Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris ManoCh 10
Caricato da
Sadaf RasheedTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris ManoCh 10
Caricato da
Sadaf RasheedCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Computer Arithmetic
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC
Arithmetic with Signed-2's Complement Numbers
Multiplication and Division
Floating-Point Arithmetic Operations
Decimal Arithmetic Unit
Decimal Arithmetic Operations
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Addition and Subtraction
SIGNED MAGNITUDEADDITION AND SUBTRACTION
Addition:
A + B ; A: Augend; B: Addend
Subtraction: A - B: A: Minuend; B: Subtrahend
Operation
(+A) + (+B)
(+A) + (- B)
(- A) + (+B)
(- A) + (- B)
(+A) - (+B)
(+A) - (- B)
(- A) - (+B)
(- A) - (- B)
Add
Magnitude
+(A + B)
- (A + B)
+(A + B)
- (A + B)
Subtract Magnitude
When A>B When A<B When A=B
+(A - B)
- (A - B)
- (B - A)
+(B - A)
+(A - B)
+(A - B)
+(A - B)
- (B - A)
+(A - B)
- (A - B)
+(B - A)
+(A - B)
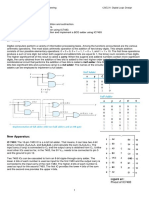
Hardware Implementation
Bs
AVF
E
B Register
Complementer
Output
Carry
Parallel Adder
M(Mode Control)
Input
Carry
S
As
Computer Organization
A Register
Load Sum
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Addition and Subtraction
SIGNED 2S COMPLEMENT ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION
Hardware
B Register
Complementer and
Parallel Adder
V
Overflow
AC
Algorithm
Subtract
Minuend in AC
Subtrahend in B
Augend in AC
Addend in B
AC AC + B+ 1
V overflow
AC AC + B
V overflow
END
Computer Organization
Add
END
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
MULTIPLICATION
Multiplication: B * A; B: Multiplicand; A: Multiplier; P: Partial Product
Multiplication of Unsigned Positive Numbers
A = An-1An-2 ... A0
B = Bn-1Bn-2 ... B0
P = B * An-1
= B * ( 2i * Ai )
i=0
= An-1 * (B2n-1) + An-2 * (B2n-2) + ... + A0 * (B20)
B shifted left
n-1 bits
B shifted left
n-2 bits
B shifted left
0 bits = A
Or
B shifted (n-1) bits to the left
P = An-1*(B2n-1 * 20) + An-2*(B2n-1 * 2-1) + ... + A0*(B2n-1 * 2-(n-1))
B2n-1
Computer Organization
B2n-1 shifted right
1 bit
B2n-1 shifted right
(n-1) bits
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
EXAMPLE
Multiplicand B=10111
Multiplier in Q
Q0 = 1; add B
First partial product
Shift right EAQ
Q0 = 1; add B
Second Partial Product
Shift right EAQ
Q0 = 0; shift right EAQ
Q0 = 0; shift right EAQ
Q0 = 1; add B
Fifth partial product
Shift right EAQ
Final Product in AQ = 0110110101
Computer Organization
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
00000
10111
10111
01011
10111
00010
10001
01000
00100
10111
11011
01101
SC
10011
101
11001
100
01100
10110
01011
011
010
001
10101
000
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
SIGNED MAGNITUDE MULTIPLICATION
Bs
Hardware
B Register
Sequence Counter
Complementer and
Parallel Adder
As
0
Qn
Qs
AC
Q Register
EAQ
B <- Multiplicand B
Q <- MultiplierA
Algorithm
As,Qs <- Qs Bs
A <- 0, E <- 0
SC <- n-1
= 0 Q =1
0
EA <- A + B
END
Product
in AQ
Computer Organization
=0
=0
shr EAQ
SC <- SC+1
SC
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
BOOTH MULTIPLICATION ALGORITHM FOR SIGNED 2S
COMPLEMENT
Multiplier
Strings of 0s: No addition; Simply shifts
Strings of 1s: String of 1s from mp to mq:
2p+1 - 2q
Example
001110 (14) -> p = 3, q = 1
001110 = 23+1 - 21
M * 14 = M24 - M21
Algorithm
[1] Subtract multiplicand for the first least significant 1
in a string of 1s in the multiplier
[2] Add multiplicand for the first 0 after the string
of 1s in the multiplier
[3] Partial Product does not change when the
multiplier bit is identical to the previous bit
110010 = -24 + 22 - 21 = -16 + 4 - 2 = -14
subtract
24
Add
22
Computer Organization
subtract
21
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
BOOTH ALGORITHM FOR SIGNED 2S COMPLEMENT
B <- Multiplicand B
Q <- Multiplier A
AC <- 0
Q-1 <- 0
SC <- n
Q0Q-1
?
