Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
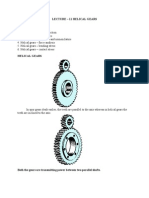
Gear Cutting Operations
Caricato da
Hossam Ali0%(1)Il 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
311 visualizzazioni23 pagineGears are used to transmit power and motion between parallel or non-parallel shafts, and can change the direction or speed of rotation. There are several types of gears classified by their configuration, axis of transmission, and pattern of motion. Common gear cutting operations include gear milling, gear shaping, gear hobbing, and gear finishing. Gear milling cuts teeth one by one using a cutting tool, while gear shaping uses a reciprocating gear-shaped cutting tool. Gear hobbing progressively cuts teeth using a helical cutting tool. Finishing operations such as grinding, lapping, and honing further improve the surface finish and accuracy of gears.
Descrizione originale:
gear production
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoGears are used to transmit power and motion between parallel or non-parallel shafts, and can change the direction or speed of rotation. There are several types of gears classified by their configuration, axis of transmission, and pattern of motion. Common gear cutting operations include gear milling, gear shaping, gear hobbing, and gear finishing. Gear milling cuts teeth one by one using a cutting tool, while gear shaping uses a reciprocating gear-shaped cutting tool. Gear hobbing progressively cuts teeth using a helical cutting tool. Finishing operations such as grinding, lapping, and honing further improve the surface finish and accuracy of gears.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0%(1)Il 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
311 visualizzazioni23 pagineGear Cutting Operations
Caricato da
Hossam AliGears are used to transmit power and motion between parallel or non-parallel shafts, and can change the direction or speed of rotation. There are several types of gears classified by their configuration, axis of transmission, and pattern of motion. Common gear cutting operations include gear milling, gear shaping, gear hobbing, and gear finishing. Gear milling cuts teeth one by one using a cutting tool, while gear shaping uses a reciprocating gear-shaped cutting tool. Gear hobbing progressively cuts teeth using a helical cutting tool. Finishing operations such as grinding, lapping, and honing further improve the surface finish and accuracy of gears.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 23
Gear Cutting Operations
Basic Purpose Of Use Of Gears
Gears are widely used in various mechanisms and
devices to transmit power and motion positively
(without slip) between parallel, intersecting ( axis)
or non-intersecting non parallel shafts,
without change in the direction of rotation
with change in the direction of rotation
without change of speed (of rotation)
with change in speed at any desired ratio
Categories of gear manufacturing
process
General Applications Of Gears
Speed gear box, feed gear box and some other kinematic units of
machine tools
Speed drives in textile, jute and similar machineries
Gear boxes of automobiles
Speed and / or feed drives of several metal forming machines
•Machineries for mining, tea processing etc.
Large and heavy duty gear boxes used in cement industries, sugar
industries, cranes, conveyors etc.
Precision equipments, clocks and watches
Industrial robots and toys.
Types Of Gears And Their
Characteristics
1.According to configuration
• External gear • Internal gear
2. According to axes of transmission
• Spur gears – transmitting rotation between parallel shafts as shown in
o Straight toothed
o Helical toothed
⎯ Single helical
⎯ double helical (herringbone)
3. According to pattern of motion
Rotation to rotation : wheel type gears
Rotation to translation or vice versa –
e.g. rack and pinion
Straight toothed
Helical toothed
Types of Gear Cutting Operations
Gear milling or Forming
Gear shaping
Gear Hobbing
Gear Finishing
1.Gear Milling or Forming
The gear milling operation is used for gear cutting. All
types of gears can be made by using gear milling.
Milling cutter is selected specifically for a particular type of
gear and module. The periphery of the gear blank is divided
into required number of equi-spaced parts.
The required number of parts should be equal to the
number teeth to be made on the gear blank.
The method of dividing the periphery is called indexing
which is an integral part of the operation of gear milling.
Gear Milling
In gear form cutting, the cutting edge of the
cutting tool has a shape identical with the shape
of the space between the gear teeth.
Disadvantages of Gear Milling
Gear milling is a slower process of gear
generation as compared to other gear generation
process.
In this process gear is generated by cutting one-
by-one tooth.
Gears are to be made, it is not suitable for larger
batch size.
The other methods required very high capital
cost and setup cost as compared to gear milling
so these are not economical for smaller batch
size, only gear cutting by milling operation is
recommended for smaller batch size.
2. Gear Shaping
Gear shaping used a cutting tool in the shape of a gear
which is reciprocated axially across the gear blank to
cut the teeth while the blank rotates around the shaper
tool.
