Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
One-To-One Functions, Inverse and Coverage of Exam
Caricato da
Airene Castaños0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
72 visualizzazioni26 pagineThe document discusses one-to-one functions and their inverses. It defines a one-to-one function as a function where no two x-values map to the same y-value. It then gives examples of relations and determines whether they are functions and if the functions are one-to-one. The document also discusses how to find the inverse of a one-to-one function by interchanging x and y and solving for y in terms of x. Finally, it outlines the material to be covered on the first periodic exam, including functions, rational functions, and one-to-one functions.
Descrizione originale:
gen. math
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses one-to-one functions and their inverses. It defines a one-to-one function as a function where no two x-values map to the same y-value. It then gives examples of relations and determines whether they are functions and if the functions are one-to-one. The document also discusses how to find the inverse of a one-to-one function by interchanging x and y and solving for y in terms of x. Finally, it outlines the material to be covered on the first periodic exam, including functions, rational functions, and one-to-one functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
72 visualizzazioni26 pagineOne-To-One Functions, Inverse and Coverage of Exam
Caricato da
Airene CastañosThe document discusses one-to-one functions and their inverses. It defines a one-to-one function as a function where no two x-values map to the same y-value. It then gives examples of relations and determines whether they are functions and if the functions are one-to-one. The document also discusses how to find the inverse of a one-to-one function by interchanging x and y and solving for y in terms of x. Finally, it outlines the material to be covered on the first periodic exam, including functions, rational functions, and one-to-one functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 26
CHAPTER III.
ONE - TO- ONE
FU NCTIONS
ONE - TO - ONE
FU NCTIONS
ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTIONS
The function 𝑓 is one-to-one if
for any 𝑥1 , 𝑥2 in the domain of f,
then 𝑓(𝑥1 ) ≠ 𝑓 𝑥2 . That is, the
same 𝑦-value is never paired
with two different 𝑥-values.
Determine whether the given relation is a function. If
it is a function, determine whether it is one-to-one.
1. The relation pairing an SSS member to his
or her SSS number.
2. The relation pairing a real number to its
square.
3. The relation pairing a person to his or her
citizenship.
Determine whether the given relation is a function. If
it is a function, determine whether it is one-to-one.
4. The relation pairing an airport to its airport code. Airport codes are
three letter codes used to uniquely identify airports around the world and
prominently displayed on checked-in bags to denote the destination of
these bags. Here are some examples of airport codes:
MNL - Ninoy Aquino International Airport (All terminals)
CEB - Mactan-Cebu International Airport
DVO - Francisco Bangoy International Airport (Davao)
JFK - John F. Kennedy International Airport (New York City)
CDG - Charles de Gaulle International Airport (Paris, France)
Airport codes can be looked up at https://www.world-airport-codes.com
How to determine if the graph is a one-
to-one functions?
Horizontal Line Test
A function is one-to-one if each horizontal line does
not intersect the graph at more than one point.
The Vertical and Horizontal Line Tests
All functions satisfy the vertical line test. All one-to-
one functions satisfy both the vertical and horizontal
line tests.
IS THIS A ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTION?
IS THIS A ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTION?
IS THIS A ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTION?
IS THIS A ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTION?
INVERSE OF
ONE - TO - ONE
FU NCTIONS
y=2x-1
y=2x-1
Inverting the values for x & y, we have
Inverting the values for x & y, we have
`INVERTING' FUNCTIONS
•if the x- and y-values of a one-to-one
function are interchanged, the result is a
function, but
• if the x- and y-values of a function that is
not one-to-one are inverted, the result is
no longer a function.
INVERSE OF ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTIONS
TO FIND THE INVERSE OF A ONE-
TO-ONE FUNCTION,
(a) write the function in the form y = f(x);
(b) interchange the x and y variables;
(c) solve for y in terms of x.
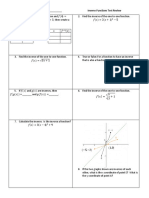
Example: Find the inverse of the ff.:
1. f(x) = 3x + 1. 2.
COVERAGE
FOR THE
1 S T PERIODICAL
EXAM
I. FUNCTIONS
1. Functions & Relations
2. Evaluating Functions
3. Operations on Functions
-Addition -Subtraction
-Multiplication -Division
-Composition
II. RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
1. Rational Function, Equations, & Inequalities.
2. Solving Rational Equations and Inequalities.
3. Graphing Rational Function:
Properties:
-Domain, Range, X-intercept,Y-intercept,
Zeroes,Vertical & Horizontal Asymptote.
PROCEDURE FOR SOLVING
RATIONAL INEQUALITIES:
To solve rational inequalities:
(a)rewrite the inequality as a single
rational expression on one side of
the inequality symbol and 0 on the
other side.
