Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electronic Payment System
Caricato da
SONAL RATHI0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
294 visualizzazioni30 pagineE Payment System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoE Payment System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
294 visualizzazioni30 pagineElectronic Payment System
Caricato da
SONAL RATHIE Payment System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 30
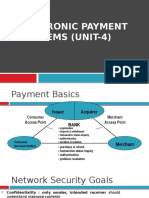
EPS is a financial exchange that take place online
between buyers and seller.
The content of this exchange is usually some form of
digital financial instrument (such as encrypted credit
card number ,e-cheque or digital cash ) that is backed
by a bank or an intermediary , or by a legal tender.
A payment system means ensuring payment security
,transaction privacy, system integrity customer
authentication and purchaser’s promise to pay.
EPS are proliferating in banking ,retail, health care,
online markets and even government infect anywhere
money needs to change hands.
A. Token based payment system
i) E-cash
ii) E-cheque
iii) Smart card or debit cards
B. Credit card based payment system
i) Encrypted credit card
ii) Third party authorization number
Entirely new forms of financial instruments are also
being developed one such new financial instrument is
electronic token. In the form of electronic cash /money.
Electronic tokens are designed as electronic analog of
various form of payment backed by a bank of financial
institution. Simply stated ,electronic tokens are
equivalent to cash that is backed by the bank.
Electronic tokens are of three types.
Cash or real time: transaction are settled with the
exchange of e-currency. An e.g. of e-currency is e-cash.
Debit or prepaid: user pay in advance for the privilege
of getting information e.g. of prepaid payment
mechanism are stored in smart cards and e-purse that
stores electronic memory.
Credit or postpaid: the server authenticates that
customer and verifies with the bank that funds are
adequate before purchase e.g. of postpaid mechanism
are credit/debit card and e-cheque.
Once the token are purchased , the digital cash s/w on
the customer's pc stores digital memory undersigned by
bank. The user spend digital money at any shop
accepting digital cash, without having to open an
account or having to transmit credit card number.
Credit card are now accepted everywhere the credit
card payment on the online network can be categorized
into three types.
a) Payment using plain credit card details
b) Payment using encrypted credit card details.
c) Payment using third party verification.
The most credit card processing is not so simple:
1. Most card issuer charges interest from the day a
charge is posted to the account if payment is not
made in full monthly.
2. For the merchant credit card, transaction result in
immediate credit to the merchant's bank account.
3. A card holder is expected to notify the issuing bank
immediately upon discovering the loss of the card.
4. A card holder may dispute charges or purchaser to the card
issuer.
The process followed in credit card transaction are given
here.
1. The customer presents his or her credit information
securely to the merchant.
2. The merchant validates the customer’s identity as the
owner of the credit card account.
3. The merchant relays the credit card charges
information and signature to its bank or online credit
card processors.
4. the bank or processing or processing party relays the
information to the customer’s bank for authorization
approval.
5.The customer’s bank returns the credit card data,
charge authentication , and authorization to the
merchant.
Debit cards are upgraded ATM cards branded with
ICICI, UTI, SBI,VISA ,MasterCards or other familiar
credit card company logo. They look exactly like credit
cards, except they directly tap your checking amount
every time you make a purchase or a withdrawal.
Debit cards can be used with or without a personal
identification number (PIN) almost everywhere- retail
stores, restaurants ,pay phones.
When used without a PIN, the procedure is simple.
The merchant’s terminal reads the card and identifies it
as a debit card that creates a debit against your bank
account. Because the transaction is off-line, instead of
debiting your account immediately, there is a 2-to-3
day wait before final processing.
A smart card is a plastic card. A smart card contains a
programmable chip, a combination of RAM and ROM
storage and an operating system of sorts, all embedded
in a plastic. It encrypt digital cash on a chip and can be
refilled by connecting to a bank.
A smart card carries more information than can be
accommodated on a card with a magnetic strip. The
chip’s ability to store information in its memory makes
the card smart. it can make a decision ,as it has
relatively powerful processing capabilities.
