Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Telephone Triggered Switches
Caricato da
Suresh Shah100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
559 visualizzazioni22 pagineThis document describes a home appliance control system that uses DTMF tones sent from a cell phone to control devices remotely. The system uses a DTMF decoder chip to detect tones from key presses and send signals to a microcontroller. The microcontroller then controls relays connected to home appliances allowing users to turn devices on and off from their phone. The system is designed to control up to 10 appliances and provides status feedback to users. It offers remote control of home devices in a secure and affordable way.
Descrizione originale:
ppt on the telephone triggered switches
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document describes a home appliance control system that uses DTMF tones sent from a cell phone to control devices remotely. The system uses a DTMF decoder chip to detect tones from key presses and send signals to a microcontroller. The microcontroller then controls relays connected to home appliances allowing users to turn devices on and off from their phone. The system is designed to control up to 10 appliances and provides status feedback to users. It offers remote control of home devices in a secure and affordable way.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
559 visualizzazioni22 pagineTelephone Triggered Switches
Caricato da
Suresh ShahThis document describes a home appliance control system that uses DTMF tones sent from a cell phone to control devices remotely. The system uses a DTMF decoder chip to detect tones from key presses and send signals to a microcontroller. The microcontroller then controls relays connected to home appliances allowing users to turn devices on and off from their phone. The system is designed to control up to 10 appliances and provides status feedback to users. It offers remote control of home devices in a secure and affordable way.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 22
TELEPHONE TRIGGERED
SWITCHES
Submitted by – Suresh Lal Shah
M.Sc. 4th semester.
Physics Department
S.S.J. Campus Almora
CONTENTS-
INTRODUCTION
A DESIGN OF HOME APPLIANCE CONTROL
SYSTEM
THE SYSTEM FEATURES
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
DTMF DETECTION UNIT
CONTROL UNIT
CONCLUSION
FUTURE WORK
REFERENCES
Introduction
A telephone triggered switching system also
called Home automation system.
It provides us Facility to know present
status to switch on or off the Home
appliances or devices like Fan ,indoor
outdoor lamps ,refrigerators, AC
temperatures, microwave ovens.
Here we use DTMF Technology which allows
the user to control the present state of
home appliances by cell phone or telephone.
A DESIGN OF HOME APPLIANCE CONTROL SYSTEM
USING CELL PHONE -
SYSTEM FEATURES
This system can control up to 10 devices, it may be any
electric or electronic appliances, and each device is given a
unique code.
There is no risk for false switching, it makes accurate
switching any false switching the device are not done.
This system doesn’t cost a lot of money, and it’s easy to
implement.
Before changing the state of the device we can confirm the
present status of the device.
The system gives an acknowledgement tone after switching
on the devices to confirm the status of the devices.
Its highly secured system using the white list programs on
the home-based phone to block any other call from
controlling the home appliances.
This system can be controlled by multi users, this feature
refer to user choice.
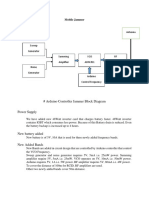
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
THE WHOLE SYSTEM CONSIST OF-
THE CONROL PHONE
HOME BASED PHONE
HOME CONTROLLER
A-DTMF Detection Unit
B- Device controlled unit
These unit consist of memory sub circuit like
Decoder, 4-16 line demultiplexer/decoder,
relay driver circuits and feedback circuitry.
DTMF DETECTION UNIT
The system is operated by an electronic device
which is based on dual tone multi frequency
(DTMF) technology.
In this technology, the cellular communication
network is used to control all electric devices
wirelessly. One has to send the command by
dialing through his cell phone. Then he can
easily control the electrical devices according
to his necessity.
Duel Tone Multi Frequency (DTMF) tone is
used to identify which key is pressed in the
keypad of cell phone. keypad is used as
password entry device.
Pressing any key generates an unique tone which consists
of two different frequencies one each of higher and lower
frequency range. Each of these tones is composed of two
pure sine waves of the low and high frequencies
superimposed on each
other.
To use the DTMF technology,
the DTMF decoder IC
(MT8870) is used. The
decoder circuit filters the
signal sent by the users and
gives the output.
