Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cours Verticaux V3.0
Caricato da
PiseyCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cours Verticaux V3.0
Caricato da
PiseyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
Driven and
Bored Piles
MADE BY :
AHMED MOHAMED ZANATY 9103710
AHMED ABDULLAH NEGM
9104441
MOHAMED AHMED EL SAEID
9103644
ABDELRAHMAN MOHAMED 9104286
AHMED YOUSSEF
9100499
DEPARTURE: COURSE:
CONSTRUCTION & BUILDING
UNDER SUPERVISION OF:
PROF. ADEL BELAL
FOUNDATION
To view online:
What is Deep foundation ?
A deep foundation is a type of foundation distinguished from
shallow foundations by the depth they are embedded into the
ground. There are many reasons a geotechnical engineer would
recommend a deep foundation over a shallow foundation, but
some of the common reasons are very large design loads, a
poor soil at shallow depth, or site constraints
There are different terms used to describe different types of
deep foundations including the pile, the pier, drilled shafts, and
caissons.
What are Piles ?
Piles are generally driven into the ground in situ; other deep
foundations are typically put in place using excavation and
drilling. The naming conventions may vary between engineering
disciplines and firms. Deep foundations can be made out of
timber, steel, reinforced concrete and pre-stressed concrete.
How piles are connected ?
Foundations relying on driven piles often have
groups of piles connected by a pile cap (a large
concrete block into which the heads of the piles
are embedded) to distribute loads which are
larger than one pile can bear.
Pile caps and isolated piles are typically
connected with grade beams to tie the
foundation elements together; lighter structural
elements bear on the grade beams, while
heavier elements bear directly on the pile cap.
Pile installation
Pile installation is as important as design. There are two
methods of installation :
a)Installation by Driving
b)Installation by Boring
Pile installation
Before going through pile installation methods understand the following
terminology.
Driven pre-cast pile: The pile is casted in a yard brought to the site and
driven by some mechanism into the soil.
Driven Cast-in-situ pile: A casing plugged at bottom is driven into the ground
and then the pile is casted by removing or retaining the casing.
Bored Pre-cast pile: A bore is made and the soil inside is removed and then a
pile
casted in some yard is put into the bore.
Bored Cast -in-situ pile: A bore is made the soil is removed and the pile is
casted at site in the bore.
Choosing Pile Type
Advantage & Disadvantage of Driven
Piles
Driven Pile installation
10
Driven Pile installation
All pile driving equipment, including the pile driving hammer,
hammer cushion, helmet, pile cushion, and other appurtenances
to be furnished by the Contractor shall be approved in advance
by the Engineer before any driving can take place.
To obtain this approval, the Contractor shall submit a description
of pile driving equipment to the Engineer before pile driving
begin. The description must contain sufficient detail so that the
proposed driving system can be evaluated by the Engineer.
11
Hammer Types
Drop hammer / Gravity hammer
Single acting power driven hammer
Double Acting Power Driven Hammer
Diesel Power Driven Hammers
Vibratory and Sonic Power Driven
Hammers
12
Hammer Types
Drop hammer / Gravity hammer: This is the
original pile driving hammer. It consists of a steel
ram that is guided within a set of leads. The
hammer is raised to a certain height and allowed to
drop on top of the pile, thus producing the driving
reaction.
13
Hammer Types
Single acting power driven hammer: Hammers of this type are
basically power gravity hammers. The difference between a
gravity hammer and a single acting power hammer is that the ram
(striking part) is encased in a steel frame work and is raised by
steam or compressed air rather than by the crane load lines. The
frequency of the blows is also considerably higher than a drop
hammer. The ram mass is usually greater than a drop hammer and
the vertical travel is usually less than that of a drop hammer. Any
type of power hammer is usually more efficient than a drop
hammer because there is less time between blows for the soil to
set up around the pile.
14
Hammer Types
Double Acting Power Driven Hammer: The ram is
raised by steam or compressed air, as in the case of
the single acting power hammer. When the ram
approaches the top of its stroke a valve is opened
into a chamber at the top of the cylinder allowing
high pressure air or steam into the cylinder forcing
the ram downward. Some double acting hammers
utilize a light ram, operating at a high frequency, to
develop the energy blows comparable to those
developed by heavier, slower acting hammers. The
advantage of the lighter ram hammer is that there is
less time between blows for soil to re-settle against
the pile, thus increasing the driving efficiency and
decreasing the drive time.