Smart card are basically of two types
1. Relationship based smart credit card and
2. Electronic purse- which replace money, are also
known as debit cards and electronic money.
Among its many uses and applications are the
following;
1. Provides users with ability to make a purchase.
2. Holds cash, ID information , and a key to house or an
office.
3. Provide identification of the cardholder , authentication of
the transaction and authentication of the data representing
the transaction.
4. A more recent development in smart card design is
capturing fingerprint for improved authentication.
5. Encryption and decryption of message to ensure security,
integrity and confidentiality.
6. A carries of value in a system similar to what is called an
electronic purse.
Smart card benefit consumers in several ways,
depending on the application. In general smart card
based application benefit consumers where their life
and business habits interest with payment processing
technologies.
Working of smart card
It require a special reader to connect the card with a
computer system card programmed for this purpose
smart cards have special contacts that match those in
the reader when the card is inserted into the slot for
processing.
The newest cards are “contactless” which use infrared
communication technology.
E-cash enables transaction between customer without
the need for banks or other third parties.
E-cash is transferred directly and immediately to the
participating merchants and vending machines.
Electronic cash is a secure and convenient alternative to
bills and coins.
E-cash usually operates on a smart cards which
includes an embedded microprocessor chip.
The microprocessor chip stores cash value and the
security features that make electronic transaction
secure.
Mondex , a subsidiary of MasterCard (Mondex Canada
Association) is a good example of e-cash.
E-cash is transferred directly from the customer’s
desktop to the merchant's site. Therefore, e-cash
transaction usually required no remote authorization or
personal identification number(PIN) code at the point
of sale.
E-cash can be transferred over a telephone line or over
the web.
The microprocessor chip embedded onto the card keep
track of the e-cash transactions.
Using e-cash the customer has two options:
a stand alone card containing e-cash or a combination
card that incorporates both e-cash and debit.
How a e-cash system works:
A customer or merchant signup with one of the
participating bank or financial institution.
The customer receives specific software to install on
his or her computer.
The software allows the customer to download
“electronic coins” to his or her desktop.
The software manages the electronic coins.
The initial purchase of coins is charged against the
customer bank account or against a credit card.
When buying goods or services from a website that
accepts e-cash ,the customer simply clicks the “pay
with e-cash ” button. The merchant’s software
generates a payment request , describing the items
purchased ,price and the time and date.
The customer can then accept or reject this request,
when the customer accepts the payment request, the
software residing on the customer’s desktop subtracts
the payment amount from the balance and creates a
payment that is sent to the bank or financial institution
of the merchant, and then is deposited to the merchant’s
account.
The attractive feature of the entire process is its
turnaround time which is a few seconds.
E-cheque are another form of electronic tokens.
A new electronic version of paper cheque. E-cheque is
an instruction to a financial institution to pay a given
amount of money to the payee.
It is a specially formatted email message sent over the
internet. It contains as the same information as on paper
based cheque.
Transaction payment sequence in e-cheque system.
Buyer must register with third party account server
using e-cheque.
On receiving the cheque, the seller presents it to
accounting system for verification and payment.
The accounting system verifies the digital signature on
the cheque.
Properly signed and endorsed cheque can be
electronically changed between financial institution
through electronic clearing house.
They work in the same way as traditional cheque.
E-cheque are suited for micro payment.
Financial risk is assumed by accounting server.
A product offered as a give way or a special promotion
encourages, receiver to pass on the word to other,
creating the potential for exponential growth in the
product sale ,a communication product.
An electronic payment system that operates like a
carries of cash and information in the same way a real
world wallet function such as carries real cash and
various IDs.
The aim is to give shoppers a single, simple and secure
way of carrying currency electronically.
The procedure for using e-wallet-
1. Decide on an online site where you would like to
shop.
2. Download a wallet from the merchant’s website you
intent to shop. The special form required you to fill
out personal information such as credit cards
numbers, phone, add etc. when making a purchase,
you click on your e-wallet and the order is
automatically completed.
