Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
FM PPT Mba
Caricato da
ipsita mishra0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
56 visualizzazioni13 paginefiancial ppt
Titolo originale
FM ppt mba
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentofiancial ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
56 visualizzazioni13 pagineFM PPT Mba
Caricato da
ipsita mishrafiancial ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 13
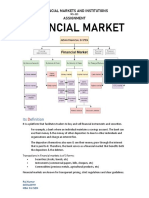
FINANCIAL
MARKET
Presented By- ANKITA PANDA,
SOUMYA PANDA,PRAGYAN NAYAK,
IPSITA MISHRA,SUPRITEE BEHERA
CONTENT:-
What is Market ?
What is Financial Market ?
Types of Financial Market ?
Types of Capital Market ?
Regulatory bodies of Capital Market in
India :
1-RBI & Its functions.
2-SEBI & Its Functions.
WHAT IS MARKET ?
A market is a place where two parties are
involved in transaction of goods and services in
exchange of money. The two parties involved
are:
1.Buyer
2. Seller
In a market the buyer and seller comes on a
common platform, where buyer purchases goods
and services from the seller in exchange of
money.
WHAT IS FINANCIAL MARKET ?
A place where individuals are involved in
any kind of financial transaction refers to
financial market.
Financial market is a platform where
buyers and sellers are involved in sale and
purchase of financial products like shares,
mutual funds, bonds and so on.
TYPES OF FINACIAL MARKET :
CAPITAL MARKET - A market where individuals
invest for a longer duration i.e. more than a year is
called as capital market. In a capital market various
financial institutions raise money from individuals and
invest it for a longer period.
SECOUNDARY
PRIMARY MARKET
MARKET
Primary Market is a
form of capital Secondary market is
market where various a form of capital
companies issue new market where stocks
stock, shares and and securities which
bonds to investors in have been previously
the form of IPO’s . issued are bought
and sold
TYPES OF CAPITAL MARKET
Stock Markets: Stock Market is a type of Capital market which
deals with the issuance and trading of shares and stocks at a
certain price.
Bond Markets: Bond Market is a form of capital market where
buyers and sellers are involved in the trading of bonds.
Commodity Market: A market which facilitates the sale and
purchase of raw goods is called a commodity market.
Money Market: As the name suggests, money market involves
individuals who deal with the lending and borrowing of money for
a short time frame.
Derivatives Market: The market which deals with the trading of
contracts which are derived from any other asset is called as
derivative market.
Future Market: Future market is a type of financial market
which deals with the trading of financial instruments at a specific
rate where in the delivery takes place in future.
Insurance Market: Insurance market deals with the
trading of insurance products. Insurance companies pay a
certain amount to the immediate family members of owner
of the policy in case of his untimely death.
Foreign Exchange Market: Foreign exchange market is
a globally operating market dealing in the sale and
purchase of foreign currencies.
Private Market: Private market is a form of market
where transaction of financial products takes place
between two parties directly.
Mortgage Market: A type of market where various
financial organizations are involved in providing loans to
individuals on various residential and commercial
properties for a specific duration is called a mortgage
market.
REGULATORY BODIES OF
CAPITAL IN INDIA:
RESERVE BANK SEBI
OF INDIA
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central
bank of India, which was established on April 1,
1935, under the Reserve Bank of India Act.
The Reserve Bank of India uses monetary policy to
create financial stability in India, and it is charged
with regulating the country's currency and credit
systems.
The RBI was originally set up as a private entity
but was nationalized in 1949. The reserve bank is
governed by a central board of directors appointed
by the national government.
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF RBI:
Monopoly of Note Issue-RBI acts as a sole
currency authority of the country.
Banker’s Bank-As bankers’ bank, the RBI holds
a part of the cash reserves of commercial banks
and lends them funds for short periods.
Banker to the Government-The RBI acts as
the banker to the government of India and State
Governments (except Jammu and Kashmir).
Controller of Credit-The RBI controls the total
supply of money and bank credit to sub serve the
country’s interest.
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF
INDIA [SEBI]
Securities and Exchange Board of India is the
regulator for all the security markets in India.
It was established in 1988 and was given
statutory power on 12 April 1992 through the
SEBI Act, 1992.
SEBI has to be responsive to 3 groups which
constitute the market:
1.The issuer of securities
2.The investor
3.The market intermediaries
FUNCTIONS OF SEBI:
• It checks price rigging
Protective • It prohibited insider trading & unfair
trading
Function • Fair practices & code of conduct in
security market
• Training of intermediaries of securities
Development exchange.
Function • Adopting flexible & acceptable approach
in stock exchange.
• Code of conduct to regulate the
Regulatory intermediaries .
• Register & regulate all type of broker,
Function agents, trustees and merchant banks.