10
01
Q-1 : shifted out bit
on shr of Q
11
00
AC<-AC+B+1
AC <- AC + B
ashr(AC&Q)
SC <- SC + 1
0
SC
?
=0
END
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
EXAMPLE OF BOOTH MULTIPLIER
Q0Q-1
10
B = 10111
B+1=01001
Initial
Subtract B
11
01
ashr
ashr
Add B
00
10
ashr
ashr
Subtract B
ashr
Computer Organization
AC
00000
01001
01001
00100
00010
10111
11001
11100
11110
01001
00111
00011
Q
10011
Q -1
0
SC
101
11001
01100
1
1
100
011
10110
01011
0
0
010
001
10101
000
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
ARRAY MULTIPLIER
A = a1a0: Multiplier
B = b1b0: Multiplicand
C = B * A = c3c2c1c0
c3
a1b1
c2
b1
b0
a1
a0
a0b1 a0b0
a 1b0
c1
c0
b1
b0
a0
a1
b1
b0
HA
C S
c3
Computer Organization
c2
HA
C
S
c 1 c0
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Multiplication
ARRAY MULTIPLIER 4-BIT X 3-BIT
a0
b3
a1
b3
b2
b1
b2
b1
b0
b0
0
Addend
Augend
4-bit Adder
Sum and Carry Outputs
a2
b3
b2
b1
b0
Addend
Augend
4-bit Adder
Sum and Carry Outputs
c6
Computer Organization
c5
c4
c3
c2
c1
c0
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Division
DIVISION
A/ B = Q + R
A: Dividend; B: Divisor; Q: Quotient; R: Remainder
Divisor B = 10001, B+ 1 = 01111
E
A
01110
Dividend:
0
11100
shl EAQ
01111
add B+1
1
01011
E=1
1
01011
Set Q0=1
0
10110
shl EAQ
01111
Add B+1
1
00101
E=1
1
00101
Set Q0=1
0
01010
shl EAQ
01111
add B+1
0
11001
E=0; Q0=0
10001
add B
1
01010
restore remainder
0
10100
shl EAQ
01111
add B+1
1
00011
E=1
1
00011
Set Q0=1
0
00110
shl EAQ
01111
add B+1
0
10101
E=0; Q0=0
10001
add B
1
00110
restore remainder
neglect E
00110
remainder in A
quotient in Q
Computer Organization
Q
00000
00000
SC
5
00001
00010
00011
00110
00110
01100
01101
11010
11010
11010
11010
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Division
FLOWCHART OF DIVIDE OPERATION
Dividend in AQ
Divisor in B
Qs As Bs
SC<- n - 1
shl EAQ
E
EA A + B+1
1
A B
EA A+B+1
0
A<B
A A+B+1
0(A<B)
EA A+B
DVF 1
EA A+B
DVF 0
A B
Q0 1
EA A+B
SC SC-1
END
(Divide overflow)
SC
END
(Quotient in Q
Remainder in R)
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Floating Point Arithmetic
FLOATING POINT ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
F = m x re
where m: Mantissa
r: Radix
e: Exponent
Registers for Floating Point Arithmetic
Bs
Parallel Adder
As A1
Qs
Computer Organization
BR
Parallel Adder
and Comparator
AC
QR
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Floating Point Arithmetic
FLOATING POINT ADD AND AUBTRACT
C
H
E
C
K
F
O
R
=0 BR 0
AC
=0
a<b
AC<-BR
add
a>b
a:b
shr A
a <- a+1
op
sub
As<-As
shr B
b <- b+1
sub
As Bs
0
EA<-A+B+1
A<-A+1
As<-As
add
op
As Bs
Align
Mantissa
0
0
E
A
A1
EA<-A+B
=0
AC<-0
shl A
a<-a+1
+ or - of
mantissa
Normalization
shr A
A1<-E
a<-a+1
END
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Floating Point Arithmetic
FLOATING POINT MULTIPLICATION
BR <- Multiplicand
QR <- Multiplier
=0
BR
0
=0
QR
0
AC <- 0
a <- q
a <- a+b
a <- a-bias
Multiply mantissa
(finxed point
multiplication)
shl AQ
a <- a-1
A1
1
END
(Product is in AC)
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Floating Point Arithmetic
FLOATING POINT DIVISION
BR<-Divisor
AC<-Dividend
=0
=0
QR <- 0
BR
0
AC
0
Qs <- As + Bs
Q<-0
SC<-n-1
divide
by 0
EA <- A+B+1
1
0
A<B
A>=B
A <- A+B
shr A
a <- a+1
A <- A+B
a <- a+b+1
a <- a+bias
q <- a
Divide Magnitude of mantissa
as in fixed point numbers
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
BCD Arithmetic
BCD ADD
BCD digit < 10
BCD digit + BCD digit + carry =< 19
K
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
Binary Sum
Z8 Z4 Z2 Z1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1
1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0
1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
Computer Organization
C
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
BCD Sum
S8 S4 S2 S1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1
Decimal
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
BCD Arithmetic
BCD ADDER
If we can convert Binary Sums to BCD Sum ,
we can use a binary adder to add two BCD numbers
SUM =< 9
BCD Sum = Binary Sum
BCD Carry = Binary Carry
19 >= SUM > 9
BCD Sum = Binary Sum + 0110
BCD Carry = Carry(Binary Sum + 0110)
