Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fermentation
Caricato da
api-4181768860 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
872 visualizzazioni8 pagineTitolo originale
fermentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
872 visualizzazioni8 pagineFermentation
Caricato da
api-418176886Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 8
Fermentation
(What cells do when they run out of
oxygen)
Alcoholic Fermentation
• Occurs in yeasts, some plants
• Glycolysis occurs first
• Pyruvate is converted into:
• 1) Ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
• 2) CO2
• Used in making bread, beer, wine
Lactic Acid Fermentation
• Occurs in the muscle cells of mammals
• Glycolysis occurs first
• Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid
Energy payoff?
• Fermentation does NOT generate any new ATP
• So…what’s the point???
It regenerates NAD+ so that glycolysis can keep
running.
Anaerobic Electron Transport
• -in bacteria
• e- are stripped from an organic compound and
sent through an e-tc in the plasma membrane
• An inorganic compound serves as the final e-
acceptor
• Energy yield varies, but is small
Alternative Energy Source
• Glycogen = 1% of stored energy
• Fats = 78%
• Proteins = 21%
Using Fats
• Triglycerides: broken down into glycerol and
fatty acids
• Glycerol is converted into an intermediate in
glycolysis
• Fatty acids are converted to acetyl-CoA and
enter the Krebs cycle
Using Proteins
• Proteins: broken down into amino acids
• The amine group is removed and excreted in
urine (NH2)
• The remaining carbon backbone may be
converted to carbs or fats and enter the Krebs
cycle
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cellular RespirationDocumento31 pagineCellular Respirationyudi prakasaNessuna valutazione finora
- GBIO1 Week18 Energy Transformation Part 5Documento25 pagineGBIO1 Week18 Energy Transformation Part 5Endeavor KutosakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerobicrespiration 7 EloopDocumento26 pagineAerobicrespiration 7 EloopJeffereyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Carbohydrates (Part 3)Documento32 pagine2 - Carbohydrates (Part 3)Sean Polo MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocumento26 pagineHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNessuna valutazione finora
- ADP ATP and Cellular RespirationDocumento128 pagineADP ATP and Cellular RespirationLeona Trinity AranasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento42 pagineCellular RespirationKate BarolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolisme Makhluk Hidup - HRDocumento61 pagineMetabolisme Makhluk Hidup - HRBagus SatariNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidative Phosphorylation Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocumento28 pagineOxidative Phosphorylation Anaerobic Respiration and Fermentationcediebanaag10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocumento23 pagineAmino Acid MetabolismZ ZNessuna valutazione finora
- J. Biosynthetic PathwaysDocumento14 pagineJ. Biosynthetic PathwaysMary Rose Bobis VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228Documento60 pagineCellular Respiration: Nelson Biology Pages 204 - 228allie3d100% (14)
- HyacinthDocumento52 pagineHyacinthHyacinth Rae Ramirez Aranas - LipatNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocumento41 pagineCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisCarissa MarchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell RespDocumento14 pagineCell RespSittie Asnile MalacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Respiration 3l 2qDocumento14 pagineCell Respiration 3l 2qMihatsu TakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Respiration: The Process by Which Cells Turn Food Molecules Into Cell EnergyDocumento14 pagineCell Respiration: The Process by Which Cells Turn Food Molecules Into Cell EnergyMihatsu TakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Intercorelation Between Metabolism PPT 2010Documento46 pagineIntercorelation Between Metabolism PPT 2010Izzah AtqaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular - Respiration LECTURE 111Documento47 pagineCellular - Respiration LECTURE 111Cynel DelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento15 pagineCellular RespirationFAtma HAnysNessuna valutazione finora
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocumento51 paginePlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint Guidelaloo01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento33 pagineCellular RespirationRhea May ZorillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aim 61Documento17 pagineAim 61Tasneem MaruhomNessuna valutazione finora
- Students - Cellular-RespirationDocumento49 pagineStudents - Cellular-RespirationechaNessuna valutazione finora
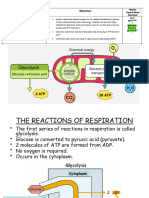
- 4 The Reactions of Respiration Jo 2024Documento6 pagine4 The Reactions of Respiration Jo 2024Himiko JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Fat MetabolismDocumento36 pagineFat MetabolismSALAUDEEN SAEFULLAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation: Bayas Conde de Leon Bse 41Documento26 pagineFermentation: Bayas Conde de Leon Bse 41Mary Jesreth Vergara BayasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell RepDocumento21 pagineCell Repvictoria.hugginsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento24 pagineCellular RespirationAdelaide CNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism 1 BGJE 2017Documento30 pagineMetabolism 1 BGJE 2017Gîrneţ AlinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Energetics PDF ResumeDocumento40 pagineEnergetics PDF ResumeketyleenbNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy & Respiration SimpliefiedDocumento6 pagineEnergy & Respiration SimpliefiedEmrul HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- IT 17 - Interkorelasi Antar Metabolisme - IBMDocumento47 pagineIT 17 - Interkorelasi Antar Metabolisme - IBMYUFFANessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL223-Lab 6Documento35 pagineBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy in CellsDocumento29 pagineEnergy in CellsNaje' GrayNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 3respiration 110923104133 Phpapp02Documento42 pagine20 3respiration 110923104133 Phpapp02Ira AgcaoiliNessuna valutazione finora
