Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Approach To Fever and Sepsis
Caricato da
Jessica Stewart0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
11 visualizzazioni12 pagineppt
Titolo originale
Approach to Fever and Sepsis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
11 visualizzazioni12 pagineApproach To Fever and Sepsis
Caricato da
Jessica Stewartppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 12
APPROACH TO FEVER AND SEPSIS
DEFINITIONS
• Fever : increase in the body core temperature
• Sepsis : temperature >38 or <36 , HR >90 , RR
>20 , TWC >12 (at least 2 of the above)
• Septic shock : sepsis with hypotension despite
adequate fluid resuscitiation
ETIOLOGY
• Many disorders can cause fever. They are
broadly catergorized as :
– Infectious
– Neoplastic
– Inflammatory
CAUSES
• NONE
– URTI / LRTI
– GI infection
– UTI
– Skin infection
• TRAVEL
– Malaria
– Dengue fever
– Diarrheal disorders
• HOSPITALIZATION
– IV catheter infection
– UTI (particularly in patients with catheter)
– Pneumonia
– DVT / PE
– Hematoma
– Transfusion reaction
• VECTOR EXPOSURE
– Dengue
– Leptospirosis
– Rabies
– Cat scratch disease
• IMMUNOCOMPRONISED
– VIRUS : CMV infection
– PARASITES : Toxoplasmosis infection
• DRUGS
– Antipsychotics
– Anesthetics
– Phenytoin
TYPES OF FEVER
• Step ladder fever
• Fever with chill and rigor
• Intermittent fever
• Continuous fever
• Remittent fever
HISTORY TAKING
• HOPI
– Duration of fever
– Character of fever
– Associating factors : chills / rigors, rashes, pain
• PMH
– Underlying diseases
– Recent surgery
• DRUG
– Corticosteroids, chemotherapeutic drugs
– Illicit drug useage
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
• GENERAL APPERRANCES :
– Weakness, lethargy, confusion, cachexic, distress
• RASHES
• LYMPHADENOPATHY
• SURGICAL SITES
• LUNGS
• CVS
• P/A
• CNS
RED FLAGS
• Altered mental status
• Headache, neck stiffness
• Hypotension
• Tachycardia / tachypnea
INVESTIGATION
• FBC
• Blood cultures
• UFEME
• Urine culture
• Chest xray
TREATMENT
• Symptomatic treatment
• Heamodynamic stabilization
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Airway Management 2018 - . - 2Documento30 pagineAirway Management 2018 - . - 2Jessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Form 4 Timetable: Subject Time DurationDocumento1 paginaForm 4 Timetable: Subject Time DurationJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- 0610 s16 QP 41Documento20 pagine0610 s16 QP 41Jessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Chap 2 PMR SC EditedDocumento2 pagineChap 2 PMR SC EditedJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
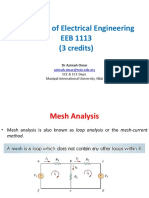
- EEB1113 DC7 Mesh&SuperMeshAnalysisDocumento13 pagineEEB1113 DC7 Mesh&SuperMeshAnalysisJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Menstruation Is The Shedding of The Lining of The UterusDocumento6 pagineMenstruation Is The Shedding of The Lining of The UterusJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Seminar Abdominal InjuryDocumento83 pagineSeminar Abdominal InjuryJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- EEB1113 DC8 SuperpositionDocumento14 pagineEEB1113 DC8 SuperpositionJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Seminar Cover PageDocumento1 paginaSeminar Cover PageJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- Trauma Care (ATLS) PICDocumento37 pagineTrauma Care (ATLS) PICJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- 9780198390183Documento14 pagine9780198390183Jessica Stewart100% (1)
- 0f F FDDocumento12 pagine0f F FDEnica RichardNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- f4 SC Chapter 3Documento64 paginef4 SC Chapter 3Jessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- What Is The Menstrual CycleDocumento4 pagineWhat Is The Menstrual CycleJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- SalpingoDocumento1 paginaSalpingoJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- SalpingoDocumento1 paginaSalpingoJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
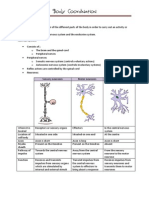
- Body Coordination NotesDocumento4 pagineBody Coordination NotescolorpencilgaloreNessuna valutazione finora
- Sym Physio To MyDocumento1 paginaSym Physio To MyJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- F3 Chapter 2 - Blood CirculationDocumento2 pagineF3 Chapter 2 - Blood CirculationJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- 2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersDocumento27 pagine2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- 1 Cell StructureDocumento41 pagine1 Cell StructureIra MunirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Documento6 pagineChemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Suriati Bt A Rashid100% (2)
- 1 Cell StructureDocumento41 pagine1 Cell StructureIra MunirahNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Short Stature.Documento77 pagineShort Stature.Jessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter3 Chemical FormulaDocumento10 pagineChemistry Form 4 Chapter3 Chemical FormulaAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Case Presentation 3Documento4 paginePediatric Case Presentation 3Ramona Bratu78% (9)
- AnatomyDocumento11 pagineAnatomyJessica StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)