3. Fill out personal information such as your credit card
number ,name , address and phone number and where
merchandise should be shipped.
4. when you’ve ready to pay , click on the wallet buttons
,the buying process is fully executed , billing
information is automatically filled out.
E.g. the most popular wallet available to data are
Entry point , AOL , Gator, Cyber cash.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- White Paper - All About Ecommerce and Payment GatewaysDocumento8 pagineWhite Paper - All About Ecommerce and Payment GatewaysschoginiNessuna valutazione finora
- Debit Card & Credit Card & Their AdvantagesDocumento24 pagineDebit Card & Credit Card & Their AdvantagesAkash Deep100% (1)
- Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento20 pagineElectronic Payment SystemsHinaJhaveriNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank of America Bank StatementDocumento4 pagineBank of America Bank Statementiimoadi333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Choosing Payments MethodDocumento3 pagineChoosing Payments MethodDenimNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of Electronic Payment SystemDocumento9 pagineDefinition of Electronic Payment Systemdharshinee1961Nessuna valutazione finora
- Payment Gateway vs. Payment Processor - What Are The DifferencesDocumento6 paginePayment Gateway vs. Payment Processor - What Are The DifferencesCarlos JesenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Security of Online TransactionsDocumento46 pagineSecurity of Online Transactionshaleem81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Payment SysyemsDocumento24 pagineConsumer Payment SysyemsMuhammad NaumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Finance GuideDocumento28 pagineConsumer Finance GuiderajatNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovation in Credit Card and Debit Card Business by Indian BanksDocumento21 pagineInnovation in Credit Card and Debit Card Business by Indian BanksProf S P GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento8 pagineElectronic Payment SystemsAbhishek NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Wallet ResearchDocumento22 pagineE-Wallet ResearchMrudul BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Payment Gateway Essentials for Ecommerce SecurityDocumento3 paginePayment Gateway Essentials for Ecommerce Securitysachin sandbhorNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Transfer SystemsDocumento2 pagineMoney Transfer SystemsMainSqNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecommerce PresentationDocumento9 pagineEcommerce PresentationSurabhi AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods to Overcome the Financial and Money Transfer Blockade against Palestine and any Country Suffering from Financial BlockadeDa EverandMethods to Overcome the Financial and Money Transfer Blockade against Palestine and any Country Suffering from Financial BlockadeNessuna valutazione finora
- E Payment SystemsDocumento17 pagineE Payment SystemsdeekshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Paymet SystemsDocumento23 pagineOnline Paymet SystemsPrabhjeet Sumit GoklaneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento17 pagineElectronic Payment SystemSandeep Shrivastava0% (1)
- Adowrds Advertising On Display NetworkDocumento52 pagineAdowrds Advertising On Display NetworkAzhar KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Card E Commerce TransactionsDocumento2 pagineCredit Card E Commerce TransactionsThuong Vy MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- CIMB Credit Card Product DisclosureDocumento17 pagineCIMB Credit Card Product DisclosureMohd Haris DrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- How Credit Cards Work: A Guide to Credit Card ProcessingDocumento4 pagineHow Credit Cards Work: A Guide to Credit Card ProcessingJyoti JhajhraNessuna valutazione finora
- SwiftcashDocumento33 pagineSwiftcashLibinNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Online payment Security and Fraud PreventionDa EverandEssentials of Online payment Security and Fraud PreventionNessuna valutazione finora
- 191 - 197 - Detection of Transaction Fraud Using Deep LearningDocumento28 pagine191 - 197 - Detection of Transaction Fraud Using Deep LearningADRINEEL SAHANessuna valutazione finora
