Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Course Learning Objectives and ACTIX Analyzer Overview
Caricato da
radhiwibowo0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
39 visualizzazioni73 pagineACTIX Basic (Sample CDMA) (1)
Titolo originale
ACTIX Basic (Sample CDMA) (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoACTIX Basic (Sample CDMA) (1)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
39 visualizzazioni73 pagineCourse Learning Objectives and ACTIX Analyzer Overview
Caricato da
radhiwibowoACTIX Basic (Sample CDMA) (1)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 73
Course Learning Objectives
Upon completions of this course you will be able to:
Use the ACTIX Analyzer to post process the drive test data,
visualize the data and analyze the data.
Have the knowledge of voice network optimization.
Identify the problems and solutions found during the
testing.
Course Pre-requisite
cdmaOne and CDMA2000 concepts and
terminology
Technical Background in Wireless
Communication Systems
Basic Call Processing in CDMA
Course History
It was aimed to be one of our
commitments to transfer the
knowledge and experiences
about ACTIX Analyzer to PT.
TELKOM.
This course was designed
based upon our technical
knowledge that was gained
from Qualcomm CDMA
University as one of CDMA
knowledge center.
ACTIX Analyzer
One of the best post processing tool that supports data
from multiple data collection vendors as well as multiple
technologies.
Able to decode the call trace collection devices.
Provide the flexibility for engineers to specify their own
analyses based on parameters collected during testing.
Using phone and scanner data for CDMA network analysis.
Automated report generation such as call statistics,
handoff states and many more.
Latest news from ACTIX 8 of the world top 10 operators
use ACTIX.
ACTIX Analyzer (continued)
Getting Started with ACTIX
Launch the ACTIX Analyzer application.
Configure the Analyzer. (Its only done once per
optimization area/workspace)
Setting up Maps
Loading Cell Site Data
Data Aggregation (Binning)
General Settings
Loading drive test data.
Create Superstream.
Export data to a file.
Generate the automated reports.
ACTIX data attributes most commonly export to a file.
Start Running the ACTIX
Launch the application by clicking the Analyzer Icon either on Desktop
Windows or Start Menu
Main Menu and
Button Bars
Workspace Explorer
Data Viewing Windows
Setting up Map
It is only required when we
want to display the data on top
of the background map.
Open the map windows by
clicking the View Menu ->
Display new Map
Setting up Map (continued)
Add map files
(MapInfo *.tab files)
from the Map windows
toolbar by clicking the
Layers Button
Setting up Map (continued)
Map toolbar reference
Loading Cell Site Data
The network data input files should be in tab, space or comma
separated files with one row of data per cell.
Basic required fields:
SiteID
Latitude
Longitude
Sector_ID
Azimuth
Beamwitdh
PN
By using import wizard feature, a user may define the format of a network
data input file and define how the source data is mapped to ACTIX
fields.
There are two types of data imported from input files which are
categorized as cell and sites data.
Loading Cell Site Data (continued)
Use the Network
Explorer to import,
view and edit the
network information.
Loading Cell Site Data (continued)
Configure the column
settings of cell with
minimum required
fields as follows:
SectorID
Azimuth
Beamwitdh
PN
Loading Cell Site Data (continued)
Configure the column
settings of site with
mininum required
fields as follows:
Site_Name
SiteID
Latitude
Longitude
Loading Cell Site Data (continued)
Using the current
network information
(CellRefs) that was just
imported through the
Tools Menu and
Preferences.
Data Aggregation (Binning)
Binning is a method of grouping and averaging the data
loaded from a log file.
Binning criterion can be specified in terms of:
Time
Geographic Location
Distance Traveled
Message Number
The Map, Chart and Table are binned views, means that
they display binned data.
The Message Browser and Protocol Stack Browser are
message based views, means that they display data taken
directly from the messages in the logfile.
Currently, we are using the location binning mode for our
data analysis purpose.
Data Aggregation (Binning Continued)
Some best practice recommendations for binning
modes:
Comparing my network to a competitors, or current
location of my network to that of 3 months ago Use
location binning, 100m or 200m square bin sizes.