4-bit Binary Add
1
Take next
higher digit
Z8
1
1
Z4
done
?
0
1
BCD Sum<-Sum + 0110
BCD C<-Carry(BCD Sum)
Computer Organization
Z2
END
0
BCD Sum = Sum
BCD C<-Carry(Sum)
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
BCD Arithmetic
BCD ADDER HARDWARE
Addend
Carry Out
Augend
4-bit Binary Addr
Z8
Z4
Z2
Carry In
Z1
BCD Carry
0
0110
4-bit Binary Adder
S 8 S 4 S 2 S1
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Computer Arithmetic
Decimal Arithmetic
DECIMAL ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
Addition
- Identical to the BCD addition
- 9s complement and 10s complement are
identical to 1s complement and 10s
complement, respectively
Computer Organization
Computer Architectures Lab
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Computer ArithmaticDocumento21 pagineComputer Arithmaticmanishbhardwaj8131Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit2 CADocumento34 pagineUnit2 CAIT HOD Nandha College of TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Design Process & ALU DesignDocumento6 pagineThe Design Process & ALU DesignNarender KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 04Documento33 pagineChapter 04Iqbal Ashfaq Joiya100% (1)
- 03 Numeric BasicsDocumento68 pagine03 Numeric BasicsGîrju AndradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento38 pagineUnit 2toshgangwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Arth CirDocumento105 pagineArth Cirnoor_dcetNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital System 1Documento6 pagineDigital System 1Debabrata GuchhaitNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Multiplication Twos Complement Multiplication (Booths Algorithm)Documento9 pagineBinary Multiplication Twos Complement Multiplication (Booths Algorithm)RiajiminNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Combinational LogicDocumento66 pagineChapter 4 Combinational LogicLacosaNessuna valutazione finora
- COA Mod 3Documento30 pagineCOA Mod 3BasithNessuna valutazione finora
- ALUDocumento21 pagineALUprathabapandianNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructions For Using The Powerpoint Slides:: To View The Animated Steps - Click Anywhere On The SlideDocumento77 pagineInstructions For Using The Powerpoint Slides:: To View The Animated Steps - Click Anywhere On The SlideAnonymous 7WsOWImuNessuna valutazione finora
- CPE 232 Computer Organization MIPS Arithmetic - Part IDocumento18 pagineCPE 232 Computer Organization MIPS Arithmetic - Part ImakayaboNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Lab ManualDocumento69 pagineDigital Lab ManualRajesh MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ix - Combinational Circuits (No Animation)Documento19 pagineIx - Combinational Circuits (No Animation)Charles Brian LunasNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Arithmatic1Documento38 pagineComputer Arithmatic1dp06vnsNessuna valutazione finora
- BTL Logic Design Lab Manual 10ESL38 3rd Sem 2011Documento67 pagineBTL Logic Design Lab Manual 10ESL38 3rd Sem 2011Manjunath JiNessuna valutazione finora
- Microcomputer Systems I: Dr. Burchard R.B. Bagile B008 CoictDocumento61 pagineMicrocomputer Systems I: Dr. Burchard R.B. Bagile B008 CoictSaid AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Organization Hamacher Instructor Manual Solution Chapter 61Documento31 pagineComputer Organization Hamacher Instructor Manual Solution Chapter 61Gorakhnath MethreNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science 37 Lecture 9Documento17 pagineComputer Science 37 Lecture 9Alexander TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- De Unit2 SlidesDocumento167 pagineDe Unit2 SlidesAravind RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Switching Circuits & Logic Design: 18 Circuits For Arithmetic OperationsDocumento8 pagineSwitching Circuits & Logic Design: 18 Circuits For Arithmetic OperationsGajinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Arithmetic: Operations and Circuits: Chapter-6Documento44 pagineDigital Arithmetic: Operations and Circuits: Chapter-6Samina TohfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Combinational CircuitsDocumento43 pagineCombinational CircuitsGanesh RockyNessuna valutazione finora
