Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Design of Bunkers and Silos
Caricato da
SagarKasarlaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Design of Bunkers and Silos
Caricato da
SagarKasarlaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Design of Storage Bins
Bunkers and Silos
By : BK Pandey
Sr Manager – Structural
MECON LTD. Ranchi
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Introduction
• Storage Containers for
Industrial purpose
BINS (IS Code - IS : 9178) • Stocking of Ores, Minerals,
Coal, Coke, Cement, Food
Grains for future processing
or disposal.
Rectangular (Pyramidal Hopper) Circular (Cone)
Shallow Shallow
Deep Deep
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Introduction
BINS (IS Code - IS : 9178)
Bunkers Silos
Rectangular (Pyramidal Hopper) Circular (Conical Hopper)
Shallow Shallow
Deep Deep
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Introduction
Bunkers
Rectangular (Pyramidal Hopper)
Shallow
Deep
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Introduction
Bunkers
Rectangular (Pyramidal Hopper)
Shallow
Deep
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Introduction
Silos
Circular (Conical Hopper)
Shallow
Deep
Orifice /Opening
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Design Considerations
1. Filling the Bunker – * Mechanical *
• Feed and Loading arrangement at the top.
• Conveyor / Tripper Conveyor Feed
• Bucket Elevator Feed
• Other Mechanical Considerations.
2. Emptying the bunker *
• free flow from Bottom opening or orifice
• avoid Material Arching, Make use mechanical
vibrator.
• Plan orifice locations to overcome discharge
problem.
3. Stocking of Material
• Bunker Hopper + Wall system to be designed
strong enough to stock the material for the
required duration.
• Proper application of Design Theories based
on geometry of bunker + Nature of material to
be stocked + type of filling and emptying.
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Design Considerations
4. Provision of Wearing Surface – * Use of
liner plates and ease of Maintenance
• Rubber Liner, SS/MS Plates, Grating
• Bricks or Tiles
5. Minimum Slope of Trough
• 50 to 60 degree Wall slope.
• Consider Corner Angle for Pyramidal Bottom.
6. Guarding Against Over Loading
• Application of Load Cells at support point.
7. Method of Support
• Bunker supporting Beam Arrangement.
• Bunker Supporting Beam Connections with
Portal Frames of Building.
• Battery of Bunkers – Common Beams,
Continuous, Multi Span Beams.
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Design Considerations
8. Materials of Construction & Method
of Construction
• MS Welded Construction as per IS:800-1984,
IS-814,
• MS Plates/Sections IS:2062 Gr-A.
• SAIL-MA or High Yield Stress Wieldable
Structural Steel may turn out to be economical
for large span bunker beams spanning more
than 9 m.
9. Factors of Safety and Working
Stresses
• Building Frame Loading as per IS-875 (Dead +
Live + Wind), IS-1893 (Eq. Load) and IS:9178
( Material Density and Angle of repose).
• Working stresses as per IS:800-1984.
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
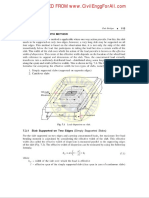
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Theory relating to
Granular Mass
Angle of Repose, A and Angle of Internal friction
Heap of free
flowing
A material
1
Plane of Rupture
2
Angle of Rupture, B and Plane of Rupture B1
B = 45 + A/2 B2
B and A are in degrees
Plane of Rupture
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Theory relating to
Granular Mass – Pressure Calculation
• Rankines Theory – Case 1 1
• Incompressible, homogeneous, granular, Plane of Rupture
cohesion less, particle of mass hold 2
together by friction on each other,
indefinite extent of mass.
• pv = Y. h B1
• ph = K.Y.h
•Pn = m .Y. h B2
Where,
Y = Volumetric or bulk Density.
K = Rankine’s factor = (1- sin ø) / (1+sin ø)
m = cos 2 + K . sin 2
• Jansen Theory ( Recommended by B1
IS:9178) – Case 2
• Friction on the wall predominant and
certain quantity of the contents will be
carried on the walls due to wall friction.
• Refer IS:1893 part 1 page 14 for formulae.
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Theory relating to
Granular Mass – Pressure Calculation
•Jansen Theory ( Recommended by
IS:9178) – Case 2
• Pressure Distribution Pz
d = dia Emptying
Pressure
h
Mn(0.75h 0r
1.2 d ) Filling
Pressure
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Analysis of Bunker
Forces : Shallow Rectangular
Ha’
A
W1
h1
P1
Hb Hb’ W2
B
W3
h2 Rv P2
a 2b P3
O Hc C
Refer : IS 9178 (Part II)
Find Hb by taking moment about O
fig 1. Page 6
and Hc abt B.
W1 = Y.a.h1 : P1 = K.Y.h1.h1/2
Ha’ = P1/3 : Hb’ = 2P1/3
W2 = Y.a.h2/2 : P2 =K.Y.h1.h2
W3 = Y.b.(h1+h2) : P3 =K.Y.h2.h2/2 By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Analysis of Bunker
Forces : Shallow Circular
A Support
for ring
Beam
h1 r
ph
B
c r1 c
h2
Hoop tension Wall = Ph. r
Hoop tension Hopper = Pn. R1. cosec
O
TL Longitudinal tension = Wt / (2. pi .
Refer : IS 9178 (Part II) r1. cosec )
fig 1. Page 14
Wt = Total weight at c-c
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Design of Bins - Bunkers and Silos :: Design Methodology
• Bunker Layout – JVSL Stock House
• Bunker Structural Components
• Bunker Beam Wall Component
• Wall or Web plate
• Vertical Stiffeners
• Horizontal Stiffeners
• Bottom Flange or Trough Beams
• Top Flange + Floor Beams
• Hopper Component
• Skin Plate or Sheathing Plate
• Ribs Beams/Angles
By BK Pandey, Structural Section, MECON Ranchi.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Design of Columns As Per IS 456-2000Documento68 pagineDesign of Columns As Per IS 456-2000S Praveenkumar87% (93)
- BMW E46 RearlightDocumento4 pagineBMW E46 RearlightLiviu CasuneanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Calculation For Fly Ash Storage Silo Stage-II - Rev.2 - Z1660 TalcherDocumento135 pagineDesign Calculation For Fly Ash Storage Silo Stage-II - Rev.2 - Z1660 TalcherSwapan Kumar BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual For Design and Detailing of RCCDocumento340 pagineManual For Design and Detailing of RCCimranmehfoozNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation (Thumb Rules) : Concentric FootingsDocumento4 pagineFoundation (Thumb Rules) : Concentric FootingsAtul Joshi100% (9)
- Grillage Foundation PDFDocumento11 pagineGrillage Foundation PDFutsav_koshtiNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure Calculation Warehouse 19 Mei'14Documento28 pagineStructure Calculation Warehouse 19 Mei'14Su NarkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Steel Bunker & Silo R1Documento22 pagineDesign of Steel Bunker & Silo R1sougata1667% (3)
- Ascorbic Acid Iodometric TitrationDocumento2 pagineAscorbic Acid Iodometric TitrationÂngelo Jesus100% (8)
- Dome Design in ExcelDocumento2 pagineDome Design in Excelجميل عبد الله الحماطي100% (2)
- Explosive Materials 1907Documento188 pagineExplosive Materials 1907kgrhoads100% (1)
- Silo WallDocumento5 pagineSilo WallMunish GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Design of Structural ElementsDocumento4 paginePreliminary Design of Structural ElementsSuson Dhital0% (1)
- Service Training BW211D-40 Eng PDFDocumento150 pagineService Training BW211D-40 Eng PDFEdnilson dos Santos89% (18)
- Deflection Limits As Per Is800-2007Documento1 paginaDeflection Limits As Per Is800-2007maheshbandhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Bunker and SiloDocumento2 pagineDifference Between Bunker and SiloSatyajit Mhatre71% (7)
- Full Analyse of JULIADocumento19 pagineFull Analyse of JULIArenan55026Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grid FloorsDocumento14 pagineGrid FloorsShashi Prakash100% (2)
- Substitute Frame AnalysisDocumento5 pagineSubstitute Frame Analysissiniann7100% (1)
- Silo Cement CalculationDocumento11 pagineSilo Cement CalculationFikriaraz AfifNessuna valutazione finora
- SP - Constructions: Industrial Training Report ON Analysis and Design of G+3 Building Using Staad ProDocumento55 pagineSP - Constructions: Industrial Training Report ON Analysis and Design of G+3 Building Using Staad ProSagarKasarla100% (1)
- SP - Constructions: Industrial Training Report ON Analysis and Design of G+3 Building Using Staad ProDocumento55 pagineSP - Constructions: Industrial Training Report ON Analysis and Design of G+3 Building Using Staad ProSagarKasarla100% (1)
- SP - Constructions: Industrial Training Report ON Analysis and Design of G+3 Building Using Staad ProDocumento55 pagineSP - Constructions: Industrial Training Report ON Analysis and Design of G+3 Building Using Staad ProSagarKasarla100% (1)
- Bin and Hopper Design LectureDocumento73 pagineBin and Hopper Design LectureGanesh Aditya100% (4)
- Shear and Moment Diagrams For FramesDocumento4 pagineShear and Moment Diagrams For FramesBasma GamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Amendment IS 1893 Part 2Documento14 pagineAmendment IS 1893 Part 2write2souravdNessuna valutazione finora
- Multistoreyed Building 3Documento26 pagineMultistoreyed Building 3V.m. RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Bunkers and SilosDocumento15 pagineDesign of Bunkers and Siloskrishna kumar70% (10)
- Silo BucklingDocumento14 pagineSilo BucklingrahilmlNessuna valutazione finora
- CIVL 392 - Chapter 6 - FormworkDocumento69 pagineCIVL 392 - Chapter 6 - FormworkGerold MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Road Note 06Documento32 pagineRoad Note 06hessian123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Conveyor Structure DesignDocumento44 pagineConveyor Structure DesignAizaz Shaikh83% (6)
- Bunkers and SilosDocumento28 pagineBunkers and Siloskalpanaadhi100% (1)
- Design ChimneyDocumento30 pagineDesign ChimneyKandavel Kandy50% (8)
- Load Estimate of A ConveyorDocumento5 pagineLoad Estimate of A ConveyorvivekNessuna valutazione finora
- 25m Single Lane Bridge Design Calculations Latest PDFDocumento16 pagine25m Single Lane Bridge Design Calculations Latest PDFshafiullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Calculations For SiloDocumento3 pagineDesign Calculations For SiloLeera Gonzaga100% (2)
- Chapter 6-Bunkers & SilosDocumento22 pagineChapter 6-Bunkers & SilosHelen Negash100% (5)
- General Hilti TheoryDocumento43 pagineGeneral Hilti TheoryMustafa UzyardoğanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Report On Structural Analysis and Design of Residential BuildingDocumento43 pagineA Report On Structural Analysis and Design of Residential BuildingSandip BudhathokiNessuna valutazione finora
- IS Code For Steel Bin Design - 9178Documento29 pagineIS Code For Steel Bin Design - 9178krishna kumar50% (2)
- Jar Test Lab Report Environmental EngineeringDocumento7 pagineJar Test Lab Report Environmental EngineeringNur Hazimah100% (1)
- 2374 - Technical Specification of Flooring Works PDFDocumento17 pagine2374 - Technical Specification of Flooring Works PDFKarthikeyan PanchatcharamNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Design of SilosDocumento12 pagineStandard Design of SilosTarun VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design BookDocumento46 pagineDesign BookAnonymous qEeH6Sl100% (1)
- Bunkers SilosDocumento82 pagineBunkers Silosurvish50% (4)
- Terminología de Un Open PitDocumento25 pagineTerminología de Un Open PitAmilcar Jairo Quiliche AraujoNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Dingley Bypass Integral Bridges: Dr. Kabir Patoary - Principal Engineer - Bridges - GHDDocumento32 pagineDesign of Dingley Bypass Integral Bridges: Dr. Kabir Patoary - Principal Engineer - Bridges - GHDkevin_au18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6-Bunkers & Silos PDFDocumento20 pagineChapter 6-Bunkers & Silos PDFFiraol TayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Silo: Prepared By:-Kishan Jaiswal Mayank Singh Parv Modh Rudra Sharma Riddhi FofariaDocumento20 pagineSteel Silo: Prepared By:-Kishan Jaiswal Mayank Singh Parv Modh Rudra Sharma Riddhi FofariaRudra SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- FuzzyDocumento75 pagineFuzzyvatsalshah24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mind Mapping of WeldingDocumento8 pagineMind Mapping of WeldingFadlanbunglonNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1. Itroduction To Wastewater TreatmentDocumento28 pagineUnit 1. Itroduction To Wastewater Treatmentsssshekhar100% (1)
- Unit 1. Itroduction To Wastewater TreatmentDocumento28 pagineUnit 1. Itroduction To Wastewater Treatmentsssshekhar100% (1)
- 13.B Design The Interior Panel of A Flat Slab 6 M × 8 M in Size For A Super Imposed Load of 5 kN/m2. Use M20 Grade Concrete and Fe415 SteelDocumento6 pagine13.B Design The Interior Panel of A Flat Slab 6 M × 8 M in Size For A Super Imposed Load of 5 kN/m2. Use M20 Grade Concrete and Fe415 SteelSaran T SNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrance Exam2Documento13 pagineEntrance Exam2Shrinath Singanamalli100% (1)
- All Plug-Ins of Arc BdsDocumento48 pagineAll Plug-Ins of Arc BdsAshish LoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- ST7006-Design of Bridges PDFDocumento9 pagineST7006-Design of Bridges PDFmiestyNessuna valutazione finora
- Airy's TheoryDocumento1 paginaAiry's TheoryAbhinav Singh50% (2)
- Design of Pile FoundationDocumento16 pagineDesign of Pile FoundationHani AboobackerNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Pile FoundationDocumento14 pagineCivil Pile FoundationDipesh Kumar83% (6)
- Substitute FrameDocumento22 pagineSubstitute FrameRAJA SEKHARNessuna valutazione finora
- Design CWRDocumento45 pagineDesign CWRMaitrayee AdityaNessuna valutazione finora
- SP10Documento16 pagineSP10Sumit Thakur100% (1)
- Civil / Structural Construction Notes: Nearest Faultline Site Location FromDocumento1 paginaCivil / Structural Construction Notes: Nearest Faultline Site Location FromVince Bagsit PolicarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Prestressed Concrete Girder (Complete Thesis)Documento27 paginePrestressed Concrete Girder (Complete Thesis)SANTOSHINessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of Steel Foot Over Bridge: Presented byDocumento28 pagineDesign and Analysis of Steel Foot Over Bridge: Presented byHARIS ALINessuna valutazione finora
- Cement SiloDocumento7 pagineCement Silowidad alamriNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforced Concrete Design: (CIVL 3320)Documento24 pagineReinforced Concrete Design: (CIVL 3320)taiman chanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nptel: Advanced Foundation Engineering - Web CourseDocumento2 pagineNptel: Advanced Foundation Engineering - Web CourseAnonymous fYHyRa2XNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Reinforced Concrete DesignDocumento1 paginaAdvanced Reinforced Concrete Designdrp100% (1)
- IRJAES - Plan Analysis and Design of A Circular RCC SiloDocumento6 pagineIRJAES - Plan Analysis and Design of A Circular RCC SiloM.RajivNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Diseno de Room and PillarDocumento49 pagine04 - Diseno de Room and PillardaniavmNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation For PT Building and DesignDocumento28 paginePresentation For PT Building and DesignAmarjeet ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Draft Semester - VIII - Ddrcs 19 R 2016Documento5 pagineSyllabus Draft Semester - VIII - Ddrcs 19 R 2016Bharati patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Drilled Caissons: Ce 477-Geotechnical Engineering IDocumento7 pagineDrilled Caissons: Ce 477-Geotechnical Engineering ISita HammondNessuna valutazione finora
- Zone 4 With Out Infill in GoundDocumento5 pagineZone 4 With Out Infill in GoundSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferncesDocumento2 pagineReferncesSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Refer NcesDocumento2 pagineRefer NcesSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Format and PicsDocumento22 pagineProject Format and PicsSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18e11d2013, Experimental Investigation of Roller Compaction Concrete With Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregates by Ceramic Waste and Marble DustDocumento8 pagine18e11d2013, Experimental Investigation of Roller Compaction Concrete With Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregates by Ceramic Waste and Marble DustSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dua 0931608Documento1 paginaDua 0931608SagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Bunkers and SilosDocumento16 pagineDesign of Bunkers and SilosSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Title Papers of PrakashDocumento4 pagineTitle Papers of PrakashSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- RajeshM - TeshProject2013 Pushover AnalysisDocumento126 pagineRajeshM - TeshProject2013 Pushover AnalysisMahiul hossain BappyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge Methods PDFDocumento8 pagineBridge Methods PDFSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- New 1Documento38 pagineNew 1SagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- 29-Apr-19 29-Apr-2019 23:05 2d Truss - STD: Job No Sheet No RevDocumento1 pagina29-Apr-19 29-Apr-2019 23:05 2d Truss - STD: Job No Sheet No RevSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Width MethodDocumento7 pagineEffective Width MethodSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- SA 2 Telugu 7th ClassDocumento7 pagineSA 2 Telugu 7th ClassSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge MethodsDocumento8 pagineBridge MethodsSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 1343 1980 R 1990Documento65 pagineIs 1343 1980 R 1990Venu PrasathNessuna valutazione finora
- Query Print of TrussDocumento1 paginaQuery Print of TrussSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- 29-Apr-19 29-Apr-2019 23:05 2d Truss - STD: Job No Sheet No RevDocumento1 pagina29-Apr-19 29-Apr-2019 23:05 2d Truss - STD: Job No Sheet No RevSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Query Print of TrussDocumento1 paginaQuery Print of TrussSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geo Polymer ConcreteDocumento20 pagineGeo Polymer ConcreteSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexibility MatrixDocumento8 pagineFlexibility MatrixSagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Partial Replacement With Corncob Ash Tiz ADocumento12 paginePartial Replacement With Corncob Ash Tiz ASagarKasarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zones of Protection and Dead or Blind Zone in Power SystemDocumento4 pagineZones of Protection and Dead or Blind Zone in Power SystemkarthikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Case Study - New Century Health ClinicDocumento6 pagineChapter 5 Case Study - New Century Health ClinicGeorge RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Liebherr Hydraulic Components For Heavy Duty On Highway Engines Application Flyer Es WebDocumento4 pagineLiebherr Hydraulic Components For Heavy Duty On Highway Engines Application Flyer Es WebDaniel Castillo PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- MUJ - Hostel B8, B9 & B10Documento12 pagineMUJ - Hostel B8, B9 & B10GanjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeDocumento4 pagineLesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeshanlbyNessuna valutazione finora
- A TCP TutorialDocumento11 pagineA TCP Tutorialpfck4589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Project 1Documento16 pagineMini Project 1SadikAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual V100-V30-70 ENGDocumento38 pagineManual V100-V30-70 ENGAzeddine LANessuna valutazione finora
- Junction Box PDFDocumento2 pagineJunction Box PDFMohan ShanmugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Study On The Cornering Behavior of An Articulated Tracked VehicleDocumento1 paginaAnalytical Study On The Cornering Behavior of An Articulated Tracked VehicleiDEvNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 Solutions To ExercisesDocumento41 pagineChapter 12 Solutions To ExercisesMuhammad Awais56% (9)
- Elements of Roads and Highways by Max Fajardo 2nd EditionDocumento6 pagineElements of Roads and Highways by Max Fajardo 2nd EditionJ-Ron Calias0% (1)
- Alfonso, Michael John Agaser 202005047MN0 Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering Enrolled SubjectsDocumento1 paginaAlfonso, Michael John Agaser 202005047MN0 Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering Enrolled SubjectsMJA.AlfonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Credazone 6 GiudeDocumento3 pagineCredazone 6 Giudeguddu84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shear StressDocumento8 pagineShear StressRommel Carlo LargadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Infrastructure and ServicesDocumento3 pagineCloud Infrastructure and ServicesShobha RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 Batch (Sem 1 11-12)Documento10 pagine2010 Batch (Sem 1 11-12)prateek_7892Nessuna valutazione finora
- One BookDocumento29 pagineOne BookOnebookNessuna valutazione finora
- S BlockDocumento27 pagineS BlockAditya BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Dtu-30 09 2019 PDFDocumento15 pagineDtu-30 09 2019 PDFRameo majumderNessuna valutazione finora