15
Hammer Types
Diesel Power Driven Hammers: They are simply a one
cylinder diesel engine consisting of a steel cylinder
containing a ram and an anvil. The ram is raised initially
by an outside power source (crane) and dropped. As the
ram drops, it activates a fuel pump, which injects fuel into
a cup in the top of the anvil. The ram continues down
blocking the exhaust ports and compressing the air in the
combustion chamber. A ball on the end of the ram,
mating closely with the cup in the anvil, forces the fuel
into the hot compressed air between the ram and the
anvil. The fuel then explodes forcing the ram up and
forcing the anvil, and in turn, the pile down.
16
Hammer Types
Vibratory and Sonic Power Driven Hammers: These
are the most recent developments in pile hammer
technology. They are comparatively heavy, requiring
handling equipment of greater capacity than required for
conventional pile hammers. The Vibratory Hammer
vibrates the pile at frequencies and amplitudes which
tend to break the bond between the pile surface and the
adjacent soils, thus delivering more of the developed
energy to the tip of the pile.
17
Driven Pile installation
1.
Raising the piston (starting)
2.
Injection of diesel fuel and
compression
3.
Impact and atomization.
4.
Exhaust
5.
Scavenging
18
Driven Pile installation
1.Raising the piston (starting): For starting the diesel hammer,
the piston (ram) is raised by means of a mechanical tripping device
and is automatically released at a given height.
2. Injection of diesel fuel and compression: As the piston falls
through the cylinders, it activates a lever on the back of the fuel
pump, which injects a measured amount of diesel fuel on to the top
of the impact block. Shortly after this, the exhaust ports are closed.
19
Driven Pile installation
3. Impact and atomization: Compressing all the air /fuel
between the exhaust ports and the top Of the impact block, the
piston continues falling until it strikes the top of the impact block.
The heat generated by the compression of air, in the presence of
atomized fuel, causes the explosion of the fuel, throwing the piston
upward and forcing the impact block downward against the pile.
20
Driven Pile installation
4. Exhaust: While moving upwards, the piston will pass and open
the exhaust ports. Exhaust gases will escape and the pressure in
the cylinder will equalize.
5. Scavenging: The piston continues its upward momentum,
which draws in fresh air for the nextcycle, cools the cylinders, and
releases the pump lever. The pump lever returns to its
startingposition, so that the pump will again be charged with fuel.
Gravity stops the upward motion of thepiston and it starts falling
through the cylinders once again.
21
Driven Pile installation
22
Driven Pile installation
Design of driven pile in sandy soil
Using static formula:
Length of pile = 25 m , Diameter of pile = 50 cm , = 18 , = 30
Qult = q Nq + KHc Po tan . 2 R H
q=
= 30 + 40/2 = 35, Nq = 75
Qb =
P=
QS = KHc Po tan . 2 R
QS = Q1 + Q2
23
Design of driven pile in sandy soil
(Cont.) Design of driven pile in sandy soil
Q2=
QS1=
QS Total = 2196 + 732 = 2927 KN
QU = 6627 + 2928 = 9555 KN
24
Design of driven pile in clay soil
Use static formula:
Length of pile = 25m, Diameter of pile = 50cm, =18 , = 30 , c = 3.8 t/ Ca
=3t/
Qb = Ab Cnc
Qb
= KN
QS= f= Ca
Qs=
QU=42.529+1178=1220.6KN
Qall=1220.6
25
26
BORED PILES
27
Pile installation
Pile installation is as important as design. There are two
methods of installation :
a)Installation by Driving
b)Installation by Boring
28
Bored Piles
Bored pilesis another type of reinforced concretepileswhich is
used to support high building which has heavy vertical load.
Bored pile is acast-in-place concrete pilewhere the bored piles
have to be cast on construction site.
29
Bored Piles
Normallybored pilinghas be to carried on those tall
buildings or massive industrial complexes, which
require foundations which can bear the load of
thousands of tons, most probably in unstable or
difficult soil conditions. Bored piling is cast by
usingbored piling machinewhich has specially
designed drilling tools, buckets and grabs, its used
to remove the soil and rock. Normally it can be
drilling into 50metres depth of soil.