- Integer Arithmetic: Chapter 10, Section 10.3Documento17 pagineInteger Arithmetic: Chapter 10, Section 10.3Saisadwik Kairam KondaNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 SubtractorsDocumento21 pagine02 SubtractorsSarita AninditaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems: Section 3 - Arithmetic Logic UnitDocumento27 pagineEE201: Digital Circuits and Systems: Section 3 - Arithmetic Logic UnitMahmoud KamelNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Gates: 2-Input EX-OR (Exclusive OR) GateDocumento35 pagineLogic Gates: 2-Input EX-OR (Exclusive OR) GateALFRED AKPONessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10Documento37 pagineCH 10Ayush UpretyNessuna valutazione finora
- Comp ArithmeticDocumento50 pagineComp ArithmeticDavid Jnr PeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Badass Tutorial Unit 6 Adders SubtractorsDocumento23 pagineBadass Tutorial Unit 6 Adders SubtractorsdjpsychoscientzNessuna valutazione finora
- A NumberingDocumento32 pagineA NumberingshashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt 4Documento72 pagineChapt 4jannngirNessuna valutazione finora
- P05-Digital Systems - Lecture - 17-20Documento46 pagineP05-Digital Systems - Lecture - 17-20JAINessuna valutazione finora
- Array MultiplierDocumento10 pagineArray MultiplierVarsha LalapuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5 Binary ArithmeticDocumento5 pagineLab 5 Binary ArithmeticIfthakharul Alam ShuvoNessuna valutazione finora
- COA Mod 3Documento25 pagineCOA Mod 3Rosh Roy GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipelining - Basic Principles, Classification of Pipeline ProcessorsDocumento30 paginePipelining - Basic Principles, Classification of Pipeline ProcessorsJoel K SanthoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Combinational LogicDocumento63 pagineChapter 4 Combinational Logicmdhuq1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Processor Design 5Z032: Arithmetic For ComputersDocumento57 pagineProcessor Design 5Z032: Arithmetic For ComputersdishatiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- l2 Combi LogicDocumento27 paginel2 Combi LogicPECMURUGANNessuna valutazione finora
- Arithmetic CircuitsDocumento69 pagineArithmetic Circuitsshivam007100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Digital Systems and Binary NumbersDocumento55 pagineChapter 1 Digital Systems and Binary NumbersAminaHameed100% (2)
- CS M151B / EE M116C: Computer Systems ArchitectureDocumento33 pagineCS M151B / EE M116C: Computer Systems ArchitecturetinhtrilacNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Design Lab Manual 10ESL38 3rd Sem 2013Documento61 pagineLogic Design Lab Manual 10ESL38 3rd Sem 2013vishvakirana75% (4)
- Number Arithmetic p2Documento8 pagineNumber Arithmetic p2manishbhardwaj8131Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Architecture: ALU (2) - Integer ArithmeticDocumento24 pagineComputer Architecture: ALU (2) - Integer ArithmeticSulochana JangraNessuna valutazione finora
- Comb CircDocumento63 pagineComb Circm.sangeethjaNessuna valutazione finora
- CS352H: Computer Systems Architecture: Lecture 5: MIPS Integer ALU September 10, 2009Documento27 pagineCS352H: Computer Systems Architecture: Lecture 5: MIPS Integer ALU September 10, 2009farah_nishuNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer ArithmeticsDocumento78 pagineComputer ArithmeticsBleron MorinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookDa EverandAdvanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Digital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesDa EverandDigital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Da EverandAdvanced AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beginning Microsoft SQL Server 2012 ProgrammingDa EverandBeginning Microsoft SQL Server 2012 ProgrammingValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Data Visualization with Excel Dashboards and ReportsDa EverandData Visualization with Excel Dashboards and ReportsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Presented By: Syeda Rida Fatima TaqviDocumento22 paginePresented By: Syeda Rida Fatima TaqviSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction CycleDocumento12 pagineInstruction CycleSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of InstructionsDocumento12 pagineTypes of InstructionsSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Stack OrganizationDocumento6 pagineStack OrganizationSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 8-6 Data Transfer and ManipulationDocumento16 pagine8-6 Data Transfer and ManipulationSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Register Transfer and Micro-OperationDocumento33 pagineRegister Transfer and Micro-OperationSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)Documento16 pagineCentral Processing Unit (CPU)Sadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 8Documento6 pagineCH 8Mustafa JumaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 05Documento11 pagineCH 05Samsul ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- RDBMS Concepts Basics Interview Questions PDFDocumento6 pagineRDBMS Concepts Basics Interview Questions PDFSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-Introduction To DBMS-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HIndiDocumento2 pagine01-Introduction To DBMS-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HIndiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Job AnalysisDocumento40 pagineJob AnalysisSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual of Digital Logic and Computer Design (2nd Edition) Morris Mano PDFDocumento40 pagineSolution Manual of Digital Logic and Computer Design (2nd Edition) Morris Mano PDFSadaf Rasheed0% (4)
- CH 06Documento11 pagineCH 06Sadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 07-OverView of Data Models-Entity Relationship Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento1 pagina07-OverView of Data Models-Entity Relationship Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- DBMS MCQDocumento8 pagineDBMS MCQbenaminsan67% (6)
- 23-Entity-Relationship Data Model - Constraints-Mapping Cardinalities - DBMS Tutorials FoDocumento3 pagine23-Entity-Relationship Data Model - Constraints-Mapping Cardinalities - DBMS Tutorials FoSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 25-Entity-Relationship Data Model-RelationShip Sets Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento2 pagine25-Entity-Relationship Data Model-RelationShip Sets Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 27-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Entity-E-R - Diagram To Tables - Rules For Reduction - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento3 pagine27-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Entity-E-R - Diagram To Tables - Rules For Reduction - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 01Documento13 pagineChapter 01Sadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 24-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Data Integrity & Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento2 pagine24-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Data Integrity & Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFDocumento3 pagine08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFDocumento3 pagine08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 02-Properties of DataBase Part-1-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento3 pagine02-Properties of DataBase Part-1-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-Various Views of Data-Data Abstraction-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento4 pagine04-Various Views of Data-Data Abstraction-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 06Documento22 pagineComputer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 06Sadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- 09-OverView of Data Models-Object Oriented Data MOdel-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocumento2 pagine09-OverView of Data Models-Object Oriented Data MOdel-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Models: Answers To Review QuestionsDocumento13 pagineData Models: Answers To Review QuestionsRosh SibalNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 08Documento43 pagineComputer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 08Sadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 07Documento24 pagineComputer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 07Sadaf RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 6 Special - Properties of MatterDocumento9 pagineScience 6 Special - Properties of MatterAxcyl Volleybolista PremaylonNessuna valutazione finora
