Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Concept of Logistics
Caricato da
Soham100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
46 visualizzazioni38 pagineLogistics involves managing the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It includes transportation, inventory management, warehousing and integrating information across the supply chain. The goal is to meet customer needs by delivering the right products to the right place at the right time in a cost-effective manner. Effective logistics is important for supply chain management as it facilitates the movement of materials between organizations and adds value for customers.
Descrizione originale:
Supply Chain Management Module 1
Titolo originale
M-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoLogistics involves managing the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It includes transportation, inventory management, warehousing and integrating information across the supply chain. The goal is to meet customer needs by delivering the right products to the right place at the right time in a cost-effective manner. Effective logistics is important for supply chain management as it facilitates the movement of materials between organizations and adds value for customers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
46 visualizzazioni38 pagineConcept of Logistics
Caricato da
SohamLogistics involves managing the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It includes transportation, inventory management, warehousing and integrating information across the supply chain. The goal is to meet customer needs by delivering the right products to the right place at the right time in a cost-effective manner. Effective logistics is important for supply chain management as it facilitates the movement of materials between organizations and adds value for customers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 38
Concept Of Logistics
• Logistics is all about providing the right
products/services at the right place and at the
right time.
• Logistics is concerned with getting products and
services where they are needed and when they
are desired.
• Logistics involves the integration of information,
transportation, inventory, warehousing, materials
handling and packaging.
Concept Of Logistics
• Logistical processes facilitates the flow of
materials from suppliers to the manufacturing
firms and the distribution of finished product
through marketing channels to the end
consumers.
• The complexity of logistics increases with the
number of industrial manufacturers, suppliers
and the channel intermediaries both in the
national scene as well as the global scenario.
Definitions of Logistics
• Logistics is defined as the process of
anticipating consumer needs and wants,
acquiring the capital, materials, people,
technologies and information necessary to
meet those needs and wants, optimizing
the goods or service ---- providing network
to customer requests and utilizing the
network to fulfill customer requests in a
timely manner.
Definitions of Logistics
• Logistics management is the process of
planning, implementing and controlling the
efficient, effective flow and storage of goods,
services and related information from point of
origin to point of consumption for the purpose of
conforming to customer requirements.
• Logistics management is also concerned with
the disposal and recycling / reuse of the
products.
• Logistics management adds value by creating
time utility and place utility.
Definitions of Logistics
• Logistics management is that part of
supply chain management that plans,
implements and controls the efficient and
effective forward and reverse flow and
storage of goods, services and related
information between the point of origin and
the point of consumption in order to meet
customer’s requirements (definition of
Council of Logistics Management).
Definitions of Logistics
• Logistics management activities include
inbound and outbound transportation
management, fleet management,
warehousing, materials handling , order
fulfillment, logistics network design,
inventory management, supply / demand
planning and management of third party
logistics service providers.
Scope and Importance of Logistics
• Logistics is not confined to manufacturing
operations alone. It is relevant to all types of
enterprises including government departments,
hospitals, universities, banks, financial service
institutions, wholesalers and retailers.
• Logistics includes cross functional co-ordination
activities. It co-ordinates the functions of
materials management, production planning and
control and physical distribution management
including finished goods inventory and selection
of transportation suppliers.
Scope and Importance of Logistics
• Logistics expenditure accounts to about 10% of the
GNP of the country.
• For individual firms, the expenditure may range from
5% to 35% of the sales depending on the type of
business, geographical area of operation and
weight/value ratio of products and materials.
• In manufacturing organizations, the activities such as
materials planning, purchasing, stores and inventory
control are centralized under materials management
and distribution of finished goods is done by
marketing department.
Components of Logistics
Management
Objectives of Logistics
Management
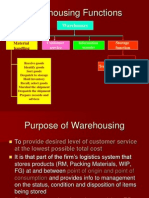
• Effectively and efficiently move the inventory in
the supply chain in order to extend the desired
level of customer service at the least possible
cost.
• Ensuring minimum or no damage to products
during transportation and storage.
• Ensuring quick response to customer
requirements.
• Achieve maximum economy in freight costs.
• Achieve consistent delivery performance.
• Building long term customer relationship.
Logistics Activities
1. Transportation – physical movement or
flow of goods through various modes.
2. Storage – proper storage and
preservation of goods.
3. Packaging – to protect the goods from
damage during transportation.
4. Materials handling – handling the
materials as it moves from storage to
packing and shipping areas.
Logistics Activities
5. Order fulfillment – reducing the delivery
lead time to the minimum and complete
the customer orders in time.
6. Inventory forecasting – accurate
forecasting of materials requirement.
7. Production planning – determining the
quantity to be produced to meet market
demand.