- Cards: Debit Card Credit Card Prepaid CardDocumento14 pagineCards: Debit Card Credit Card Prepaid CardJAHID HOSSAINNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 Introduciton: 1.1 What Is Debit C Ard?Documento60 pagineChapter-1 Introduciton: 1.1 What Is Debit C Ard?glorydharmarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 E Commerce Payment SystemDocumento4 pagineUnit 5 E Commerce Payment SystemAltaf HyssainNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento23 pagineElectronic Payment SystemBiswajit Chowdhury100% (2)
- Capgemini - World Payments Report 2013Documento60 pagineCapgemini - World Payments Report 2013Carlo Di Domenico100% (1)
- Client Account MaintenanceDocumento18 pagineClient Account MaintenanceNirajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Five: E-Commerce Payment SystemsDocumento17 pagineChapter Five: E-Commerce Payment SystemsAgmasie TsegaNessuna valutazione finora
- E PaymentDocumento8 pagineE PaymentPrashant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- EMTM 553: E-Commerce Systems: Lecture 8: Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento59 pagineEMTM 553: E-Commerce Systems: Lecture 8: Electronic Payment SystemsD Attitude KidNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Payment Systems SeminarDocumento26 pagineMobile Payment Systems Seminarkrishnaganth kichaaNessuna valutazione finora
- How Visa Makes Money and Understaning Visa Business ModelDocumento5 pagineHow Visa Makes Money and Understaning Visa Business ModelAchintya MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Online BankingDocumento66 pagineOnline BankingSatyam JaniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rising Tide of US Electronic Payments: White PaperDocumento11 pagineThe Rising Tide of US Electronic Payments: White Papervatimetro2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Questionsv3Documento222 pagineAdditional Questionsv3Konstantin TsolovNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento5 pagineElectronic Payment SystemSwati HansNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment System111Documento43 pagineElectronic Payment System111negirakes100% (1)
- Online Banking SystemDocumento63 pagineOnline Banking SystemvenkeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile PaymentsDocumento36 pagineMobile Paymentsadnan67Nessuna valutazione finora
- A B C D of E-BankingDocumento75 pagineA B C D of E-Bankinglove tannaNessuna valutazione finora
- E Payment SystemDocumento47 pagineE Payment SystemNamrata KshirsagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento28 pagineElectronic Payment Systemnehapaspuleti4891100% (1)
- MDZ01-200 Seller Contract 13sept2018Documento5 pagineMDZ01-200 Seller Contract 13sept2018Vaithiswari100% (1)
- Electronic Payment SystemDocumento25 pagineElectronic Payment SystemTarun Garg100% (1)
- On-Line Payment System Survey - EcashDocumento9 pagineOn-Line Payment System Survey - EcashJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)Nessuna valutazione finora
- E COMMERCE FINAL COVERAGE MODULE 1 and 2Documento9 pagineE COMMERCE FINAL COVERAGE MODULE 1 and 2BRIAN CORPUZ INCOGNITONessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Payment IndustryDocumento6 pagineDigital Payment Industrywubetie SewunetNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile BankingDocumento66 pagineMobile BankingNalini SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Payment System: Amit Kumar Nayak Roll No:29401 Regd No:1005105001Documento17 pagineElectronic Payment System: Amit Kumar Nayak Roll No:29401 Regd No:1005105001Amit Kumar NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Payment SystemDocumento30 pagineOnline Payment SystemDjks YobNessuna valutazione finora
- Degital Payment SystemDocumento20 pagineDegital Payment SystemJaivik PanchalNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Literature:: Definition of Electronic Payment SystemsDocumento3 pagineReview of Literature:: Definition of Electronic Payment SystemsAvula Shravan YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic MoneyDocumento3 paginePlastic MoneysachinremaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhavik BlackbookDocumento29 pagineBhavik BlackbookBhavik khairNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle East/Africa: Purchase Volume 2015 vs. 2014Documento11 pagineMiddle East/Africa: Purchase Volume 2015 vs. 