Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basic Medical Wide QRS Arrhythmia
Caricato da
Jee Junpyo0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
20 visualizzazioni39 pagine123
Titolo originale
8. Basic Medical Wide QRS Arrhythmia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documento123
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
20 visualizzazioni39 pagineBasic Medical Wide QRS Arrhythmia
Caricato da
Jee Junpyo123
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 39
Wide QRS Tachycardia
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Definition
• Wide QRS tachycardia is tachycardia having a
QRS duration of > 120 milliseconds (ms).
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Mechanisms for Wide QRS
Tachycardia
• supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) with
aberrant conduction
• pre-excited tachycardia
• ventricular tachycardia (VT)
• pacemaker-mediated tachycardia
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Clinical Assessment
• History
- younger patient with recurrent tachycardia
favors SVT with aberrancy or pre-excited
tachycardia
- older patient with structural heart disease,
e.g. coronary disease, favors VT
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Clinical Assessment (con’t.)
• Physical examination
- hemodynamic status
- carotid sinus massage
- evidence of AV dissociation
• cannon A waves on jugular venous pulse
• variable intensity of the S1
• variability in systolic blood pressure
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
ECG Assessment
• obtain a previous ECG if available
• important clues to differentiate VT vs SVT
- AV dissociation
- fusion or capture beats
- QRS width
- QRS axis
- QRS regularity
- QRS concordance
- QRS morphology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
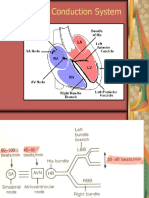
AV Dissociation
• independent atrial and ventricular
activation
• seen in 50% of patients with VT
• exceedingly rare in SVT
• best seen in leads V1 and inferior leads
• “Lewis” lead amplifies P waves
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Capture and Fusion Beats
• dissociated P wave totally (capture) or
partially (fusion) activates the ventricle in
advance of the next VT cycle.
• appears as a premature “narrow” QRS
complex during VT
• highly specific for VT
• infrequently seen
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Width
• consider VT if:
- RBBB pattern > 140 ms
- LBBB pattern > 160 ms
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Axis
• normal axis favors SVT
• left or right axis deviation favors VT
• extreme left or right axis deviation
(“northwest”) axis strongly favors VT
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Irregularity
• slight irregularity in the R - R interval
may be seen in SVT and VT
• marked irregularity of R - R interval
suggests atrial fibrillation conducted via
accessory pathway
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Concordance
• strongly favors VT
• positive concordance (positive QRS in V1
to V6) suggests posterobasal origin
• negative concordance (negative QRS in
V1 to V6) suggests anteroapical origin
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Morphology
• leads V1 and V6 most useful
• a very “typical” right or left bundle branch
block pattern is more likely to be SVT and a
very “atypical” pattern is more likely to be VT
• abrupt change from one QRS morphology to
another during regular tachycardia suggests
VT
• QRS morphology during tachycardia similar to
isolated PVC during sinus rhythm suggests VT
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Morphology Favoring
SVT
• RBBB morphology QRS
- triphasic pattern with rsR` or rR` in V1
- qRs in V6
• LBBB morphology QRS
- rS (r < 30 ms; rapid downslope of S) or QS
in V1
- monophasic R in V6
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
QRS Morphology Favoring VT
•RBBB morphology QRS
-monophasic or biphasic in V1; R > R’
-rS or QS in V6
•LBBB morphology QRS
-rightward axis
-broad R wave (> 40 ms); notching in the
downslope of the S wave in V1
-qR or QS in V1
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Ancilliary Investigations
• echocardiography
• esophageal ECG
• pharmacologic maneuver
- e.g., adenosine
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Therapy for Wide QRS
Tachycardia
• if patient is hemodynamically unstable, prompt
electrical cardioversion is indicated
• if patient is stable, and tachycardia mechanism
is uncertain, therapeutic trial with:
- adenosine
- procainamide
- lidocaine
- Cardioversion
• avoid verapamil unless VT has been ruled out
with certainty
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
When in doubt, the working
diagnosis is VT until proven
otherwise!