- 077 Mining Challenge at El SoldadoDocumento6 pagine077 Mining Challenge at El SoldadoKenny CasillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bartec Enclosure B201167 - 1EDocumento6 pagineBartec Enclosure B201167 - 1EsilvioNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Schedule Template 05Documento7 pagineConstruction Schedule Template 05bharat gadaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Yagi Antenna Design For The ExperimenterDocumento9 pagineBasic Yagi Antenna Design For The ExperimenterKrista JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts Catalog: This Catalog Gives The Numbers and Names of Parts On This MachineDocumento39 pagineParts Catalog: This Catalog Gives The Numbers and Names of Parts On This MachinePericoNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Vibration Chapter03Documento130 pagineAdvanced Vibration Chapter03Alooy MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Broadcast BillDocumento22 pagineBroadcast BillLidwin SoundariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Office 2003Documento41 pagineMicrosoft Office 2003Jas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationDocumento6 pagineExp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationlovehopeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Spring-And-Lever Balancing Mechanism, George Carwardine and The Anglepoise LampDocumento8 pagineThe Spring-And-Lever Balancing Mechanism, George Carwardine and The Anglepoise Lampmg504Nessuna valutazione finora
- Charpy Impact Test - STP 1072Documento219 pagineCharpy Impact Test - STP 1072biancogallazzi100% (3)
- MCQs On Queue With AnswersDocumento7 pagineMCQs On Queue With AnswersBabuLalSainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calibration InstrumnetDocumento14 pagineCalibration InstrumnetDwi Mulyanti DwimulyantishopNessuna valutazione finora
- Rohit Bebarta CVDocumento1 paginaRohit Bebarta CVRohit BebartaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear StressDocumento8 pagineShear StressRommel Carlo LargadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nse Past Questions and AnswersDocumento10 pagineNse Past Questions and Answersadesloop85% (13)
- 7.0 Configuration Guide en USDocumento395 pagine7.0 Configuration Guide en USakdenizerdemNessuna valutazione finora
- Web Pacs Viewer 2008Documento68 pagineWeb Pacs Viewer 2008Devair VieiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Fundamentals Questions and Answers - Application SoftwaresDocumento3 pagineComputer Fundamentals Questions and Answers - Application SoftwaresSANDIP ROYNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Thermal Design of Heat Ex ChangersDocumento530 pagineAdvances in Thermal Design of Heat Ex ChangersBabbare Voltaire100% (3)
- S BlockDocumento27 pagineS BlockAditya BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- AmarnathDocumento26 pagineAmarnathsandeshasNessuna valutazione finora
- SchedulingDocumento41 pagineSchedulingBeing VikramNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel Wire Mesh and Wire ClothDocumento3 pagineStainless Steel Wire Mesh and Wire ClothStela LjevarNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspen Manual v11.1Documento112 pagineAspen Manual v11.1api-3750488100% (6)
- 00001Documento14 pagine00001LuhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Frs 3.4.0f 05-31-11Documento467 pagineFrs 3.4.0f 05-31-11SRKNessuna valutazione finora
- ZbirkicaDocumento520 pagineZbirkicaVladimir MilovanovicNessuna valutazione finora