Logistics Activities
8. Purchasing – procurement of the
materials from the suppliers.
9. Customer service – decisions about
product availability and inventory lead
time are critical to customer service.
10. Site location – deciding the location of a
plant or a warehouse to minimize costs
of transportation.
Role of Logistics in Supply Chain
Management
• A supply chain refers to the way that materials
flow through different organizations, starting with
raw materials and ending with finished products
delivery to the ultimate consumer.
• Supply chain management can be viewed as a
pipeline or conduit for efficient and effective flow
of materials, services, information & money from
suppliers’ suppliers through the various
intermediate organizations to the customers’
customers.
Role of Logistics in Supply Chain
Management
• Supply chain management represents a logical
extension of the logistics concept and it is also
known as demand network management, value
chain management etc.
• The inbound and outbound logistics are primary
components of the value chain, that is
contributing value to the firm’s customers and
thereby making the firm financially viable.
• The inbound logistics involves transportation of
raw materials and components from suppliers to
the firm.
• The outbound logistics involves physical
distribution of finished goods.
Supply Chain & Value Chain
Logistics Costs
1. Cost of lost sales – the cost trade-off resulting
from varying levels of customer service is the
cost of lost sales.
2. Cost of customer service – expenses for
customer service support includes the costs of
order fulfillment, parts and service support and
costs of return goods handling.
3. Transportation costs – these vary with volume
of shipment, weight of shipment, distance
between point of origin and destination, mode
of transportation.
Logistics Costs
4. Warehousing costs – costs incurred for
storage activities.
5. Order processing costs – includes costs of
order transmission, order entry, order
processing etc.
6. Lot quantity costs – due to procurement /
production in lot quantities. These include (a)
setup costs (b) loss in capacity (c ) material
handling costs (d) price differentials (e) order
placement & follow up.
Logistics Costs
7. Inventory carrying costs – this is made up of
(a) capital costs or opportunity costs (b)
inventory service costs i.e. insurance and
taxes (c ) storage space costs (d) inventory
risk cost i.e. obsolescence, pilferage, damage
etc.
8. Total costs – effective logistics management
has the goal of reducing the total cost of
logistics rather than merely focusing on each
cost in isolation.
Integrated Logistics Management
• Involves managing the movement of raw
materials and components from sources of
supply to the manufacturing plant and the
movement of the finished goods from the
manufacturing plant to the warehouses or
to the retailers or to the final consumer.
• The network of relationships to be
managed by logistics can be explained
through a diagram.
Integrated Logistics Management
Systems Approach
• All functions or activities need to be understood
in terms of how they affect or are affected by
other elements or activities with which they
interact.
• Systems analysis views how specific functions
can be combined to create a whole that is
greater than the sum of the individual parts or
functions.
• Such a holistic approach stimulates a synergistic
relationship between the individual parts of a
system.
Systems Approach
• For e.g., even though it is desirable to
have high inventory levels to fulfill
customer orders, it also increases storage
costs as well as the risk of obsolescence.
Hence the necessity to trade-off the
unfavorable factors with the favorable
aspects before deciding the optimum
inventory levels.
Integrated Logistics
• The process of anticipating customer
needs and wants, acquiring the capital,
materials, people, technologies and
information necessary to meet those
needs, optimizing the goods or service i.e.
producing a network to fulfill customer
requests and utilizing the network to fulfill
customer requirements in a timely manner.
Integrated Logistics
• Integrated logistics is a service oriented
process. It supports marketing and
production. Even if the advertising
campaign and the salesforce are efficient,
marketing cannot fill customer orders
without integrated logistics. Even if the
products are produced in time, if they can
not be moved efficiently the purpose is not
met.
Integrated Logistics Information
Requirements
1. Inventory flow – information on the movement
of materials right from the initial shipment from
the supplier till the delivery of finished goods to
the customer.
2. Logistical operations – three areas
a. Physical distribution – linking manufacturers,
wholesalers & retailers to provide product
availability.
b. Manufacturing support – managing WIP, help
in formulation of MPS.
c. Procurement – co-ordination with suppliers.
Integrated Logistics Information
Requirements
3. Information flow – integrates the three
operating areas i.e. physical distribution,
manufacturing support and procurement.
Information facilitates co-ordination of
planning and control in day-to-day
operations. In the absence of
information, there will be wastage of
effort in the logistics system.
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• An ILIS can be defined as the involvement
of people, equipment and procedures
required to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate
and then distribute needed information to
the appropriate decision maker in a timely
and accurate manner so that they can
make quality logistics decisions.