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
UP-PGH Section of Cardiology
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- How To: Read ECG?Documento63 pagineHow To: Read ECG?Let BNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Interpretation UnismaDocumento178 pagineECG Interpretation UnismadefinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication Error 2017Documento51 pagineMedication Error 2017Christina100% (1)
- Name: Abdirahman Sheikh Abdillahi Farah Faculty: Clinical Officers (CO8) Course: Pediatric Lecturer: DR Amin Assingment: Pleural EffusionDocumento46 pagineName: Abdirahman Sheikh Abdillahi Farah Faculty: Clinical Officers (CO8) Course: Pediatric Lecturer: DR Amin Assingment: Pleural EffusionAbdirahman Abdillahi FarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pleural Infection - Past, Present, and Future DirectionsDocumento15 paginePleural Infection - Past, Present, and Future DirectionsCamilo VidalNessuna valutazione finora
- Warfarin: Prof DR Shah MuradDocumento63 pagineWarfarin: Prof DR Shah Muradshahmurad653376Nessuna valutazione finora
- Screening and Early Detection: Epidemiological Basis For Disease Control - Fall 2001Documento28 pagineScreening and Early Detection: Epidemiological Basis For Disease Control - Fall 2001Kharisma Rizqiah WahyuniNessuna valutazione finora
- D01 Pink Floyd Shine On You Crazy DiamondDocumento1 paginaD01 Pink Floyd Shine On You Crazy Diamond박승길Nessuna valutazione finora
- Epi Confounding AssignmentDocumento4 pagineEpi Confounding Assignmentcharles100% (2)
- ECG Interpretations DR RPDocumento109 pagineECG Interpretations DR RPArnis Putri RosyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG 2 KidsDocumento72 pagineECG 2 KidsRonald Rey GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Ecg: in The Eyes of NURSEDocumento112 pagineBasic Ecg: in The Eyes of NURSESam jr TababaNessuna valutazione finora
- Warfarin Q and ADocumento40 pagineWarfarin Q and AAbdul-Rhman Hamdy KishkNessuna valutazione finora
- 11U Poetry Analysis Four LevelsDocumento1 pagina11U Poetry Analysis Four Levelsseiranhoj0901100% (1)
- PT InrDocumento3 paginePT InrJeniah Lerios OcsioNessuna valutazione finora
- Bundle Branch BlockDocumento37 pagineBundle Branch BlocksyukronchalimNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Due 13th JanDocumento9 pagine06 Due 13th JanWinson LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia ThrombocytopeniaDocumento12 pagineThrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia ThrombocytopeniaRashed ShatnawiNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Complete The Dialogue With These WordsDocumento19 pagineA. Complete The Dialogue With These WordsAnaMariaRamirezNavarrete100% (1)
- Basic Clinical UrologyDocumento7 pagineBasic Clinical Urologyreza sakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg BSTDocumento204 pagineEcg BSTAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Vascular Surgery TNDocumento4 pagineVascular Surgery TNVictor Matias BarriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Textbook Reference-Unit VI (p449) : Part 1 of 3Documento53 pagineTextbook Reference-Unit VI (p449) : Part 1 of 3glenn johnstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento25 pagineDiabetes MellitusjljoioiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidural Analgesia - A Self-Directed Learning Module 3rdDocumento41 pagineEpidural Analgesia - A Self-Directed Learning Module 3rdAnnisa Chaerani BurhanuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft CabgsurgeryDocumento26 pagineCoronary Artery Bypass Graft Cabgsurgeryfatha100% (1)
- Nephrostomy ReportDocumento4 pagineNephrostomy ReportPatrick Lloyd Merino Jackson100% (1)
- Screening Case Study Exercises - Hannah TurnerDocumento4 pagineScreening Case Study Exercises - Hannah Turnerapi-457299309Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cot Death ReportDocumento16 pagineCot Death Reportchris@mitchellbridges.com100% (1)
- Patof Spell PDFDocumento3 paginePatof Spell PDFAnggi CalapiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Documento46 paginePacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Zahangir Kabir AshikNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Vascular SurgeryDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To Vascular Surgeryapi-3858544100% (1)
- Faltering Growth: Straight To The Point of CareDocumento35 pagineFaltering Growth: Straight To The Point of Careftah ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Ecg ModulesDocumento150 pagineLearning Ecg ModulesdodiNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 - Abnormalities of R Wave ProgressionDocumento3 pagine08 - Abnormalities of R Wave ProgressionSharan Murugaboopathy100% (1)
- ArrhyDocumento26 pagineArrhyMouriyan AmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg For InternsDocumento25 pagineEcg For InternszeshooNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinics in Pediatrics: Growth Faltering: The New and The OldDocumento10 pagineClinics in Pediatrics: Growth Faltering: The New and The OldJayantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac PacingDocumento89 pagineCardiac Pacingsandwhale056Nessuna valutazione finora
- EKG InterpretationDocumento63 pagineEKG InterpretationMiriam Cindy MathullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Long QT SyndromeDocumento3 pagineCauses of Long QT SyndromeJetco LawNessuna valutazione finora
- Paeds ECG InterpretationDocumento28 paginePaeds ECG InterpretationMuhammad Moazzam GulzarNessuna valutazione finora
- Glascow Coma ScaleDocumento15 pagineGlascow Coma ScalePaul Henry RoxasNessuna valutazione finora
- Retroperitoneal and Soft TissueDocumento59 pagineRetroperitoneal and Soft TissueLucas Phi100% (1)
- Arrhythmia ReviewDocumento33 pagineArrhythmia ReviewMark Hammerschmidt100% (3)