2014Charan TejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile banking conceptual model summaryDocumento21 pagineMobile banking conceptual model summaryGill Varinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Report On Future Prospects of Debit and Credit CardsDocumento4 pagineStudy Report On Future Prospects of Debit and Credit CardsaishwaryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Card Fraud Prevention Strategies A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandCredit Card Fraud Prevention Strategies A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Trends and New Product Opportunities in The Food SectorDocumento59 pagineConsumer Trends and New Product Opportunities in The Food SectorSONAL RATHINessuna valutazione finora
- 4 P'S of MaggiDocumento21 pagine4 P'S of MaggiSONAL RATHI100% (2)
- Indias Export 2862Documento53 pagineIndias Export 2862suresh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- HR JournalDocumento3 pagineHR JournalSONAL RATHINessuna valutazione finora
- Irda Q&aDocumento100 pagineIrda Q&aRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ATM Banking in Kenya: A Customer Retention Strategy PresenterDocumento11 pagineATM Banking in Kenya: A Customer Retention Strategy PresentersagirskaziNessuna valutazione finora
- UnitronUC32 Building Management System ArchitectureDocumento1 paginaUnitronUC32 Building Management System ArchitectureAnonymous XYAPaxjbYNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline IFMDocumento3 pagineCourse Outline IFMWedaje AlemayehuNessuna valutazione finora
- Joko Mulyanto Dept. of Public Health and Community Medicine Faculty of Medicine Jenderal Soedirman UniversityDocumento29 pagineJoko Mulyanto Dept. of Public Health and Community Medicine Faculty of Medicine Jenderal Soedirman UniversityErica SkinnerNessuna valutazione finora
- V-EMUX-1 and V-EMUX-2Documento22 pagineV-EMUX-1 and V-EMUX-2Eko IndriatmokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bangladesh Railway e Ticket 01723244631Documento1 paginaBangladesh Railway e Ticket 01723244631Ujjwal MondolNessuna valutazione finora
- E7 Introduction To Islamic FinanceDocumento5 pagineE7 Introduction To Islamic FinanceTENGKU ANIS TENGKU YUSMANessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-4: Iot Architecture and ProtocolsDocumento22 pagineUnit-4: Iot Architecture and ProtocolsMahesh ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Government of West Bengal GRIPS 2.0 Acknowledgement Receipt Payment SummaryDocumento2 pagineGovernment of West Bengal GRIPS 2.0 Acknowledgement Receipt Payment SummaryPratik JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Configure and Verify A Site To Site IPsec VPN Using CLIDocumento4 pagineConfigure and Verify A Site To Site IPsec VPN Using CLICristhian HadesNessuna valutazione finora
- StatementDocumento3 pagineStatementDarshan70Nessuna valutazione finora
- Accounts DecemberDocumento28 pagineAccounts DecemberSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimize Network Traffic and Security with Allot ProductsDocumento10 pagineOptimize Network Traffic and Security with Allot ProductsPandu PriambodoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is eDocumento6 pagineWhat Is eUdaya Mudgal100% (2)
- Bank ChallanDocumento1 paginaBank Challansulaimankhokher0Nessuna valutazione finora
- ePMP AX 5.4.1 Release NotesDocumento9 pagineePMP AX 5.4.1 Release NotesOmar PalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tally Spss PDFDocumento42 pagineTally Spss PDFAkshay PoplyNessuna valutazione finora
- White Paper c11 741490 16 35Documento20 pagineWhite Paper c11 741490 16 35Mohamed Aly SowNessuna valutazione finora
- DTCP Online AckDocumento1 paginaDTCP Online Ackmohan SNessuna valutazione finora
- Drone Communication - Data LinkDocumento1 paginaDrone Communication - Data LinkNur khairul DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- CR ViewerDocumento2 pagineCR ViewerJehan ZebNessuna valutazione finora
- ManualDocumento121 pagineManualccmcmNessuna valutazione finora
- Ias 8 PDFDocumento21 pagineIas 8 PDFJoedy Mae MangampoNessuna valutazione finora
- ARIBA, Fretzyl Bless A. - Chapter 9 - Substantive Test of Receivables and Sales - ReflectionDocumento3 pagineARIBA, Fretzyl Bless A. - Chapter 9 - Substantive Test of Receivables and Sales - ReflectionFretzyl JulyNessuna valutazione finora