Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Solar Cell FINAL
Caricato da
Shanck940 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni12 paginedefac
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentodefac
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni12 pagineSolar Cell FINAL
Caricato da
Shanck94defac
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 12
Solar cell & marketing
MUHD SYAFIQ BIN MOHD YUSOF
172799
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE MAJOR IN
CHEMISTRY
BGY2001 (BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT)
1. Introduction
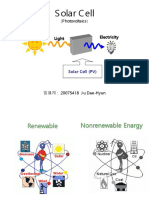
Traditional energy
Increase demand
Limited resources of the fossil fuels
Coal, oil, and gas as dominant
sources
Renewable energy
Continue flows of energy
Widely used for industrial
One of them is Solar radiation (infinite source)
Cleaner environment
2. Environmental problems
Massive consumption has a negative impact
The greenhouse effect linked to the CO2 in the
atmosphere.20th century
Conc. CO2 from 280 ppm to 350 ppm.
(Houghton, 2004)
Gases (CO2,SOX,NOX)
are produced from burning
of the fossil fuels
Plants and algae that grew by taking
in CO2 (Eutrophication)
3. Objectives
To determine the effenciency of solar cell on
environmental issues
To identify the different between photovoltaic and
photoelectrochemical cell
4. Solar energy
Directly into the chemical energy or electrical energy
(P. Salvador et al. 1996)
Sun delivers 1.2 10^14 kW energy on the Earth
Several ways can be collected
Photovolatic
Photoelectrochemical (PV)
(Solid State) solar cells, such as
conventional SINGLE CRYSTAL Solar
(PEC)solar cells (Becquerel. 1839).
(Liquid)
Cells (Chapins et al. 1975).
Current flow by conversion energy
p-n junction is formed between solid and a
from sunlight
liquid layer
Irradiation by light of appropriate frequency p-n junction is formed between two
on an electrode in contact with suitable solid layers
electrolyte (M.A.Russak et al. 1980)
PEC & PV solar
energy
Advantages Disadvantages
Environmentally friendly PV cannot operate without light
No emissions Large area needed for large scale
applications
PV operates even in cloudy weather High initial costs that overshadow the
conditions low maintenance costs
Electricity is generated wherever there -
is
light or solar
No use of fuels and water -
Long lifetime, up to 30 years -
(Halls, J.J et al. 2001)
5. Market and Applications
o Low cost thin-film solar cells successfully achieved in laboratory
efficiency light conversion typical used for commercial
o Consumer products (watches, calculators etc), roofs and outer
walls of buildings
o Cost of solar electricity depends on performance PV module
o 1997
0.5 billion US$ of PV modules
As costs & technology ,more markets be captured,
leading to production & further cost reduction
o 2010
Current predictions show a 6 billion US$
global market for PV systems (Mero Zeman, 2011)
Source: http://www.google .com.my
6. Improve cost of solar
1. Concentrator
These are mirrors that concentrate
the suns energy to improve efficiency
(C. Jayewardena et al. 1998)
2. Hybrid solar system
Combine solar with other
forms of energy to make
reliability higher and cost
cheaper
(Solar-wind)
7. Conclusion
Solar energy can be used to power electronic
appliances while not polluting the environment
The expanded use of energy can have a positive
impact on job creation in the technology nowadays
Other than that, this would bring solar electricity to
allow people represents an enormous market
8. References
1. Halls, J.J. and R.H. Friend, Organic Photovoltaic devices,
in Clean electricity from photovoltaics, M.D. Archer and
R. Hill, Editors. (2001).
2. P. Salvador, A.M. Chaparro and A. Mir, Journal of
Physical Chemistry, 100(2) (1996).
3. Gregg, B.A., Excitonic solar cells. Journal of Physical
Chemistry B, (2003).
4. Photoelectrochemistry and Photovoltaics of Layered
Semiconductors. Ed. by A. Aruchamy, Kluwer, Academic
Publishers Dordrecht-Holland/Boston, U.S.A., (1992).