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• ILIS is all about:
1. Getting the right information
2. Keeping the information accurate
3. Communicating the information effectively
• Components of ILIS:
1. Order processing system
2. Research and intelligence system
3. Decision support system
4. Reports and output system
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Order processing system has direct impact on
the customer
• Research and intelligence systems scans and
monitors both the internal and external
environment. It covers (1) the integration of
logistics planning with overall corporate planning
(2) the management of interface with other
functions (3) strategic options for organization
and staffing (4) integration of information
technologies (5) make or buy decisions (6)
emphasis on productivity and quality
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Decision support systems (DSS) – provide
solutions to complex logistics problems
making use of analytical modelling. It
consists of (1) basic file of internal &
external data (2) critical factor data file
which defines the scope of decision
making (3) policy and parameter data files
for each functional area (4) solution file of
past analysis results which are compared
against future analyses.
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Reports and output system – planning outputs
include sales trends, economic forecasts and
other information pertaining to market place.
• Operating reports are useful for inventory
control, transportation scheduling and routing,
purchasing and production scheduling.
• Control reports are used to analyze expenses,
budgets & performance.
Integrated Logistics Information System (ILIS)
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Electronic data interchange (EDI) – it is
the electronic transfer of standard
business documents between
organizations. EDI is used extensively in
ILIS to enhance the breadth, timeliness &
quality of data. EDI transmissions allow a
development to be directly processed and
acted upon by the organization which
receives the information.
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Advantages of EDI:
1. Cost reduction
2. Increased productivity
3. Faster order cycle times
4. Better customer focus
5. Reduced clerical work
6. Reduced paper and postage
7. Better working relationships with partners
8. Means to achieve a competitive advantage
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Artificial intelligence (AI) – it is concerned
with the concept and methods of inference
by a computer and the symbolic
representation of the knowledge used in
making inferences.
• AI includes a number of areas such as
computer aided instruction, voice
synthesis and recognition, robotics etc.
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Artificial intelligence is used in logistics
management to:
1. Model response time requirements for
customer delivery
2. Model transportation cost and time for various
transportation modes and routings
3. Determine which warehouses should serve
which plants and which products
4. Model customer service response with various
levels of reliability
Integrated Logistics Information
System (ILIS)
• Expert systems (ES) – an expert system is a
computer program which uses knowledge and
reasoning techniques to solve problems
normally requiring the abilities of human experts.
• An expert system is an artificial intelligence
program which achieves competence in
performing specialized tasks by reasoning with
a body of knowledge about the task and the task
domain.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Logistics ManagementDocumento32 pagineLogistics ManagementPrashanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics AnswersDocumento23 pagineLogistics AnswersSagar NankaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Dr. Abhijeet ChatterjeeDocumento50 pagineLogistics and Supply Chain Management: Dr. Abhijeet Chatterjeechaterji_aNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics MGTDocumento28 pagineLogistics MGTJanmejai Bhargava100% (2)
- 305 OSCM - Logistics Management Unit-1Documento63 pagine305 OSCM - Logistics Management Unit-1Shil ShambharkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics ManagementDocumento50 pagineLogistics ManagementOlawaleAbolarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics Management-Unit2 CompleteDocumento93 pagineLogistics Management-Unit2 CompleteVasanthi Donthi100% (1)
- Unit 1logistics ManagementDocumento13 pagineUnit 1logistics ManagementSidhu boiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1 Introduction To Logistics ManagementDocumento38 pagineChapter - 1 Introduction To Logistics ManagementShruti100% (1)
- Logistics - Unit 1Documento34 pagineLogistics - Unit 1etiNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics NotesDocumento18 pagineLogistics NotesRadha Raman SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistic Management: Unit 3Documento23 pagineLogistic Management: Unit 3Akhil CrastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To LogisticsDocumento38 pagineIntroduction To LogisticsVivekanand SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 Different Types of Logistics ManagementDocumento21 pagine1.4 Different Types of Logistics ManagementLara Camille CelestialNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventory ManagementDocumento38 pagineInventory ManagementMckarey RobinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Logistics Management Module 5Documento33 pagineIntroduction To Logistics Management Module 5Kyle SikorskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Course PowerpointDocumento58 pagineCourse Powerpointmoges lakeNessuna valutazione finora