Keypad of cell phone with 12 keys and
frequencies (Hz)
The hardware of the proposed system
Circuit diagram of DTMF decoder
METHODOLOGY
The control of the electric devices of home is
monitored by the user through his cell phone.
Another cell phone is needed in the controlling
device.
So first one has to give a call to the cell phone
near to the controlling device. This signal is
received by the 3.5mm headphone jack
connected with that cell phone.
When the user presses any key of his cell phone, the
DTMF tone corresponding to that key is passed to
the DTMF decoder circuit through the headphone
jack. The DTMF decoder circuit filters the signal
and gives the output to the microcontroller. There
are four outputs which are denoted by Q1, Q2, Q3
and Q4
The respective DTMF data into BCD digits
F low F high Key Q4 Q3 Q2 Q1
697 1209 1 0 0 0 1
697 1336 2 0 0 1 0
697 1477 3 0 0 1 1
770 1209 4 0 1 0 0
770 1336 5 0 1 0 1
770 1477 6 0 1 1 0
852 1209 7 0 1 1 1
852 1336 8 1 0 0 0
852 1477 9 1 0 0 1
941 1209 0 1 0 1 0
941 1336 * 1 0 1 1
941 1477 # 1 1 0 0
697 1633 A 1 1 0 1
770 1633 B 1 1 1 0
852 1633 C 1 1 1 1
941 1633 D 0 0 0 0
Continues………
Now these outputs are sent the control Unit
according to the key pressed by the user.
micro-controller then sends the voltage to the
relay. By this relay is being switched and drives
the different kinds of electric devices.
Relay is used in this circuit because it can drive
the high voltage devices also. So all kind of
electrical devices which are used by the people
at home can be easily controlled by this
electronic controlling device.
Complete set up
Advantages
Utilization Of Electrical power.
Power Conservation.
Design is small and portable.
Easy to use.
Economical.
limitation -
• The receiver must reside where sufficient
signal can be received from a cellular phone
network.
• The receiver must have a power source
attached at all times.
CONCLUSION
It is simple to control the operation of any where
appliances by exploiting the existing mobile network, i.e.
it’s not necessary to install a specific network.
Any type of mobiles can do the job.
The control circuit is reliable and simple to build.
The system is secure, by black listing all the call
number except that of the specific users (installed in
the white list).
The system can let the user know the status of the
appliances, before and after the switching.
The system is implemented practically and the
expected results are obtained.
Some practical problems are encountered during the
realization of the practical implementation and are
solved using the substitution component.
Future works
In this system we did not use any applications on
the control mobile, so for a future work it will be
useful to develop programs for the mobile devices
to give more control options and security control.
As a future work in the field of the presented
project, we suggest to develop the system using
PLCs or Microcontrollers instead of the control
unit, to give more reliability and control options, as
temperature control, security and more
computational work so the system can do more
than just turn On/Off the devices.
References-
Fathia H. A. Salem, A Design of a Home Appliances
Control System using Cell phone & J2ME, A Thesis
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for
the Degree of Master of Science in Electrical and
Electronic Engineering, University of Garyounis, Benghazi-
Libya, 2008.
Sanjit K. Mitra, Digital Signal Processing, Second Edition,
McGraw-Hill, University of California, International
Edition, 2002.
Sen M Kuo, Bob H Lee, Wenshun Tian, Real-Time Digital
Signal Processing Implementations and Applications,
Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2006.