5. C. Jayewardena, K. P. Hewaparakarma, D. L. A. Wijewardana
and H. Guruge., Solar Energy Material and Solar Cells,
(1998)
Halls, J.J. and R.H. Friend, Organic Photovoltaic devices, in
Clean electricity from
photovoltaics, M.D. Archer and R. Hill, Editors. (2001)
P. Salvador, A.M. Chaparro and A. Mir,
J. Phys. Chem., 100(2) (1996)
Click icon to add picture
ADD A SLIDE TITLE
- 5
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Renewable Energy Resources: 23 August 2016Documento33 pagineRenewable Energy Resources: 23 August 2016zakir abbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy: The Ultimate Renewable Resource: Bhim KafleDocumento57 pagineSolar Energy: The Ultimate Renewable Resource: Bhim KafleAadeem NyaichyaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Cells and LEDsDocumento21 pagineSolar Cells and LEDsSamreen ShabbirNessuna valutazione finora
- Transparent Solar CellDocumento13 pagineTransparent Solar CellSakshi GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy ChallengesDocumento15 pagineEnergy ChallengesabyzenNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdul-Rahman and WangDocumento27 pagineAbdul-Rahman and Wangchaith86Nessuna valutazione finora
- El Bassam 2013Documento19 pagineEl Bassam 2013IsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transparent Solar Panel Aditya LuthraDocumento28 pagineTransparent Solar Panel Aditya LuthraYogesh Rathi100% (1)
- Solar EnergyDocumento15 pagineSolar EnergyRycca DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Grid-Connected PV SystemDocumento42 pagineGrid-Connected PV SystemrevjangerNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar CellDocumento19 pagineSolar CellMamta GargNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento45 pagineDocumentFemi AjenifujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hybrid Solar Lighting Small HouseDocumento6 pagineHybrid Solar Lighting Small HouseDerek MerkNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To PV SystemsDocumento42 pagineIntroduction To PV SystemsMinh TranNessuna valutazione finora
- Files 1 2021 September NotesHubDocument 1632364811Documento3 pagineFiles 1 2021 September NotesHubDocument 1632364811goels0798Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solar PV Individual ReportDocumento7 pagineSolar PV Individual ReportshathishNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 PDFDocumento13 pagine5 PDFEsra AbdulhaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Different Types of Solar Cells and Future TrendsDocumento17 pagineReview of Different Types of Solar Cells and Future TrendsLokesh LokuNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Light Wavelength on PV Module PerformanceDocumento5 pagineEffects of Light Wavelength on PV Module PerformanceRamadan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH4a - Wk7-8. Photovoltaic Solar Cell Design and InstallationDocumento35 pagineCH4a - Wk7-8. Photovoltaic Solar Cell Design and InstallationAhmed AbdulrhmanNessuna valutazione finora
- University of BahrainDocumento35 pagineUniversity of Bahrainapi-291560513Nessuna valutazione finora
- List of Figures: S. No Fig No Name of The Fig Page NoDocumento19 pagineList of Figures: S. No Fig No Name of The Fig Page NoAkshitha ManchukondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Cell: (Photovoltaics)Documento37 pagineSolar Cell: (Photovoltaics)Akshay PabbathiNessuna valutazione finora
- SKEE 4653 - Chapter 1 - Introduction 20212022 1Documento97 pagineSKEE 4653 - Chapter 1 - Introduction 20212022 1gdd ddNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Stree - T - Rack ModuleDocumento57 pagineSolar Stree - T - Rack ModuleDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENessuna valutazione finora
- Solar IeeeDocumento7 pagineSolar IeeeDinesh Venkata RamaGopal MorlaNessuna valutazione finora
- February 14Documento15 pagineFebruary 14noorNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Development-2546Documento21 pagineDesign and Development-2546Kint PanenNessuna valutazione finora
- Dambhare 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1913 012053Documento17 pagineDambhare 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1913 012053hussain AlfatihNessuna valutazione finora
- Irjet V9i2681Documento12 pagineIrjet V9i2681Faisal Hossain Reevu ,160021026Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Power Generation With Auto Tracking SystemDocumento77 pagineSolar Power Generation With Auto Tracking Systemrahulanand090100% (3)