Creating bins only when there is a change in GPS
coordinates Use distance binning at 50m or 100m
intervals, is the best alternative.
Examining a small section of a drive test to solve a very
specific problem Use either message-based binning or
time-based binning at 500ms.
Data Aggregation (Binning continued)
To set the default
binning settings for the
workspace, from the
Tools menu, select
Preferences.
General Settings
Make Distance Units
into Kilometres
Adjust the Mobile and
Switch Time Offset to
our local time zone
which is GMT +7
Loading Drive Test Data
From the Analyzer
toolbar, click the Open
Logfiles button, and
this display the Open
dialog window
Select an appropriate
file
Loading Drive Test Data (continued)
Navigate the workspace
explorer to view the loaded
data.
The only objects that you
actually need to recognize
are filenames, data streams
and data attributes.
Data attributes will be
used by map, chart and
table windows.
Data streams will be used
by message browser and
protocol stack browser
windows.
Loading Drive Test Data (continued)
Filename
Loaded Data Stream
Loaded Data Attributes
Create Superstream
A superstream is a data stream that has been
generated by correlating and merging data streams
from different sources.
Data from the superstream can be displayed in maps,
charts and table.
With ACTIX, it is possible to merge the drive test and
call trace data by superstreaming.
Create Superstream
(continued)
From the Tools menu,
select Create
Superstream to open
the Superstreaming
dialog window. This
dialog shows all
currently available data
streams.
Check each data
stream that you want
to combine as a
superstream
Create Superstream
(continued)
Merge Method Settings:
Use Timestamps this uses timestamp data within each stream to
synchronize the data.
Correlated Parameters use specified data attributes to correlate
the data streams.
Time Offsets use this to apply a shift to the time value for one of
the streams. It is a good option for superstreaming mobile and land-
based log files collected using speech quality equipments
Currently, we are using the timestamps method for our
analysis purpose.
Create Superstream
(continued)
Export Data to a File
From the File menu, select
Export Text File to open the
Export Wizard.
Select the data stream, one or
more data attributes that are to
be exported and lastly specify
the export format using the
options provided.
This step is only required if we
are going to use the 3rd party
application such as MapInfo to
produce the drive test plots or
manipulate data within a MS
Excel.
Export Data to a File
(continued)
Generate The Automated Reports
Most commonly reports produce by ACTIX such
as:
CDMA Summary Report that consist of the following
reports:
Call Statistics
FER and EcIo
Mtx and Mrx
Handoff State
CDMA Event Inspection that consist of the following
reports:
Call Dropped Window Stats: For every dropped call, this
reports key performance metrics for a 5-second window before
the drop.
Setup Failure Window Stats: For every dropped call, this
Generate The Automated Reports (continued)
Sample of Call
Statistics
Summary
Generate The Automated Reports (continued)
Sample of Handoff
State Report
Generate The Automated Reports (continued)
Sample of Call
Dropped Window
Stats Report
Generate The Automated Reports (continued)
Sample of
Setup Failure
Window Stats
Generate The Automated Reports (continued)
Sample of FER and
EcIo Reports
Generate The Automated Reports (continued)
Sample of MS Rx and
Tx Power
ACTIX Data Attributes
There are two types of Data Attributes:
Handset Data Attributes that consist of:
Downlink Measurements
Dedicated Radio Link
Pilot Measurements
Call Events
Scanner or Receiver Data Attributes that consist of:
Pilot Measurements
Event Data
Those ACTIX Data Attributes are most commonly
used for our data analysis purposes.
CDMA RF Optimization
Course Outlines:
3 Major Steps in Optimizing Network
RF Optimization Process
Key Performance Metrics
Cluster and Drive Route
Infrastructure Data Collection
Post Processing and Analysis
CDMA Handset States
MS Call Processing
Soft Handoff Process
MS Timer Values
CDMA Layer 3 Messages
CDMA Event Technical Reference
Originating Call Flows
Paging Channel Messages
Dropped Calls
Outgoing Call Fail
Network Tuning
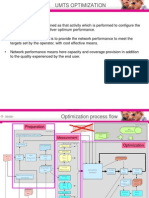
Three Major Steps in Optimizing Network
RF Optimization is the process
of measuring, analyzing, and
tuning an existing network to
Test
meet network performance
criteria.
