Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ib CH 12
Caricato da
Himansu Bisoi0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
130 visualizzazioni25 pagineTitolo originale
ib_ch_12.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
130 visualizzazioni25 pagineIb CH 12
Caricato da
Himansu BisoiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 25
Automotive Brake Systems
CHAPTER 12
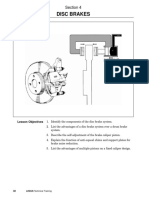
Disc Brakes
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
OBJECTIVES
• Describe the parts and operation of disc
brakes.
• Describe the construction of disc brake
pads.
• Discuss the brake pad assembly
methods and brake lining composition.
• Describe the difference between fixed
caliper and floating or sliding caliper.
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKES
• Parts and Operation
Piston(s) squeeze friction material
(pads) on both sides of rotating disc
(rotor)
Used on front wheels of late-model
vehicles
Used on rear wheels of increasing
number of automobiles
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKES
Adopted because supply greater
stopping power than drum brakes with
less likelihood of fade
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Pad Assembly
Block of friction material attached to
stamped steel backing plate
Some pad backing plates have tabs that
bend over caliper to hold pad in place
Others have tabs with holes in them
• Pin slips through holes and fastens to
caliper body to hold pads
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
Still others have retainer spring that
locks pad to caliper piston
Lining material can be one of a number
of products
Can be fastened to backing plate in
several ways
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Pad Assembly
Edges of lining material usually
perpendicular to rotor surface
A few larger pads have tapered edges to
help combat vibration and noise
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Pad Assembly Methods
Riveted linings
• Brake block attached to backing plate
with metal rivets
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Pad Assembly Methods
Bonded linings
• Glue brake block directly to shoe pad
backing plate
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Pad Assembly Methods
Mold-bonded linings
• Combines advantages of bonding with
mechanical strength of riveting
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Ingredients mixed and molded into
shape of finished product
Fibers in material only thing holding
mixture together
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Large press forces ingredients together
to form brake block, which becomes
brake lining
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Semimetallic friction material
• Uses metal rather than asbestos in its
formulation
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Semimetallic friction material
• Require very smooth finish on rotor
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Nonasbestos friction material
• Use synthetic material such as aramid
fibers instead of steel
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Carbon fiber friction material
• Newest and most expensive of the lining
materials
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
DISC BRAKE PADS
• Brake Lining Composition
Ceramic friction material
• Most pads today are ceramic and use
little, if any steel
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
• Fixed Caliper Design
Body manufactured in two halves
Uses two, four, or six pistons to apply
brake pads
Caliper rigidly mounted to suspension
When brakes applied, pistons extend
from caliper bores and apply brake pads
with equal force from both sides of rotor
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
No part of caliper body moves when
brakes applied
• Floating and Sliding Caliper Design
Used in front brakes of most vehicles
Caliper free to move within limited
range on anchor plate solidly mounted
to vehicle suspension
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
• Floating and Sliding Caliper Design
When brakes applied, caliper piston
applies inner brake pad
At same time, caliper body moves in
opposite direction on anchor plate and
applies outer brake pad
Caliper body moves every time brakes
applied
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
• Floating Caliper Operation
Body of floating caliper does not make
direct contact with anchor plate
Body supported by bushings and/or O-
rings
• Allow it to “float” or slide on metal guide
pins attached to anchor plate
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
• Floating Caliper Operation
Depend on proper lubrication of pins,
sleeves, bushings, and O-rings for
smooth operation
Special high-temperature brake grease
must be used
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
• Sliding Calipers
Body of sliding caliper mounts in direct
metal-to-metal contact with anchor
plate
Calipers move on ways cast and
machined into caliper body and anchor
plate
Retaining clips and design of caliper
prevent body from coming out of ways
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
CALIPER DESIGNS
Depend on good lubrication of ways for
proper operation
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
SUMMARY
• Piston(s) squeeze friction material
(pads) on both sides of rotating disc
(rotor)
• Fixed caliper design is body
manufactured in two halves
• In floating and sliding caliper design
the caliper free to move within limited
range on anchor plate solidly mounted
to vehicle suspension
Automotive Brake Systems, 7e Copyright © 2017 by Pearson Education, Inc.