PROCEDURE FOR SOLVING RATIONAL INEQUALITIES:
(b)Determine over what intervals the rational expression
takes on positive and negative values.
i. Locate the x values for which
the rational expression is zero or
undefined (factoring the numerator
and denominator is a useful
strategy).
PROCEDURE FOR SOLVING RATIONAL INEQUALITIES:
(b)Determine over what intervals the rational expression
takes on positive and negative values.
ii. Mark the numbers found in (i) on a
number line. Use a shaded circle to
indicate that the value is included in the
solution set, and a hollow circle to
indicate that the value is excluded.
These numbers partition the number line
into intervals.
PROCEDURE FOR SOLVING RATIONAL INEQUALITIES:
(b)Determine over what intervals the rational expression
takes on positive and negative values.
. Select a test point within the
iii
interior of each interval in (ii). The
sign of the rational expression at
this test point is also the sign of the
rational expression at each interior
point in the aforementioned interval.
II. RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
1. Rational Function, Equations, & Inequalities.
2. Solving Rational Equations and Inequalities.
3. Graphing Rational Function:
Properties:
-Domain, Range, X-intercept,Y-intercept,
Zeroes,Vertical & Horizontal Asymptote.
III. ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTIONS
1. One-to-one functions.
2. Inverse of one-to-one functions.
3. Graphs of Inverse functions.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Rational FunctionDocumento4 pagineRational FunctionDianne PaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen. Math Chapter 1 4 OtherDocumento2 pagineGen. Math Chapter 1 4 OtherMary Beth Ed MartelNessuna valutazione finora
- General Mathematics 11 Notes 1ST SemDocumento25 pagineGeneral Mathematics 11 Notes 1ST SemPhilippine Expeditionary Force to RonogradNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen. Math Q1 W5 StudentDocumento20 pagineGen. Math Q1 W5 StudentMykhaela Louize GumbanNessuna valutazione finora
- L No 15-ADocumento25 pagineL No 15-AThiyagu VasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverse FunctionsDocumento23 pagineInverse FunctionsL AlcosabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra I Notes Functions and Function Notation Unit 4 Unit 4 - Functions and Function Notation Prerequisite SkillsDocumento22 pagineAlgebra I Notes Functions and Function Notation Unit 4 Unit 4 - Functions and Function Notation Prerequisite SkillsThiyagu VasuNessuna valutazione finora
- ExpressionsDocumento10 pagineExpressionsAmna MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Minimum and Maximum ValuesDocumento5 pagineExploring Minimum and Maximum ValuesRobert TalbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 11: Chapter 16-17 Predictive AnalysisDocumento38 pagineSession 11: Chapter 16-17 Predictive AnalysisLi PerfectNessuna valutazione finora
- General MathematicsDocumento42 pagineGeneral MathematicsGlenn Puralan FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- FunctionsDocumento13 pagineFunctionspedztotNessuna valutazione finora
- GenMath ReviewerDocumento5 pagineGenMath ReviewerMaze MazikeenNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Range and FunctionDocumento43 pagine06 Range and FunctionBapiki CadiakNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH01 CO1 Lesson 2 Inverse FunctionsDocumento16 pagineMATH01 CO1 Lesson 2 Inverse FunctionsMitzie LorraineNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts On FunctionsDocumento32 pagineBasic Concepts On FunctionsChelsea RoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- One To OneDocumento114 pagineOne To OneHazel SajuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Xii Chapter 12 Linear ProgrammingDocumento39 pagineMaths Xii Chapter 12 Linear ProgrammingAimen AyubNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6: Functions of One and More VariablesDocumento3 pagineLesson 6: Functions of One and More VariablesBotnaru LaurentiuNessuna valutazione finora
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Intercepts, Zeroes and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDocumento15 pagineGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Intercepts, Zeroes and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsAshley Kait Marcelo100% (1)
- General Mathematics PowerPointDocumento20 pagineGeneral Mathematics PowerPointMarie DirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pertemuan Iii Even and Odd FunctionsDocumento11 paginePertemuan Iii Even and Odd FunctionsMadinahNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary (Preliminaries)Documento16 pagineSummary (Preliminaries)Beyzanur BektaşNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1.1 Real Numbers, Relation and FunctionsDocumento49 pagineLesson 1.1 Real Numbers, Relation and FunctionsImone BunoNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT II - Chapter IDocumento10 pagineUNIT II - Chapter ISARATH CHANDRANessuna valutazione finora
- FunctionsDocumento10 pagineFunctionsphamha9947Nessuna valutazione finora
- General Mathematics - Week 1Documento13 pagineGeneral Mathematics - Week 1Daniel IrlandezNessuna valutazione finora
- General MathematicsDocumento6 pagineGeneral MathematicsFelipe AlfonsóNessuna valutazione finora