It usually occurs after the
network planning is
Tune Analyze
completed
It can be performed
frequently, to respond to:
Changes or growth in the
network
Customer Complaints such as
coverage, dropped calls etc
RF Optimization Process
Key Performance Metrics
It was defined to evaluate the network performance depend on what is
important to the network operator.
The specific metric may vary (not standardized)
The key performance metrics can change over time.
The primary key performance metrics are specified on most network.
These include:
Access Failure Rate (Mobile Origination and Termination Failures)
Drop Call Rate
Forward Frame Error Rate
MS Receive Power
MS Transmit Power
Pilot Ec/Io
Other metrics are specified on some, but not all networks. These
include:
Average Call Setup Time
Soft Handoff Percentage
Area Availability
Cluster and Drive Route
Network should be divided into cluster if it consist of more
than 10 sites and the network coverage area is bigger.
Clustering will make it easily to identify the problems and
determine the causes.
Drive route should be defined and meet the following
criteria:
The route should go through all the sectors and extend to the cell
boundary.
The route should include the points of interests such as stadiums,
arenas, location with high wireless usage and trouble spots/hot
spots.
Infrastructure Data Collection
OMCR Data
MIB Database.
CDL Logs for the ESN that were used during the test.
Daily/Hourly Reports such as PM Sum, XCAT and CEM
Reports.
MSC Data
Call Trace Data (if required).
Site Audit Data
Antenna Checklist.
BTS Pilot Power Output.
Physical Installation Checklist.
Antenna Sweep Test Result.
Post Processing and Analysis
Use ACTIX to post process the mobile log files
based upon location and time.
The drive test plots are produced during the post
processing base upon the following ACTIX
handset data attributes:
MS Receive Power
Ec/Io 1st Best
Mobile Transmit Power
Forward FER
PN 1st Best Ec/Io
Handoff State
Post Processing and Analysis (continued)
This step also produce the call statistics such as:
Call Setup Time
Dropped Call Rate
Origination and Termination Failure Rate
Use ACTIX to identify the problems and solutions
through layer 3 messages (message browser and
protocol stack browser)
CDMA Handset States
Idle States This is the state that the phone is in,
before a call is originated or received. After a call is
terminated through normal or abnormal means, it
returns to the Idle States.
Origination State This is the state that the
phone is in after an Origination or Page Response
is sent on the access channel, but before the
forward and reverse traffic channels are active.
Dedicated State (Conversation) This is the
state that the phone is in, after transmission has
started on both link (forward and reverse traffic
channels).
MS Call Processing
MS Call Processing (continued)
Soft Handoff Process
Soft Handoff Process
(continued)
1. Pilot strength exceed T_ADD. MS sends a Pilot Strength
Measurement Message and transfers pilot to the Candidate Set.
2. BS sends an Extended Handoff Direction Message, a General Handoff
Direction Message or a Universal Handoff Direction Message.
3. MS transfers pilot to the Active Set and sends a Handoff Completion
Message.
4. Pilot strength drops below T_DROP. MS starts the handoff drop
timer TT_DROP.
5. Handoff drop timer expires. MS sends a Pilot Strength Measurement
Message.
6. BS sends an Extended Handoff Direction Message, a General Handoff
Direction Message or a Universal Handoff Direction Message.
7. MS moves pilot from the Active Set to the Neighbor Set and sends a
Handoff Completion Message.
