Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Heredity Why You Look The Way You Do
Caricato da
Florencio Coquilla0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
95 visualizzazioni28 pagineheredity and genetics why yo look the way you look
Titolo originale
Heredity Why You Look the Way You Do
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoheredity and genetics why yo look the way you look
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
95 visualizzazioni28 pagineHeredity Why You Look The Way You Do
Caricato da
Florencio Coquillaheredity and genetics why yo look the way you look
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 28
HEREDITY
WHY WE LOOK THE WAY WE DO ?
BY: JEAN T. CAMINO
Heredity = the passing on of traits from one
generation to the next.
A trait is a specific characteristic that is unique.
Traits affect the way we look
Traits affect how our bodies function
Traits are inherited
Examples are hair color, eye color, handedness, etc.
We use a pedigree chart to keep track of how
traits are passed on from generation to
generation.
Traits are either Dominant or Recessive.
A dominant trait is a trait that is always
expressed, or shown.
Examples are brown hair, brown eyes, right handed
A recessive trait is a trait that is covered up or
seems to disappear.
Examples are blonde hair, blue eyes, left handed
Factors that make up an individual come from both
parents.
The trait information is passed on from generation
to generation in the form of genes.
A gene is a specific location on a
chromosome that controls a certain
trait.
An individual needs 2 genes for each trait
one gene from each parent.
This gene pair is called an allele.
One gene comes from the sperm cell (from the
Father)
One gene comes from the egg cell (from the Mother)
A chromosome is a structure in the cell that
contains the genetic information.
This information is passed on from one
generation to the next generation.
The name of the dominant trait determines what letter is
used to represent the gene.
Use a capital of the first letter of the dominant trait to
represent the dominant gene.
Use a small version of the first letter of the dominant trait
for the recessive gene.
Example: Right-handedness is the dominant trait so use R
for the dominant gene and use r for the recessive gene for
Left-handedness.
Example 2: Tall is the dominant trait so we use T and we use
t for the recessive gene for Short.
Traits are how our genes show and since traits are
formed from two genes, they are described by
the combination of genes that make the pair.
Traits are described as either:
homogeneous, (pure)
heterogeneous, (mixed)
Pure Dominant: the individual only has genes
for the dominant trait.
Example: TT = a pure tall individual has only tall (T)
genes.
Pure Recessive: the individual only has genes
for the recessive trait.
Example: tt = a pure short individual has only short (t)
genes.
A heterozygous individual has one dominant
gene and one recessive gene for a trait. The
result is the dominant gene is the one
expressed, or shown.
Example: Tt = a heterozygote tall individual has both
tall (T) and short (t) genes but looks tall.
A Punnett Square is a way to show the
possible combinations of genes that
offspring of parents could have.
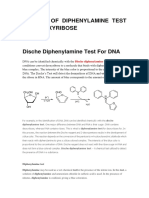
DNA is the instruction code that the genes use
to form traits.
DNA is long threads of material found in all cells.
DNA contains the master code that instructs all cells
in their daily jobs.
Genes are short pieces of DNA that make up our
chromosomes.
Each piece of DNA that is related to a gene makes up one
trait.
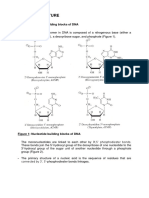
DNA looks like a twisted ladder made
of chemical compounds called bases.
There are 4 types of bases in DNA: Adenine,
Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine.
These bases fit together like puzzle
pieces
Adenine with Thymine
Cytosine with Guanine
Genes are pieces of DNA that make up a trait
Different genes consist of different arrangements of the
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine bases.
These bases can be arranged to form different proteins
(chemical messages)
These messages control different traits (some determine
how we look, some determine how we feel and function).
There are many millions of possible combinations of
these 4 bases this accounts for the differences, and
similarities, between life forms on earth.
All characteristics are affected by the DNA in
the cells of the individual organism.
These characteristics are called traits. Traits
depend on the types of proteins that the 4 bases
(A,C,G,T) make up.
Parents pass on copies of their DNA to their
offspring.
The DNA from each parent combines to form the
DNA of the offspring.
How the offspring develops depends on the
instructions coded in the DNA donated by both
parents.
Offspring are similar to parents, but different due
to the many possible combinations of the 4 bases.
Every individual is unique.
To predict looks of offspring
To predict risks of diseases/defects
Sickle-cell Anemia is a genetically inherited
disease where red blood cells are misshaped.
Red blood cell shape is an inherited trait.