- SCM SummaryDocumento47 pagineSCM SummaryEmanuelle BakuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro of Supply Chain Management Lecture 1Documento20 pagineIntro of Supply Chain Management Lecture 1Syeda SidraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Inventory ManagementDocumento17 pagineUnit 1 - Introduction To Inventory ManagementNguyễn Thành NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Components of Logistics Management: Supportive Component: ProcurementDocumento2 pagineComponents of Logistics Management: Supportive Component: ProcurementNaveen KaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Role of Logistics in Supply Chains Learning ObjectivesDocumento13 pagineChapter 2 Role of Logistics in Supply Chains Learning ObjectivesAshik AlahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic of Logistics Management - 1553484948 PDFDocumento34 pagineBasic of Logistics Management - 1553484948 PDFManoj Kuchipudi100% (1)
- SCM ProcessesDocumento20 pagineSCM ProcessesVishnu Kumar S100% (1)
- Introduction To Supply Chain Management: Syed Tabish Hussain Iqra UniversityDocumento54 pagineIntroduction To Supply Chain Management: Syed Tabish Hussain Iqra UniversityfarahsayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations and Warehouse ManagementDocumento3 pagineOperations and Warehouse ManagementJaiprakash RajpurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics ManagementDocumento3 pagineLogistics ManagementSUNIL DUTTNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics ManagementDocumento16 pagineLogistics ManagementsmtbnmNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistical Interfaces With ProcurementDocumento7 pagineLogistical Interfaces With ProcurementJaymark CasingcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Warehouse FunctionsDocumento27 pagineWarehouse FunctionsSheila Ibay VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- SCM - Chapter 01Documento68 pagineSCM - Chapter 01Talha6775Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Supply Chain Integration CollaborationDocumento42 pagine3 - Supply Chain Integration CollaborationKumar Gaurab Jha0% (2)
- UNIT 1 LogisticsDocumento10 pagineUNIT 1 Logisticsanon_124527471Nessuna valutazione finora
- Defining Purchasing, Procurement, Supply Management, Materials Management & SCMDocumento34 pagineDefining Purchasing, Procurement, Supply Management, Materials Management & SCMaharish_iitkNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics Supply Chain StrategyDocumento27 pagineLogistics Supply Chain StrategymuhibNessuna valutazione finora
- Material ManagementDocumento38 pagineMaterial ManagementanushavergheseNessuna valutazione finora
- ConclusionDocumento2 pagineConclusionMuthu Kumaran100% (1)
- Definition of LogisticsDocumento44 pagineDefinition of LogisticsPooja TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Ba 5025 Logistics Management Notes - Compress PDFDocumento96 paginePDF Ba 5025 Logistics Management Notes - Compress PDFUdayanidhi RNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment LogisticsDocumento9 pagineAssignment LogisticsArham Orb100% (1)
- Designing Distribution Network: in A Supply ChainDocumento55 pagineDesigning Distribution Network: in A Supply ChainShambhavi AryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Logistics ManagementDocumento27 pagineIntroduction To Logistics ManagementFaisal Tanwar100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management - An Overview - RGDocumento71 pagineSupply Chain Management - An Overview - RGprakashinaibs100% (2)
- 1 - Business Functions, Processes and Data RequirementsDocumento64 pagine1 - Business Functions, Processes and Data Requirementsugurum668Nessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted To: Submitted byDocumento18 pagineSubmitted To: Submitted byRohit Patel100% (2)
- Inventory MGTDocumento35 pagineInventory MGTPankaj Agrawal100% (1)
- Inventory ManagementDocumento14 pagineInventory ManagementEoin Ornido100% (2)
- Module 1 Introduction To Logistics PDFDocumento49 pagineModule 1 Introduction To Logistics PDFChispa BoomNessuna valutazione finora
- L8 Logistics ManagementDocumento41 pagineL8 Logistics ManagementShahmien SevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Role of Logistics in Supply ChainsDocumento37 pagineChapter 2 - Role of Logistics in Supply ChainsArman100% (7)
- Elements of Logistics Management NotesDocumento59 pagineElements of Logistics Management Notesaksr27100% (5)
- Inventory ManagementDocumento7 pagineInventory ManagementSozo Net WorkNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Between Logistics and Supply ChainDocumento3 pagineDifferences Between Logistics and Supply ChainNikhil BhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 01 Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementDocumento30 pagineCH 01 Introduction To Supply Chain Managementgadde bharatNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics ManagementDocumento167 pagineLogistics Managementakaash023100% (1)