This Soft Handoff Process will occur if
P_REV_IN_USEs is 3 or SOFT_SLOPEs = 000000
MS Timer Values
CDMA Layer 3 Messages
Synch Channel Messages (Forward Link)
Paging Channel Messages (Forward Link)
General Page Message
Access Parameter
System Parameter
Extended System Parameter
CDMA Channel List
Extended CDMA Channel List
Extended Channel Assignment
Neighbor List
Access Channel Messages (Reverse Link)
Origination Message
Paging Response Message
CDMA Layer 3 Messages (continued)
Forward Traffic Channel Messages (Forward Link)
Universal Handoff Direction Message
BS Acknowledgement
Service Connect
In Traffic System Parameter Update
In Traffic Neighbor List Update
Service Request
Reverse Traffic Channel Messages (Reverse Link)
Pilot Strength Measurement Messages
Power Measurement Report Messages
Service Connect Completion
Handoff Completion
MS Acknowledgment
Service Response
CDMA Layer 3 Messages (continued)
Use ACTIX Protocol Stack Browser to view the signaling
messages.
CDMA Layer 3 Messages (continued)
Message Browser
combines an event
panel (sequentially
listing call events)
with a panel of
Layer 3 Messages,
allowing you to
pinpoint the root
causes of problems.
CDMA Event Technical Reference
Call Completed: This attribute indicates successful
outgoing call initiations triggered by the following
sequence of messages:
Origination or Enhanced Origination Messagee
Followed by a Service Connect or a Service Connect Completion Message
Call Dropped: This attribute indicates abnormal call
terminations triggered by the following sequence of events:
Outgoing Call Setup OK or Incoming Call Setup OK (defined below)
Not followed by a Forward Release Order
Followed by a return to the Sync Channel
Call Setup Time: It provides the difference in time
between the Service Connect Completion message and the
associated Origination, Enhance Origination, or Page
Response Message.
CDMA Event Technical Reference (continued)
CDMA Call Type: It provides a description for
each call in a log file:
0 Outgoing Call Successfully Terminated
1 Incoming Call Successfully Terminated
2 Outgoing Call Failed Initiation
3 Incoming Call Failed Initiation
4 Outgoing Call Dropped
5 Incoming Call Dropped
Handoff OK: This attribute indicates handoff
events for mobiles handing off within the same
carrier of a CDMA system. This attribute is
triggered by the following sequence of messages:
CDMA Event Technical Reference (continued)
Extended Handoff Direction, Universal Handoff
Direction, or General Handoff Direction messages.
Followed by a Handoff Completion or Extended
Handoff Completion messages.
Incoming Call Fail: This attribute indicates failed
incoming call attempts triggered by the following
sequence of messages:
Page Response message.
Not followed by a Service Connect Completion.
Followed by another Page Response message or a
transition back to Idle mode.
CDMA Event Technical Reference (continued)
Incoming Call OK: This attribute indicates
successful incoming call initiations triggered by
the following sequence of messages:
Page Response message.
Followed by a either a Service Connect or Service
Connect Completion message.
Outgoing Call Fail: This attribute indicates failed
outgoing call initiations triggered by the following
sequence of messages:
Origination or Enhanced Origination messages.
Not followed by a Service Connect Completion message.
CDMA Event Technical Reference (continued)
Followed by an Origination message or a transition back
to idle mode.
Outgoing Call OK: This attribute indicates successful
outgoing call initiations triggered by the following
sequence of messages:
Origination or Enhanced Origination messages.
Followed by a Service Connect or a Service Connect
Completion message.
Paging Channel Messages
(General Page Message)
Paging Channel Messages
(Access Parameter)
Paging Channel Messages
(CDMA Channel List)
Paging Channel Messages
(Neighbor List)
Paging Channel Messages
(System Parameters)
Paging Channel Messages
(Extended System Parameter)
Paging Channel Messages
(Extended CDMA Channel List)
Dropped Calls
Dropped Calls are caused by the inability to maintain a
closed loop path for signaling and traffic between the
mobile and the base station once the call is established.
Key Observations:
Drive Test Plots produced by ACTIX Handset Data Attributes such
as MS Rx Power, MS Tx Power, Forward FER and 1st Best Ec/Io.
Call Drop Window Stats 5 Secs Before Drop (ACTIX CDMA Event
Inspections).
Infrastructure Logs (CDL and MSC Call Trace Data).
CDMA Layer 3 Messages and Mobile Diagnostic Messages that are
viewed by protocol stack browser and message browser.