James D. Halderman All Rights Reserved
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- GM G-Body Performance Upgrades 1978-1987: Chevy Malibu & Monte Carlo, Pontiac Grand Prix, Olds Cutlass Supreme & Buick RegalDa EverandGM G-Body Performance Upgrades 1978-1987: Chevy Malibu & Monte Carlo, Pontiac Grand Prix, Olds Cutlass Supreme & Buick RegalValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- New Hemi Engines 2003-Present: How to RebuildDa EverandNew Hemi Engines 2003-Present: How to RebuildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (10)
- Detroit Speed's How to Build a Pro Touring CarDa EverandDetroit Speed's How to Build a Pro Touring CarValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Swap LS Engines into Chevelles & GM A-Bodies: 1964-1972Da EverandSwap LS Engines into Chevelles & GM A-Bodies: 1964-1972Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Oxy AcetyleneDocumento43 pagineOxy Acetyleneregupathi100% (1)
- 2019 IL and Federal Pharmacy Law Review PDFDocumento176 pagine2019 IL and Federal Pharmacy Law Review PDFAnonymous 3YNJfYNQ100% (5)
- 7 Tools for Continuous ImprovementDocumento202 pagine7 Tools for Continuous Improvementvivekanand bhartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalog Arnott AirsuspensionDocumento20 pagineCatalog Arnott AirsuspensionAntonioPalloneNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 TTWDocumento67 pagineUnit 4 TTWMohsin EngrNessuna valutazione finora
- Brake Design ReportDocumento29 pagineBrake Design ReportGökhan Yazar0% (4)
- Wheels and TiresDocumento31 pagineWheels and TiresSri NavinNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Hook & Launch: Traction Mods for Street & StripDa EverandHow to Hook & Launch: Traction Mods for Street & StripNessuna valutazione finora
- Suspension Design Rajeev - MokashiDocumento16 pagineSuspension Design Rajeev - MokashiJatin351100% (1)
- Design - Report (PDR)Documento8 pagineDesign - Report (PDR)Abhishek DixitNessuna valutazione finora
- Session4 Automotive Front End DesignDocumento76 pagineSession4 Automotive Front End DesignShivprasad SavadattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vehicle Dynamics and Damping: First Revised EditionDa EverandVehicle Dynamics and Damping: First Revised EditionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Lightweight Materials For AutomotiveDocumento67 pagineLightweight Materials For AutomotiveFWEFWEFW100% (1)
- 12.1.tires and WheelsDocumento115 pagine12.1.tires and WheelsEbe Nezer GNessuna valutazione finora
- Automotive E-Coat Paint Process Simulation Using FEADocumento20 pagineAutomotive E-Coat Paint Process Simulation Using FEAflowh_100% (1)
- Service Information, Tools and SafetyDocumento110 pagineService Information, Tools and SafetyzeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Engine Design and Operation: © INFINEUM INTERNATIONAL LIMITED 2017. All Rights ReservedDocumento62 pagineFundamentals of Engine Design and Operation: © INFINEUM INTERNATIONAL LIMITED 2017. All Rights ReservedJahmia Coralie100% (1)
- Chap 67Documento37 pagineChap 67Eslam KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- LM PodDocumento4 pagineLM PodHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Book3 79 111000 0000100120 DAH MPL RPT 000005 - ADocumento101 pagineBook3 79 111000 0000100120 DAH MPL RPT 000005 - ANassif Abi AbdallahNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar 6 Precision AttachmentsDocumento30 pagineSeminar 6 Precision AttachmentsAmit Sadhwani67% (3)
- PHILHIS Executive Summary - EditedDocumento7 paginePHILHIS Executive Summary - EditedMaxy Bariacto100% (1)
- Basic Car Maintenance Braking - SystemDocumento6 pagineBasic Car Maintenance Braking - SystemCrepin Miguel Jn BaptisteNessuna valutazione finora
- Disc BrakesDocumento52 pagineDisc BrakesLin AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Disc BrakesDocumento28 pagine12 Disc BrakesdrayetorNessuna valutazione finora
- Drum BrakesDocumento34 pagineDrum BrakesdrayetorNessuna valutazione finora
- FSAE Design Report 2ndversionDocumento24 pagineFSAE Design Report 2ndversionananNessuna valutazione finora
- Baja SAE Collegiate Design Series Report-Brigham Young University-IdahoDocumento5 pagineBaja SAE Collegiate Design Series Report-Brigham Young University-IdahoKarlos QuintanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering AssDocumento10 pagineEngineering Assapi-3833502Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brake04 Disc Brake PDFDocumento0 pagineBrake04 Disc Brake PDFPushkar NathNessuna valutazione finora
- Landcruiser Brochure PDFDocumento9 pagineLandcruiser Brochure PDFJohn AlajoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disc Brakes: Section 4Documento9 pagineDisc Brakes: Section 4rabitosanNessuna valutazione finora
- MET2013 Hinojosa RicardoDocumento27 pagineMET2013 Hinojosa RicardoAmal GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted byDocumento34 pagineSeminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted bySouraj PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- (PDF) Design Report Quad Bike Design Challenge - 2016Documento13 pagine(PDF) Design Report Quad Bike Design Challenge - 2016abhijitakadamNessuna valutazione finora