Advantage & Disadvantage of Bored
Piles
Advantage
Disadvantage
Absence of vibrationwill not disturb adjacent
piles or structures.
Susceptible to "wasting" or "necking" in
"squeezing" ground.
Extremelyhigh capacity caissonscan be
obtained by expanding the base of the shaft
up to three times the shaft diameter, thus
eliminating construction of caps over multiple
pile groups.
Concrete is not placed under ideal conditions
and cannot be subsequently inspected.
For many design situations bored piles
offerhigher capacities with potentially better
economics than driven piles.
Water under artesian pressure may pipe up
pile shaft washing out cement.
30
31
Bored Pile installation
32
Bored Pile installation
To install a pile you should drill a borehole of a specified
diameter and depth. Next the borehole should be filled by fineaggregated concrete and reinforced with a metal frame of a
required cut. So, the bored piles are installed and concreted
directly on a site. The diameter varies up to 1500mm and depth
- up to 10m or 30 m and more. To increase bearing capacity the
piles should be installed with a widening at the bottom of the
borehole (a foot of pile). Mostly such types of bored piles are
used in situations when there are heavy loads to a foundation
and the few compressible soils are deep-seated.
33
Bored Pile installation
The installation of bored piles is free of dynamic effects to soils
and foundations of existing buildings. This main advantage of
bored piles is more appreciable during a construction within the
urban zone. Moreover this type of foundations allows installing
of a pile in any soil; even there are construction waste, remains
from the previous structures and boulder and cobble deposits.
34
Bored Pile installation
Quality control is very important during installation of bored
piles. All rigs are equipped with a special computer system to
control a pile concreting process. The monitoring piles
parameters are depth, pressure of concrete mix, concrete
volume and shape of piles.
35
Design of Bored Piles in sandy soil
=1.8 t/, = 25 , D = 50 cm , L = 18 m
Q = 1.8 x 18 = 32.4 t/
= 25 3= 22
Bored piles:
= 20.27
Concrete material
= 0.75 , = 18.75
=0.7-1.5 , taken =1.1
36
Design of Bored Piles in sandy soil
266.2 TON
= = 88.73 TON
37
Design of Bored Piles in clay soil
= 1.9t/, C = 3.8 T/, D= 50 cm , L=25m
Medium soil
=2.5-5
= 0
=5.7
taken =3t/
38
Design of Bored Piles in clay soil
122.06 Ton
= =40.69 Ton
39
THANK YOU
Made by :
1.
Ahmed Mohamed Zanaty
9103710
2.
Ahmed Abdullah Negm
9104441
3.
Mohamed Ahmed El Saeid
9103644
4.
Abdelrahman Mohamed
9104286
5.
Ahmed Youssef
9100499
Departure:
Construction &
Building
Course:
Foundation
Under supervision of:
Prof. Adel Belal
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Designers Guide To EN1992 1 1 and EN1992 1 2Documento234 pagineDesigners Guide To EN1992 1 1 and EN1992 1 2Cristiana Jipescu100% (9)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Service Manual PerkinsDocumento130 pagineService Manual Perkinsgelu2003home100% (12)
- Jamalpur Earthing Calculation Final PDFDocumento10 pagineJamalpur Earthing Calculation Final PDFarafinNessuna valutazione finora
- English Presentation OutlineDocumento1 paginaEnglish Presentation OutlinePiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Slope Stabliity - Bishop MethodDocumento1 paginaSlope Stabliity - Bishop MethodPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
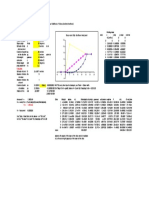
- D de Nu D'appui: 110kN 110kN 110kN 110kN 110kN 110kNDocumento1 paginaD de Nu D'appui: 110kN 110kN 110kN 110kN 110kN 110kNPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil, ShrinkageDocumento10 pagineSoil, ShrinkagePiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Slope Factor of SafetyDocumento2 pagineSlope Factor of SafetyPisey100% (2)
