Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Demand
Caricato da
Shayesta Begum0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
7 visualizzazioni14 pagineWhat is demand
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoWhat is demand
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
7 visualizzazioni14 pagineDemand
Caricato da
Shayesta BegumWhat is demand
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 14
DEMAND
WHAT IS DEMAND?
• Demand refers to the quantity of
a commodity or a service that
people are willing to buy at a
certain price during a particular
time.
DEMAND FUNCTION
• It is an algebraic expression which
shows the functional relationship
between demand for a commodity
and its various determinants
affecting it.
• DX=F(PX,PR,Y,T,F,PO,S,D)
DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND
• PX(Price of given good):if the price of the
commodity decreases its demand will increase
and vise-versa.the demand for a commodity is
inversely related to its price
• PR(Price of Related goods):Demand also
changes due to change in price of the related
goods i.e. substitute or complementary.
• Y(Income of a consumer): Increase in
income of a consumer leads to an increase
in purchasing power of quantity demanded.
• T(Taste And Preferences): Demand for a
commodity can also change due to change
in taste, preference and fashion.
EX: Trousers and dhotis
• P(Population):A change in size of the
population will affect the demand for
certain goods.
• Technological change: As new discoveries
enter into the market the old goods are
substituted by the new goods.EX: mobile
and landline.
LAW OF DEMAND
• According to MARSHALL “the amount
demanded increases with the fall in price and
diminishes with the rise in price ,being other
things remaining constant”
• Law of demand explains the relationship
between the price and quantity demanded.
DEMAND SCHEDULE AND GRAPH
ASSUMPTIONS
• No change in income of a consumer
• No change in taste and preference of a
consumer.
• No change in price of the related goods.
• No new substitute are discovered.
• No expectation of future price change.
EXCEPTIONS
• Giffen’s Paradox
• Veblen Effect(prestigious goods)
• Speculation effect
• Illusion
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
• Elasticity of demand means percentage
change in quantity demand in response
percentage change in one variable on which
the demand depends.
• Ed=%change in quantity demanded/% change
in price.
TYPES OF ELASTICITY
• Perfectly elastic demand:
small change in price causes
infinite change in quantity
demand. It is also called as
horizontal curve and Ed=∞
• Perfectly Inelastic Demand:
change in price does not have
any influence or change in
demand curve. It is also called
as vertical curve and Ed=0
• Relatively Elastic Demand(Ed>1):
Small percentage change in
the price of the commodity
leads to greater percentage
change in quantity demanded.
The demand curve is flatter
• Relatively Inelastic Demand(Ed<1):
percentage change in price
of commodity leads to
smaller percentage
change in quantity demanded.
The demand curve is steeper.
• Unitary Elastic Demand(Ed=1):
percentage change in the price of the
commodity leads to equal percentage change
in quantity demanded.
THANK YOU
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Cambridge IGCSE and O Level Business Studies Workbook Sample PDFDocumento55 pagineCambridge IGCSE and O Level Business Studies Workbook Sample PDFPablo Paris78% (9)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Symphony Orchestra Case StudyDocumento3 pagineSymphony Orchestra Case StudyBrandon ElkinsNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBMGT605Documento32 pagineBSBMGT605snehal_patel_467% (6)
- Project Charter TDocumento2 pagineProject Charter TAnonymous Kg2Ji34100% (3)
- Gruen 2010Documento15 pagineGruen 2010Jean KarmelNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Test - Ii STD - Xii (Economics) : Seventh Day Adventist Higher Secondary SchoolDocumento7 pagineRevision Test - Ii STD - Xii (Economics) : Seventh Day Adventist Higher Secondary SchoolbhavyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Brand ElementsDocumento4 pagineThe Brand ElementsMaisha MunawaraNessuna valutazione finora
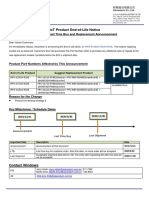
- Product Phase Out Notice IPPC 6152 6172 6192 R2AEDocumento1 paginaProduct Phase Out Notice IPPC 6152 6172 6192 R2AEguruh anindraNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study of Consumer Buying Behavior Towards Branded Casual Shoes in Ludhiana CityDocumento8 pagineA Study of Consumer Buying Behavior Towards Branded Casual Shoes in Ludhiana CityGaurang VelaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand Audit NestleDocumento10 pagineBrand Audit NestleAqib tanoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Success Factors of Nbfcs NBFCS: 1. Technology UtilizationDocumento3 pagineKey Success Factors of Nbfcs NBFCS: 1. Technology UtilizationdevrajkinjalNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Place Price Promotion People Packaging and PositioningDocumento4 pagineProduct Place Price Promotion People Packaging and PositioningDimple MontemayorNessuna valutazione finora
- Perodua CompanyDocumento5 paginePerodua CompanyIka Din100% (7)
- Chapter 4 Value ChainDocumento24 pagineChapter 4 Value ChainashlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Product MixDocumento16 pagineProduct Mixvinod_auraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kamal AhujaDocumento3 pagineKamal Ahujaapi-21345158Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ppt-Materi Kuliah: LITERATUR: Kotler - KellerDocumento30 paginePpt-Materi Kuliah: LITERATUR: Kotler - KellerAaron LiemantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Article: Progress and Performance of Oyo Rooms-A Research Based Case StudyDocumento6 pagineResearch Article: Progress and Performance of Oyo Rooms-A Research Based Case StudyRuchika JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmetics and Toiletries To Hong KongDocumento5 pagineCosmetics and Toiletries To Hong KongTzinNui ChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Break-Even Occurs Between The Production Volume Interval of 20,000 To 30,000Documento6 pagineBreak-Even Occurs Between The Production Volume Interval of 20,000 To 30,000kripsNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 (19PMHS010)Documento4 pagineAssignment 2 (19PMHS010)GOURAB ROYNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary Activity-E-Commerce and Startups-20202-10Documento3 pagineVocabulary Activity-E-Commerce and Startups-20202-10Sergio ArroyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Istituto Marangoni Miami Catalog 2019 PDFDocumento75 pagineIstituto Marangoni Miami Catalog 2019 PDFAndres GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10 E-Commerce Digital Markets, Digital Goods CH 10 E-Commerce Digital Markets, Digital GoodsDocumento7 pagineCH 10 E-Commerce Digital Markets, Digital Goods CH 10 E-Commerce Digital Markets, Digital GoodsRidhi BNessuna valutazione finora
- Article Critique OmDocumento4 pagineArticle Critique OmFatin Syafira ZakariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Booth Casebook 2004 PDFDocumento168 pagineBooth Casebook 2004 PDFAnqi ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical DilemmaDocumento3 pagineEthical DilemmaJose Antonio VillarbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Assortment Strategies: Written ReportDocumento10 pagineProduct Assortment Strategies: Written ReportMiguel FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Internship Report 2020: Biju Patnaik Institute of It & Management StudiesDocumento33 pagineSummer Internship Report 2020: Biju Patnaik Institute of It & Management StudiesArpita MohapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand Architecture Strategies: Domino's Pizza HutDocumento24 pagineBrand Architecture Strategies: Domino's Pizza HutVibhor SethiNessuna valutazione finora