Sickle-cell shape vs Normal cell shape
Sickle-cell anemia is cause by incomplete
dominance.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Reciept Flying VDocumento1 paginaReciept Flying VFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Visitation FormDocumento1 paginaHome Visitation FormFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Visitation FormDocumento1 paginaHome Visitation FormFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial StatementDocumento1 paginaFinancial StatementFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pass SLIPDocumento1 paginaPass SLIPFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Quarter Final Exam (Tle 10-Handicraft)Documento2 pagine4th Quarter Final Exam (Tle 10-Handicraft)Florencio Coquilla100% (1)
- Student Centered LearningDocumento1 paginaStudent Centered LearningFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Helen's DocumentDocumento2 pagineHelen's DocumentFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jean Signage Gcash EtcDocumento3 pagineJean Signage Gcash EtcFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate of Enrollment 4psDocumento1 paginaCertificate of Enrollment 4psFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Outline For Grade 9 PresentationDocumento1 paginaOutline For Grade 9 PresentationFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Root Cause ValidationDocumento1 paginaRoot Cause ValidationFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Substitution Slip SFISDocumento2 pagineSubstitution Slip SFISFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Child Adolescent ReflectionDocumento5 pagineChild Adolescent ReflectionFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 Attendance Sheet 2ND QAURTERDocumento1 paginaGrade 7 Attendance Sheet 2ND QAURTERFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- OBEREZDocumento1 paginaOBEREZFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shop HeaderDocumento1 paginaShop HeaderFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Frame Alex LourdesDocumento2 pagineFrame Alex LourdesFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beatuy and SufferingDocumento1 paginaBeatuy and SufferingFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Bread LessonDocumento1 paginaThe Bread LessonFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 Classroom OfficersDocumento1 paginaGrade 7 Classroom OfficersFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Application LetterDocumento2 pagineApplication LetterFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- DM OUCI 2021 346 - Os - 8 26 CSDD O 2585 - Homeroom Guidance Program For SY 2021 2022Documento38 pagineDM OUCI 2021 346 - Os - 8 26 CSDD O 2585 - Homeroom Guidance Program For SY 2021 2022Florencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Learning 1 Task Card 8Documento1 paginaAssessment of Learning 1 Task Card 8Florencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Outline For Grade 10 PresentationDocumento1 paginaOutline For Grade 10 PresentationFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blooms TaxonomyDocumento2 pagineBlooms TaxonomyFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Google CertDocumento1 paginaGoogle CertFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Completion Type of TestDocumento5 pagineCompletion Type of TestFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adventurous StorytellerDocumento1 paginaAdventurous StorytellerFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Demo-Teaching-Lesson-Plan ICT 8Documento7 pagineDemo-Teaching-Lesson-Plan ICT 8Florencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- DNA PackagingDocumento4 pagineDNA PackagingPriyanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA StructueDocumento74 pagineDNA StructueNeha VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Worksheet For SBQ1-AKDocumento17 paginePractice Worksheet For SBQ1-AKShamma AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.1007@s00216 019 02113 5Documento10 pagine10.1007@s00216 019 02113 5habib diopNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Evolution in Historical Perspective-SuarezDocumento10 pagineMolecular Evolution in Historical Perspective-SuarezStefani MiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- KOD - Plus-Neo: Store at - 20°CDocumento12 pagineKOD - Plus-Neo: Store at - 20°CArga GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology: Hussein Sabit, PHDDocumento26 pagineMolecular Biology: Hussein Sabit, PHD19740730Nessuna valutazione finora
- History of Diphenylamine TestDocumento2 pagineHistory of Diphenylamine Testkenneth VonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh 7 Final ExamDocumento5 pagineMapeh 7 Final Examapi-313517608100% (1)
- What Is DNA ReplicationDocumento2 pagineWhat Is DNA ReplicationAmmar SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna StructureDocumento23 pagineDna StructureAnonymous mHS76aNessuna valutazione finora
- Feulgen Reaction For DnaDocumento2 pagineFeulgen Reaction For DnaTapan Kumar PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unacademy Mock Paper 2Documento48 pagineUnacademy Mock Paper 2VipulNessuna valutazione finora
- Reverse TranscriptionDocumento9 pagineReverse TranscriptionzahraNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 8Documento13 pagineCH 8Qais Bani HaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts in MicroarraysDocumento51 pagineConcepts in MicroarraysAnjali WadhwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Module For Grade 10: Guagua National Colleges, Inc. Guagua, PampangaDocumento62 pagineScience Module For Grade 10: Guagua National Colleges, Inc. Guagua, PampangaNorman Punla SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- A 2.3 HL VirusesDocumento25 pagineA 2.3 HL Virusestaiga.aisaka14404Nessuna valutazione finora
- Winfree E, Et Al. Design and Self-Assembly of Two-Dimensional DNA Crystals (Nature)Documento6 pagineWinfree E, Et Al. Design and Self-Assembly of Two-Dimensional DNA Crystals (Nature)Mario PuppiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotech GuideDocumento242 pagineBiotech GuidekamalleNessuna valutazione finora
- 9701 w15 QP 43 PDFDocumento20 pagine9701 w15 QP 43 PDFAl BeruniNessuna valutazione finora
- BS BiotechDocumento47 pagineBS BiotechSyed Sheraz ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Sat Practice Test 1 Reading Assistive TechnologyDocumento79 pagineSat Practice Test 1 Reading Assistive TechnologyJaes MkaomNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 - Chapter 16-Heredity and VariationDocumento7 pagineClass 9 - Chapter 16-Heredity and Variationshreedhulap7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sequence by Synthesis.Documento6 pagineSequence by Synthesis.bladeralienNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 4 WorksheetDocumento6 pagineBiology Chapter 4 WorksheetShirmei WangNessuna valutazione finora
- GegDocumento126 pagineGegRicardo RodriguesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Exploring The Diversity of Life Fifth Canadian Edition Shelby Full ChapterDocumento67 pagineBiology Exploring The Diversity of Life Fifth Canadian Edition Shelby Full Chapterharry.duberry284100% (3)
- Biopsych Trans Chap 2Documento13 pagineBiopsych Trans Chap 2Chantelle SiyNessuna valutazione finora
- F - 071215 - Trizol and Trizol LS RNA IsolationDocumento33 pagineF - 071215 - Trizol and Trizol LS RNA IsolationKhalid AbduNessuna valutazione finora