Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Environmental Pollution: Air - Water. Soil. Light. Noise (Part 2)
Caricato da
Ahmad Sharief Bin Jaylani0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
5 visualizzazioni24 pagineTitolo originale
Lesson-3b-Soil-and-Land-Pollution.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
5 visualizzazioni24 pagineEnvironmental Pollution: Air - Water. Soil. Light. Noise (Part 2)
Caricato da
Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 24
Environmental pollution
AIR.WATER. SOIL. LIGHT. NOISE (Part 2)
Soil Properties
Definition
• soil pollution is defined as the change in
physical, chemical and biological conditions of
the soil through man’s intervention resulting
in degradation in quality
• 2 components: solid waste and soil pollution
• 2 types: natural causes and manmade causes
• natural: landslides, flooding, hurricanes etc.
• man-made= wastes: urbanisation, industrial
wastes, mining, agricultural, domestic,
garbage and radioactive
Definition
2 components:
solid waste and soil pollution
2 types: natural causes and manmade causes
natural: landslides, flooding, hurricanes etc.
man-made= wastes: industrial wastes, mining, agricultural,
domestic, garbage etc.
contaminants in soils depends on several physical and
chemical processes:
reduction/oxidation (redox), absorption,
precipitation and desorption
Whether a soil absorbs or releases a pollutant depends on:
types of mineral present, amount of organic material
present
soil ph level (acidity), redox potential and moisture
Land: Solid Waste Issues
landfill and municipal waste
contamination of soil due to landfills and municipal waste water
industrial and hazardous waste
discharge of toxic, flammable, non- biodegradable substances
erosion, mining and quarrying waste
non-renewable substances and valuable minerals are extracted from
earth that change the composition of soil
pesticides and agricultural waste
chemical fertilizers like pesticides
domestic or household solid waste
food wastes, paper, glass, plastic materials, cans and metal cylinders
chemical, nuclear and radioactive waste
nuclear power plants, nuclear testing, and explosion results to
variable amount of radioactive materials to soil
Land: Soil Pollution Issues
Chemical Contamination
Plastics, toxins in wastes and other chemicals seep into the ground
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) Contaminate the Ground
POPs in pesticides, insecticides etc., takes a long time
POPs by-products are also produced by burning coal, peat, wood, hospital waste,
hazardous waste, municipal waste and from car emissions
Impact on Biodiversity
adverse effect on the food-chain, that affect the fora, fauna and human life
adverse effect and threat to marine life due to bioaccumulation
damage soil fertility affect plant growth and the food source of the ecosystem
Spread of Invasive Species
soil pollution will affect native plants while invasive weeds can propagate
Loss of Soil Fertility
excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides kills beneficial soil microorganisms
adverse impact on the energy and nutrient cycle of the ecosystem
Soil Degradation
deforestation, irrigation, land conversion, quarrying, mining … erosion etc.