www.datasheetcatalog.com
Gunter Schmer, DTMF Tone Generation and Detection: An
Implementation Using the TMS320C54x, Application Report,
Texas Instrument, May 2000
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Variable Power Supply With Digital ControlDocumento15 pagineVariable Power Supply With Digital ControlSubhash Bajaj100% (1)
- Corona2Inspect TranscriptDocumento6 pagineCorona2Inspect TranscripttrashbinfoodieNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Level IndicatorDocumento7 pagineWater Level IndicatorAnuj DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- FM JammerDocumento13 pagineFM JammerKumar R Ranjan100% (3)
- Cell Phone DetectorDocumento5 pagineCell Phone DetectorLarry DanganNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide Crystal Tester Frequency Counter enDocumento5 pagineGuide Crystal Tester Frequency Counter enSetiawan AR100% (1)
- RF Controlled ApplianceDocumento14 pagineRF Controlled ApplianceNEX456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gregg College Keyboarding Document Processing (GDP) Lessons 1-60Documento321 pagineGregg College Keyboarding Document Processing (GDP) Lessons 1-60Charmainne Kathlene Arellano100% (3)
- Siemens OptiPoint 500 Handset User GuideDocumento125 pagineSiemens OptiPoint 500 Handset User GuideMarcin MiechowiakNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple FM Radio Jammer CircuitDocumento2 pagineSimple FM Radio Jammer CircuitMajid Mehmood0% (1)
- Mobile Jammer Circuit: Project Report OnDocumento6 pagineMobile Jammer Circuit: Project Report OnSaurabh ChardeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellphone JammerDocumento3 pagineCellphone Jammerneek4uNessuna valutazione finora
- EMP-2000 Main Board User's Manual: - IndexDocumento61 pagineEMP-2000 Main Board User's Manual: - IndexMamadou djibril Ba100% (1)
- Rfid Based Voting MachineDocumento91 pagineRfid Based Voting MachineRakesh kumar100% (1)
- Simple GSM JammerDocumento7 pagineSimple GSM JammerDalia M-aNessuna valutazione finora
- Spin Valve TransistorDocumento22 pagineSpin Valve Transistorbvenugopal_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Documento10 pagineWifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Sathwik YadalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Scrap Collecting RobotDocumento53 pagineScrap Collecting Robotkumarravishankar100% (3)
- Wireless DoorbellDocumento8 pagineWireless DoorbellnicklingatongNessuna valutazione finora
- TV Remote JammerDocumento8 pagineTV Remote JammerSantosh NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- LaserSec: Laser Security Built With ArduinoDocumento3 pagineLaserSec: Laser Security Built With ArduinoRave ArevaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Full ReportDocumento47 pagineFull ReportSanjivee SachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Antenna Full ReportDocumento9 pagineSmart Antenna Full ReportPriyanka Kushwaha100% (1)
- Cell Phone DetectorDocumento20 pagineCell Phone DetectorsubhajitNessuna valutazione finora
- Black Book 3Documento34 pagineBlack Book 3Nguyễn ThànhNessuna valutazione finora
- GBPPR Active Denial SystemDocumento30 pagineGBPPR Active Denial SystemRobert EckardtNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16 - Digital CMOS CircuitsDocumento27 pagineChapter 16 - Digital CMOS CircuitsPrabhakar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- TCL Series Solid State Tesla CoilDocumento20 pagineTCL Series Solid State Tesla CoilNayanka SpringerNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI-Signal GeneratorsDocumento7 pagineEMI-Signal GeneratorsVineela ThonduriNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Awesome Auto Projects For The Evil Genius.9780071458238.43450Documento11 pagine50 Awesome Auto Projects For The Evil Genius.9780071458238.43450cristi_pet4742Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Project Mobile Bug....Documento18 pagineMini Project Mobile Bug....Sambhu RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 5Documento12 pagineChap 5Ayman Younis0% (1)
- RFID and GSM Based Advanced Vehicle Parking Slot Booking SystemDocumento3 pagineRFID and GSM Based Advanced Vehicle Parking Slot Booking SystemVidhyadhar Kasukurthi100% (1)
- Web Catalog 2006Documento32 pagineWeb Catalog 2006scribedeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Xcell Dynamic Imei User ManualDocumento13 pagineXcell Dynamic Imei User ManualaodvNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Security System For Smart Home Applications PDFDocumento6 pagineA Review of Security System For Smart Home Applications PDFEmin KültürelNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated File - Mobile Jammer 31082017Documento4 pagineUpdated File - Mobile Jammer 31082017Amol SarodeNessuna valutazione finora
