Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basic Immunology of Allergic Disease: Tutik Ida Rosanti Laboratorium Parasitologi
Caricato da
Fiqrotul Umam0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni17 paginealergi
Titolo originale
Allergy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoalergi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni17 pagineBasic Immunology of Allergic Disease: Tutik Ida Rosanti Laboratorium Parasitologi
Caricato da
Fiqrotul Umamalergi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 17
Basic Immunology of Allergic
Disease
Tutik Ida Rosanti
Laboratorium Parasitologi
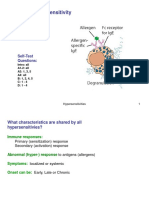
Hypersensitivity Diseases
• Disorders caused by immune responses:
– failure of self tolerance autoimmunity
– uncontrolled / excessive immune reactions
against non-self (foreign) antigens
• Classified into 4 type of reactions based
on their effector mechanisms responsible
for cell & tissue injury:
– types I, II, III, and IV
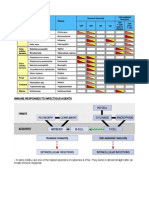
Table 1 Classification of Immunologic Diseases
Type of Pathologic immune Mechanisms of tissue
hypersensitivity mechanisms injury and disease
Type I: immediate type IgE antibody Mast cells + mediators:
hypersensitivity vasoactive amines, lipid
(Allergy) mediators, cytokines:
TNF-a, Il-4, IL-5, IL-
13, MIP-1a, IL-3
Type II: antibody- IgM, IgG antibodies * Opsonization &
mediated against cell surface or phagocytosis of cells
extracellular antigens * Complement (C) & Fc
receptor-mediated inflam
Type III: immune Imm. complex of C & Fc receptor-mediated
complex-mediated circulating Ags. and IgM recruitment and activation
or IgG Abs. of leukocytes
Type IV: cell-mediated • CD4+ T cells * Macrophage activation,
(delayed type (Tdth) cytokine-mediated inflam
hypersensitivity) • CD8+ CTL * Direct target cell lysis
The nature of allergens
• Proteins or chemicals bound to proteins
• Low molecular weight, glycosylated-, high
soluble:
– Dietary proteins
• Not often accompanied by natural adjuvant
– Fail to induce IL-12 & IL-18 secreting Th1 cell
responses
• Many potent allergens
– Cysteine protease of house dust mite
– Phospholipase A2 in bee venom
– Others: pollen, mold spores, latex, certain drug, ie.
penicillin
Genetic basis of atopy
Table 2 Candidate genes assoc. with atopy
Chromosome Candidate genes Role of gene
location products
5q31 IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 IL-4 & IL-3 IgE
IL-5 eosinophils
5q32 b2-adrenergic receptor Regulates arterial &
bronchial smooth
muscle contraction
6p Class II MHC Regulates T cell
response Th2
6p21.3 TNF-a Mast cell inflammatory
mediator
11q13 Fce RI b -chain Mast cell IgE receptor
Role of T cells
• Allergen specific IL-4 secreting T cells
– Overnumbered in atopic than non-atopic
individuals
• CD4+ Th 2 cells produce cytokines
– IL-4, for isotype switching to IgE, and promotes
eosinophil recruitment
– IL-5, for eosinophil activation
– IL-13, has a similar effect to IL-4, and regulates
inflammation independently to IgE
Role of IgE antibodies
• Mediate mast cell activation degranulation
– Through their Fce that interact with a high affinity
to Fce RI cytophilic (reaginic) antibody
– Antigen-cross linked IgE/FceR
• Normal serum conc: less than 1mg/ml
– Can rise to over 1000 mg/ml in severe atopy and
helminthic infection
• Has totally 5 domains (4 heavy chain constant-
and 1 heavy chain variable domains)
Role of mast cells
• Effector cell of immediate hypersensitivity /
allergy
• Contain cytoplasmic granules whose contents are
the major mediators of allergic reaction:
– Vasoactive amines, lipid mediators, cytokines
• Two subpopulations are detected:
– Connective tissue (CTMC) and mucosa (MMC)
• Specific locations throughout the body:
– Near blood vessels, nerve, beneath epithelia
Table 2 Mediators produced by mast cells
Mediator category Mediator Function(s)
Preformed structure Histamine Increases vasc. permeability, smooth
muscle contraction
Tryptase, acid hydrolase, Degrade microbial structure, tissue
cathepsin G, carboxypeptidase damage/remodelling
Lipid mediators produced Prostaglandin D2 Vasodilatation, bronchoconstriction,
on activation neutrophil chemotaxis
Leukotrien C4, D4, E4, PAF Prolonged bronchoconstriction,
mucus secretion, increased vasc.
permeability
Cytokines IL-3 Promotes mast cell proliferation
TNF-, MIP-1 Promote inflam./late phase reaction
IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5 Promote Th2 differentiation, and
eosinophil production
Sequence of events in allergic
reaction
• Initial exposure of antigen/allergen
– Stimulatation of CD4+ T cells TH2
– IL-4 promotes different. of B cells IgE AFC
– Sensitization of mast cells by IgE Ab. & subsequent
Ag degranulation
• Immediate/early vascular & muscular changes
– Increased vascular permeability& vasodilatation
(eg. ‘wheal and flare reaction’), visceral and
bronchial smooth muscle contraction
• Late phase reaction
– Infiltration of inflammatory cells: eosinophils,
basophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes)
CONCLUSION
Contributing factors to allergic reactions
• Allergens:
– environmental protein antigens genetically
susceptible individuals
• CD4+ Th cells, esp. Th2 subpopulations
- IL-4 IL-4-induced IgE switching factor
• IgE B cells
– IgE antibodies
• Mast cells (tissue) / basophils (blood circul.)
– FceRI
• Others: eosinophils, neutrophils, basophils
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hypersensitivity: Robert Beatty MCB150Documento48 pagineHypersensitivity: Robert Beatty MCB150Lop LlorinNessuna valutazione finora
- Type I Hypersensitivity: Understanding Allergic ReactionsDocumento48 pagineType I Hypersensitivity: Understanding Allergic Reactionsrido rahmad saputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Undisarable and Alterd ImmunotyDocumento81 pagineChapter 11 Undisarable and Alterd ImmunotyTofikNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityDocumento191 pagine19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityGwyneth Adrienne Leigh VillapandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocumento31 pagineAcute and Chronic InflammationaqilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocumento66 pagineHypersensitivity ReactionsA. PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- HYPERSENSITIVITYDocumento87 pagineHYPERSENSITIVITYinfo.foodbitNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunology: E. A. JalalDocumento60 pagineImmunology: E. A. JalalazlinnursulianyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 CytokinesDocumento29 pagineUnit 6 CytokinesamirahaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ImmunologyDocumento38 pagineBasic ImmunologythreeayuNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Hypersensitive ReactionsDocumento32 pagine14 Hypersensitive ReactionsrahuldhodapkarNessuna valutazione finora
- (MID) IMMUNOSERO - Chapter 13 - Hypersensitivity (Reviewer)Documento6 pagine(MID) IMMUNOSERO - Chapter 13 - Hypersensitivity (Reviewer)Aisle Malibiran PalerNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunity Innate Immunity: When The Going Gets Tough, The Tough Gets Going...Documento7 pagineImmunity Innate Immunity: When The Going Gets Tough, The Tough Gets Going...dtimtimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityDocumento12 pagineStudy Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityxxxxxxxNessuna valutazione finora
- Allergy & Hypersensitivity HajeerDocumento29 pagineAllergy & Hypersensitivity Hajeerbader1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Immunology & Immunopathology: Key Immune ResponsesDocumento43 pagineImmunology & Immunopathology: Key Immune Responsesdogzmania4ever7270Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 21 - HypersensitivityDocumento25 pagineLecture 21 - Hypersensitivityapi-3703352100% (2)
- Kapita Selekta ImunologiDocumento29 pagineKapita Selekta ImunologiAsyha KantifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity: - Innate Is FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE: No Prior Exposure Needed - Comprised OfDocumento31 pagineInnate and Adaptive Immunity: - Innate Is FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE: No Prior Exposure Needed - Comprised OfBegumHazinNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 超敏反应Documento32 pagine14 超敏反应Jennifer DixonNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay ImmuneDocumento8 pagineEssay ImmuneAishah Najihah100% (1)