- Chapter 21Documento19 pagineChapter 21Fire BoltNessuna valutazione finora
- L3 Fundamentals of LogisticsDocumento40 pagineL3 Fundamentals of LogisticsDu Lich Vung TauNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated LogisticsDocumento9 pagineIntegrated Logisticsyuktim100% (2)
- 2 Logistics in SCM 1Documento29 pagine2 Logistics in SCM 1Khai Wen OnexoxNessuna valutazione finora
- FintechDocumento2 pagineFintechSohamNessuna valutazione finora
- Zara: IT For Fast Fashion: Soham Dakhole ISM 24148Documento11 pagineZara: IT For Fast Fashion: Soham Dakhole ISM 24148SohamNessuna valutazione finora
- Automobile SectorDocumento2 pagineAutomobile SectorSohamNessuna valutazione finora
- Zara 24148 SohamDocumento11 pagineZara 24148 SohamSohamNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspiring Entrepreneur: Individual Assignment 1Documento2 pagineInspiring Entrepreneur: Individual Assignment 1SohamNessuna valutazione finora
- 3M Post It: Soham Dakhole 24148Documento2 pagine3M Post It: Soham Dakhole 24148SohamNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcon IncDocumento44 pagineAlcon IncDanilo Avalos100% (1)
- Business Intelligence BrochureDocumento12 pagineBusiness Intelligence BrochuregvozdokNessuna valutazione finora
- Foodworld NewDocumento4 pagineFoodworld NewS Vidya LakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Warehouse CV1Documento1 paginaWarehouse CV1Curtis KimberlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Assignment 2Documento9 pagineSupply Assignment 2yasarinuNessuna valutazione finora
- CEBA-IARW Design Maintenance Modernization Guide - 2018 Update - FINALDocumento402 pagineCEBA-IARW Design Maintenance Modernization Guide - 2018 Update - FINALEduardo Depiné TarnowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stores ManagementDocumento43 pagineStores Managementatul_gaikwad_967% (3)
- Inventory Management-UssDocumento66 pagineInventory Management-UssShahid SyedNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 12 Case Study-Home Style CookiesDocumento3 pagineAssignment 12 Case Study-Home Style CookiesFish de Paie100% (2)
- Logistics Management, 3e Author: Vinod V. SopleDocumento15 pagineLogistics Management, 3e Author: Vinod V. Soplenithish patkarNessuna valutazione finora
- JLL Future of LogisticsDocumento8 pagineJLL Future of LogisticsAnirban DasguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Port Pricing PDFDocumento86 paginePort Pricing PDFMw. MustolihNessuna valutazione finora
- Ome752 - SCM Unit IDocumento51 pagineOme752 - SCM Unit IlingeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Distribution Channel of LGDocumento3 pagineDistribution Channel of LGBadal BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3PL-Billing Functionality-Oracle WMS Cloud PDFDocumento16 pagine3PL-Billing Functionality-Oracle WMS Cloud PDFAnthonyStraussNessuna valutazione finora
- International Inventory Issues, Packaging Issues, Storage Issues & OthersDocumento5 pagineInternational Inventory Issues, Packaging Issues, Storage Issues & OthersAnuranjanSinha100% (4)
- Value Proposition - Marketing Assignment - Parimal Bobade-1Documento4 pagineValue Proposition - Marketing Assignment - Parimal Bobade-1Parimal bobadeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1DB - Inbound of Batch-Managed Products From Vendor 1/3: Vendor Purchaser System Warehouse ClerkDocumento3 pagine1DB - Inbound of Batch-Managed Products From Vendor 1/3: Vendor Purchaser System Warehouse ClerkminhasajayNessuna valutazione finora
- 3PLDocumento42 pagine3PLsanjeev kumar100% (1)
- NetworkDocumento16 pagineNetworkavnish kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Presentation On LG and SamsungDocumento30 pagineSales Presentation On LG and SamsungasifkingkhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Group12 Ho Thi Thu Hoa Cold Storage Warehouse A Case For Fruit ProductsDocumento71 pagineGroup12 Ho Thi Thu Hoa Cold Storage Warehouse A Case For Fruit ProductsKhánh AnNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Process Modeling: Using Ibm Websphere Business ModelerDocumento46 pagineBusiness Process Modeling: Using Ibm Websphere Business ModelerAlfonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Warehouse Management System Literature ReviewDocumento7 pagineWarehouse Management System Literature Reviewzufehil0l0s2Nessuna valutazione finora
- case-study-Amazon.comDocumento8 paginecase-study-Amazon.comBaldeep Kaur100% (1)
- Lecture 7 - WAREHOUSING MANAGEMENTDocumento51 pagineLecture 7 - WAREHOUSING MANAGEMENTsamwel100% (1)
- Discussion QuestionsDocumento3 pagineDiscussion QuestionsGokul DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Compilation 2Documento105 pagineResearch Compilation 2angelicanulla423Nessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practice: Data Volume Management For RetailDocumento67 pagineBest Practice: Data Volume Management For Retaildri0510Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operations & Supply Chain Management (Unit 1)Documento43 pagineOperations & Supply Chain Management (Unit 1)Kiril IlievNessuna valutazione finora