Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MC 3 2019 Student Notes
Caricato da
Ronaky1234560 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
24 visualizzazioni18 pagineThe document discusses various approaches and models for effective managerial communication. It outlines the key elements that must be considered when formulating a communication strategy, including defining the overall message, intended audience, potential barriers, establishing credibility, and assessing feedback. Proper message organization and delivery are important, depending on whether the direct or indirect approach is most appropriate. The document emphasizes that communication is probabilistic and context-dependent, and effective communication strategies must account for contingencies.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
MC 3 2019 Student Notes.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses various approaches and models for effective managerial communication. It outlines the key elements that must be considered when formulating a communication strategy, including defining the overall message, intended audience, potential barriers, establishing credibility, and assessing feedback. Proper message organization and delivery are important, depending on whether the direct or indirect approach is most appropriate. The document emphasizes that communication is probabilistic and context-dependent, and effective communication strategies must account for contingencies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
24 visualizzazioni18 pagineMC 3 2019 Student Notes
Caricato da
Ronaky123456The document discusses various approaches and models for effective managerial communication. It outlines the key elements that must be considered when formulating a communication strategy, including defining the overall message, intended audience, potential barriers, establishing credibility, and assessing feedback. Proper message organization and delivery are important, depending on whether the direct or indirect approach is most appropriate. The document emphasizes that communication is probabilistic and context-dependent, and effective communication strategies must account for contingencies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 18
Managerial Communication
Nature, Barriers and Communication Strategy
Arrow Approach:
Effective Expression= Effective Communication
(Shannon and Weaver)
The Circuit Approach:
Understanding= Effective Communication
(Wilbur Schramm)
Message
• What is my overall message?
• How do I formulate my message to make it acceptable to my
audiences?
• What do I expect others to do because of my message>
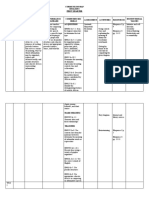
Message Organization
Direct Approach Indirect
Approach
Audience Reaction Eager/Interested/Pleased Displeased Uninterested/Unwilling
/Neutral
Message Opening Start with the main idea, Start with a neutral Start with a statement or
the request or the good statement that acts as a question that captures
news transition to the reasons attention
for the bad news
Message Body Provide Necessary Give reasons to build up Arouse the audience’s
Details to the negative answer interest in the subject.
or announcement. State Build the audience’s
or imply the bad news desire to comply.
and make a positive
suggestion
Message Close Close with a cordial Close cordially Request Action
comment, a reference to
the good news or a
statement about the
specific action desired
Communicator Credibility: Initial and
Acquired:
Credibility Circuit
Communicator Questions:
• Am I the best person to deliver the message?
• If not, who should deliver the message
• Who would be the most credible person or otherwise effective
communicator for different messages or audiences?
Audiences Questions:
• Who are my primary audiences? Secondary audiences?
• What are their interests in this situations?
• What are their stakes in the outcomes?
• How will they be affected by my messages?
• How should I ask for feedback from this audience?
Barriers to Communication
Semantic Socio-Psychological Personal
• Vocabulary Barriers Organizational • Emotional Conflicts
• Jargons Perceptual • Poor Listening
• Euphemisms Physical Barriers Organizational • Poor retention
Differences Structure
• Slangs • Premature Evaluation
Noise
• Abstract and Ambiguous Attitudinal Rules and
Words differences Distance Regulations
• Wrong translation
Conflicting Signals Faulty Equipment Role and Status
Halo Effect
Stereotyping
Probabilistic nature of Communication
• Communication is the transmission and/or reception of signals
through some channel/s that humans interpret based on a
probabilistic system that is deeply influenced by context.
Communication Breakdown
• When only one possibility is perceived
• The sender purposely used language that has multiple
interpretations: Strategic Ambiguity.
• The Receiver May purposely Misunderstand
• The receiver may constructively understand
a message
Assessing the value of Ambiguity
Variables of Contingency Theory
Dance Approach:
Coordinated Management of Meaning
Communication is the process by which persons co-create, maintain
and alter patterns of social order, but … the coordination of talk
through which patterns of order emerge is not necessarily based on
mutual understanding or a shared social reality.
-W.B.Pearce, L.M.Harris, and V.E. Cronen. Rigor and Imagination.