- 11-1. in Case of Putting The Precast Girder in Abuttement:: CIP CIPDocumento6 pagine11-1. in Case of Putting The Precast Girder in Abuttement:: CIP CIPPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Book 1,1 YyDocumento17 pagineBook 1,1 YyPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- RC Precast Slab Bridge: Institute of Technology of Cambodia Bridge Assignment Professor: KAING SaosereyDocumento46 pagineRC Precast Slab Bridge: Institute of Technology of Cambodia Bridge Assignment Professor: KAING SaosereyPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil ClassificationDocumento3 pagineSoil ClassificationPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Technology:: EnergyDocumento24 pagineGreen Technology:: EnergyPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic: Green Technology: Presentation OutlineDocumento1 paginaTopic: Green Technology: Presentation OutlinePiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansive Urban Growth Boundary: Tomoru HiramatsuDocumento15 pagineExpansive Urban Growth Boundary: Tomoru HiramatsuPiseyNessuna valutazione finora
- VolvoDocumento38 pagineVolvoMarculescu Nicolae CatalinNessuna valutazione finora
- RMG 4015 Crack Depth MeasurementDocumento4 pagineRMG 4015 Crack Depth MeasurementJozmel Blancas CamarenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notice Installation Maintenance GE215000aDocumento40 pagineNotice Installation Maintenance GE215000amuhammad nazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project ReportDocumento23 pagineFinal Project ReportMayank SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- QSL9-G3: Emissions Compliance: EU Stage IIIA at 50 HZ EPA NSPS Stationary Emergency Tier 3Documento10 pagineQSL9-G3: Emissions Compliance: EU Stage IIIA at 50 HZ EPA NSPS Stationary Emergency Tier 3mohsen_cumminsNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Petroleum GeologyDocumento23 pagineBasics of Petroleum GeologyShahnawaz MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sneak WireDocumento36 pagineSneak WireMeraSultanNessuna valutazione finora
- LT1460DCS8 5Documento26 pagineLT1460DCS8 5charkearNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing To The South African Consumer, 2021Documento352 pagineMarketing To The South African Consumer, 2021sherly juuNessuna valutazione finora
- Deerfield, NH 2008 Updated Master PlanDocumento305 pagineDeerfield, NH 2008 Updated Master PlanForumNewsNessuna valutazione finora
- BatteryDocumento3 pagineBatteryrtcaluyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Waste Minimization Practices in The Petroleum Refining IndustryDocumento9 pagineWaste Minimization Practices in The Petroleum Refining IndustryTaha Lemdjed BelahçeneNessuna valutazione finora
- 33KV GTP WbsebDocumento13 pagine33KV GTP Wbsebmaniking1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochlorination Basic Process TrainingDocumento40 pagineElectrochlorination Basic Process Trainingraghuvarma50% (2)
- XCMGDocumento841 pagineXCMGYafet Sigembala100% (1)
- Roto-Glide: Heavy-Duty Bearing Grease For Electric MotorsDocumento1 paginaRoto-Glide: Heavy-Duty Bearing Grease For Electric MotorsJoao Botas50% (2)
- Sources of Energy Class 10Documento17 pagineSources of Energy Class 10Maan NmNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture01 - Introductory ConceptsDocumento30 pagineLecture01 - Introductory ConceptsCarl PNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuously Variable Transmission - CVTDocumento18 pagineContinuously Variable Transmission - CVTPratheep Srinivas100% (3)
- SteamTurbineGenerator Datasheet 500MWDocumento8 pagineSteamTurbineGenerator Datasheet 500MWParantap RahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cracking in Fire Tube BoilersDocumento8 pagineCracking in Fire Tube BoilersRui AlexandreNessuna valutazione finora
- C-00 & Er 91april - May-2012Documento39 pagineC-00 & Er 91april - May-2012John SandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohammad Shadab Khan - Field OperatorDocumento6 pagineMohammad Shadab Khan - Field OperatorDonNessuna valutazione finora
- Reiki Book PDFDocumento108 pagineReiki Book PDFGurpreet Singh Sohal100% (1)
- LUMS Daily Student The H' WordDocumento16 pagineLUMS Daily Student The H' WordKhawaja DaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Open ChannelDocumento51 pagineChapter 2 - Open Channeladeliene 25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current Transformer: Engineering DepartmentDocumento8 pagineCurrent Transformer: Engineering DepartmentbinodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Building - Thesis Report (Administrative Block of NIT Raipur, New Campus)Documento86 pagineGreen Building - Thesis Report (Administrative Block of NIT Raipur, New Campus)Pranav Mishra89% (47)