THANK YOU
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Unit-10 Bs-Xii RK SinglaDocumento30 pagineUnit-10 Bs-Xii RK SinglaThe stuff unlimitedNessuna valutazione finora
- PreviewpdfDocumento34 paginePreviewpdfipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech Talk Food Safety CultureDocumento2 pagineTech Talk Food Safety CulturePrerna Dingal RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Competitive Advantage of Corporate PhilanthropyDocumento2 pagineCompetitive Advantage of Corporate PhilanthropyJona Mae Milla100% (1)
- Some of The Features of The Financial Market Are As FollowsDocumento4 pagineSome of The Features of The Financial Market Are As FollowsabcdNessuna valutazione finora
- IAPM 1 (26 Oct)Documento8 pagineIAPM 1 (26 Oct)Akriti JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bba Notes 6Documento53 pagineBba Notes 6RAJATNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Financial MarketDocumento20 pagineIndian Financial MarketAnaniya TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Raj Kumar, MBA 3rd Sem, FMI AssignmentDocumento4 pagineRaj Kumar, MBA 3rd Sem, FMI AssignmentRaj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Detailed Project On Secondary Market.Documento40 pagineA Detailed Project On Secondary Market.Jatin Anand100% (1)
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocumento78 pagineFinancial Markets and Institutionsamol_more37100% (1)
- Indian Financial Market: Rahul Kumar Department of Business AdminestrationDocumento52 pagineIndian Financial Market: Rahul Kumar Department of Business AdminestrationDhruv MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudiesDocumento5 pagineCase StudiesShalu PurswaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Market OperationsDocumento28 pagineFinancial Market OperationsdeepeshmahajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Marketing: 26 Oct. 09 Duration: 1 Hour 30 MinsDocumento13 pagineCapital Marketing: 26 Oct. 09 Duration: 1 Hour 30 MinsChand BashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 2 FmeDocumento9 pagineUnit - 2 FmeTanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Money MarketDocumento4 pagineMoney MarketThiên TrangNessuna valutazione finora
- FMI All ModulesDocumento81 pagineFMI All ModulesSandeepMishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Busu CursDocumento173 pagineBusu CursAndreea Cristina DiaconuNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes - Money MarketDocumento7 pagineNotes - Money MarketShivshankar KhemnarNessuna valutazione finora
- Objectives of The Money Market in IndiaDocumento13 pagineObjectives of The Money Market in IndiaVineet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- IFS - Chapter 2Documento17 pagineIFS - Chapter 2riashahNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Money Market?Documento12 pagineWhat Is The Money Market?Vishnu AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Financial MarketsDocumento12 pagineClassification of Financial Marketsvijaybhaskarreddymee67% (6)
- Bba 5 Unit 2Documento5 pagineBba 5 Unit 2gorang GehaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Financial SystemDocumento34 pagineIndian Financial SystemVivek SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Market and Money MarketDocumento17 pagineCapital Market and Money MarketSwastika Singh100% (1)
- What Is A Financial MarketDocumento1 paginaWhat Is A Financial Marketamitrao1983Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - Financial MarketsDocumento79 pagineUnit 1 - Financial Marketsvishwa princeNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial System and MarketsDocumento32 pagineFinancial System and Marketsmohamedsafwan0480Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Financial Markets and Instruments Group 1 FM7Documento23 pagineModule 2 Financial Markets and Instruments Group 1 FM7hikunanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module - 4 Money Market & Capital Market in IndiaDocumento11 pagineModule - 4 Money Market & Capital Market in IndiaIshan GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Markets FinalDocumento59 pagineFinancial Markets FinaltestNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary Market Regulatory Framework and Sebi Fuctions and RolesDocumento20 pagineSecondary Market Regulatory Framework and Sebi Fuctions and RolesBADAM NAVINA Finance2019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Black Book 2 1Documento60 pagineBlack Book 2 1Madeeha MukadamNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Market in IndiaDocumento8 pagineFinancial Market in IndiaAashutosh ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Market in IndiaDocumento8 pagineFinancial Market in IndiaAashutosh ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Financial SystemDocumento46 pagineIndian Financial SystemRaja KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial/ Securities Markets Notes: For Sebi Grade A & Rbi Grade BDocumento10 pagineFinancial/ Securities Markets Notes: For Sebi Grade A & Rbi Grade BAadeesh JainNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW WDocumento15 pagineWWW WSuraj MaityNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial MarketsDocumento9 pagineFinancial MarketsyounazNessuna valutazione finora