Most Probably Causes: System Release, RF Loss, MS/BS
Bad Frames, MS Fade Timer, Forward FER Too High, Weak
Ec/Io and Missing Potential Neighbor.
Sample of Dropped Calls
Drive test plot shows too high
Forward FER but good RSSI and
Ec/Io. This is indication of weak
traffic channel.
CDL logs shows CFC=26 (System
Release).
MSC logs shows Fail Reason (System
Failure).
Outgoing Call Fail
Key Observations:
Drive Test Plots produced by ACTIX Handset Data
Attributes such as MS Rx Power, MS Tx Power, Forward
FER and 1st Best Ec/Io.
Setup Failure Window Stats 5 secs. Before Event
Outgoing Failures (ACTIX CDMA Event Inspection
Report).
Infrastructure Logs (CDL and MSC Call Trace Data).
CDMA Layer 3 Messages and Mobile Diagnostic
Messages that are viewed by protocol stack browser and
message browser.
Most probably causes: link imbalance, access
failure, repeater problems and communicates with
distant site.
Sample of Outgoing Call Fail
MS communicates with
distant sites which was
shown by searcher and
finger info messages.
Max number of access
probe sequences were
reached (num_step=3
and max_rsp_seq=3)
Network Tuning
After a network has been tested and the test data
has been analyzed, the network is tuned to bring
it up its defined performance specifications.
Hardware Changes:
Antenna Adjustments (Orientation, Tilt and Height)
Software Changes:
Neighbor List Add/Delete
BTS Pilot Power
MAHO Parameter
Search Windows Parameter
Access Parameter
Cell Radius
Thank You Very Much for Your Attention
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Benokraitis, Benokraitis Nijole Vaicaitis - Marriages & Families - Changes, Choices, and Constraints-Pearson (2015)Documento617 pagineBenokraitis, Benokraitis Nijole Vaicaitis - Marriages & Families - Changes, Choices, and Constraints-Pearson (2015)colleen100% (1)
- Bread Machine Sunbeam 5891Documento44 pagineBread Machine Sunbeam 5891Tyler KirklandNessuna valutazione finora
- Journey To The ARI-ARhAyas AL-Uma-UN Core of The Krystar Seed Atom FileDocumento14 pagineJourney To The ARI-ARhAyas AL-Uma-UN Core of The Krystar Seed Atom FileSungwon Kang100% (2)
- Data Historian: GE Industrial SystemsDocumento15 pagineData Historian: GE Industrial Systemsman_y2kNessuna valutazione finora
- GooglepreviewDocumento69 pagineGooglepreviewtarunchatNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Acquisition from HD Vehicles Using J1939 CAN BusDa EverandData Acquisition from HD Vehicles Using J1939 CAN BusNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoll 3 Drive Test PDFDocumento14 pagineAtoll 3 Drive Test PDFAmin KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aligning With New Digital Strategy A Dynamic CapabilitiesDocumento16 pagineAligning With New Digital Strategy A Dynamic Capabilitiesyasit10Nessuna valutazione finora
- German BasicDocumento60 pagineGerman BasicchahirNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Driven System Engineering: Automotive ECU DevelopmentDa EverandData Driven System Engineering: Automotive ECU DevelopmentNessuna valutazione finora
- HOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Documento27 pagineHOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Hiếu KoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Peptan - All About Collagen Booklet-1Documento10 paginePeptan - All About Collagen Booklet-1Danu AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultima Forte Required Data Inputs For ZTE InfrastructureDocumento15 pagineUltima Forte Required Data Inputs For ZTE InfrastructureVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- SAS Programming in the Pharmaceutical Industry, Second EditionDa EverandSAS Programming in the Pharmaceutical Industry, Second EditionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Google Cloud Platform for Data Engineering: From Beginner to Data Engineer using Google Cloud PlatformDa EverandGoogle Cloud Platform for Data Engineering: From Beginner to Data Engineer using Google Cloud PlatformValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 236b3 Esquema Electrico Mini Cargador CatDocumento29 pagine236b3 Esquema Electrico Mini Cargador Cathenry laviera100% (2)
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationDa EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- GSM Network KPI Guide for OptimizationDocumento36 pagineGSM Network KPI Guide for OptimizationJosue Jeremie100% (1)
