Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
What Is Production?: Production Is Closely Linked To Marketing It Can Be Defined As
Caricato da
mohdportman0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
19 visualizzazioni6 paginePRODUCTION
Titolo originale
01 Production Methods
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoPRODUCTION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
19 visualizzazioni6 pagineWhat Is Production?: Production Is Closely Linked To Marketing It Can Be Defined As
Caricato da
mohdportmanPRODUCTION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
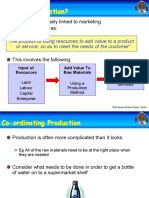
What Is Production?
Production is closely linked to marketing
It can be defined as:
“The process of using resources to add value to a product
or service, so as to meet the needs of the customer”
This involves the following:
Input of Add Value To Outputs
Resources Raw Materials
Goods
Land Using a Services
Labour Production
Capital Method
Enterprise
© Business Studies Online: Slide 1
Co-ordinating Production
Production is often more complicated than it looks.
Eg All of the raw materials need to be at the right place when
they are needed
Consider what needs to be done in order to get a bottle
of water on to a supermarket shelf
© Business Studies Online: Slide 2
Producing A Bottle of Water
In order to get something as simple as a bottle of water on
a supermarket shelf the following things must be done:
Bottle needs filling with water
Plastic cap must
be produced,
placed on bottles
Plastic bottle and sealed
needs to be
produced Label must be
designed, printed
and stuck on bottle
Water must be
sourced, treated Then product can be
and purified transported to retailer
© Business Studies Online: Slide 3
What Is Value-Added?
This is an important business term
It can be defined as:
“The increase in the benefits of a good or service which
are created at each stage of production”
This means that value can be added simply by making
a product more appealing to customers
Value-added is closely linked to the CHAIN OF
PRODUCTION
© Business Studies Online: Slide 4
Calculating Value Added
The Value added at each stage of production is
calculated using the formula:
Value Added = Value of Output – Value of Input
For example:
Farmer sells Milk for £1000, that cost him £300 £700
Milk Packaging Firm sells the same milk in cartons £1000
to a supermarket for £2000
Supermarket sells the same milk to customers for £1500
a total of £3500 £3200
The Value that has been added at each stage is shown in red
© Business Studies Online: Slide 5
Methods of Production
There are 3 main methods of production:
Job Production
Each item (or job) is completed before the next one is started
Eg Tailor-made clothing, Construction jobs (ie Wembley)
Batch Production
Involves dividing work into different tasks
Each task is completed on a number of products before they move
onto the next task
Eg Bread, Paint
Flow
Items are continuously moved from one task to another
Sometimes called MASS production
Eg car manufacturing, Tinned products
© Business Studies Online: Slide 6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Toyota Supply Chain Management ProcessDocumento16 pagineToyota Supply Chain Management ProcessLicece ImhNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report ON Cost Sheet Analysis OF Coca - Cola: Institute of Technology and ManagementDocumento11 pagineA Project Report ON Cost Sheet Analysis OF Coca - Cola: Institute of Technology and Managementkattyperrysherry33% (3)
- Q4 Principles of Marketing 12 - Module 5 (W2)Documento18 pagineQ4 Principles of Marketing 12 - Module 5 (W2)Oreo McflurryNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource WasDocumento7 pagineThis Study Resource Wasklm klmNessuna valutazione finora
- دليلك لإنشاء مصنع: خطوة بخطوة لدراسة وتأسيس وإدارة مؤسسة صناعية صغيرةDa Everandدليلك لإنشاء مصنع: خطوة بخطوة لدراسة وتأسيس وإدارة مؤسسة صناعية صغيرةValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Concise PRINCE2® - Principles and essential themes: Third editionDa EverandThe Concise PRINCE2® - Principles and essential themes: Third editionNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow of Accounting Entries in Oracle ApplicationsDocumento99 pagineFlow of Accounting Entries in Oracle ApplicationsRaj100% (5)
- Product Launch 123: Launch a New Product or Service in 3 Proven StepsDa EverandProduct Launch 123: Launch a New Product or Service in 3 Proven StepsValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Business Plan Milk Tea Break: MemberDocumento11 pagineBusiness Plan Milk Tea Break: MemberMarlo100% (7)
- Oracle SCM Cloud Using Planning CentralDocumento114 pagineOracle SCM Cloud Using Planning CentralMiguel FelicioNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Model Shifts: Six Ways to Create New Value For CustomersDa EverandBusiness Model Shifts: Six Ways to Create New Value For CustomersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Ent Task 2 New Product Development 2018Documento18 pagineEnt Task 2 New Product Development 2018Balqis BahriNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Plan Business Name: Aquafinite Bottled Water Production LogoDocumento7 pagineBusiness Plan Business Name: Aquafinite Bottled Water Production Logokaesha ermitanio100% (1)
- Retail ManagementDocumento80 pagineRetail Managementsheemankhan75% (4)
- Life Cycle CostingDocumento14 pagineLife Cycle CostingMUNAWAR ALI87% (15)
- Products that Last: Product Design for Circular Business ModelsDa EverandProducts that Last: Product Design for Circular Business ModelsNessuna valutazione finora
- Block2 ProductionDocumento23 pagineBlock2 ProductionSumolmal SrisukriNessuna valutazione finora
- Business PlanDocumento7 pagineBusiness PlanSaturday RainsNessuna valutazione finora
- MGT236 Power Point, Chapter03Documento42 pagineMGT236 Power Point, Chapter03Faisal KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- INTRODUCTIONSDocumento17 pagineINTRODUCTIONSUzzwal GhimireNessuna valutazione finora
- Feasibility FinalDocumento19 pagineFeasibility FinalrpmabuhaycityacademyincNessuna valutazione finora
- NestleDocumento12 pagineNestleSuhana BajracharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5. ManufacturingDocumento8 pagineUnit 5. Manufacturingpapa1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Got Ya Back - ReportDocumento12 pagineGot Ya Back - Reportapi-514538937Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statement of VisionDocumento11 pagineStatement of VisionAsia Marie AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper MGT 304 Term Paper MGT 304Documento10 pagineTerm Paper MGT 304 Term Paper MGT 304Md. Titu Mia 191-11-840Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Production of Goods and ServicesDocumento8 pagine4.1 Production of Goods and Servicesgeneva conventionsNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.0 Executive Summary: San Bartolome CampusDocumento46 pagine1.0 Executive Summary: San Bartolome CampusArabella GallanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sunshine Beverages Pvt. LTD.: Thirst Meets AmritDocumento19 pagineSunshine Beverages Pvt. LTD.: Thirst Meets AmritSuraj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Entrepreneurial Finance 6th Edition Leach Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineFull Download Entrepreneurial Finance 6th Edition Leach Solutions Manualcoctilesoldnyg2rr100% (28)
- Eyyys Candy Business PlanDocumento12 pagineEyyys Candy Business PlanDesederio MonrealNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 1Documento38 pagineSession 1janvi nagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Entrepreneurial Finance 6th Edition Leach Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Entrepreneurial Finance 6th Edition Leach Solutions Manual PDFdorissamuelqpnrrz100% (12)
- Compiled Business PlanDocumento17 pagineCompiled Business PlanClarence Abainza BalmeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocumento46 pagineIntroduction To Operations ManagementHakimi kaminiNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Micro Econ - Semi Final ModuleDocumento11 pagineBasic Micro Econ - Semi Final ModuleCristy RamboyongNessuna valutazione finora
- New Product Development Product Life CycleDocumento21 pagineNew Product Development Product Life CyclePRATIK BhosaleNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2 Production Methods (Operations Management)Documento26 pagine5.2 Production Methods (Operations Management)MIGUEL ALEJANDRO VALENTIN PERALTANessuna valutazione finora
- CostingDocumento12 pagineCostingpikalucky202Nessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Managerial Accounting The Cornerstone of Business Decision Making 7th Edition Mowen Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineFull Download Managerial Accounting The Cornerstone of Business Decision Making 7th Edition Mowen Solutions Manualaideneba100% (38)
- Complete Business Plan JhanelleDocumento18 pagineComplete Business Plan JhanelleCASTOR Z CMNHSNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Managerial Accounting The Cornerstone of Business Decision Making 7th Edition Mowen Solutions Manual PDFDocumento12 pagineDwnload Full Managerial Accounting The Cornerstone of Business Decision Making 7th Edition Mowen Solutions Manual PDFrucaizatax100% (9)
- Fruit ShakerDocumento23 pagineFruit ShakerJuna Lyn RañisesNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Introductory Page Name and Address of Business Bottle Brothers Glass Bottle Distributor, #69 Sipat, Plaridel, BulacanDocumento51 pagineI. Introductory Page Name and Address of Business Bottle Brothers Glass Bottle Distributor, #69 Sipat, Plaridel, Bulacanmarichu apiladoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3 - LearnerDocumento19 pagine1.3 - LearnerDhivya LakshmirajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Product DevDocumento28 pagineProduct Devpankajdeshwal@gmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Cornerstones of Managerial Accounting 5th Edition Mowen Solutions ManualDocumento12 pagineFull Download Cornerstones of Managerial Accounting 5th Edition Mowen Solutions Manualcolagiovannibeckah100% (37)
- Fill in This Form: Project On Business PlanDocumento10 pagineFill in This Form: Project On Business PlanRaquel Husayan ParanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Operation Management PaperDocumento22 pagineSample Operation Management PapertacangbadetteNessuna valutazione finora
- Sherjil CostDocumento20 pagineSherjil CostSherjil Tahir100% (1)
- Adding Value: Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies Section 1 Understanding Business ActivityDocumento3 pagineAdding Value: Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies Section 1 Understanding Business ActivityShaikh Ghassan AbidNessuna valutazione finora
- Entre Module 3Documento14 pagineEntre Module 3Anne GimoteaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Financial Number GameDocumento4 pagineThe Financial Number GamerafaeltrikostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Balmes Feas-StudyDocumento31 pagineBalmes Feas-StudyAngelo Bon BalmesNessuna valutazione finora
- Production 3Documento13 pagineProduction 3nrv2hcm25cNessuna valutazione finora
- Feasibility Study Tamuno Divine Get201Documento12 pagineFeasibility Study Tamuno Divine Get201Tamuno DivineNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento48 pagineModule 2RhealynBalboaLopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 Research Nestle Case StudyDocumento18 pagineGroup 4 Research Nestle Case StudyMohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- English Type 2020 EditbbbDocumento15 pagineEnglish Type 2020 EditbbbChanuka PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Production (2497) PDFDocumento3 pagine2 Production (2497) PDFLoudjeineNessuna valutazione finora
- ONLINE LESSON 5 Manufacturing OperationsDocumento19 pagineONLINE LESSON 5 Manufacturing OperationsKimberly Claire AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting For Joint Products and By-ProductsDocumento14 pagineAccounting For Joint Products and By-Productsnicole bancoroNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4 Mision: 2.5 VisionDocumento1 pagina2.4 Mision: 2.5 VisionRaja NaniNessuna valutazione finora
- When, If Ever Should A Govt Intervene To Prevent A Merger or Takeover?Documento2 pagineWhen, If Ever Should A Govt Intervene To Prevent A Merger or Takeover?mohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply, Demand, and Government PoliciesDocumento16 pagineSupply, Demand, and Government PoliciesmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- TK/PPD: Presentation Planning DocumentDocumento3 pagineTK/PPD: Presentation Planning DocumentmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 24: Demand For Factors of ProductionDocumento13 pagineUnit 24: Demand For Factors of ProductionmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 1: Exam Preparation - AnswersDocumento4 paginePart 1: Exam Preparation - Answersmohdportman0% (1)
- Unit 12-Use of ResourcesDocumento7 pagineUnit 12-Use of ResourcesmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To IGCSE BUSINESS STUDIESDocumento13 pagineWelcome To IGCSE BUSINESS STUDIESmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To IGCSE BUSINESS STUDIESDocumento13 pagineWelcome To IGCSE BUSINESS STUDIESmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute Cost and Comparative Cost AdvantagesDocumento11 pagineAbsolute Cost and Comparative Cost AdvantagesmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Technology and Marketing MixDocumento8 pagineTechnology and Marketing MixmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gov Intervention 1b ExemplarDocumento2 pagineGov Intervention 1b ExemplarmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento14 pagineChapter 8mohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ib Economics HL Paper-3: (Home Work Book)Documento14 pagineIb Economics HL Paper-3: (Home Work Book)mohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocumento24 pagineChapter 9: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplymohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Wise Choir ScheduleDocumento8 pagineClass Wise Choir SchedulemohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 0450 Business Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocumento9 pagine0450 Business Studies: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Price Discrimination IB EconomicsDocumento13 paginePrice Discrimination IB EconomicsmohdportmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Option 1 - Commercial InvoiceDocumento2 pagineOption 1 - Commercial InvoiceStacey lukeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Manajemen Operasi Stroller Case Kelompok 1 PDFDocumento4 pagineTugas Manajemen Operasi Stroller Case Kelompok 1 PDFDwi Permana100% (1)
- ERP ALL Full FormsDocumento5 pagineERP ALL Full FormsRajdipsinh N JadejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flipkart-Group 5Documento33 pagineFlipkart-Group 5Arjun BhanushaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Packing List 0081063852 Fecha:30/06/21: Orden Destino Pallet Master SSCC # Pallet Caja Master SSCC ArtículoDocumento26 paginePacking List 0081063852 Fecha:30/06/21: Orden Destino Pallet Master SSCC # Pallet Caja Master SSCC Artículoyeison gavilanNessuna valutazione finora
- DB Aabggibgfaah0x089bDocumento3 pagineDB Aabggibgfaah0x089bvijucool16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pre QualificationDocumento33 paginePre QualificationMỹ HạnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key Chapter 9 ConsignmentDocumento6 pagineAnswer Key Chapter 9 Consignmentkaren perrerasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unilever in Brazil AnswersDocumento1 paginaUnilever in Brazil AnswersMelody LalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study No. 1 - GRP 7Documento14 pagineCase Study No. 1 - GRP 7Shuu SanNessuna valutazione finora
- MBA101Documento10 pagineMBA101Reeya ElixirNessuna valutazione finora
- Anurag Joshi: EducationDocumento1 paginaAnurag Joshi: EducationThe Cultural CommitteeNessuna valutazione finora
- King JouetDocumento3 pagineKing JouetAndres Jaramillo BoteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Supply Chain Management: by MR - Rupesh Sakhare M.B.A Ii (Ope)Documento10 pagineGreen Supply Chain Management: by MR - Rupesh Sakhare M.B.A Ii (Ope)kashijee40Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maersk Sealand Shipping Instruction AllDocumento3 pagineMaersk Sealand Shipping Instruction AllArturo Chávez MogollónNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Quick Response To Supply ChainDocumento15 pagineRole of Quick Response To Supply ChainSanuwar RashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Marginal CostingDocumento42 pagineMarginal CostingAbdifatah SaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Sovereign Container Line, Inc: 10644481 SCLI40008202Documento1 paginaSovereign Container Line, Inc: 10644481 SCLI40008202ORLANDO GONZALEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Thinking Made EasyDocumento96 pagineThinking Made EasysweethanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- BOL MapclorakDocumento2 pagineBOL MapclorakAbdullah LimonNessuna valutazione finora
- UAS BING Ferdy Setyaluhur 2001061057Documento11 pagineUAS BING Ferdy Setyaluhur 2001061057kibooNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study IDocumento5 pagineCase Study IDimas Ahmad AlimuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- MQM Flyer NewDocumento1 paginaMQM Flyer NewAHS ManajemenNessuna valutazione finora
- Distribution Channel of LGDocumento3 pagineDistribution Channel of LGBadal BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Mirjam Beltrami, Guido Orzes, Joseph Sarkis, Marco SartorDocumento21 pagineJournal of Cleaner Production: Mirjam Beltrami, Guido Orzes, Joseph Sarkis, Marco SartorJames RCNessuna valutazione finora
- An Evaluation of Demand and Capacity Planning Processes - A Qualitative Case Study On Completely-Knocked-Down Vehicles at Mercedes-Benz CarsDocumento276 pagineAn Evaluation of Demand and Capacity Planning Processes - A Qualitative Case Study On Completely-Knocked-Down Vehicles at Mercedes-Benz Carsmiracle ndeuleNessuna valutazione finora