- BY: Osama Tariq. Sajawal. Adnan Shahzad. Shaikh Ahmed AliDocumento36 pagineBY: Osama Tariq. Sajawal. Adnan Shahzad. Shaikh Ahmed Alishaikh ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of Money MarketDocumento17 pagineDefinition of Money MarketSmurti Rekha JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Financial Markets: Class of MBADocumento43 pagineIndian Financial Markets: Class of MBAaksid1Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Money MarketDocumento77 pagineA Study On Money MarketNaveen KuttyNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3 FMDocumento21 pagineCH 3 FMTHRISHA JINKALANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 A Study of Indian Share MarketDocumento33 pagineChapter-1 A Study of Indian Share MarketManisankar SenapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Markets Notes-1Documento2 pagineFinancial Markets Notes-1munna bhaiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment NotesDocumento30 pagineInvestment Notesshantanu100% (2)
- Finance Vs Financial SystemDocumento61 pagineFinance Vs Financial Systempriyasumit100% (1)
- Chapter 1: About The Industry Finance IndustryDocumento3 pagineChapter 1: About The Industry Finance IndustryDeepak GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting and FinancialDocumento31 pagineAccounting and FinancialAkash ArvikarNessuna valutazione finora
- 105 - Financial Institution & MarketDocumento29 pagine105 - Financial Institution & MarketRahul MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1.1Documento36 pagineUnit 1.1pravinkalepkkNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Script - Money Market in India200324060603035050Documento15 pagine3 - Script - Money Market in India200324060603035050DWITI RavariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Market in IndiaDocumento33 pagineCapital Market in IndiaAnonymous Rz2JhINessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 Financial MarketsDocumento30 pagineUnit-3 Financial MarketsPiyu VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- History of StockDocumento19 pagineHistory of StockSIddharth CHoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 - Capital Market PrimaryDocumento35 pagine03 - Capital Market PrimaryManjuNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Market InstrumentDocumento40 pagineMoney Market InstrumentAkanksha ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Economics 6th Sem Compiled by Aasif-Ur-RahmanDocumento45 pagineFinancial Economics 6th Sem Compiled by Aasif-Ur-RahmanKhan HarisNessuna valutazione finora
- SA Operations of Stock MarketDocumento7 pagineSA Operations of Stock MarketPublik SecttorNessuna valutazione finora
- Itr-1 Sahaj Indian Income Tax Return: Acknowledgement Number: Assessment Year: 2020-21Documento7 pagineItr-1 Sahaj Indian Income Tax Return: Acknowledgement Number: Assessment Year: 2020-21Prérńã K K ŚhãhNessuna valutazione finora
- Print Application Receipt - Passport SevaDocumento1 paginaPrint Application Receipt - Passport Sevaipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Assessment YearDocumento1 paginaIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Assessment Yearipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Payment Receipt: Applicant DetailsDocumento1 paginaOnline Payment Receipt: Applicant Detailsipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayusmita Mishra: Mahavirpada, Dhanupalli, Sambalpur, OD Ph. +91-8917252896Documento2 pagineAyusmita Mishra: Mahavirpada, Dhanupalli, Sambalpur, OD Ph. +91-8917252896ipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Training & Development: Training As A Management Skill / Training and Developing Your StaffDocumento36 pagineTraining & Development: Training As A Management Skill / Training and Developing Your StaffVijay AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Provisional M.Phil. Merit ListDocumento21 pagineProvisional M.Phil. Merit Listipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- COVID-19 Vaccination Appointment Details: Center Date Time Preferred Time SlotDocumento1 paginaCOVID-19 Vaccination Appointment Details: Center Date Time Preferred Time Slotipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume Sample-Fresher MBADocumento2 pagineResume Sample-Fresher MBAipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- AcademicConsultant November2020Documento2 pagineAcademicConsultant November2020ipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Undertaking PDFDocumento1 paginaUndertaking PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- PG M.phil P.HDDocumento39 paginePG M.phil P.HDipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership Agility HRPS Reprint RevisedDocumento7 pagineLeadership Agility HRPS Reprint RevisedHastin Istiqomah NingtyasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sambalpur University: A Peep Into The PastDocumento22 pagineThe Sambalpur University: A Peep Into The Pastipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- SP EnglishDocumento3 pagineSP Englishdeekshith kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Conducting Baseline & Need Assesment Study of Undertake Sustainable Intervation Towards Improvement of Sambalpuri Handloom WeaversDocumento2 pagineConducting Baseline & Need Assesment Study of Undertake Sustainable Intervation Towards Improvement of Sambalpuri Handloom Weaversipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Topics in Linear Programming-1Documento3 pagineAdvanced Topics in Linear Programming-1Shivansh TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Scrollnews 1610434108Documento2 pagineScrollnews 1610434108ipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Mod15TrainingDesigntext PDFDocumento15 