Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Eye Emergencies
Caricato da
saemed0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
67 visualizzazioni25 pagineeye emergency wec
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoeye emergency wec
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
67 visualizzazioni25 pagineEye Emergencies
Caricato da
saemedeye emergency wec
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 25
Eye Emergency
Eye emergencies are over
5% of all emergency
presentation
Copyright, 1996 © Dale Carnegie &
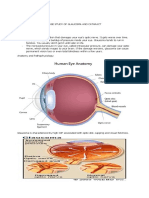
Assessment of intra ocular
damage
• Obtain accurate history
• Ask about vision
• Test for visual acuity
• