Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture 2 Big Data
Caricato da
farheen0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
51 visualizzazioni15 paginebig data lecture 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentobig data lecture 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
51 visualizzazioni15 pagineLecture 2 Big Data
Caricato da
farheenbig data lecture 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 15
Big Data Computing
Dr. Syed Saood Zia
Assistant Professor Lecture # 2
Software Engineering Department
Sir Syed University of Engineering & Technology
Content
• Idea of Big Data
• Example Models
• Relevance of Big Data
• Key Computing Resources for Big Data
• Scalability — Scale Up & Scale Out
• Techniques towards Big Data
• Why Big Data now?
• Contrasting Approaches in Adopting High-Performance Capabilities
• Big Data Market
Idea of Big Data
• Methods of obtaining knowledge
Theory (model), hypothesis, experiment, analysis (repeat)
▫ Explorative: start theory with observations of phenomena
▫ Constructivism: starts with axioms and reason implications
• (Big) Data + Analytics ) Insight (prediction of the future)
▫ For industry: insight = business advantage and money...
• Analytics: follow an explorative approach and study the data
▫ To infer knowledge, use statistics / machine learning
• Construct a theory (model) and validate it with the data
Example Models
• Similarity is a (very) simplistic model and predictor for the world
▫ Humans use this approach in their cognitive process
▫ Uses the advantage of Big Data
• Weather prediction
▫ You may develop and rely on complex models of physics
▫ Or use a simple model for a particular day; e.g. expect it to be similar to the
weather of the day over the last X years.
• Preferences of Humans
▫ Identify a set of people which liked items you like
▫ Predict you like also the items those people like (items you haven’t rated so far)
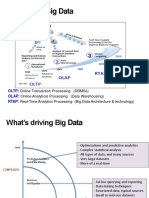
Relevance of Big Data
• Big Data Analytics is emerging
• Relevance increases compared to supercomputing
Google Search Trends, relative searches
Key Computing Resources for Big Data
Key Computing Resources “Big Data Analytics”, David Loshin, 2013
• Processing capability: CPU, processor, or node.
• Memory
• Storage
• Network
Scalability — Scale Up & Scale Out
• Scale out
▫ Use more resources to distribute workload in parallel
▫ Higher data access latency is typically incurred
• Scale up
▫ Efficiently use the resources
▫ Architecture-aware algorithm design
Scalability — Scale Up & Scale Out
• For independent data ==> scale up may not have obvious
advantage than scale out
• For linked data ==> utilizing scale up as much as possible
before scale out
Techniques towards Big Data
• Massive Parallelism • Data Mining and Analytics
• Huge Data Volumes Storage • Data Retrieval
• Data Distribution • Machine Learning
• High-Speed Networks • Data Visualization
• High-Performance Computing
• Task and Thread Management
➔ Techniques exist for years to
decades. Why is Big Data hot now?
Why Big Data now?
• More data are being collected and stored
• Open source code
• Commodity hardware / Cloud ➔
• High-Volume
• High-Velocity
• High-Variety ➔
• Artificial Intelligence
Contrasting Approaches in Adopting High-Performance
Capabilities
Aspect Typical Scenario Big Data
Applications that take advantage of A simplified application execution model
massive parallelism developed by encompassing a distributing file system, application
Application specialized developers skilled in programming model, distributed database and
Development high-performance computing, program scheduling is packaged within Hadoop, an
performance optimization, and open source framework for reliable, scalable,
code tuning distributed and parallel computing.
Uses high-cost massively parallel Innovative methods of creating scalable and yet
processing (MPP) computers, elastic virtualized platforms take advantage of
Platform utilizing high-bandwidth networks clusters of commodity hardware components
and massive I/O devices. (Cloud-based utility computing services) coupled
with open source tools and technology.
Contrasting Approaches in Adopting High-Performance
Capabilities
Aspect Typical Scenario Big Data
Limited to file-based or relational Alternate models or data management (i.e. No SQL)
database management systems provide a variety of methods for managing
(RDBMS) using standard row- information to best suit specific business process
Data
oriented data layouts needs, such as in-memory data management (for
Management
rapid access), columnar layouts to speed query
response and graph databases (for social network
analytics)
Requires large capital investment The ability to deploy systems like Hadoop on
in purchasing high-end hardware virtualized platforms allows small and medium
Resources
to be installed and managed in- businesses to utilize cloud-based environments
house.