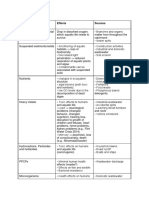
Main Soil Potential Specific Sources Some Common Symptoms/Effects
pollutant of Poisoning with the Polluted Soil
Mercury (Hg) mining • Itching, burning, pain
incineration of coal • damage to brain kidney and lungs
alkali and metal • pink disease (acrodynia) – skin
processing discoloration (pink cheeks,
medical and other waste fingertips, toes), while red cheeks
volcanoes and geologic and nose in affected children
deposits (natural sources) • desquamation (peeling off in
accumulation in plants layers of dead skin)
and vegetables grown on • high blood pressure and
polluted soils hypersalivation
• tachycardia
• loss of hair, teeth, nails,
photofobia
• kidney dysfunction
• memory impairment
• insomnia - in children
Some Common Symptoms/Effects
Main Soil pollutant Potential Specific Sources of Poisoning with the Polluted Soil
Arsenic (As) Mining If ingested –the most specific
Coal-fired power plants effects relates to skin pattern
Lumber facilities (used changes
as CCA – chromate cancer (including liver, kidney,
copper arsenate in bladder, prostate and lung
pressure treated wood) cancer)
Electronic Industry also at lower doses the
Foundry activities digestive system may be
Agriculture (Pesticides - affected with symptoms such
including some of those as: nausea vomiting, stomach
currently used) irritation, diarrhea, damage of
Natural accumulation blood vessels
under specific If inhaled – skin changes;
conditions irritation of throat and lungs,
circulatory problems
nervous system disorders
Some Common
Main Soil pollutant Potential Specific Sources Symptoms/Effects of
Poisoning with the
Polluted Soil
Other metals (Mn, Mining • Depend on metals
Cd, Cu, Zn, Ni, etc.) Foundry activities
Construction activities
PAHs (polyaromatic coal burning and vehicle emissions • harm to skin, body
hydrocarbos) accumulation in plants and fluids, and autoimmune
vegetables grown on polluted soils system
cigarette smoke and wood burning • eye irritation
wildfires, agricultural burning • nausea and vomiting
asphalt roads (construction • diarrhea
activities) • cataracts
industrial plants (e.g., coal tar, • kidney and liver damage
bitumen, coal-gasification) • cancer (skin, lung,
accumulation in plants and bladder,
vegetables grown on polluted soils gastrointestinal)
construction activities
Herbicides and Agricultural activities • large range of effects
Insecticides Gardening • skin rashes
• death
THINK TANK…
THINK TANK…
Action Plan
http://www.sustainability.umd.edu/content/campus/recycling_what.php
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PPTDocumento14 paginePPTDiane Agcaoili EdraNessuna valutazione finora
- PollutionDocumento5 paginePollutionzazamazaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 PB PDFDocumento2 pagine1 PB PDFIwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution: Causes, Effects and Solutions in 40 CharactersDocumento45 pagineAir Pollution: Causes, Effects and Solutions in 40 CharactersprashantbaraskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Land PollutionDocumento13 pagineSoil Land Pollutioniril liquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Water ContaminantsDocumento2 pagineWater ContaminantsMau CárdenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Evs - Final Unit 2 - Environment DegradationDocumento92 pagineEvs - Final Unit 2 - Environment DegradationchhaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Soil On Health: Dept: Geography and Environmental StudiesDocumento3 pagineImpact of Soil On Health: Dept: Geography and Environmental StudiesTaheraNessuna valutazione finora
- ES200WaterPollution L2Documento37 pagineES200WaterPollution L2Ruchi Aayush MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Contaminated Land An Overview - SirDocumento35 pagineContaminated Land An Overview - Sirsakshitripathii302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Pollution PartDocumento5 pagineEnvironmental Pollution PartKgNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8: Chemicals in Industry: 8.3 The Effects of Industrial Waste Disposal On The EnviromentDocumento30 pagineChapter 8: Chemicals in Industry: 8.3 The Effects of Industrial Waste Disposal On The EnviromentNorhayaty AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil pollution causes and effectsDocumento4 pagineSoil pollution causes and effectsJaime Tene EscobarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 Environmental ChemistryDocumento62 pagineLecture 6 Environmental ChemistryGuilbert FajardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Activities That Threaten THE EcosystemDocumento20 pagineHuman Activities That Threaten THE EcosystemnabilahsolehahNessuna valutazione finora