- 4.chronic InflammationDocumento29 pagine4.chronic Inflammationyaqeenallawi23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of innate immunity (Abbas Chapter 4Documento31 paginePrinciples of innate immunity (Abbas Chapter 4foreveraldyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 5215254675862849909Documento85 pagine2 5215254675862849909Tamara ElyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On Immunology-HypersensitivityDocumento45 pagineSeminar On Immunology-HypersensitivitySalman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitivity: Mark Christian D. Duatin, RMTDocumento43 pagineHypersensitivity: Mark Christian D. Duatin, RMTJoyce Anne Faith Estrella100% (1)
- Understanding the 4 Types of HypersensitivityDocumento34 pagineUnderstanding the 4 Types of HypersensitivityEvie WulansariNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyDocumento7 pagineUniversity of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Veterinary Immunology HypersensitivityDocumento36 pagineVeterinary Immunology HypersensitivityBEKUMA SHIBIRUNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitivity: M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM UniversityDocumento87 pagineHypersensitivity: M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM UniversityJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflammation & Immune-Mediated Diseases: Introduction of Biomedical ScienceDocumento30 pagineInflammation & Immune-Mediated Diseases: Introduction of Biomedical SciencekimmyrereNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphylaxis: Ige Mediated HypersensitivityDocumento23 pagineAnaphylaxis: Ige Mediated HypersensitivityAbi ZakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assoc. Prof. Ma. Jennifer R. Tiburcio, MSMT Department of Med Tech UST Faculty of PharmacyDocumento44 pagineAssoc. Prof. Ma. Jennifer R. Tiburcio, MSMT Department of Med Tech UST Faculty of PharmacyJaellah MatawaNessuna valutazione finora
- DR - Tjok. Istri Anom Saturti, Sppd. MarsDocumento16 pagineDR - Tjok. Istri Anom Saturti, Sppd. MarsYogiswara KarangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytokines 2Documento29 pagineCytokines 2Essington BeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytokines in Acute and Chronic Inflammation: Carol A. Feghali, PH.D., and Timothy M. Wright, M.DDocumento17 pagineCytokines in Acute and Chronic Inflammation: Carol A. Feghali, PH.D., and Timothy M. Wright, M.DWahyu Tri KusprasetyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hipersensitivity: Inapropriate Immune Response Due To: Exessive Amount of Antigen Heightened Level of Immune ResponseDocumento36 pagineHipersensitivity: Inapropriate Immune Response Due To: Exessive Amount of Antigen Heightened Level of Immune ResponseKrisna MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Type 1 HypersensitivityDocumento38 pagineType 1 Hypersensitivitychocoholic potchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Allergy Hypersensitivity TypesDocumento53 pagineAllergy Hypersensitivity TypesAnonymous Bh6y0TuVHiNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunopharmacology: Ma. Janetth B. Serrano, M.D., DPBADocumento33 pagineImmunopharmacology: Ma. Janetth B. Serrano, M.D., DPBAJendrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitive Reactions 2-4Documento29 pagineHypersensitive Reactions 2-4Ammara ZulqarnainNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation of Cd8+ T Cells Into Effector Ctls InvolvesDocumento6 pagineDifferentiation of Cd8+ T Cells Into Effector Ctls InvolvesMutaz KhatatbehNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of The Immune Response and Inflammation 3Documento47 pagineDisorders of The Immune Response and Inflammation 3Cres Padua QuinzonNessuna valutazione finora
- 978 3 319 92336 9 - Chapter - 3Documento16 pagine978 3 319 92336 9 - Chapter - 3Cesar GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Opal2000 PDFDocumento11 pagineOpal2000 PDFKrisztián TóthNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic InflammationDocumento17 pagineChronic InflammationMuhammad FaheemNessuna valutazione finora