- Rational Functions - Week 2Documento41 pagineRational Functions - Week 2Jennifer MagangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra 1 StandardsDocumento6 pagineAlgebra 1 Standardsapi-306943671Nessuna valutazione finora
- Full Notes For Chapter1 FunctionsDocumento28 pagineFull Notes For Chapter1 FunctionsChong Hou YiNessuna valutazione finora
- Genmath - Module 1Documento6 pagineGenmath - Module 1Rex Reu PortaNessuna valutazione finora
- w3q2 Relations and Functions Autosaved AutosavedDocumento33 paginew3q2 Relations and Functions Autosaved Autosavedjezzaniexyane28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: Functions and Their Graphs Lesson 1: Functions About The LessonDocumento17 pagineChapter 1: Functions and Their Graphs Lesson 1: Functions About The LessonlyxineNessuna valutazione finora
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Blk. 40 Lot 73 Road 1 Minuyan II, CSJDM BulacanDocumento2 pagineJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Blk. 40 Lot 73 Road 1 Minuyan II, CSJDM BulacanJi PaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1functions IntroductionDocumento31 pagine1functions Introductiondog octopussNessuna valutazione finora
- Runge Phenomenon: Guided By: Dr. Geetanjali PradhanDocumento29 pagineRunge Phenomenon: Guided By: Dr. Geetanjali PradhanSwarupa SarangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 3.6 One-To-One Functions Inverse FunctionsDocumento4 pagineSection 3.6 One-To-One Functions Inverse FunctionsRaul VillalunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of FunctionsDocumento59 pagineConcept of FunctionsFernando PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling Approaches To Common Functions: General Mathematics For Grade 11Documento23 pagineModeling Approaches To Common Functions: General Mathematics For Grade 11sample sampleNessuna valutazione finora
- CalcAB - Chapter 1 NotesDocumento15 pagineCalcAB - Chapter 1 NotesSri PatNessuna valutazione finora
- Math - 7th Grade Teaching NotesDocumento16 pagineMath - 7th Grade Teaching NotesPara ParadiseNessuna valutazione finora
- MGT555 CH 6 Regression AnalysisDocumento19 pagineMGT555 CH 6 Regression AnalysisSITI MADHIHAH OTHMANNessuna valutazione finora
- GenMathQ1W2 02Documento8 pagineGenMathQ1W2 02gabosara298Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 - Inverse FunctionDocumento14 pagineModule 4 - Inverse FunctionkayiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Bhilai Study MaterialDocumento97 pagineMaths Bhilai Study MaterialVarun SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Neral Mathematics Functions Relation f2fDocumento51 pagineNeral Mathematics Functions Relation f2fjaninepenelope07Nessuna valutazione finora
- TOPIC 4 - FunctionsDocumento18 pagineTOPIC 4 - FunctionsChona BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- GEC 104 Final Week - Function and RelationsDocumento7 pagineGEC 104 Final Week - Function and RelationsReygie FabrigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Labview ProgrammingDocumento20 pagineLabview ProgrammingJames WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 B - Trendlines and Regression AnalysisDocumento73 pagineChapter 8 B - Trendlines and Regression AnalysisPankaj MaryeNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming in C EssayDocumento42 pagineProgramming in C EssayPRANAV CNessuna valutazione finora
- Regression ANOVADocumento42 pagineRegression ANOVAJamal AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute Value FunctionsDocumento9 pagineAbsolute Value FunctionsRenalyn Claire VenturaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverse Test ReviewDocumento2 pagineInverse Test ReviewLandrie PolkNessuna valutazione finora
- Rational FunctionDocumento14 pagineRational Functionawyne nozulNessuna valutazione finora
- The Normal CurveDocumento85 pagineThe Normal CurveAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Basketball Waiver FormatDocumento1 paginaBasketball Waiver FormatAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics and Probability-Lesson 1Documento109 pagineStatistics and Probability-Lesson 1Airene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Diploma Senior High BCSAT LETTERDocumento1 paginaDiploma Senior High BCSAT LETTERAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Random SamplingDocumento26 pagineRandom SamplingAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Bcsat Academics ProspectusDocumento4 pagineBcsat Academics ProspectusAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Name For DoorDocumento2 pagineName For DoorAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate of Completion-DBMDocumento1 paginaCertificate of Completion-DBMAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher's ScheduleDocumento1 paginaTeacher's ScheduleAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Learners' Names: Input Data Sheet For SHS E-Class RecordDocumento25 pagineLearners' Names: Input Data Sheet For SHS E-Class RecordAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Business MathDocumento33 pagineBusiness MathAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Republic of The Philippines: Butuan City School of Arts and TradesDocumento10 pagineRepublic of The Philippines: Butuan City School of Arts and TradesAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Learners' Names: Input Data Sheet For SHS E-Class RecordDocumento27 pagineLearners' Names: Input Data Sheet For SHS E-Class RecordAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Learners' Names: Input Data Sheet For SHS E-Class RecordDocumento28 pagineLearners' Names: Input Data Sheet For SHS E-Class RecordAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- A Legacy of Filipino Dance: Paul Alexander Morales (Contributor)Documento2 pagineA Legacy of Filipino Dance: Paul Alexander Morales (Contributor)Airene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- National Id SystemDocumento21 pagineNational Id SystemAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions & RelationsDocumento26 pagineFunctions & RelationsAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio Media and InformationDocumento55 pagineAudio Media and InformationAirene CastañosNessuna valutazione finora
- Legal, Ethical, and Societal Issues in Media & InformationDocumento26 pagineLegal, Ethical, and Societal Issues in Media & InformationAirene Castaños100% (1)
- Graphology PDFDocumento5 pagineGraphology PDFpuneeth87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pebl 2 ManualDocumento306 paginePebl 2 ManualEstebanGiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Testing and Diagnostics of A-D Converter 565Documento11 pagineDynamic Testing and Diagnostics of A-D Converter 565Marius260Nessuna valutazione finora
- MTH302 Solved MCQs Alotof Solved MCQsof MTH302 InonefDocumento26 pagineMTH302 Solved MCQs Alotof Solved MCQsof MTH302 InonefiftiniaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Limits of Trigonometric Functions PDFDocumento5 pagineLimits of Trigonometric Functions PDFJoe Satriawan25% (4)
- Experiment # 6: PurposeDocumento5 pagineExperiment # 6: PurposeHamza HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- FreeRTOS - TasksDocumento31 pagineFreeRTOS - TasksMani Kandan KNessuna valutazione finora
- Amenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Documento284 pagineAmenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Javier100% (1)
- 05 SlideDocumento42 pagine05 SlideAtheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocumento37 pagineInductive and Deductive ReasoningGadela KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- FEEDBACKDocumento43 pagineFEEDBACKMenaka kaulNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 3 and 4Documento6 pagineMODULE 3 and 4Jellene Jem RonarioNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-Angle Pair Relationships PDFDocumento4 pagine2-Angle Pair Relationships PDFLeigh YahNessuna valutazione finora
- PMP Cheat SheetDocumento9 paginePMP Cheat SheetzepededudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deterministic and Probabilistic Liquefac PDFDocumento6 pagineDeterministic and Probabilistic Liquefac PDFFarras Puti DzakirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sep 02Documento19 pagineSep 02c_nghia100% (1)
- Interpreting and Using Statistics in Psychological Research 1St Edition Christopher Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento41 pagineInterpreting and Using Statistics in Psychological Research 1St Edition Christopher Test Bank Full Chapter PDFhungden8pne100% (12)
- Mechanics of Tooth Movement: or SmithDocumento14 pagineMechanics of Tooth Movement: or SmithRamesh SakthyNessuna valutazione finora
- DD2434 Machine Learning, Advanced Course Assignment 2: Jens Lagergren Deadline 23.00 (CET) December 30, 2017Documento5 pagineDD2434 Machine Learning, Advanced Course Assignment 2: Jens Lagergren Deadline 23.00 (CET) December 30, 2017Alexandros FerlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Symmetry in The Music of Thelonious Monk PDFDocumento97 pagineSymmetry in The Music of Thelonious Monk PDFMicheleRusso100% (1)
- 1 5 PacketDocumento12 pagine1 5 Packetapi-326933003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Between Full Order and Minimum Order Observer Controller For DC MotorDocumento6 pagineComparison Between Full Order and Minimum Order Observer Controller For DC MotorInternational Journal of Research and DiscoveryNessuna valutazione finora
- FMEA Minus The Pain FiguresDocumento3 pagineFMEA Minus The Pain FiguresMUNISNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuzzy Quasi Regular RingDocumento3 pagineFuzzy Quasi Regular RingIIR indiaNessuna valutazione finora
- P3 Mock PaperDocumento10 pagineP3 Mock PaperRahyan AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- PHP Array FunctionsDocumento54 paginePHP Array FunctionsDeepak MitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Engineering Design - 2021 - Schlicke - Calculation of Maximum Crack Width For Practical Design of Reinforced ConcreteDocumento17 pagineCivil Engineering Design - 2021 - Schlicke - Calculation of Maximum Crack Width For Practical Design of Reinforced Concretedmt7nzztcmNessuna valutazione finora
- STA642 Handouts Topic 1 To 187 by Mahar Afaq Safdar MuhammadDocumento1.739 pagineSTA642 Handouts Topic 1 To 187 by Mahar Afaq Safdar Muhammadhumairamubarak2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- AMSGradDocumento16 pagineAMSGradRoja Reddy SareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Measure of Location and DispersionDocumento11 pagineChapter 3 - Measure of Location and DispersionNelly MalatjiNessuna valutazione finora