- PollutionDocumento16 paginePollutionPrasanth KNessuna valutazione finora
- ET Unit 2BDocumento38 pagineET Unit 2BYash JinghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Pollution & Issues Module - IIDocumento43 pagineEnvironmental Pollution & Issues Module - IIVidhya MohananNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Activities That Threaten THE EcosystemDocumento13 pagineHuman Activities That Threaten THE EcosystemnabilahsolehahNessuna valutazione finora
- ET Unit 2BDocumento37 pagineET Unit 2BSharonNessuna valutazione finora
- What is Soil Pollution and its EffectsDocumento6 pagineWhat is Soil Pollution and its EffectsManu Jacob Steaphen 19MST0050Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2B: Soil Contamination Is The Presence of Man-Made Chemicals or Other Alteration of The Natural SoilDocumento37 pagineUnit 2B: Soil Contamination Is The Presence of Man-Made Chemicals or Other Alteration of The Natural SoilSharonNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution Air PollutionDocumento33 pagineAir Pollution Air PollutionHridiNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental ScienceDocumento41 pagineEnvironmental ScienceNila ArivoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 20 EE DR - NoamanDocumento22 pagineLec 20 EE DR - NoamanHadia SAULATNessuna valutazione finora
- Heavy Metal Water Pollution-A Case Study: Recent Research in Science and Technology 2013, 5 (5) : 98-99 ISSN: 2076-5061Documento2 pagineHeavy Metal Water Pollution-A Case Study: Recent Research in Science and Technology 2013, 5 (5) : 98-99 ISSN: 2076-5061Zari Sofia LevisteNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental pollution and natural hazardsDocumento7 pagineEnvironmental pollution and natural hazardsxyzNessuna valutazione finora
- NOTESDocumento2 pagineNOTESMary Joy Heraga PagadorNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Environment ?? Threats To Environment Air PollutionDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Environment ?? Threats To Environment Air PollutionDaryl Dometita DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Issues ListDocumento11 pagineEnvironmental Issues ListDharsini PalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE PollutionDocumento2 pagineENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE PollutionEdralin dalgo jrNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental PollutionDocumento11 pagineEnvironmental PollutionErika WidiariniNessuna valutazione finora
- EvsDocumento15 pagineEvschandru.ramaraj161Nessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Management System .Documento18 pagineEnvironmental Management System .G-IOSH International-Pvt LTDNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollution Causes and Effects in 40 CharactersDocumento4 paginePollution Causes and Effects in 40 CharactersThapelo JeremiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Vargas - Partial ReqDocumento4 pagineVargas - Partial ReqHannah VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 12 SWMDocumento25 pagineLecture 12 SWMTejas MhaiskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Man and Environment ProblemsDocumento6 pagineMan and Environment Problemsabbas othman alwaseefNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec-2-Week (1) (Water Pollution)Documento30 pagineLec-2-Week (1) (Water Pollution)Arsalan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhagalpur Air Pollution Health EffectsDocumento20 pagineBhagalpur Air Pollution Health EffectsDr-Ambika KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Marlyn Geverola Activity 04122023Documento5 pagineMarlyn Geverola Activity 04122023glenswaberNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Form 3 Science notes- SitholeDocumento76 pagineRevised Form 3 Science notes- Sitholetegokate008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Environmental EngineeringDocumento34 pagineIntroduction To Environmental EngineeringAbdul Wafiy NaqiuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution: Effects and Control: CEL212 Dr. Divya Gupta 28 April 2021Documento20 pagineAir Pollution: Effects and Control: CEL212 Dr. Divya Gupta 28 April 2021Prashant Kumar SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- EVS - Soil Pollution N Solidwaste ManagementDocumento88 pagineEVS - Soil Pollution N Solidwaste Management22052724Nessuna valutazione finora
- ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES FOR B.TECHDocumento31 pagineENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES FOR B.TECHManoj ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- ENSO36 AssignmentDocumento3 pagineENSO36 AssignmentCendie Navarro MarmojadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Identify Pollution Types and Sources Near YouDocumento3 pagineIdentify Pollution Types and Sources Near YouCendie Navarro MarmojadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ambiente 8º Mto BomDocumento5 pagineAmbiente 8º Mto Bomcajoca1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adsorption of Heavy Metals - A Review Ijerdv4n1spl - 08Documento8 pagineAdsorption of Heavy Metals - A Review Ijerdv4n1spl - 08Anonymous i71HvPXNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 14-18Documento56 pagineWeek 14-18Ako lang ToNessuna valutazione finora
- Envr.E-Lect-Air PollotionDocumento8 pagineEnvr.E-Lect-Air PollotionAbdullah RamzanNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil PollutionDocumento17 pagineSoil Pollutionaraj518181Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation For B.SC - III Environmental PollutionDocumento19 paginePresentation For B.SC - III Environmental PollutionprabhamusturNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 LECTURE 7Documento16 pagineModule 3 LECTURE 7Temp LordNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil ContaminationDocumento3 pagineSoil ContaminationDaredevil CreationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Waste Managenent IDocumento4 pagineWaste Managenent Imail2shanthithevarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollution NotesDocumento10 paginePollution NotesMeghana YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Vegetable Production in Greenhouses: greenhouse Production, #3Da EverandVegetable Production in Greenhouses: greenhouse Production, #3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Pollution: Air - Water. Soil. Light. Noise (Part 3)Documento37 pagineEnvironmental Pollution: Air - Water. Soil. Light. Noise (Part 3)Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecological, Urban Poverty, Spatial Concentration, Environmental Footprint & Spatial NotesDocumento1 paginaEcological, Urban Poverty, Spatial Concentration, Environmental Footprint & Spatial NotesAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Biogeochemical Cycle: Environmental CyclesDocumento21 pagineBiogeochemical Cycle: Environmental CyclesAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- GroundwaterDocumento4 pagineGroundwaterAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- I. SIDEWALK LABS (Summary)Documento3 pagineI. SIDEWALK LABS (Summary)Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- OPTIC AnalysisDocumento3 pagineOPTIC AnalysisAhmad Sharief Bin Jaylani100% (1)
- Name - Criteria Excellent (10) Very Good (8) FAIR (6) Needs ImprovementDocumento3 pagineName - Criteria Excellent (10) Very Good (8) FAIR (6) Needs ImprovementAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Pollution: Air - Water. Soil. Light. NoiseDocumento36 pagineEnvironmental Pollution: Air - Water. Soil. Light. NoiseAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- SewerageDocumento4 pagineSewerageAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- BSCE-5 ES09 ASSIGNMENT 3 Pollution Management StrategiesDocumento2 pagineBSCE-5 ES09 ASSIGNMENT 3 Pollution Management StrategiesAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento1 pagina1Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Documento1 pagina2Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- TtestDocumento1 paginaTtestAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 5Documento1 pagina5Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Family of Prophet Muhammad (SAW)Documento23 pagineFamily of Prophet Muhammad (SAW)Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ResDocumento1 paginaResAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 6Documento1 pagina6Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 3Documento2 pagine3Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 4Documento1 pagina4Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam & Stirrup Design: Change HereDocumento12 pagineBeam & Stirrup Design: Change HereAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam & Stirrup Design: Change HereDocumento12 pagineBeam & Stirrup Design: Change HereAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 7Documento1 pagina7Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Iii. Additional Source and PhotoDocumento2 pagineIii. Additional Source and PhotoAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Coastal and River StructuresDocumento5 pagineCoastal and River StructuresAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PassDocumento1 paginaPassAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento3 pagine1Ahmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Month of JulyDocumento5 pagineMonth of JulyAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- GroundwaterDocumento4 pagineGroundwaterAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Science Notes Ch01 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocumento6 pagine09 Science Notes Ch01 Matter in Our SurroundingsFiraz CompNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry The Central Science 14th Edition Ebook PDFDocumento61 pagineChemistry The Central Science 14th Edition Ebook PDFjoyce.stewart332100% (41)