- Cytokine Roles and Functions in the Immune SystemDocumento53 pagineCytokine Roles and Functions in the Immune SystemBima Ewando KabanNessuna valutazione finora
- General Features of Immune System Immune System: DefinitionDocumento17 pagineGeneral Features of Immune System Immune System: Definitionمحمد نعیم اقبالNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Endodontic Immunology 2Documento4 pagine8 Endodontic Immunology 2doctorgame085Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lec6 Sem5 HEMWK4 20140207Documento9 pagineLec6 Sem5 HEMWK4 20140207Elly ElizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of Immunity ADocumento10 pagineDiseases of Immunity AspringdingNessuna valutazione finora
- Innate Immunity 2 1 1Documento36 pagineInnate Immunity 2 1 1King DomNessuna valutazione finora
- Innate 2005 AbDocumento93 pagineInnate 2005 AbAnonymous wVgEAr6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bt302 Current SolvedDocumento5 pagineBt302 Current SolvedMuzamil RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Immune Hypersensitivity: Self-Test QuestionsDocumento13 pagineImmune Hypersensitivity: Self-Test QuestionszaheerbdsNessuna valutazione finora
- Innate Immunity and Acute InflammationDocumento29 pagineInnate Immunity and Acute InflammationRyan ColeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.imunitas PD FilariasisDocumento20 pagine2.imunitas PD FilariasisZalfa Salsabila ApriliaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENI Immunity To Bacteria-Fungi InfectionDocumento28 pagineENI Immunity To Bacteria-Fungi InfectionEnny WulandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology: RoductionDocumento6 paginePathophysiology: RoductionDhila SafirinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988Da EverandImmunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988J. F. BachNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzim DIGESTIVEDocumento59 pagineEnzim DIGESTIVEFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah Hipertensi KrisisDocumento30 pagineKuliah Hipertensi KrisisFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemostasis and ThrombosisDocumento23 pagineHemostasis and ThrombosisFiqrotul Umam100% (1)
- Kuliah Hipertensi KrisisDocumento30 pagineKuliah Hipertensi KrisisFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- FUNGIDocumento17 pagineFUNGIFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroendocrine DrugsDocumento156 pagineNeuroendocrine DrugsFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- CardiovascularDocumento56 pagineCardiovascularFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- CardiovascularDocumento56 pagineCardiovascularFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Water and electrolyte balance maintained by osmosis and ion transportDocumento74 pagineWater and electrolyte balance maintained by osmosis and ion transportFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Water and electrolyte balance maintained by osmosis and ion transportDocumento74 pagineWater and electrolyte balance maintained by osmosis and ion transportFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- K2 - The Histology of Female Reproductive SystemDocumento91 pagineK2 - The Histology of Female Reproductive SystemNininghrNessuna valutazione finora
- Fisiologi Sistem Reproduki Pria-2015Documento41 pagineFisiologi Sistem Reproduki Pria-2015Fiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Interaksi Obat Hematologi (DR - Wati) 22-12-15 PDFDocumento5 pagineInteraksi Obat Hematologi (DR - Wati) 22-12-15 PDFFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Obat AntiTB (OAT) (DR - Fajar) 16-03-16 PDFDocumento135 pagineObat AntiTB (OAT) (DR - Fajar) 16-03-16 PDFFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of the Female Reproductive SystemDocumento47 pagineAnatomy of the Female Reproductive SystemFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- MarketingDocumento7 pagineMarketingFiqrotul UmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocumento35 pagineHypersensitivity ReactionsFarlogy100% (1)