- System Control Secret CodeDocumento1 paginaSystem Control Secret Codemudassir2640Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: A Six Week Training and Project Report OnDocumento35 pagine8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: A Six Week Training and Project Report OnsnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project PPT 1Documento11 pagineProject PPT 1Mahesh ShendeNessuna valutazione finora
- Jammer ReportDocumento81 pagineJammer Reportbharathimmk100% (1)
- Diamond Security System in A Museum With Loud 60dB SireN1Documento50 pagineDiamond Security System in A Museum With Loud 60dB SireN1Midde ShekarNessuna valutazione finora
- FM TransmitterDocumento24 pagineFM Transmitterrethunkb5548100% (2)
- Report - RFid Based Security SystemDocumento46 pagineReport - RFid Based Security SystemDhaval Rana50% (6)
- Sniffer For Lost Mobile Phones: Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocumento18 pagineSniffer For Lost Mobile Phones: Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDEDIPYA HANUMANOLA100% (1)
- Laser Security System: A Mini Project ONDocumento11 pagineLaser Security System: A Mini Project ONRama KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started With The Internet of Things (IoT) Using The Texas Instruments CC3200Documento55 pagineGetting Started With The Internet of Things (IoT) Using The Texas Instruments CC3200Kunal Khandelwal100% (1)
- Formatting and Baseband ModulationDocumento16 pagineFormatting and Baseband Modulationlongyeuhuong50% (2)
- IEEE Research PAPER On Cell Phone JammerDocumento2 pagineIEEE Research PAPER On Cell Phone JammerAkshay JayantNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplificator Chitara 60WDocumento5 pagineAmplificator Chitara 60WMărian IoanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Phone Charger ReportDocumento16 pagineMobile Phone Charger ReportVarun Khanna100% (3)
- Field Strength MeterDocumento9 pagineField Strength MeterVinod JagdaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Various Sensors TutorialsDocumento7 pagineVarious Sensors TutorialsJostin PunnasseryNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1: 1.1 ObjectivesDocumento37 pagineChapter - 1: 1.1 ObjectivesmohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Microcontroller Based Vehicle Security SystemDocumento67 pagineMicrocontroller Based Vehicle Security Systemlokesh_045Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Controlled Electrical ApplianceDocumento17 pagineMobile Controlled Electrical ApplianceSmile AravindNessuna valutazione finora
- Device Control Using Telephone: Nagabhooshan S. ShetDocumento15 pagineDevice Control Using Telephone: Nagabhooshan S. ShetNicholas TaliNessuna valutazione finora
- DTMF Based Home AutomationDocumento28 pagineDTMF Based Home AutomationRenjith RavikumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of ProjectDocumento14 pagineOverview of ProjectdbpalNessuna valutazione finora
- HOME AUTOMATION Control System USING DTMFDocumento27 pagineHOME AUTOMATION Control System USING DTMFdixant tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- SynopsisDocumento3 pagineSynopsisRudra Pratap SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- UP TGT PGT Heat and Thermodynamics TEST SERIESDocumento161 pagineUP TGT PGT Heat and Thermodynamics TEST SERIESSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- GravitationDocumento6 pagineGravitationSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in Straight LineDocumento28 pagineMotion in Straight LineSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Htet 2018 PGT PhysicsDocumento19 pagineHtet 2018 PGT PhysicsSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat & Thermodynamics PDFDocumento10 pagineHeat & Thermodynamics PDFSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospherechemistry 161203132228Documento20 pagineAtmospherechemistry 161203132228Suresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Htet PGT 2017 PhysicsDocumento16 pagineHtet PGT 2017 PhysicsSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- SSJ Campus Almora, Kumaun University: Nanotechnology and Its ApplicationDocumento24 pagineSSJ Campus Almora, Kumaun University: Nanotechnology and Its ApplicationSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Mass-Media in Education in IndiaDocumento21 pagineRole of Mass-Media in Education in IndiaSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Media