2Documento4 pagineGas Turbines Tutorial Part 1 of 2Gulain MayomboNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Gas Power CyclesDocumento26 pagineModule 5 Gas Power CyclesJatskinesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Thermal Engineering UPDATEDDocumento6 pagineQuestion Bank Thermal Engineering UPDATEDIrfan ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFDocumento5 pagineME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFVikasKumarSharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grado en F Isica. Curso 2013-14Documento1 paginaGrado en F Isica. Curso 2013-14Juanmi AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocumento3 pagineTutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesShariff Mohamad Fairuz0% (1)
- Assignment 1Documento1 paginaAssignment 1Billy LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Test #2Documento3 pagineTest #2Dar QuetzalNessuna valutazione finora
- QUESTION BANK ThermodynamicsDocumento6 pagineQUESTION BANK Thermodynamicsvikas_1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan Soal-Soal Sistem Tenaga GasDocumento6 pagineLatihan Soal-Soal Sistem Tenaga GasDhira GunawanNessuna valutazione finora
- 062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankDocumento12 pagine062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankAjay KaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 Gas Power CycleDocumento16 pagineTutorial 1 Gas Power CycleshaunyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringDocumento5 pagineDepartment of Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringDawood AljumayahNessuna valutazione finora
- Rankine Cycle ProblemDocumento2 pagineRankine Cycle ProblemJohn Paul RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- (2018) Final Exam +solutions PDFDocumento23 pagine(2018) Final Exam +solutions PDFTman LetswaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 10 ProblemsDocumento2 pagineTutorial 10 ProblemsRudhraa.RNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Experiment ReportDocumento11 pagineBoiler Experiment ReportMuhammad Khuzairi33% (3)
- Exercise PyeqDocumento2 pagineExercise PyeqNaufal SyafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Exam Me 322aDocumento1 paginaMidterm Exam Me 322aStephanie ParkNessuna valutazione finora
- ME267 Assignment01Documento1 paginaME267 Assignment01InsaneNessuna valutazione finora
- ME6301-Engineering Thermodynamics 2013 RegulationDocumento12 pagineME6301-Engineering Thermodynamics 2013 RegulationLogesh LoganNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - 7 (IC Engine)Documento6 pagineTutorial - 7 (IC Engine)Vaikunth PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 1 STEAM GENERATION (Complete Slide)Documento25 pagineCHAPTER 1 STEAM GENERATION (Complete Slide)nisasoberiNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Task 2Documento1 paginaLearning Task 2zyx xyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 6 - ME 211TDocumento2 pagineSheet 6 - ME 211TOmar AlkadyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Topic 5Documento2 pagineTutorial Topic 5李世聪Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problemario MFCDocumento31 pagineProblemario MFCPonce MrlnNessuna valutazione finora
- YgDocumento2 pagineYgVincent Martinez0% (1)
- Question Bank MechDocumento102 pagineQuestion Bank MechKaradam PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Adv Therm Week 10Documento16 pagineAdv Therm Week 10Tegin Berkay BudakNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocumento3 pagineThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Sheet 02 2014Documento11 pagineTutorial Sheet 02 2014checkmeout803Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea de CiclosDocumento6 pagineTarea de CiclosSebastiánGarcía100% (1)
- Assign#4 Vapor CycleDocumento3 pagineAssign#4 Vapor Cyclemihreteab ghebregzabherNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Tut. 3 Rankine Part 1Documento12 pagineThermodynamics Tut. 3 Rankine Part 1Atif MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet (2) Reheat Rankine CycleDocumento4 pagineSheet (2) Reheat Rankine CycleHamadaMohassabNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 - Vapor Power CyclesDocumento64 pagineTopic 2 - Vapor Power CyclesMang TomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemario MFCDocumento80 pagineProblemario MFCBassaldua AlfreedNessuna valutazione finora
- ET II Assignment 2 - ModifiedDocumento3 pagineET II Assignment 2 - ModifiedbaliamajhiNessuna valutazione finora
- SHEET (6) Simple Rankine CycleDocumento1 paginaSHEET (6) Simple Rankine CycleAhmedTahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدDocumento16 pagineThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 CalculationsDocumento11 pagine2 CalculationsThiện KhiêmNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 331 Thermo II Steam Cycle 2Documento81 pagineME 331 Thermo II Steam Cycle 2Mimo Ammar90% (10)
- (TKK61016) 8. Production of Power From HeatDocumento28 pagine(TKK61016) 8. Production of Power From HeatNaufal FawwazNessuna valutazione finora
- AMME2200 RevisionQuestions ThermodynamicsDocumento2 pagineAMME2200 RevisionQuestions ThermodynamicsMatthew LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PDocumento2 pagineLectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PPritam PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid SemDocumento2 pagineMid SemVivekananda NandamNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-Sheet 01Documento9 pagine01-Sheet 01samir mohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Vapour Power CycleDocumento65 pagineVapour Power CycleRajan GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 2-5 GasturbineDocumento2 pagineSheet 2-5 Gasturbinedaanish petkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Assingment 2Documento2 pagineAssingment 2habtish100% (1)
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Lecture # 18Documento9 pagineVapor and Combined Power Cycles: Lecture # 18zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER # 4 Fluid KinematicsDocumento53 pagineCHAPTER # 4 Fluid KinematicszabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Lecture # 20Documento12 pagineVapor and Combined Power Cycles: Lecture # 20zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 13 - Thermo II SEPT 23-bDocumento9 pagineLecture 13 - Thermo II SEPT 23-bzabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 17 - Thermo II OCT 1Documento11 pagineLecture 17 - Thermo II OCT 1zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 19 - Thermo-II OCT 7Documento16 pagineLecture 19 - Thermo-II OCT 7zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Power Cycles: Lecture # 10Documento9 pagineGas Power Cycles: Lecture # 10zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics-Ii ME 332: Complex Engineering ProblemDocumento5 pagineThermodynamics-Ii ME 332: Complex Engineering ProblemzabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Power Cycles: Lecture # 9Documento10 pagineGas Power Cycles: Lecture # 9zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- CH # 6: The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Lecture # 3Documento34 pagineCH # 6: The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Lecture # 3zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Thermo-II 27 AugustDocumento30 pagineLecture 2 - Thermo-II 27 AugustzabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 11 Thermo-II Sept 19Documento8 pagineLecture 11 Thermo-II Sept 19zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 EXERGYDocumento37 pagineChapter 8 EXERGYzabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Title:: Group Name/s (Author)Documento3 pagineTitle:: Group Name/s (Author)zabidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 GAS Power CycleDocumento87 pagineChapter 9 GAS Power CyclezabidullahNessuna valutazione finora