It is a true shape-generation process in which the gear-
shaped tool cuts itself into mesh with the gear blank as
shown in fig.
The accuracy is good, but any errors in one tooth of the
shaper cutter will be directly transferred to the gear.
Internal gears can be cut with this method as well.
i). Shaping with a pinion-shaped
cutter
Gear Shaping Machine
ii).Shaping with a rack-shaped cutter
2. Gear Hobbing
Gear hobbing is a machining process in
which gear teeth are progressively
generated by a series of cuts with a
helical cutting tool (hob).
All motions in hobbing are rotary, and the
hob and gear blank rotate continuously as
in two gears meshing until all teeth are
cut.
4. Gear Finishing
As produced by any of the process described,
the surface finish and dimensional accuracy may
not be accurate enough for certain applications.
Several finishing operations are available,
including the conventional process of shaving,
and a number of abrasive operations, including
grinding, honing, and lapping , shaping.
1. Grinding
II. Lapping and Honing:
III. Gear shaving
While interacting with the gears, the
cutting teeth of the shaving cutter keep
on smoothening the mating gear flanks by
fine machining to high accuracy and
surface finish.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Copia de BINSDocumento3 pagineCopia de BINSCarlos100% (5)
- Helical GearsDocumento24 pagineHelical GearsPrakash Joshi88% (8)
- Power Electronics Question BankDocumento3 paginePower Electronics Question BankHarish SudhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Shaving PDFDocumento8 pagineGear Shaving PDFwolviakNessuna valutazione finora
- GT 0916Documento84 pagineGT 0916Davide MaranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ar Manufacturing PDFDocumento6 pagineAr Manufacturing PDFTharindu Chathuranga100% (2)
- Module IV: Gears and Gear TrainsDocumento38 pagineModule IV: Gears and Gear TrainsSuraj VinayNessuna valutazione finora
- 0611 GearSolutionsDocumento72 pagine0611 GearSolutionspoorianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20x102mm Fact SheetDocumento2 pagine20x102mm Fact SheetHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Deutsche Bank - Cloud Computing. Clear Skies AheadDocumento20 pagineDeutsche Bank - Cloud Computing. Clear Skies AheadkentselveNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing of GearsDocumento47 pagineManufacturing of GearsMuhammad UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To GearsDocumento30 pagineIntroduction To GearsPrakash Joshi100% (5)
- Backlash PDFDocumento12 pagineBacklash PDFkorray1100% (1)
- Gear Quality PDFDocumento3 pagineGear Quality PDFvijaykumarnNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Tooth ProfileDocumento5 pagineGear Tooth ProfilepremnathgopinathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear TechnologyDocumento52 pagineGear TechnologyJithinNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Manufacturing Process With QuestionsDocumento60 pagineGear Manufacturing Process With QuestionsUjwala Sonawane100% (1)
- Gear ManufacturingDocumento31 pagineGear Manufacturingvinu1175Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bev Gear Design PDFDocumento5 pagineBev Gear Design PDFMawan BentzNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To GearsDocumento28 pagineIntroduction To Gearssandeep_gaikwad2100% (4)
- Gears: A Gear Is A Wheel With Teeth On Its Outer Edge. The Teeth of One Gear Mesh (Or Engage) With The Teeth of AnotherDocumento12 pagineGears: A Gear Is A Wheel With Teeth On Its Outer Edge. The Teeth of One Gear Mesh (Or Engage) With The Teeth of AnotherAniruddh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrostatic Linear Motor Guide TacrockfordDocumento1 paginaHydrostatic Linear Motor Guide Tacrockfordanantj18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Documento8 pagineGears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Satish Dhandole100% (1)
- Bevel GearDocumento9 pagineBevel GearAadil KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Spline BroachingDocumento28 pagineSpline BroachingFaraz IshaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Gearmanufacturing MethodsDocumento9 pagineGearmanufacturing Methodskumar pNessuna valutazione finora
- Gears - Engineering InformationDocumento138 pagineGears - Engineering InformationGiang T LeNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Training Program Gear 2013Documento56 pagine02 Training Program Gear 2013amrit002Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.6 Gear Manufacturing: Form MillingDocumento6 pagine6.6 Gear Manufacturing: Form MillingDeepak ChandhokNessuna valutazione finora
- The Study of Continuous Rolling Mill Inter-Stand T PDFDocumento8 pagineThe Study of Continuous Rolling Mill Inter-Stand T PDFSantosh Kumar Pandey100% (1)
- Reverse Engineering of Spur GearDocumento4 pagineReverse Engineering of Spur GearInaamNessuna valutazione finora