Big Data Market
Human Brain is a Graph/ Network of 100 B nodes and 1 T
Edges
Summary
• Idea of Big Data
• Example Models
• Relevance of Big Data
• Key Computing Resources for Big Data
• Scalability — Scale Up & Scale Out
• Techniques towards Big Data
• Why Big Data now?
• Contrasting Approaches in Adopting High-Performance Capabilities
• Big Data Market
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Introduction To Big Data-0Documento77 pagineIntroduction To Big Data-0AbhishreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data AnalyticsDocumento79 pagineBig Data Analyticssania2011100% (2)
- HadoopDocumento23 pagineHadoopsowjanya kandukuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Big DataDocumento8 pagineLecture 2 - Big DataHarshita BadwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Authors Seema Maitreya, C.K. JhabDocumento23 pagineAuthors Seema Maitreya, C.K. JhabIan RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Unit 1 AKTU NotesDocumento87 pagineBig Data Unit 1 AKTU Notesabhijitraj229Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bda - M1Documento64 pagineBda - M1Chandan A HNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit No. 4Documento67 pagineUnit No. 4vishal phuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Big DataDocumento1 paginaBig DataDhruvi SavajNessuna valutazione finora
- BDA - Lecture 3Documento17 pagineBDA - Lecture 3rumman hashmi100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Big Data Architecture Part 1Documento41 pagineChapter 6 - Big Data Architecture Part 1Suren DevNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper ReviewDocumento5 pagineTerm Paper ReviewDeleesha BolluNessuna valutazione finora
- MOOCDocumento32 pagineMOOCAravindNessuna valutazione finora
- BlueGranite Data Lake EbookDocumento23 pagineBlueGranite Data Lake EbookPrasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- CS8091 BIGDATA ANALYTICS QUESTION BANK - WatermarkDocumento95 pagineCS8091 BIGDATA ANALYTICS QUESTION BANK - WatermarkMarianinu antonyNessuna valutazione finora
- VTU Exam Question Paper With Solution of 18CS72 Big Data and Analytics Feb-2022-Dr. v. VijayalakshmiDocumento25 pagineVTU Exam Question Paper With Solution of 18CS72 Big Data and Analytics Feb-2022-Dr. v. VijayalakshmiWWE ROCKERSNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Architecture Big DataDocumento3 pagineReference Architecture Big Datajuergen_urbanski100% (1)
- Syllabus - Big Data Analytic Strategic PlanningDocumento1 paginaSyllabus - Big Data Analytic Strategic PlanningHendra PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data 2021 - 6,7,8 Big Data TechnologiesDocumento55 pagineBig Data 2021 - 6,7,8 Big Data TechnologiesPutri Nur ainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks TCPDocumento48 pagineComputer Networks TCPtesthelsingNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparison of Big Data Analytics Approaches Based On Hadoop MapreduceDocumento9 pagineA Comparison of Big Data Analytics Approaches Based On Hadoop MapreduceKyar Nyo AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Analytics On Large Scale Shared Storage System: First SeminarDocumento22 pagineBig Data Analytics On Large Scale Shared Storage System: First SeminarKyar Nyo AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Harnessing Big DataDocumento29 pagineHarnessing Big DataDipak ShowNessuna valutazione finora
- Ism 6404 CH 7Documento47 pagineIsm 6404 CH 7Noemer OrsolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data 101 Brief PDFDocumento4 pagineBig Data 101 Brief PDFAruna PattamNessuna valutazione finora
- DSX InfoSphere DataStage Is Big Data Integration 2013-05-13Documento30 pagineDSX InfoSphere DataStage Is Big Data Integration 2013-05-13parashara0% (1)
- LS1.1 - V6 Generalized Architecture of Big Data SystemsDocumento8 pagineLS1.1 - V6 Generalized Architecture of Big Data SystemsR KrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Dan Cloud ComputingDocumento19 pagineBig Data Dan Cloud ComputingKarenNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Analytics CSE704 Module-1Documento76 pagineData Analytics CSE704 Module-1suryanshmishra425Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data EngineeringDocumento48 pagineData EngineeringsaisuvarnayathamNessuna valutazione finora
- BDA Unit 2 1Documento42 pagineBDA Unit 2 1Jerald RubanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bigdata Overview PDFDocumento98 pagineBigdata Overview PDFmanindra1kondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data-Intensive ComputingDocumento88 pagineData-Intensive ComputingAmogh B SNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 LTDocumento16 pagineUnit 4 LTSahil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Big Data and Business AnalyticsDocumento6 pagineFundamentals of Big Data and Business Analyticsjitendra.jgec8525Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Perusal of Big Data Classification andDocumento13 pagineA Perusal of Big Data Classification andmanitenkasiNessuna valutazione finora
- BigData BriefDocumento4 pagineBigData BriefFarid100% (1)
- Principal Architect - Big Data Architect - Solutions Architect ResumeDocumento9 paginePrincipal Architect - Big Data Architect - Solutions Architect ResumenareshbawankarNessuna valutazione finora
- AI Data ScienceDocumento17 pagineAI Data Scienceteshu wodesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hadoop V.01Documento24 pagineHadoop V.01Eshan BhatejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data ComponentsDocumento31 pagineBig Data Components4241 DAYANA SRI VARSHANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two: Data ScienceDocumento19 pagineChapter Two: Data SciencemahammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento40 pagineChapter 1SANG VÕ NGỌCNessuna valutazione finora
- Dinesh KhanalDocumento6 pagineDinesh KhanalshubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Team 8, Monika Kashyap, 085Documento11 pagineTeam 8, Monika Kashyap, 085Sangita AdakNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Intro. To Data Sciences (Autosaved)Documento25 pagineChapter 2 - Intro. To Data Sciences (Autosaved)Daniel DamessaNessuna valutazione finora
- Powercenter Big Data Edition - Data Sheet - 2194 PDFDocumento4 paginePowercenter Big Data Edition - Data Sheet - 2194 PDFFarhaan ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Unit 1 NotesDocumento27 pagineBig Data Unit 1 Notesfewoho4495Nessuna valutazione finora
- BDA UNIT 1 and 2Documento34 pagineBDA UNIT 1 and 2Gaurav GujjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bda EseDocumento66 pagineBda Esejasbutani1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Big dataaRCHITECTURES FoundationsDocumento42 pagineBig dataaRCHITECTURES FoundationsGilbert DwasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Big Data PDFDocumento16 pagineIntroduction To Big Data PDFAurelle KTNessuna valutazione finora
- Day1 2Documento110 pagineDay1 2patil_555Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1.1 - Introduction To DEDocumento27 pagineLecture 1.1 - Introduction To DEzakiamine97Nessuna valutazione finora
- BD MergedDocumento330 pagineBD MergedAman CSE050Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTI Data As Service Data Mesh Architecture - v2 1Documento10 pagineLTI Data As Service Data Mesh Architecture - v2 1kpalanivel123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optimizing Big Data Storage and AnalysisDocumento12 pagineOptimizing Big Data Storage and AnalysisDeleesha BolluNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Security and Privacy Issues in Cloud Computing: Presented by Moe Myint Myint 14Ph.D-14Documento23 pagineBig Data Security and Privacy Issues in Cloud Computing: Presented by Moe Myint Myint 14Ph.D-14Moe MyinttMyinttNessuna valutazione finora
- Big DataDocumento25 pagineBig DataVIJAYA PRABA PNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning and Mortality in Kierkegaard and Heidegger - Origins of The Existential Philosophy of Death PDFDocumento204 pagineMeaning and Mortality in Kierkegaard and Heidegger - Origins of The Existential Philosophy of Death PDFAndrijaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Decline of Eastern Christianity Unde PDFDocumento523 pagineThe Decline of Eastern Christianity Unde PDFArto Kantarcıyan100% (2)
- Aureli Pier Vittorio The Project of Autonomy Politics and Architecture Within and Against Capitalism 1Documento16 pagineAureli Pier Vittorio The Project of Autonomy Politics and Architecture Within and Against Capitalism 1Yorgos RimenidisNessuna valutazione finora
- Eyeing The Ear. Roland Barthes and The Song Lyric, by Maija BurnettDocumento108 pagineEyeing The Ear. Roland Barthes and The Song Lyric, by Maija BurnettDavid FielNessuna valutazione finora
- BPA 26 Advanced Office Systems & ProceduresDocumento5 pagineBPA 26 Advanced Office Systems & ProceduresValerie SniderNessuna valutazione finora
- GarciaDocumento10 pagineGarciaMarco Toledo BastosNessuna valutazione finora
- Participation's Influence On Job StafisfactionDocumento23 pagineParticipation's Influence On Job Stafisfactionslangevar04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sistemas Complejos Como Modelo de ComputacionDocumento224 pagineSistemas Complejos Como Modelo de ComputacionUlises Perez Montiel100% (2)
- Montessori-Primary-Curriculum Infant ToddlerDocumento7 pagineMontessori-Primary-Curriculum Infant ToddlerMaria Cristina100% (1)
- The Life Story InterviewDocumento7 pagineThe Life Story Interviewvasile.ada7716Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sem 1 Topic 6 Seg TGTDocumento20 pagineSem 1 Topic 6 Seg TGTanuragmehta1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- RHETI SamplerHCDocumento5 pagineRHETI SamplerHCaveeno101Nessuna valutazione finora
- TeachYourselfLatinBett PDFDocumento380 pagineTeachYourselfLatinBett PDFmeanna93% (14)
- Qcfi Durgapur Chapter: Question & Answers BankDocumento13 pagineQcfi Durgapur Chapter: Question & Answers Bankdeepakhishikar24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8 Management Functions: ReadingDocumento11 pagineUnit 8 Management Functions: ReadingNegru CiprianNessuna valutazione finora
- KV Physics ImportantDocumento87 pagineKV Physics Importantpappu khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectures On DemocracyDocumento60 pagineLectures On DemocracymanhioNessuna valutazione finora
- 210-Article Text-764-1-10-20160318Documento21 pagine210-Article Text-764-1-10-20160318wendyNessuna valutazione finora
- Codex VaticanusDocumento2 pagineCodex VaticanusJesus LivesNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Isometric DrawingsDocumento10 pagineIntroduction To Isometric Drawingsbarnibar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Dangers of ReikiDocumento38 pagineThe Dangers of ReikiAnn Onimous100% (1)
- The Basic Outline of A KhutbahDocumento4 pagineThe Basic Outline of A KhutbahhasupkNessuna valutazione finora
- Stenhouse-1979-Research As A Basis For TeachingDocumento24 pagineStenhouse-1979-Research As A Basis For TeachingNicolás Borgmann0% (1)
- Sycip, Salazar, Luna & Manalo & Feliciano Law For Petitioners. Albert, Vergara, Benares, Perias & Dominguez Law Office For RespondentsDocumento8 pagineSycip, Salazar, Luna & Manalo & Feliciano Law For Petitioners. Albert, Vergara, Benares, Perias & Dominguez Law Office For RespondentsYieMaghirangNessuna valutazione finora
- DePauw Magazine Spring 2005Documento55 pagineDePauw Magazine Spring 2005DePauw University100% (2)
- The Tell-Tale Heart Full TextDocumento4 pagineThe Tell-Tale Heart Full Textapi-325785569Nessuna valutazione finora
- Community Organizing ReportDocumento38 pagineCommunity Organizing ReportCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanNessuna valutazione finora
- Concurrent Delay ApproachDocumento5 pagineConcurrent Delay ApproachMazuan LinNessuna valutazione finora
- PH 102 SyllabusDocumento4 paginePH 102 SyllabusHarry BoNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement Scale SlideDocumento40 pagineMeasurement Scale Slideginish12Nessuna valutazione finora