- Online Test 2016Documento19 pagineOnline Test 2016EM KautsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Avanto Magnet System Error MessagesDocumento21 pagineAvanto Magnet System Error MessagesMuhammad Ahmad75% (4)
- Actix PresentationDocumento64 pagineActix PresentationSarfaraz AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Plus-Minus Method of Refraction Seismic Data Analysis in RadExPro SoftwareDocumento24 paginePlus-Minus Method of Refraction Seismic Data Analysis in RadExPro SoftwareJ Andre Medina DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To DNP3: TutorialDocumento3 pagineIntroduction To DNP3: TutorialWesleyNahNessuna valutazione finora
- Endodontic Emergencies GuideDocumento27 pagineEndodontic Emergencies GuideJitender Reddy100% (1)
- TEMS-Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSMDocumento94 pagineTEMS-Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSMapi-26684041100% (23)
- Network OptimizationDocumento201 pagineNetwork Optimizationjitendra_engNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 Cambridge Lower Second Progression Test Science Stage 8 QP Paper 2 - tcm143-430409Documento16 pagine2018 Cambridge Lower Second Progression Test Science Stage 8 QP Paper 2 - tcm143-430409AnisahNessuna valutazione finora
- ACTIX and Basic CDMA Voice OptimizationDocumento73 pagineACTIX and Basic CDMA Voice OptimizationNak SandyNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM ActixDocumento64 pagineGSM ActixNenad100% (1)
- Huawei GENEX Series Assistant V300R003 Main SlidesDocumento49 pagineHuawei GENEX Series Assistant V300R003 Main SlidesNgweno Mzito100% (1)
- Tips For Maximizing Performance in The A-Platform: System RequirementsDocumento5 pagineTips For Maximizing Performance in The A-Platform: System RequirementsTahir MuneerNessuna valutazione finora
- Com Site Pro Brochure 2010Documento4 pagineCom Site Pro Brochure 2010rlopezrlopezNessuna valutazione finora
- GENEX Assistant Customer Training SlideDocumento49 pagineGENEX Assistant Customer Training Slidealiuddin1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agilent E6474A Analysis SolutionDocumento8 pagineAgilent E6474A Analysis SolutionMakanaqui1971Nessuna valutazione finora
- CW Model Calibration ProcedureDocumento35 pagineCW Model Calibration ProcedureVineet KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Parameter Practical ValuesDocumento36 pagineGSM Parameter Practical Valuestingtong1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Relayer GuideDocumento19 pagineRelayer Guidecg7316Nessuna valutazione finora
- RF Master Protek A434 GUI Manual PDFDocumento14 pagineRF Master Protek A434 GUI Manual PDFiAZHTONNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation NASTARDocumento42 paginePresentation NASTARking13101Nessuna valutazione finora
- RF Log File Analysis and OptimizationDocumento4 pagineRF Log File Analysis and Optimizationmohas92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Model Tuning Using AssetDocumento35 pagineModel Tuning Using AssetDorra HammamiNessuna valutazione finora
- mDACS User Manual for RRC3 and RTx GPSDocumento18 paginemDACS User Manual for RRC3 and RTx GPSSantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Release Notes: Actix DV For Agilent Version 1.1Documento20 pagineRelease Notes: Actix DV For Agilent Version 1.1Areej El-ShriefNessuna valutazione finora
- GladiatorDocumento12 pagineGladiatorvickyaryanNessuna valutazione finora
- UMTSDocumento104 pagineUMTSHatem OdatAllahNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Network Planning and Optimization ToolsDocumento86 pagineGSM Network Planning and Optimization ToolsSushmita KoulNessuna valutazione finora
- BEx FrontEnd PerformanceDocumento9 pagineBEx FrontEnd PerformanceFabrizio ReginiNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-03 Single Site Verification PDFDocumento5 pagine01-03 Single Site Verification PDFKrist Aristotelius100% (3)
- Automated Substation Monitoring System Requirements & EvaluationDocumento11 pagineAutomated Substation Monitoring System Requirements & Evaluationpvenky_kkdNessuna valutazione finora
- hh99DD HTMDocumento4 paginehh99DD HTMOmar PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pilot Pioneer Operation Guide V9.2Documento47 paginePilot Pioneer Operation Guide V9.2Efosa AigbeNessuna valutazione finora
- 32Documento18 pagine32Fredyusa 01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drive Test PDFDocumento3 pagineDrive Test PDFRaymond Katungi100% (1)