- BMSC11005 2022 T2 Week 8Documento64 pagineBMSC11005 2022 T2 Week 8Zain Hafeez-BaigNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of LipidsDocumento21 pagineMetabolism of LipidsViragNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Cellular RespirationDocumento25 pagineSummary of Cellular RespirationHeric ValdemoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 BIO 1510Documento25 pagineChapter 7 BIO 1510Chachi CNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento36 pagineCellular RespirationWillow ItchiroNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL CH 9Documento21 pagineBIOL CH 9Nouf AlshareefNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration1Documento40 pagineCellular Respiration1Danken Mathew P. TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Cell RespirationDocumento20 pagine4 Cell RespirationCristina MaquintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Dono Chapter 13 - How Cells Obtain EnergyDocumento41 pagineDr. Dono Chapter 13 - How Cells Obtain EnergyMuhammad Thoriqur Rohman Al-KhotamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8-MetabolismDocumento103 pagineUnit 8-Metabolismnumberr515Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lipid MetabolismDocumento32 pagineLipid MetabolismIskandar IdrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration: Trisha Vinch D. NavarceDocumento34 pagineCellular Respiration: Trisha Vinch D. NavarceTrisha NavarceNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell RespirationDocumento27 pagineCell RespirationJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolic Processes - Pr. PirouziDocumento32 pagineMetabolic Processes - Pr. PirouzipirouziNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation 09912Documento11 pagineFermentation 09912zhao YingingNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration Fermentation 2017 UPDATED Use For 2019Documento36 pagineCellular Respiration Fermentation 2017 UPDATED Use For 2019aNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Firecracker QuestionsDocumento92 pagineBiochemistry Firecracker QuestionsSatishAdvaniNessuna valutazione finora
- III UG Physiology Respiration AVJDocumento27 pagineIII UG Physiology Respiration AVJHead 4KNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocumento17 pagineChapter 7 Cellular RespirationbubabozN aOIDHao8nxNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Cellular Respiration?: The Complex Process in Which Cells Make ATP by Breaking Down Organic CompoundsDocumento46 pagineWhat Is Cellular Respiration?: The Complex Process in Which Cells Make ATP by Breaking Down Organic CompoundsCarolina SolorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature RegulationDocumento11 pagineNutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature RegulationSNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 9 PPT Cellular RespirationDocumento47 pagineCH 9 PPT Cellular RespirationJackie Swift FuntanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Keto Drinks: Tasty Ketogenic Cocktails, Warm Drinks and Lemonades for Weight Loss - The Collection of Low-Carb Recipes That Will Keep You In Ketosis: Keto Diet, #1Da EverandKeto Drinks: Tasty Ketogenic Cocktails, Warm Drinks and Lemonades for Weight Loss - The Collection of Low-Carb Recipes That Will Keep You In Ketosis: Keto Diet, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- WaterDocumento17 pagineWaterapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Humans and The EnvironmentDocumento17 pagineHumans and The Environmentapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Population EcologyDocumento18 paginePopulation Ecologyapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal AdaptationsDocumento10 pagineAnimal Adaptationsapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant AdaptationsDocumento13 paginePlant Adaptationsapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Biology Basic Chemistry VocabDocumento2 pagineAp Biology Basic Chemistry Vocabapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Why Organelles 1Documento5 pagineWhy Organelles 1api-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of The 6 KingdomsDocumento23 pagineOverview of The 6 Kingdomsapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- SpeciationDocumento15 pagineSpeciationapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evolutionary TheoryDocumento14 pagineEvolutionary Theoryapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Early Earth and The Origin of LifeDocumento22 pagineEarly Earth and The Origin of Lifeapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- MicroevolutionDocumento11 pagineMicroevolutionapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification Based On EvolutionDocumento12 pagineClassification Based On Evolutionapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2004 EoctDocumento20 pagineBiology 2004 Eoctapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial and Viral GeneticsDocumento20 pagineBacterial and Viral Geneticsapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemsDocumento27 pagineNervous Systemsapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control Over The Cell CycleDocumento11 pagineControl Over The Cell Cycleapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Reception G Proteins KinasesDocumento20 pagineSignal Reception G Proteins Kinasesapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- TranslationDocumento6 pagineTranslationapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Genetic Basis of CancerDocumento31 pagineThe Genetic Basis of Cancerapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Communication OverviewDocumento12 pagineCell Communication Overviewapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control of Gene Expression in EukaryotesDocumento16 pagineControl of Gene Expression in Eukaryotesapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Viruses Lytic and Lysogenic CyclesDocumento19 pagineViruses Lytic and Lysogenic Cyclesapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis SimplifiedDocumento5 pagineProtein Synthesis Simplifiedapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology in PicturesDocumento61 pagineBiology in Picturesapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento13 pagineMeiosisapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptionDocumento11 pagineTranscriptionapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription SimplifiedDocumento5 pagineTranscription Simplifiedapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- MitosisDocumento25 pagineMitosisapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora
- MitosisDocumento25 pagineMitosisapi-418176886Nessuna valutazione finora