Feedback
• How will I determine if my audience is receiving my messages as I
intend?
• How will I measure or assess the impact?
Variables of Communication Strategy in
Contingency Approach:
• PMI’s 2013 Pulse of the ProfessionTM report revealed that US$135
million is at risk for every US$1 billion spent on a project. Further
research on the importance of effective communications uncovers
that a startling 56 percent (US$75 million of that US$135 million) is
at risk due to ineffective communications.
Timing
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- English 8 Curriculum MapDocumento65 pagineEnglish 8 Curriculum MapMary Kryss DG Sangle80% (5)
- Most Common Research Questions Being Asked by PanelistDocumento27 pagineMost Common Research Questions Being Asked by PanelistRexMichael12260% (1)
- Building Competency Models Approaches For HR ProfessionalsDocumento12 pagineBuilding Competency Models Approaches For HR ProfessionalsNathalyLGNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Affairs Philosophy StatementDocumento5 pagineStudent Affairs Philosophy Statementapi-532999262Nessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiated Instruction PresentationDocumento16 pagineDifferentiated Instruction Presentationapi-254516641Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test and Non Test AssessmentDocumento2 pagineTest and Non Test AssessmentMuammar Rifqi75% (12)
- Communication Skills Week-1 Lecture-1 Powr FleDocumento53 pagineCommunication Skills Week-1 Lecture-1 Powr FleMusab AbbasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers To Communication: By: Yesha VyasDocumento28 pagineBarriers To Communication: By: Yesha Vyasmehulshah_619Nessuna valutazione finora
- Doctor-Patient CommunicationDocumento25 pagineDoctor-Patient CommunicationHugo BoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Skills (RIU) Week-1 2-1Documento49 pagineCommunication Skills (RIU) Week-1 2-1Muhammad TahirNessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers To Effective Communication and Their ManagementDocumento36 pagineBarriers To Effective Communication and Their ManagementRuchika Duggal100% (1)
- Barrirs For CommunicationDocumento35 pagineBarrirs For CommunicationShivu Yati100% (1)
- BC - Topic 2.1 - (Cheesebro Ch2)Documento16 pagineBC - Topic 2.1 - (Cheesebro Ch2)31221020980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers TO Effective CommunicationDocumento34 pagineBarriers TO Effective CommunicationSubratKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication BarriersDocumento40 pagineCommunication BarriersCarl Andrie MontefalcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Communication in The Workplace: Thursday May 21, 2009Documento27 pagineEffective Communication in The Workplace: Thursday May 21, 2009Mudassir HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication BarriersDocumento41 pagineCommunication Barrierskabibhandari100% (1)
- CH1 - Introduction To Communication2023nDocumento37 pagineCH1 - Introduction To Communication2023nHANA AHMEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers To Communication 5584627b1b18fDocumento28 pagineBarriers To Communication 5584627b1b18fSuryansh RantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Conversastion Skills 1234278345934814 3+com ProcessDocumento71 pagineCommunication Conversastion Skills 1234278345934814 3+com Processankurbehl1989100% (1)
- Communication BarriersDocumento41 pagineCommunication BarriersMayankNessuna valutazione finora
- BC - Topic 2.1 - (CHEESEBRO Ch2)Documento16 pagineBC - Topic 2.1 - (CHEESEBRO Ch2)Gà KonNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicatiin NursingDocumento39 pagineCommunicatiin NursingchuniadsuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 - Barriers To CommunicationDocumento29 pagineWeek 2 - Barriers To CommunicationMotlatsi JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 PersuasionDocumento18 pagineLecture 7 PersuasionSyed Anis u RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Speaking in PublicDocumento50 pagineIntro To Speaking in PublicAlmira Francia AbadNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Skills PDFDocumento34 pagineCommunication Skills PDFManishNessuna valutazione finora