pagine15 Mod15TrainingDesigntext PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Mod7LearningTheoriestext PDFDocumento11 pagine7 Mod7LearningTheoriestext PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- paperinMathematicstodayDec2018 PDFDocumento8 paginepaperinMathematicstodayDec2018 PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Cannos Road PDFDocumento79 pagineTwo Cannos Road PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Factory Act PDFDocumento26 pagineFactory Act PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- M.a.hrmapp-24 - R&S PDFDocumento32 pagineM.a.hrmapp-24 - R&S PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Test Booking System PDFDocumento1 paginaOnline Test Booking System PDFipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- L O H S Pbso E Aq H Aq So S Pbo: Section:ADocumento10 pagineL O H S Pbso E Aq H Aq So S Pbo: Section:AKalpit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial LegionDocumento10 pagineIndustrial Legionipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- (Part - I) Strategic Management (Eng)Documento209 pagine(Part - I) Strategic Management (Eng)vaishnavforever100% (3)
- Cross-National Cooperation and AgreementsDocumento19 pagineCross-National Cooperation and Agreementsipsita mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Resisting The Rise of Non-Unionism: The Case of The Press Workers in The Newspaper IndustryDocumento19 pagineResisting The Rise of Non-Unionism: The Case of The Press Workers in The Newspaper IndustryMarwa MohNessuna valutazione finora
- RMS Stock Ledger White Paper-14.1.xDocumento94 pagineRMS Stock Ledger White Paper-14.1.xanvesh5435Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Consumer Satisfaction Towards Dell LaptopsDocumento46 pagineA Study On Consumer Satisfaction Towards Dell LaptopsINSTITUTE OF PROFESSIONAL ACCOUNTANTSNessuna valutazione finora
- Resale Price Lor Lew LianDocumento2 pagineResale Price Lor Lew LianAlex Ng W HNessuna valutazione finora
- Budgetary Control System - HeritageDocumento82 pagineBudgetary Control System - HeritageSwathi Manthena50% (4)
- 2023 Article 1185Documento27 pagine2023 Article 1185panthi utsavNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pearson Series in FinanceDocumento1 paginaThe Pearson Series in FinanceYo_amaranthNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance WikiDocumento101 pagineFinance WikiJenő TompiNessuna valutazione finora
- CSI1241 Assignment 1 1Documento3 pagineCSI1241 Assignment 1 1Nik Yusof Nik FaridNessuna valutazione finora
- Banasthali Vidyapith: Master of Business AdministrationDocumento112 pagineBanasthali Vidyapith: Master of Business AdministrationRuchi AgarwallNessuna valutazione finora
- PopExpert PetitionDocumento79 paginePopExpert PetitionChapter 11 DocketsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelaksanaan Program Pembinaan Koperasi Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (Umkm)Documento7 paginePelaksanaan Program Pembinaan Koperasi Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (Umkm)Razief Firdaus 043Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nism 8 - Equity Derivatives - Test-1 - Last Day RevisionDocumento54 pagineNism 8 - Equity Derivatives - Test-1 - Last Day RevisionAbhijeet Kumar100% (1)
- Audit ReportsDocumento31 pagineAudit ReportsAid BolanioNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Integration Point Setup Between People Soft Enterprise Campus Solutions and People Soft Enterprise CRMDocumento92 pagineEnterprise Integration Point Setup Between People Soft Enterprise Campus Solutions and People Soft Enterprise CRMmilindsusNessuna valutazione finora
- 2307 WestmeridianDocumento2 pagine2307 WestmeridianRheddy RaymundoNessuna valutazione finora
- POM Chapter 9Documento46 paginePOM Chapter 9Mazhar Ul HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- ACIOE Capability Statement UpdatedDocumento18 pagineACIOE Capability Statement UpdatedAHMEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Finance Module 1Documento7 pagineBusiness Finance Module 1Kanton FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Enron ScandalDocumento9 pagineEnron ScandalRohith MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- D:/Desktop/scanned/Circular No. 2012-001/circular-Without Number - JPG 2012-001Documento11 pagineD:/Desktop/scanned/Circular No. 2012-001/circular-Without Number - JPG 2012-001barcelonnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asean Region Ip SuccessesDocumento86 pagineAsean Region Ip SuccessesTran Q ThaiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Marketing in Strategic PlanningDocumento45 pagineThe Role of Marketing in Strategic PlanningAnu JinrisulNessuna valutazione finora
- Bid Notice Abstract: Request For Proposal (RFP)Documento1 paginaBid Notice Abstract: Request For Proposal (RFP)John Rheynor MayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Examples SMART GOALSDocumento1 paginaExamples SMART GOALSMinh TranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Three Golis UniversityDocumento40 pagineChapter Three Golis UniversityCabdixakiim-Tiyari Cabdillaahi AadenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost and Benefit Analysis of Outsourcing From The Perspective of Datapath LTDDocumento59 pagineCost and Benefit Analysis of Outsourcing From The Perspective of Datapath LTDranzlorenzoo100% (1)
- OpenSAP s4h11 Week 2 TranscriptDocumento34 pagineOpenSAP s4h11 Week 2 TranscriptUmar FarooqNessuna valutazione finora