- Asset Planning Tool1Documento177 pagineAsset Planning Tool1Hamad AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Meter and Data Management SoftwareDocumento6 pagineMeter and Data Management SoftwarechangbcNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Data Logger and Control SystemDocumento11 pagineMobile Data Logger and Control SystemcandancanerNessuna valutazione finora
- OPNET Modeler - Introduction LTE SimulationDocumento16 pagineOPNET Modeler - Introduction LTE SimulationAnonymous TTVlXoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ê ICT System Support: C C C C CCCCC C CDocumento6 pagineÊ ICT System Support: C C C C CCCCC C CAdnan Zubair Abul CassimNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Software XbeeDocumento16 pagineManual Software XbeeJboscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lab Experimental ManualDocumento21 pagineSample Lab Experimental ManualMauricio LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Link Analysis For Protocol-Test: Actix A-RLAP For GSMDocumento2 pagineLink Analysis For Protocol-Test: Actix A-RLAP For GSMAKiselev72Nessuna valutazione finora
- LSMWDocumento7 pagineLSMWPatil MgNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Genex Assistant Wcdma (Ver2.3)Documento45 pagine05 Genex Assistant Wcdma (Ver2.3)Harvinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Terms of ReferenceDocumento12 pagineTerms of ReferenceChristian NkoumouNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei GENEX Series Introduction To GENEX Nastar For WCDMA: InternalDocumento35 pagineHuawei GENEX Series Introduction To GENEX Nastar For WCDMA: InternalLuis Von MatterhornNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Introduction To GENEX NastarDocumento35 pagine10 Introduction To GENEX NastarVincenzo GuglielmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specifications and Scope of Work of AMRDocumento34 pagineTechnical Specifications and Scope of Work of AMRApurwa PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- GERAN/RAN Optimization ToolsDocumento57 pagineGERAN/RAN Optimization Toolsᗩᑿᘢ ᙜᘢᖺᗩᙜᗰᗅᖱNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognex DataMan 8000 Quick ReferenceDocumento31 pagineCognex DataMan 8000 Quick ReferenceadelbzhNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 PresentationDocumento38 pagine03 Presentation18-QADEER AHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Implementation of Error Detection Mechanism Using NetSimDocumento3 pagineImplementation of Error Detection Mechanism Using NetSimeditorijsaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tems ConfigurationDocumento21 pagineTems ConfigurationPoetri Sagitarius LoveLy BlueNessuna valutazione finora
- Actix Analyzer Update May 08 Release NotesDocumento7 pagineActix Analyzer Update May 08 Release NotesradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto PilotDocumento20 pagineAuto PilotradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Analyzer Update March2009Documento8 pagineReleaseNotes Analyzer Update March2009radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell ExportDocumento5 pagineCell ExportradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Analyzer Update August2008Documento11 pagineReleaseNotes Analyzer Update August2008radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Unify3G UMTS Sept2005Documento10 pagineReleaseNotes Unify3G UMTS Sept2005radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Actix OverviewDocumento76 pagineActix OverviewKapil MathurNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Analyzer Update April2009Documento11 pagineReleaseNotes Analyzer Update April2009radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes UnifyIP 1 0 Feb2006Documento8 pagineReleaseNotes UnifyIP 1 0 Feb2006radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Analyzer Update December2008Documento7 pagineReleaseNotes Analyzer Update December2008radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes UMTS Events Dec20Documento4 pagineReleaseNotes UMTS Events Dec20radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Troubleshooter Sept2005Documento20 pagineReleaseNotes Troubleshooter Sept2005radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Veritune June2005Documento86 pagineReleaseNotes Veritune June2005radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- InstructionsDocumento1 paginaInstructionsBeedjoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseNotes Veritune30 June2006Documento6 pagineReleaseNotes Veritune30 June2006radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawe 2G&3G Driver Test Training V1.3Documento83 pagineHuawe 2G&3G Driver Test Training V1.3radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- User Guide 1Documento397 pagineUser Guide 1nmtien1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- Release Notes: Veritune 2.1Documento5 pagineRelease Notes: Veritune 2.1radhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- A-IVS-UM Overview v2 1 1 PDFDocumento86 pagineA-IVS-UM Overview v2 1 1 PDFradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Missing Neighbour Analysis in RVSDocumento12 pagineMissing Neighbour Analysis in RVSrfnotesNessuna valutazione finora
- UserGuide2 PDFDocumento157 pagineUserGuide2 PDFradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gpeh: The Quick Reference Guide For Xeus ProDocumento40 pagineGpeh: The Quick Reference Guide For Xeus ProradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started GuideDocumento90 pagineGetting Started GuidefatehmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Actix Analyzer CDMA1 X Training ManualDocumento163 pagineActix Analyzer CDMA1 X Training Manualdidemir0% (1)
- Course Learning Objectives and ACTIX Analyzer OverviewDocumento73 pagineCourse Learning Objectives and ACTIX Analyzer OverviewradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Actix TutorialDocumento59 pagineActix TutorialradhiwibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aexio Xeus 2012 Quick GuideDocumento10 pagineAexio Xeus 2012 Quick GuideFajar KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aexio Xeus 2012 Quick GuideDocumento10 pagineAexio Xeus 2012 Quick GuideFajar KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Carbon-Polymer Based Composite Electrodes For Microbial Fuel CellsDocumento26 pagineApplication of Carbon-Polymer Based Composite Electrodes For Microbial Fuel Cellsavinash jNessuna valutazione finora
- Vee 2003Documento14 pagineVee 2003Syed faizan Ali zaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- PublicReviewDraft2742 (1) (002)Documento75 paginePublicReviewDraft2742 (1) (002)dhruv.encontrolsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nec TutorialDocumento5 pagineNec TutorialbheemasenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st ClassDocumento18 pagine1st Classchitl.23bi14075Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure - One Shot by Sakshi Mam #BounceBackDocumento231 pagineAtomic Structure - One Shot by Sakshi Mam #BounceBackchansiray7870Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theravada BuddhismDocumento21 pagineTheravada BuddhismClarence John G. BelzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Development Associates, IncDocumento3 pagineMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Development Associates, IncDedi MulyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Percentage Practice Sheet - RBEDocumento11 paginePercentage Practice Sheet - RBEankitNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit Switch 1LX7001-J AZBILDocumento8 pagineLimit Switch 1LX7001-J AZBILHoàng Sơn PhạmNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Financial Accounting Chapter 2 LECTURE - NOTESDocumento14 pagineAdvanced Financial Accounting Chapter 2 LECTURE - NOTESAshenafi ZelekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rostam's Seven LaboursDocumento3 pagineRostam's Seven LaboursArifin SohagNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication & Collaboration: Lucy Borrego Leidy Hinojosa Scarlett DragustinovisDocumento44 pagineCommunication & Collaboration: Lucy Borrego Leidy Hinojosa Scarlett DragustinovisTeacherlucy BorregoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lewis Carrol: Birth: DeathDocumento21 pagineLewis Carrol: Birth: DeathmarialuvsjeffNessuna valutazione finora
- (Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Documento4 pagine(Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Salim RossNessuna valutazione finora
- Split Plot Design GuideDocumento25 pagineSplit Plot Design GuidefrawatNessuna valutazione finora
- BCMEDocumento9 pagineBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Rise of NationalismDocumento19 pagineRise of NationalismlolaNessuna valutazione finora