- Strengthening of Human Resources For Health: Rajni Bagga NihfwDocumento50 pagineStrengthening of Human Resources For Health: Rajni Bagga NihfwMrityunjay SanwalotNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To CommunicationDocumento19 pagineIntroduction To CommunicationJyotishree PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1-Communication ProcessDocumento41 pagineLesson 1-Communication ProcessAnagirl LynNessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocumento5 pagineBarriers To Effective CommunicationsangeethadurjatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership and Communication: Engr. Ranie B. CanlasDocumento25 pagineLeadership and Communication: Engr. Ranie B. CanlasNiño RonquilloNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF DocumentDocumento32 paginePDF DocumentSasha DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Communication: Ns. Bayu Lesmono, S.KepDocumento19 pagineEffective Communication: Ns. Bayu Lesmono, S.KepJuritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Communication (Reporting)Documento11 pagineEffective Communication (Reporting)Lenlen CabaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication SkillsDocumento55 pagineCommunication SkillsWeza WezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication BarrierDocumento8 pagineCommunication BarrierRetail Fashion MerchandisingNessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers of CommunicationDocumento27 pagineBarriers of CommunicationAlica MPNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial CommunicationDocumento77 pagineManagerial CommunicationTulasi PatleNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Communication Skills 3-Month StudentsDocumento58 pagineEffective Communication Skills 3-Month StudentsAsmaa MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- RBR - Act. Sheet June10Documento5 pagineRBR - Act. Sheet June10reaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmitters and ReceptorsDocumento4 pagineTransmitters and ReceptorsChristian HisolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 MBA Barriers To Communication NewDocumento32 pagineUnit 1 MBA Barriers To Communication Newusless018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers To Effective Communication and Their ManagementDocumento30 pagineBarriers To Effective Communication and Their ManagementBurhan sherwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- BarriersDocumento20 pagineBarriersomkarlakhutework2Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Communication BarriersDocumento42 pagine6 Communication BarriersjiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1: Introduction To Communication SkillsDocumento42 pagineWeek 1: Introduction To Communication SkillsYasir MalikthNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Analyzing The AudienceDocumento5 pagineChapter 2 Analyzing The AudienceAtiqah Nadirah100% (1)
- Week 4 (BC-HS 218)Documento49 pagineWeek 4 (BC-HS 218)razaaziz9191Nessuna valutazione finora
- CommunicationDocumento6 pagineCommunicationFaye ArribeNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Communication Week 1 SlidesDocumento38 pagineBusiness Communication Week 1 SlidesUzair RazzaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Of Meaningful Interaction Among Human BeingsDocumento25 pagineOf Meaningful Interaction Among Human BeingsDenisa CarageaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiating BIas and Prejudice G-9 Presentation Final PPT For Beltran 9Documento47 pagineDifferentiating BIas and Prejudice G-9 Presentation Final PPT For Beltran 9Elysa MicuNessuna valutazione finora
- CMI Reference Form CEF Worker or Ministry SupervisorDocumento4 pagineCMI Reference Form CEF Worker or Ministry SupervisorEmmanuel GodfreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication SkillsDocumento18 pagineCommunication SkillsKaranpreet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Introduction To Business CommunicationDocumento51 pagine1 Introduction To Business Communicationfazilshareef1885Nessuna valutazione finora
- COMMunication BARRIERSDocumento36 pagineCOMMunication BARRIERSGelyn Torrejos GawaranNessuna valutazione finora
- CH2&3 - Communication in An OrganizationDocumento106 pagineCH2&3 - Communication in An OrganizationBarkhad HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Strengthening of Human Resources For Health: Rajni Bagga NihfwDocumento50 pagineStrengthening of Human Resources For Health: Rajni Bagga NihfwRaj MaanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership CommunicationDocumento21 pagineLeadership CommunicationJigs SeñaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Skills-IntroDocumento59 pagineCommunication Skills-IntroUmair HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicating Effectively With Health Care ProfessionalsDocumento17 pagineCommunicating Effectively With Health Care ProfessionalsKhairunnisa HaziraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ha ReviewerDocumento14 pagineHa ReviewerMj Eliser MenorNessuna valutazione finora