- 20mm M50 SeriesDocumento2 pagine20mm M50 SeriesHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Spur GearsDocumento96 pagineSpur GearsVamshi Reddy100% (1)
- Production Technology (IV Sem)Documento24 pagineProduction Technology (IV Sem)Shubham AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Gears: by Aknath MishraDocumento20 pagineGears: by Aknath Mishrasamurai7_77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of GearsDocumento22 pagineTypes of GearsAnonymous 2RbW9dNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-2 Design of Spur GearDocumento56 pagineUNIT-2 Design of Spur GearMarthandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stepper Motor KTDocumento18 pagineStepper Motor KTSankula Siva SankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear CuttingDocumento56 pagineGear Cuttingiyerrahul2679350% (2)
- Long Series Power Collet ChuckDocumento1 paginaLong Series Power Collet ChuckSchneider S TamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear DesignDocumento5 pagineGear DesignKrishnadev Madhavan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Drive Selection of Rolling MillsDocumento4 pagineDrive Selection of Rolling MillsCihan OzturkNessuna valutazione finora
- Gears - Gear EfficiencyDocumento4 pagineGears - Gear Efficiencyavinashchauhan2695Nessuna valutazione finora
- LS Retail Training Manual Version 4.2Documento170 pagineLS Retail Training Manual Version 4.2MOHAMMED AARIFNessuna valutazione finora
- gt0519 PDFDocumento68 paginegt0519 PDFАндрей ГайнановNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 16 - Worm Gears Worked Out ProblemsDocumento19 pagineLecture 16 - Worm Gears Worked Out ProblemsApurba haldar50% (2)
- 1662SMC CommissioningDocumento28 pagine1662SMC Commissioningcyspasat100% (1)
- ADAS Automotive EngineeringDocumento15 pagineADAS Automotive EngineeringAman PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gears and Gear TrainsDocumento127 pagineGears and Gear TrainsVikki KotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentDocumento5 pagineManufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentParameshwara MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- U 4 Surface Finishing Process PDFDocumento37 pagineU 4 Surface Finishing Process PDFSubhadip MaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Making Room For Productivity and Quality Requirements in Gear GrindingDocumento4 pagineMaking Room For Productivity and Quality Requirements in Gear GrindingJitu InduNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Universal Gear ShavingDocumento48 pagineIntroduction To Universal Gear ShavingNagesh KamannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete CatalogDocumento651 pagineComplete CatalogFernando EscriváNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - V: Manufacturing TechnologyDocumento54 pagineUnit - V: Manufacturing TechnologyIjanSahrudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Fabrication of GearBoxDocumento21 pagineDesign and Fabrication of GearBoxSanjeev SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ReportDocumento45 pagineFinal ReportKuppu Raj100% (1)
- Standards Development: Enclosed Drives: Agma VoicesDocumento2 pagineStandards Development: Enclosed Drives: Agma VoicesRittik ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Manufacturing Methods: Prepared by Kaushal PatelDocumento42 pagineGear Manufacturing Methods: Prepared by Kaushal Patelashoku24007Nessuna valutazione finora
- MM Unit 4Documento21 pagineMM Unit 4Spartan 117100% (1)
- Unit - 4 Gear Generation & Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesDocumento69 pagineUnit - 4 Gear Generation & Non-Traditional Machining Processesnikhils_15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 4 Gear Generation & Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesDocumento57 pagineUnit - 4 Gear Generation & Non-Traditional Machining Processesvibhorjain18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mod5 1Documento71 pagineMod5 1jojo pantherNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Hobbing - Parts, Working, Diagram, Advantages, DisadvantagesDocumento1 paginaGear Hobbing - Parts, Working, Diagram, Advantages, DisadvantagesDhruv SutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear CuttingDocumento13 pagineGear Cuttingmuhammad umarNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 2252 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY - II-Unit-IV. (B)Documento87 pagineME 2252 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY - II-Unit-IV. (B)Tariq Aziz100% (2)
- BAB 5 Nota Handout DJJ1043 GearDocumento37 pagineBAB 5 Nota Handout DJJ1043 GearSyfull musicNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing of Gears and Its ProcessDocumento21 pagineManufacturing of Gears and Its ProcessAnonymous uaKq5PQWcNessuna valutazione finora
