Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pathophysiology Leptospirosis
Caricato da
Nathan Vince Cruz0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
27 visualizzazioni1 paginaTitolo originale
Pathophysiology Leptospirosis.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
27 visualizzazioni1 paginaPathophysiology Leptospirosis
Caricato da
Nathan Vince CruzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
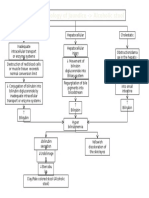
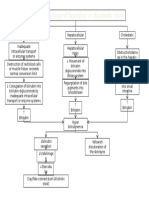
Pathophysiology
Leptospirosis
Modifiable risk factors
Breast feeding mothers (Can be
transmitted through breast milk)
Environment (Drinking water
contaminated with animal
urine/feces/semen)
Occupation
Sanitation
Water sports
Medication (hepatotoxic)
Non-modifiable risk factors
Age
Climate (Tropical)
Rainfall (higher incidence
during rainy season)
Direct or indirect contact with infected animal
urine/feces
Nursing Care Plans
Physical Assessment
findings
Lab result findings
Infiltration of Leptospira into
body
Septicemi
a
WBC
Temperature
Warm to touch
Shaking chills
Headache
Lung
s
Eye
s
Capillary vasculitis
Subconjunctival
hemorrhage
capillary permeability
Migration into organs
N/V
Diarrhe
a
adhesion to cell surfaces and cellular
toxicity
Potassiu
m
Chloride
Sodium
Kidneys
Liver
Proliferation
inside renal
tubules
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Neutrophils imbed
into tissue,
releasing basophils
Frequent
ingestion of
hepatotoxic
drugs
(Paracetamol)
Hepatic ischemia
Hepatosplenomegaly
Centrilobular necrosis
Abdominal pain
Hepatotoxicity
Acute Renal Failure
Liver cell death/tissue injury
Surfactant
Difficulty of breathing
Dry cough
Swollen lymph glands
Blood Urea
Nitrogen
Serum Creatinine
WBC
Presence of
urobilinogen
Oliguria
Impaired bilirubin metabolism
SGOT (AST)
SGPT (ALT)
Bilirubinemia
Jaundice
Dark yellow
urine
Bilirubin +++
Headac
he
N/V
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
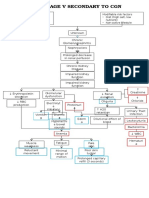
- Pathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Modifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Physical Assessment Findings Lab Result FindingsDocumento1 paginaModifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Physical Assessment Findings Lab Result FindingsNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Pathophysiology of JaundiceDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of JaundiceNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Pathophys of JaundiceDocumento1 paginaPathophys of JaundiceNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Pathophy CKD Secondary To CGNDocumento1 paginaPathophy CKD Secondary To CGNNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case PresentationDocumento37 pagineDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case PresentationNathan Vince Cruz100% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Infective Endocarditis: Non-Modifiable Age Congenital Heart Disease Gender Preexisting Heart Conditions ModifiableDocumento1 paginaInfective Endocarditis: Non-Modifiable Age Congenital Heart Disease Gender Preexisting Heart Conditions ModifiableNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Glumerulo NephritisDocumento13 pagineAcute Glumerulo NephritisNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)