- Talk with Confidence: A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless Communication with Anyone, Anytime, About AnythingDa EverandTalk with Confidence: A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless Communication with Anyone, Anytime, About AnythingNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 - CC 6 2019 Student NotesDocumento16 pagine0 - CC 6 2019 Student NotesRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Publicly Listed Infrastructure Mutual Fund (WDocumento17 paginePublicly Listed Infrastructure Mutual Fund (WRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Financing Clean Technology Ventures: Session-9 Vidheeavashia 3 S E Ptembe R, 2 0 1 9Documento11 pagineFinancing Clean Technology Ventures: Session-9 Vidheeavashia 3 S E Ptembe R, 2 0 1 9Ronaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Special Economic Zone Public Purpose and Private PropertyDocumento14 pagineSpecial Economic Zone Public Purpose and Private PropertyRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Session3 CoalDocumento23 pagineSession3 CoalRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bnasari Patel: C/14 Aaradhya Devine Bungalows, W.T.P.S Road, Thermal-388235 8347888649Documento2 pagineBnasari Patel: C/14 Aaradhya Devine Bungalows, W.T.P.S Road, Thermal-388235 8347888649Ronaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group Discussion Topics ListDocumento1 paginaGroup Discussion Topics ListRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Summer InternshipsDocumento2 pagineSummer InternshipsRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- ResumeDocumento2 pagineResumeRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Public Private PartnershipDocumento4 paginePublic Private PartnershipRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix D - Evaluation by Industry GuideDocumento3 pagineAppendix D - Evaluation by Industry GuideRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate Program in Project ManagementDocumento2 pagineCertificate Program in Project ManagementRonaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- RRM-Day 1Documento18 pagineRRM-Day 1Ronaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- SIP Presentation March 2019Documento15 pagineSIP Presentation March 2019Ronaky123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kirsner Interviews LaingDocumento25 pagineKirsner Interviews LaingCelso ChiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Animated Optical Illusion ProjectDocumento6 pagineAnimated Optical Illusion ProjectBaron Lopez Fernando JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Okun y Kantrowitz - Cap4 - Stage1Documento15 pagineOkun y Kantrowitz - Cap4 - Stage1AntoniettaNessuna valutazione finora
- NITTT M-7 MCQ-1 Online DegreeDocumento2 pagineNITTT M-7 MCQ-1 Online DegreeSwapna HNessuna valutazione finora
- Tree Sorting Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagineTree Sorting Lesson Planapi-478219036Nessuna valutazione finora
- StressFree ExtractDocumento34 pagineStressFree ExtractHay HouseNessuna valutazione finora
- Speaking and Listening Instructional Philosophy and Teaching SuggestionsDocumento13 pagineSpeaking and Listening Instructional Philosophy and Teaching SuggestionsMatsoni LorinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of HRM 2nd SemDocumento2 pagineCase Study of HRM 2nd SemBirat Raj Sing Thapa100% (1)
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento23 pagineAnnotated BibliographyAnyss100% (1)
- Analytic PhilosophyDocumento8 pagineAnalytic PhilosophyJerald M JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing A Comprehensive Report in Special EducationDocumento54 pagineWriting A Comprehensive Report in Special EducationBrady Arnold100% (1)
- تست بانك جزء الفاينل اختياري فقطDocumento75 pagineتست بانك جزء الفاينل اختياري فقطemadNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional IdentityDocumento5 pagineProfessional IdentityElise RichardsNessuna valutazione finora
- Steven Norquist - What Is Enlightenment, No, I Mean Really, Like What Is It? PDFDocumento8 pagineSteven Norquist - What Is Enlightenment, No, I Mean Really, Like What Is It? PDFSKYHIGH444Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rap RubricDocumento1 paginaRap RubricCherlyn Arias IbañezNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoltan Dienes' Six-Stage Theory of Learning MathematicsDocumento2 pagineZoltan Dienes' Six-Stage Theory of Learning MathematicsChin Boon KingNessuna valutazione finora
- HR Activities Devolved With Line ManagerDocumento4 pagineHR Activities Devolved With Line Managersaf999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Position and Program. Helio OiticicaDocumento3 paginePosition and Program. Helio OiticicasenseyitoNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT III - Unpacking The SelfDocumento47 pagineUNIT III - Unpacking The SelfRosana Celeste CañonNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard 1: Learner Development: Lesson Plan Lesson Plan TwoDocumento4 pagineStandard 1: Learner Development: Lesson Plan Lesson Plan Twoapi-563561542Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Q and A TypeDocumento21 pagineUnit 1 Q and A TypebalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deepak Chopra QuotesDocumento7 pagineDeepak Chopra QuotesDeviJo100% (3)
- Assessment of Learning Chapter 1Documento30 pagineAssessment of Learning Chapter 1Christine Anne ClementeNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Log Personal Dev TDocumento34 pagineDaily Lesson Log Personal Dev TFèdòrá MischkáNessuna valutazione finora