- AutomobileDocumento25 pagineAutomobileNitin VarmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Wheels and Tyres: - Types of Wheel, Construction of Wired Wheel, DiscDocumento15 pagineWheels and Tyres: - Types of Wheel, Construction of Wired Wheel, DiscajaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Brakes Design ReportDocumento4 pagineBrakes Design ReportYogesh SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-2 Drum BrakesDocumento3 pagineChapter-2 Drum BrakesKranthi Kk0% (1)
- Engineering Studies Report - Yr9 2015Documento5 pagineEngineering Studies Report - Yr9 2015Three Went DownNessuna valutazione finora
- SAE BAJA 2013 Preliminary Design ReportDocumento10 pagineSAE BAJA 2013 Preliminary Design Reportrudey18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Testing and Rating: © INFINEUM INTERNATIONAL LIMITED 2017. All Rights ReservedDocumento42 pagineEngine Testing and Rating: © INFINEUM INTERNATIONAL LIMITED 2017. All Rights ReservedJahmia CoralieNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramic Disc BrakeDocumento19 pagineCeramic Disc BrakeSandeepkumar SgNessuna valutazione finora
- RAYS PresentationDocumento17 pagineRAYS PresentationKarol CzerwińskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tire and Wheel Theory: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocumento25 pagineTire and Wheel Theory: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningRonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Team Yuyutsu Svnit Surat FinalDocumento11 pagineTeam Yuyutsu Svnit Surat FinalSambit SunyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chrysler Sebring 1996-06 - Sierra PDFDocumento14 pagineChrysler Sebring 1996-06 - Sierra PDFChris BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Drums Are SimpleDocumento6 pagineDrums Are SimpleisaacamankwaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brake FDRDocumento3 pagineBrake FDRabdul quadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Brake System Fundamentals: BrakesDocumento90 pagineBrake System Fundamentals: Brakesashigupta143100% (1)
- Ceramic Disc BrakeDocumento16 pagineCeramic Disc BrakesachinNessuna valutazione finora
- 150X180X12 HMS5 RG_20220905Documento3 pagine150X180X12 HMS5 RG_20220905t1o2n3i4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Santanu PPTDocumento11 pagineSantanu PPTASHUTOSH SAHOOLME011 (LME011)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Page 0228Documento1 paginaPage 0228WathoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Disk Brakes: A Technical OverviewDocumento19 pagineDisk Brakes: A Technical OverviewLokesh MahawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Tyre Pressure Inflation SystemDocumento3 pagineAutomatic Tyre Pressure Inflation SystemKarthick MNessuna valutazione finora
- Wheels and Tires: Look at E-Mail From John Under Inbox Tab, Brakes Class FolderDocumento100 pagineWheels and Tires: Look at E-Mail From John Under Inbox Tab, Brakes Class Foldereizz88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breaker Test & Maintenance Webinar: June 28, 2017Documento46 pagineCircuit Breaker Test & Maintenance Webinar: June 28, 2017Luis Febres100% (1)
- Passenger Car Tires and Wheels: Development - Manufacturing - ApplicationDa EverandPassenger Car Tires and Wheels: Development - Manufacturing - ApplicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Problems: Guoming TangDocumento26 pagineAssignment Problems: Guoming TangManueli Kebbles MckubwaNessuna valutazione finora
- InvoiceDocumento1 paginaInvoiceHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Parrott Connor A 2017Documento66 pagineParrott Connor A 2017Himansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDDocumento51 pagineIntroduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDBilal AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- LetterDocumento3 pagineLetterHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDDocumento51 pagineIntroduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDBilal AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- New PDFDocumento1 paginaNew PDFHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTL Shipment Details from Chennai to NizamabadDocumento4 pagineLTL Shipment Details from Chennai to NizamabadHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- NewDocumento1 paginaNewHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer DatabaseDocumento2 pagineConsumer DatabaseHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer DatabaseDocumento2 pagineConsumer DatabaseHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDDocumento51 pagineIntroduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDBilal AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDDocumento51 pagineIntroduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDBilal AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Marbella Rest Time Mattress Warranty and Configuration