- Band Theory in Solid StateDocumento4 pagineBand Theory in Solid StatePaulami Bose100% (1)
- 08252016122551manual of ProcedureDocumento305 pagine08252016122551manual of ProcedureSuyog patilNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento112 pagineIntroductionAnkit ChikaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Modelling of Electric MachinesDocumento56 pagineThermal Modelling of Electric MachinesRoly Cabrera100% (1)
- Learning Module BTECH TBC - Part1.chem Module1Documento9 pagineLearning Module BTECH TBC - Part1.chem Module1Jen LabaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual of Procedures for Chemical Analysis of Ores and MineralsDocumento305 pagineManual of Procedures for Chemical Analysis of Ores and MineralsSuyog patilNessuna valutazione finora
- M.SC Chemistry (2018 Regulation)Documento48 pagineM.SC Chemistry (2018 Regulation)Aparna A KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- GaAs Crystal Growth TechniquesDocumento20 pagineGaAs Crystal Growth TechniquesdilaawaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrothermal Synthesis of Transition Metal Oxides Under Mild ConditionsDocumento6 pagineHydrothermal Synthesis of Transition Metal Oxides Under Mild ConditionsbhrNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Introduction and Overview of ManufacturingDocumento64 pagine01 Introduction and Overview of ManufacturingMuhammad Khan Khoso100% (6)
- Microstructure Characterization and Quantitative Analysis of Copper Alloy Matrix Composites Reinforced With Wc-Xni Powders Prepared by Spontaneous InfiltrationDocumento9 pagineMicrostructure Characterization and Quantitative Analysis of Copper Alloy Matrix Composites Reinforced With Wc-Xni Powders Prepared by Spontaneous Infiltrationnorthpole_plNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Tools For Improved ProductivityDocumento55 pagineSoftware Tools For Improved ProductivityseacnliNessuna valutazione finora
- Science8 Q3 SLM5Documento14 pagineScience8 Q3 SLM5ANGEL MANGLICMOTNessuna valutazione finora
- 3RD Periodic Lesson Plan ScienceDocumento28 pagine3RD Periodic Lesson Plan ScienceJhuvzCLunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling of Counter Current Moving Bed Gas-Solid Reactor Used in Direct Reduction of Iron Ore - PlusDocumento10 pagineModeling of Counter Current Moving Bed Gas-Solid Reactor Used in Direct Reduction of Iron Ore - PlusJavier GómezNessuna valutazione finora
- VERY IMP - in Text (1.9-1.11 Page 29) Che 12Documento2 pagineVERY IMP - in Text (1.9-1.11 Page 29) Che 12iqbal siddiqueyNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Properties of Matter (Larson, Dewey B)Documento308 pagineBasic Properties of Matter (Larson, Dewey B)campanero primeroNessuna valutazione finora
- LeaP-Science-G8-Week 4-Q3Documento4 pagineLeaP-Science-G8-Week 4-Q3Richard ViseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcse Typed QPDocumento145 pagineIgcse Typed QPnmahmud75Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Cell SimulationDocumento6 pagineFuel Cell SimulationvigneyshNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 10 - 12 PDFDocumento283 pagineChemistry 10 - 12 PDFRon ShamendeNessuna valutazione finora
- The 39th Solid Mechanics Conference, SolMech 2014, First AnnouncementDocumento2 pagineThe 39th Solid Mechanics Conference, SolMech 2014, First AnnouncementRyszard B. PecherskiNessuna valutazione finora
- ICMST2010 ProcsidingDocumento36 pagineICMST2010 ProcsidingelrohmNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 7 Q1W45Documento15 pagineScience 7 Q1W45Nhet Ytienza75% (4)
- Plasma Antenna Guide - Everything You Need to KnowDocumento20 paginePlasma Antenna Guide - Everything You Need to Knowsanapashok100% (1)
- Solid States Question PaperDocumento1 paginaSolid States Question PaperSomu Yashawant ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Reviewer-Science (151-180)Documento3 pagineFinal Reviewer-Science (151-180)KAREN BUENAVISTANessuna valutazione finora
- Five Fluid PDFDocumento14 pagineFive Fluid PDFاحمد ابوبكر اشقيفهNessuna valutazione finora