- Plastic Solar Cell Technology: Submitted To: - Submitted byDocumento37 paginePlastic Solar Cell Technology: Submitted To: - Submitted bynavya100% (3)
- Study of Different Type of Solar CellDocumento4 pagineStudy of Different Type of Solar CellInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Renewable Energy Sources and Solar CellsDocumento3 pagineRenewable Energy Sources and Solar Cellsmuhammad shahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Causes TransistorDocumento4 pagineThe Effect of Causes TransistoryashasvaagarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals and Application of Solar PhotovoltaicsDocumento24 pagineFundamentals and Application of Solar PhotovoltaicsEmmanuel OgoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Cell Basics and Future TechnologyDocumento37 pagineSolar Cell Basics and Future TechnologyMuhammad FauzanNessuna valutazione finora
- Renewable Energy Sources: Principles of Solar RadiationDocumento10 pagineRenewable Energy Sources: Principles of Solar RadiationDEEPANessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Report on 12V 150W Solar PV System DesignDocumento7 pagineAssessment Report on 12V 150W Solar PV System DesignshathishNessuna valutazione finora
- FALLSEM2020-21 MEE1011 ETH VL2020210107697 Reference Material I 10-Oct-2020 SPV PDFDocumento99 pagineFALLSEM2020-21 MEE1011 ETH VL2020210107697 Reference Material I 10-Oct-2020 SPV PDFAllNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar CoolingDocumento29 pagineSolar CoolingSudhanwa KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Li2014 3Documento6 pagineLi2014 3Hry EngineNessuna valutazione finora
- New Solar EnergyDocumento3 pagineNew Solar EnergyiG么RayGNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Solar Cells Review Recent DevelopmentsDocumento12 paginePlastic Solar Cells Review Recent DevelopmentsjonbilbaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy: Ali Samet Sarkın, Nazmi Ekren, Şafak Sağlam TDocumento11 pagineSolar Energy: Ali Samet Sarkın, Nazmi Ekren, Şafak Sağlam Tpalpandian.mNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento29 paginePresentation 1api-666280932Nessuna valutazione finora
- New For Engr BakriDocumento7 pagineNew For Engr Bakrioyetunde ridwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Graduation Project BookDocumento116 pagineGraduation Project BookKaffel AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar (Photovoltaic) System PresentationDocumento39 pagineSolar (Photovoltaic) System PresentationGeorge AsuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Solar Cell Fundamentals andDocumento13 pagineA Review of Solar Cell Fundamentals andDonny TNessuna valutazione finora
- Dye Sensitized Solar Cells - Working Principles, ChallengesDocumento35 pagineDye Sensitized Solar Cells - Working Principles, ChallengesaaaahsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Supervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi AgarwalDocumento27 pagineSupervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi AgarwalMr. K.S. Raghul Asst Prof MECHNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Solar Cell A ND ProcessesDocumento19 pagineIntroduction of Solar Cell A ND Processesnimas fathinNessuna valutazione finora
- Renewable Energy and Physics - Harnessing The Power of Solar CellsDocumento7 pagineRenewable Energy and Physics - Harnessing The Power of Solar CellsRaj MallickNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study of Materials For Solar PV Technology and Challenges: March 2017Documento14 pagineA Study of Materials For Solar PV Technology and Challenges: March 2017Tanmay HazraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee8703 - Res - Unit 3Documento55 pagineEe8703 - Res - Unit 3mokkai of the day videos100% (1)
- Atlantic UniversityDocumento9 pagineAtlantic UniversityValeria SanjuaneloNessuna valutazione finora
- Grid Connected Solar: Technical and Policy Issues Outline: Dr. Md. Zahurul HaqDocumento10 pagineGrid Connected Solar: Technical and Policy Issues Outline: Dr. Md. Zahurul Haqmz_haqNessuna valutazione finora
- Embodied Energy Analysis of PV Systems at Micro and Macro LevelsDocumento9 pagineEmbodied Energy Analysis of PV Systems at Micro and Macro LevelsBranislavPetrovicNessuna valutazione finora
- INSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageDa EverandINSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemist and Lab Assistant PostDocumento1 paginaChemist and Lab Assistant PostShanck94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Indemnity (Example)Documento1 paginaIndemnity (Example)Shanck94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Last BioDocumento1 paginaLast BioShanck94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Last BioDocumento1 paginaLast BioShanck94Nessuna valutazione finora
- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF DELHI METRO RAIL PROJECT - Environmental PerspectiveDocumento19 pagineENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF DELHI METRO RAIL PROJECT - Environmental PerspectiveMAYANK VIKHONA100% (6)
- Chapter 29 RadioactivityDocumento21 pagineChapter 29 RadioactivityAlicia WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fixed Temperature Thermostats: - 1Nt SeriesDocumento3 pagineFixed Temperature Thermostats: - 1Nt Serieschouaib kennicheNessuna valutazione finora
- PSV Forces in Closed SystemDocumento3 paginePSV Forces in Closed SystemayoungaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNH Solar Policy Clear - Notification - Electricity - Dept.Documento10 pagineDNH Solar Policy Clear - Notification - Electricity - Dept.aniketNessuna valutazione finora
- Válvulas ConcentricasDocumento1 paginaVálvulas ConcentricasOdlanier José MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- PB Max-Amine 70b Suez-GeDocumento5 paginePB Max-Amine 70b Suez-GeDavid Cruz ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode: 30D2 30D2 30D2 30D2Documento3 pagineDiode: 30D2 30D2 30D2 30D2Deilyn RivasNessuna valutazione finora
- K 98 MCC 7Documento389 pagineK 98 MCC 7Kapil ChetiaNessuna valutazione finora
- iC60H Circuit Breakers (Curve B, C, D)Documento4 pagineiC60H Circuit Breakers (Curve B, C, D)Abdullrahim AlastalNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Register Template Free Download - h4GzPV3NB5EEFnVDocumento11 pagineRisk Register Template Free Download - h4GzPV3NB5EEFnVNeo MothaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics of Producing Fuel Pellets From BiomassDocumento7 pagineEconomics of Producing Fuel Pellets From Biomassuser121821Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant OptimizationDocumento8 paginePlant OptimizationNaveen RathaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumatics Technical CataloqueLDocumento168 paginePneumatics Technical CataloqueLClaudio AllubNessuna valutazione finora
- Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger: Mme 9516 Hvac 1 Project PresentationDocumento16 pagineGasketed Plate Heat Exchanger: Mme 9516 Hvac 1 Project PresentationrudyNessuna valutazione finora
- NU-Q235F4 Data Sheet PDFDocumento2 pagineNU-Q235F4 Data Sheet PDFRES SupplyNessuna valutazione finora
- Material TechnologyDocumento46 pagineMaterial TechnologyVarunNessuna valutazione finora
- 047 Quotation Ovh Engine - Cv. Tretes Utama - Dx500lca - Sn. 10867Documento7 pagine047 Quotation Ovh Engine - Cv. Tretes Utama - Dx500lca - Sn. 10867Ifan saputroNessuna valutazione finora
- Energie&Umwelt 78-05 PDFDocumento569 pagineEnergie&Umwelt 78-05 PDFAnuj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Haskel Liquid PumpsDocumento9 pagineHaskel Liquid PumpsWong JowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation RecommendationsDocumento64 pagineInstallation RecommendationsMdava0% (1)
- (D. A. Bradley, D. Dawson, N. C. Burd, A. J. Loade (B-Ok - CC) PDFDocumento518 pagine(D. A. Bradley, D. Dawson, N. C. Burd, A. J. Loade (B-Ok - CC) PDFchinnapparaj.sNessuna valutazione finora
- Jeep Cherokee - Grand Cherokee 1993 - 1997Documento1 paginaJeep Cherokee - Grand Cherokee 1993 - 1997sluis770% (1)
- Emt 1Documento2 pagineEmt 1AdityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification Sheet - 3328QC 300aDocumento2 pagineSpecification Sheet - 3328QC 300aElias ZabanehNessuna valutazione finora
- Early Career Forum Advancing Your Engineering Career AgendaDocumento5 pagineEarly Career Forum Advancing Your Engineering Career AgendajwlatimerNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio-renewable materials for sustainable building developmentsDocumento82 pagineBio-renewable materials for sustainable building developmentsSudsiri Hemsri100% (1)
- Cause Andprevention of Dust Explosions in GR in Elevators and FlourDocumento11 pagineCause Andprevention of Dust Explosions in GR in Elevators and FlourTiago LigabueeNessuna valutazione finora
- General Description: Range ZNDocumento7 pagineGeneral Description: Range ZNAykut BacakNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of Chemical Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocumento45 pagineConcepts of Chemical Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenBoNwoawaNessuna valutazione finora