- Dysrhythmias: Sinus Node Dysrhythmias Tachycardia, and Sinus ArrhythmiaDocumento5 pagineDysrhythmias: Sinus Node Dysrhythmias Tachycardia, and Sinus ArrhythmiaKayelyn-Rose Combate100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infections PowerpointDocumento22 pagineUrinary Tract Infections Powerpointsamdhathri100% (1)
- Cyanotic Spell: Dr. Shirley L A, Sp. A 12 April 2011Documento6 pagineCyanotic Spell: Dr. Shirley L A, Sp. A 12 April 2011Kahfi Rakhmadian KiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Left Bundle Branch BlockDocumento10 pagineLeft Bundle Branch BlockMochamad BasriNessuna valutazione finora
- Failure To Thrive: An UpdateDocumento6 pagineFailure To Thrive: An UpdateErna MiraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Algorithm For Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation1Documento8 pagineAlgorithm For Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation1andi namirah100% (1)
- ABC of Pediatric ECGDocumento5 pagineABC of Pediatric ECGThalita SophiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Examination Inspection, Palpation & Percussion : Dr. Rajesh Bhat UDocumento38 pagineCardiac Examination Inspection, Palpation & Percussion : Dr. Rajesh Bhat URanjith RavellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternating Bundle Branch BlockDocumento9 pagineAlternating Bundle Branch BlockSyifa Mahmud Syukran AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Precocious PUBERTYDocumento4 paginePrecocious PUBERTYjprakashjjNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Management of AnticoagulationDocumento33 paginePerioperative Management of Anticoagulationmonge20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Ulcers and Wounds: by Monica Warhaftig, D.O. Assistant Professor of Geriatrics N.S.UDocumento64 paginePressure Ulcers and Wounds: by Monica Warhaftig, D.O. Assistant Professor of Geriatrics N.S.UEvaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 AHA Guidelines BradicardiaDocumento106 pagine2018 AHA Guidelines BradicardiaArio Richard NinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Intern 2021Documento53 paginePre-Intern 2021Jemima MalaikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitral ValveDocumento48 pagineMitral Valvestoicea_katalinNessuna valutazione finora
- Robbins Chapter 11Documento5 pagineRobbins Chapter 11Luming LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecganalysisreport 5Documento28 pagineEcganalysisreport 5AlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated - Science 7Documento187 pagineUpdated - Science 7Mushtaq AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension CaseDocumento3 pagineHypertension CaseArnold Christian QuilonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic DacryocystitisDocumento29 pagineChronic Dacryocystitissajjad hossainNessuna valutazione finora
- The Equine Cardiovascular SystemDocumento5 pagineThe Equine Cardiovascular SystemSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory System WebquestDocumento4 pagineCirculatory System Webquestapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Goldbergers Clinical Electrocardiography 9th Edition PDFDocumento360 pagineGoldbergers Clinical Electrocardiography 9th Edition PDFdr_mego75% (4)
- Myasthenia GravisDocumento71 pagineMyasthenia GravisRyan-Jay AbolenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acs 2022 Bav 18Documento10 pagineAcs 2022 Bav 18Mathew McCarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory SystemDocumento16 pagineCirculatory SystemHarinder KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento8 pagineCardiovascular SystemChelsie NicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Bringing Down High Blood Pressure-ManteshDocumento298 pagineBringing Down High Blood Pressure-Manteshzulmohd1100% (3)
- Pe 221 DoneDocumento42 paginePe 221 DoneElma QuiselNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-7 - Bio 10th - Life Process - Revision AssignmentDocumento8 pagineCh-7 - Bio 10th - Life Process - Revision AssignmentDharmendra SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Quarter ScienceDocumento3 pagine2nd Quarter Sciencesusan h. bucasasNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2post Resus Algorithms 1Documento1 pagina7.2post Resus Algorithms 1Massimo Di BenedettoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge Primary Science Activity Book 6, Fiona Baxter and Liz Dilley, Cambridge University Press - PublicDocumento16 pagineCambridge Primary Science Activity Book 6, Fiona Baxter and Liz Dilley, Cambridge University Press - PublicAsma Nasreen mim100% (1)
- Sci9 Q1 Mod2 Effects of Lifestyle On The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems.Documento28 pagineSci9 Q1 Mod2 Effects of Lifestyle On The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems.Mary Grace UntalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Echo CardiogramDocumento2 pagineEcho CardiogramReyschelle Dela Rosa HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Paida and Lajin Self - Healing (Hongchi Xiao 2012)Documento44 paginePaida and Lajin Self - Healing (Hongchi Xiao 2012)rajaleidur100% (7)
- Lecture Cardio Physiotherapy 1Documento318 pagineLecture Cardio Physiotherapy 1Nurse GhanemNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme (Results) : January 2017Documento23 pagineMark Scheme (Results) : January 2017Raashed RamzanNessuna valutazione finora
- Andrómeda Shock 2Documento13 pagineAndrómeda Shock 2Cristian Daniel Espinoza ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- NBME Form 26 Questions Only PDFDocumento54 pagineNBME Form 26 Questions Only PDFFaizan KhawajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antianginal Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineAntianginal Drug StudymariaNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento11 pagineElectrocardiogramAbby BhevNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Tamponade: Zhiarina Kyla M. BizDocumento12 pagineCardiac Tamponade: Zhiarina Kyla M. BizMatt Joseph Cabanting100% (1)