PPT and PDF ForDocumento8 pagineMass Media PPT and PDF ForSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Cycle of SelaginellaDocumento6 pagineLife Cycle of SelaginellaSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Gamma Ray Spectroscopy by Suresh ShahDocumento19 pagineGamma Ray Spectroscopy by Suresh ShahSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Name Nida Afzal KhanDocumento23 pagineName Nida Afzal KhanSuresh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Phone Operated Land Rover SynopsisDocumento13 pagineCell Phone Operated Land Rover SynopsiscatkatiyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of A TelephoneDocumento9 pagineMechanism of A TelephoneRhix UmlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Yap Jack Plus User GuideDocumento94 pagineYap Jack Plus User GuidemohkkkNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Manual: PC1616 / PC1832 / PC1864Documento68 pagineReference Manual: PC1616 / PC1832 / PC1864bfahmed1100% (2)
- IP Phone Cisco 7942 - User GuideDocumento16 pagineIP Phone Cisco 7942 - User GuideerasmodarotterdamNessuna valutazione finora
- SV9100 Quick ReferenceDocumento3 pagineSV9100 Quick ReferenceMichael JordanNessuna valutazione finora
- Karel Telefon Santrali MS48-ProgDocumento102 pagineKarel Telefon Santrali MS48-ProgÖmer AvcıNessuna valutazione finora
- Fältcom ECII Flex: ManualDocumento41 pagineFältcom ECII Flex: ManualMohamed HajjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellphone Based DTMF Load Controlled SystemDocumento14 pagineCellphone Based DTMF Load Controlled SystemSHIREESHA.RNessuna valutazione finora
- Argus Monitoring Prototype ASecurity Sentry Support NCITE2015Documento13 pagineArgus Monitoring Prototype ASecurity Sentry Support NCITE2015Gourvankit singh BhatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Manual FOR Model Wpp-531-Fd AND Model Ssp-511-Fd: Hands Free Weatherproof TelephoneDocumento21 pagineService Manual FOR Model Wpp-531-Fd AND Model Ssp-511-Fd: Hands Free Weatherproof TelephonePayphone.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Dual Tone Multi Frequency (DTMF) Signal Generation and DetectionDocumento7 pagineDual Tone Multi Frequency (DTMF) Signal Generation and DetectionDaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lil Buttie Prof Telephone Test Set User'S GuideDocumento36 pagineLil Buttie Prof Telephone Test Set User'S GuideJason CosbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Psoc DTMF Detection PDFDocumento16 paginePsoc DTMF Detection PDFCarlos OzunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Informer-IP Series C: Setup, Program, and User ManualDocumento102 pagineInformer-IP Series C: Setup, Program, and User ManualRagdex RockNessuna valutazione finora
- University of The East - Caloocan College of Engineering: Experiment # 3: Tone DialingDocumento5 pagineUniversity of The East - Caloocan College of Engineering: Experiment # 3: Tone DialingJerick CulabresNessuna valutazione finora
- 236 InstallDocumento28 pagine236 InstallCarlos MaldonadoNessuna valutazione finora
- AMZ Motorola CP200 Radio XLS SpecsDocumento2 pagineAMZ Motorola CP200 Radio XLS SpecsAmerizon WirelessNessuna valutazione finora
- DTMF Decoder WorkingDocumento5 pagineDTMF Decoder WorkingRahul SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- DTMF Based DC Fan ControllerDocumento60 pagineDTMF Based DC Fan ControllerShanksSharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual OpenStage 15 T HP3000-HP5000Documento113 pagineUser Manual OpenStage 15 T HP3000-HP5000casamentoNessuna valutazione finora
- User-Interface Design For Embedded SystemsDocumento12 pagineUser-Interface Design For Embedded SystemsHeriberto AguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- Yaesu FT-1900R Operating ManualDocumento90 pagineYaesu FT-1900R Operating ManualpaknuxNessuna valutazione finora
- TIF-2000A User ManualDocumento24 pagineTIF-2000A User Manualanubis23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teleservicio Orona - Es.enDocumento13 pagineTeleservicio Orona - Es.enamcneelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome: C115.CG - Book Page 1 Friday, June 25, 2004 3:23 PMDocumento69 pagineWelcome: C115.CG - Book Page 1 Friday, June 25, 2004 3:23 PMsgtmarconNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposal Title: Cell Phone Controlled Vehicle Using DTMFDocumento34 pagineProposal Title: Cell Phone Controlled Vehicle Using DTMFFìrœ Lōv MånNessuna valutazione finora
- Dvi-300 S User's Guide (Doc0499) r01-001Documento14 pagineDvi-300 S User's Guide (Doc0499) r01-001trungdungtb73Nessuna valutazione finora