- C784 Spec 2009 02 03 MertenCDocumento6 pagineC784 Spec 2009 02 03 MertenCHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- 61-2CIR-18 120mm Fin Stabilised Armour Piercing Discarding Sabot Mark-IIDocumento1 pagina61-2CIR-18 120mm Fin Stabilised Armour Piercing Discarding Sabot Mark-IIHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Library: Design and Fabrication of A Prototype Tracer Surveillance TesterDocumento42 pagineTechnical Library: Design and Fabrication of A Prototype Tracer Surveillance TesterHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuze UTIU M85 AU20 - Encyclopedia of Arms and AmmunitionDocumento1 paginaFuze UTIU M85 AU20 - Encyclopedia of Arms and AmmunitionHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuze UTIU M85 AU20 - Encyclopedia of Arms and AmmunitionDocumento3 pagineFuze UTIU M85 AU20 - Encyclopedia of Arms and AmmunitionHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7Documento43 pagineCH 7Hossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ada 246346Documento131 pagineAda 246346Hossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- ARCADENE 360bbDocumento12 pagineARCADENE 360bbHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- 077201Documento59 pagine077201Hossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- M793Documento29 pagineM793Hossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- M 762Documento110 pagineM 762Hossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Interior Ballistics of SpinningDocumento3 pagineInterior Ballistics of SpinningHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Boundary CFXDocumento6 pagineWave Boundary CFXHossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- M 995Documento43 pagineM 995Hossam AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee111 Experiment 4Documento6 pagineEee111 Experiment 4Amirul 0205Nessuna valutazione finora
- Education Course Catalog enDocumento8 pagineEducation Course Catalog enlipasot781Nessuna valutazione finora
- Construction:: Retenax Flam RVMV 0,6/1Kv Npi-C orDocumento2 pagineConstruction:: Retenax Flam RVMV 0,6/1Kv Npi-C ormehdi HKNessuna valutazione finora
- Samsung 12k84 Washing Machine - User ManualDocumento68 pagineSamsung 12k84 Washing Machine - User ManualFidelis NdanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Core Java Vol 1 2 For The Impatient and Effective Pack 12Th Ed Cay S Horstmann Full ChapterDocumento51 pagineCore Java Vol 1 2 For The Impatient and Effective Pack 12Th Ed Cay S Horstmann Full Chapterkatherine.whipkey756100% (8)
- Cli 72 PDFDocumento604 pagineCli 72 PDFsudhakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Questions... DbmsDocumento10 pagineShort Questions... DbmsMuhammad Jamal ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Fire Alarm System Using ArduinoDocumento2 pagineSmart Fire Alarm System Using Arduinokritwik barua100% (1)
- Resistron: Operating InstructionsDocumento51 pagineResistron: Operating Instructions16_45_2013_gabri0% (1)
- EIE412 - Lecture Modules & Contents (2021 - 22)Documento18 pagineEIE412 - Lecture Modules & Contents (2021 - 22)sopuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2Documento12 pagineDay 2anamika soodhNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide For Using PTM and The CIBANO 500 To Test Circuit Breakers in North AmericaDocumento36 pagineA Guide For Using PTM and The CIBANO 500 To Test Circuit Breakers in North AmericaargaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Setup Mobility Extension On 2n OfficerouteDocumento14 pagineHow To Setup Mobility Extension On 2n Officeroutegnatagbi8696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Kick Scooter SwagTron Metro SK3 Official User ManualDocumento21 pagineElectric Kick Scooter SwagTron Metro SK3 Official User ManualBruno CoutoNessuna valutazione finora
- ST Vid10523-St444Documento65 pagineST Vid10523-St444Sistel HuanucoNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-04 CDR ConsoleDocumento56 pagine01-04 CDR ConsoleJUCARLCNessuna valutazione finora
- General InformationDocumento13 pagineGeneral InformationRamón Eduardo ColmenaresNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 PagesDocumento3 pagine2 PagesJohn Manuel BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Automation TestingDocumento104 pagineAutomation TestingAnant ChavanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Concrete Works CompuDocumento14 pagine2 Concrete Works CompuALFONSO RAPHAEL SIANessuna valutazione finora
- Panel Coker BP PDFDocumento2 paginePanel Coker BP PDFAlejandro José Poveda GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 204.4118.01 DmSwitch EDD Command ReferenceDocumento247 pagine204.4118.01 DmSwitch EDD Command ReferencemoxdyNessuna valutazione finora
- IWE SyllabusDocumento4 pagineIWE Syllabusmdasifkhan2013Nessuna valutazione finora