GuideDocumento2 pagineMarbella Rest Time Mattress Warranty and Configuration GuideHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Elegant Premia+Documento2 pagineElegant Premia+Himansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Matt Desc. Details at MH GNDocumento2 pagineMatt Desc. Details at MH GNHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- EcstasyDocumento2 pagineEcstasyHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Matt Description at MHDocumento2 pagineMatt Description at MHHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Marbella Rest Time Mattress Warranty and Configuration GuideDocumento2 pagineMarbella Rest Time Mattress Warranty and Configuration GuideHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bapu - 17 January 1959 Maa - 12 May 1968Documento1 paginaBapu - 17 January 1959 Maa - 12 May 1968Himansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mattresses DeatilsDocumento2 pagineMattresses DeatilsHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 2 ETE Rubric-20 MarksDocumento14 pagineProject 2 ETE Rubric-20 MarksHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Salesman Territory WiseDocumento1 paginaSalesman Territory WiseHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Blank FormDocumento7 pagineApplication Blank FormBipin KishanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mech Automaticgatealarmwithlight ReportDocumento25 pagineMech Automaticgatealarmwithlight ReportHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Salesman Territory WiseDocumento1 paginaSalesman Territory WiseHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Circle Meeting (QCM) Session: Winter 2018-19: Name of The SchoolDocumento1 paginaQuality Circle Meeting (QCM) Session: Winter 2018-19: Name of The SchoolHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Jamia Ba (Pol. Sci.) Syllabus PDFDocumento37 pagineJamia Ba (Pol. Sci.) Syllabus PDFHimansu BisoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface water drainage infiltration testingDocumento8 pagineSurface water drainage infiltration testingRay CooperNessuna valutazione finora
- E.sybox - Esybox All Information PDFDocumento56 pagineE.sybox - Esybox All Information PDFnle_16948Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Support Untuk Managemen HRDocumento102 pagineTeaching Support Untuk Managemen HRFernando FmchpNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex 2 6 FSC Part2 Ver3Documento16 pagineEx 2 6 FSC Part2 Ver3Usama TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotic End Effectors - Payload Vs Grip ForceDocumento8 pagineRobotic End Effectors - Payload Vs Grip ForcesamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Financial Performance of Conventional and Islamic BanksDocumento9 pagineComparing Financial Performance of Conventional and Islamic BanksIkbal HardiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Centre CatalogDocumento26 pagineMini Centre CatalogJohn EarleyNessuna valutazione finora
- China Sichuan Province Se'Ergu Hydro Power Project PDD 20080821Documento50 pagineChina Sichuan Province Se'Ergu Hydro Power Project PDD 20080821akhilkuwarNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Veterinary MedicineDocumento25 pagineHistory of Veterinary MedicineAli AsadullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce125-2500 Open FrameDocumento48 pagineCe125-2500 Open FrameRomão OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- OS9000 AOS 6.1.5 R01 Network Configuration GuideDocumento846 pagineOS9000 AOS 6.1.5 R01 Network Configuration GuideclaupasinaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Seven Kings of Revelation 17Documento9 pagineThe Seven Kings of Revelation 17rojelio100% (1)
- Your Results For: "Multiple-Choice Questions: B": DelayDocumento4 pagineYour Results For: "Multiple-Choice Questions: B": DelayawairmalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Developments in Testing Item Response Theory (IRT) : Prepared byDocumento32 pagineCurrent Developments in Testing Item Response Theory (IRT) : Prepared byMalar VengadesNessuna valutazione finora
- E.bs 3rd-Unit 22Documento46 pagineE.bs 3rd-Unit 22DUONG LE THI THUYNessuna valutazione finora
- Serto Up To Date 33Documento7 pagineSerto Up To Date 33Teesing BVNessuna valutazione finora
- Axel LeijonhufvudDocumento7 pagineAxel LeijonhufvudDario CoceresNessuna valutazione finora
- Examples of IELTS Speaking Part 1 QuestionsDocumento15 pagineExamples of IELTS Speaking Part 1 QuestionsThanh TrầnNessuna valutazione finora
- D2DDocumento2 pagineD2Dgurjit20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soft StarterDocumento6 pagineSoft StarterEric Maglinte TolosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jeremy Hughes ReviewDocumento5 pagineJeremy Hughes ReviewgracecavNessuna valutazione finora
- 4D - Yulianti Viviana - Exercise 9Documento7 pagine4D - Yulianti Viviana - Exercise 9Uli JennerNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Network For PLC PDFDocumento7 pagineNeural Network For PLC PDFMarcelo Moya CajasNessuna valutazione finora