- Adverse Drug Reactions ExplainedDocumento108 pagineAdverse Drug Reactions ExplainedBinod Sah100% (2)
- HypersensitivityDocumento15 pagineHypersensitivityTejpalNessuna valutazione finora
- New Biologics in The Treatment of UrticariaDocumento7 pagineNew Biologics in The Treatment of UrticariaArezoo JamNessuna valutazione finora
- PEOPLE AS OMNIVORES: COSTS AND BENEFITS OF DIETDocumento10 paginePEOPLE AS OMNIVORES: COSTS AND BENEFITS OF DIETsuleimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mehu525 U4 T3 INTOXICACIONES2-4Documento32 pagineMehu525 U4 T3 INTOXICACIONES2-4jorgealonsosaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphylaxis: A Severe Allergic ReactionDocumento6 pagineAnaphylaxis: A Severe Allergic ReactionFityan Aulia RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Challanage Case in Autoimmune DiseaeDocumento349 pagineChallanage Case in Autoimmune DiseaeheshamNessuna valutazione finora
- Autacoids & RSDocumento14 pagineAutacoids & RSIsmail Bazly ZarirNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective TissuesDocumento5 pagineConnective Tissuesraphael100% (1)
- 2014 Neurogenic NeuroinflammationDocumento11 pagine2014 Neurogenic NeuroinflammationrendyjiwonoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocumento140 pagineThe Lymphatic System and ImmunityAditya Bayukusuma100% (1)
- Delayed Hypersensitivity and Type IV ReactionsDocumento12 pagineDelayed Hypersensitivity and Type IV Reactionsella Sy100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Exam QuestionsDocumento11 paginePathophysiology Exam Questionsjimmy100% (2)
- AnaphylaxisDocumento17 pagineAnaphylaxisPutriAyuWidyastutiRNessuna valutazione finora
- (Advances in Food and Nutrition Research Volume 73) Kim, Se-Kwon-Marine Carbohydrates - Fundamentals and Applications, Part B-ADocumento291 pagine(Advances in Food and Nutrition Research Volume 73) Kim, Se-Kwon-Marine Carbohydrates - Fundamentals and Applications, Part B-ASugiyanto GunadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions 4th Edition FrazierDocumento6 pagineTest Bank For Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions 4th Edition Frazierbevisphuonglc1u5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic Science International: Ugo Da Broi, Carlo MoreschiDocumento5 pagineForensic Science International: Ugo Da Broi, Carlo MoreschiAlifiah Putri BaharuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTHMA - WatermarkedDocumento7 pagineASTHMA - WatermarkedShubhangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Long Covid Syndrome-Associated Brain Fog and ChemofogDocumento10 pagineLong Covid Syndrome-Associated Brain Fog and ChemofogindanazulfaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Virology AssignmentDocumento3 pagineVirology AssignmentSharifah NurainNessuna valutazione finora
- Hamza DissertDocumento108 pagineHamza DissertMobin Ur Rehman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - Immune Diseases (Part I) (Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease)Documento6 pagineChapter 6 - Immune Diseases (Part I) (Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease)Ernie G. Bautista II, RN, MD90% (21)
- Practice Quiz 4Documento10 paginePractice Quiz 4Alex VongNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitivity ReactionDocumento36 pagineHypersensitivity ReactionMohana Sundaram100% (1)
- Laserneedle Acupuncture: A Critical Review and Recent ResultsDocumento7 pagineLaserneedle Acupuncture: A Critical Review and Recent ResultsBeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Allergic RhinitisDocumento11 pagineAllergic RhinitisCarmila Olbe ArroyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Immune System REVISION AnswersDocumento22 pagineImmune System REVISION Answersinder191100% (1)
- AP Biology Practice Exam: Section I: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocumento83 pagineAP Biology Practice Exam: Section I: Multiple-Choice QuestionsKamilla DzhanzakovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Text Question Type PointsDocumento25 pagineQuestion Text Question Type PointsMagda Tvildiani100% (1)