Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Compounding
Caricato da
Sob0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
14 visualizzazioni7 pagineWSEGrammar
Titolo originale
Ppt compounding
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoWSEGrammar
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
14 visualizzazioni7 pagineCompounding
Caricato da
SobWSEGrammar
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 7
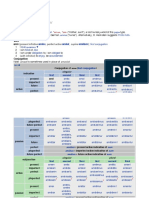
Inflectional Morpheme
Inflectional Morpheme (IM) is morphemes that
change neither part of speech nor meaning and
give extra grammatical information about the
already existing meaning of word.
The types of the Inflectional Suffixes in English:
-s (present), -ed (past), -ing (continous), -en
(past participle), -s (plural), -’s (possessive), -er
(comparative), -est (supperlative)
Inflectional vs. Derivational
NO CHANGE in CHANGE in meaning
meaning or part of or part of speech.
speech. Eg.
Eg.
((hospital)N –ize)v
((book)N –s)N
((work)v –ed)v ((govern)v–ment)N
Inflectional vs. Derivational
Occur at the margins of Occur before
words. Inflectional Suffix/must
Eg. –s (plural) always be closer to the root.
comes last a word, as in Eg.
neighborhoods. neighbor + hood + s
root DM IM
Inflectional vs. Derivational
Occur with all members Occur with only some
of some large class of members of class of
morphemes. morphemes.
Eg. Plural (-S) occurs Eg. Suffix (-hood) with
with most nouns. brother, neighbor,
Have very few knight.
exception. But not with friend,
daughter,etc.
Although they are
NOUN.
Inflectional vs. Derivational
Indicates syntactic or Indicate semantic
semantic relations relations within the
between different word word.
in a sentence. Eg. Painful
Eg. She waits for me. (-ful)has no particular
(-s) shows agreement connection with any
with Subject of the verb other morpheme beyond
the word painful.
Divide the words below into their component
morphemes and identify the nature of
morphemes by answering these question for
each:
1. How many morphemes?
2. Is it Free or Bound morpheme?
3. What kind of affixes are involved?
4. Is it Inflectional or Derivational Morpheme?
1. Cats 9. Comfortable
2. Catsup 10. Reconditioned
3. Succotash 11. Directional
4. Entrust 12. Thickeners
5. Unhappy 13. Rationalization
6. Milder 14. Fixation
7. Bicycle 15. Monstrous
8. Signpost
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Apostila de Inglês Five Hundred English QuestionsDocumento67 pagineApostila de Inglês Five Hundred English QuestionsGrammar Eng100% (5)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Present TenseDocumento6 paginePresent Tenseapi-326210415Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Module About Root Words Prefixes COMPOUND WORDSDocumento12 pagineModule About Root Words Prefixes COMPOUND WORDSphenoren33% (3)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Quran Short Course Workbook EngDocumento35 pagineQuran Short Course Workbook Engelbee_2k921Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Agir - To Act - Lawless FrenchDocumento4 pagineAgir - To Act - Lawless FrenchBisto MasiloNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Adjective Clause, Finite Clause and Non-Finite ClauseDocumento14 pagineAdjective Clause, Finite Clause and Non-Finite ClauseRizky Tri Atmojo50% (2)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Tema 10Documento6 pagineTema 10gnNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- English Grammar 101 - All You Need To KnowDocumento12 pagineEnglish Grammar 101 - All You Need To KnowSylvia Al-a'maNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Essay On The Grammar of The Yukaghir Language PDFDocumento60 pagineEssay On The Grammar of The Yukaghir Language PDFsatand2121100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- GrammarDocumento5 pagineGrammarSofiko ChanturidzeNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Chapter 4Documento6 pagineChapter 4Oanh NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Compounding EXERCISEDocumento2 pagineCompounding EXERCISEngocminhtran101100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Syllabus For Final-K.GDocumento3 pagineSyllabus For Final-K.GSolutions Zone100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Tips and Notes: JJJJJDocumento55 pagineTips and Notes: JJJJJAnifa100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Morphology: The Study of Word Structure and Word FormationDocumento18 pagineMorphology: The Study of Word Structure and Word FormationShahirah ZafirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sincro DestinoDocumento9 pagineSincro DestinoClaudia CañasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Simple Past Tense: Presented by Indah Dwi Permanawati 1305020082Documento7 pagineSimple Past Tense: Presented by Indah Dwi Permanawati 1305020082Indah Dwi PNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcalauagan-Kinaray-A RelectionDocumento1 paginaIgcalauagan-Kinaray-A RelectionIvan RodrigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics (Scrabble and Word Factory)Documento39 pagineMechanics (Scrabble and Word Factory)Ralph JimNessuna valutazione finora
- Raghus EnglishDocumento136 pagineRaghus EnglishJaveed GurramkondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning DovahzulDocumento53 pagineLearning DovahzulDammNetNessuna valutazione finora
- The Kalaam (Speech/Words) Is Only of Three Kinds:: A Noun A Verb A ParticleDocumento10 pagineThe Kalaam (Speech/Words) Is Only of Three Kinds:: A Noun A Verb A Particleias1969Nessuna valutazione finora
- English Test: Basic 1Documento21 pagineEnglish Test: Basic 1jack123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar of SeriDocumento1.119 pagineGrammar of SeriKarl EinsamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- ''Amo'' in LatinDocumento4 pagine''Amo'' in LatinThriwNessuna valutazione finora
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocumento22 pagineCountable and Uncountable Nounsjordanita100% (1)
- Navi DictionaryDocumento60 pagineNavi DictionaryShaman Vajra WolfNessuna valutazione finora
- QUANTIFIERS: A Quantifier Is A Word or Phrase Which Is Used Before A Noun ToDocumento2 pagineQUANTIFIERS: A Quantifier Is A Word or Phrase Which Is Used Before A Noun Todawidh78Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 The Five Grammatical UnitsDocumento3 pagine2 The Five Grammatical UnitsAlejandra de Santiago100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Test Bank For Comprehensive Medical Terminology 4th Edition JonesDocumento24 pagineTest Bank For Comprehensive Medical Terminology 4th Edition JonesVeronicaKellypcts100% (45)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)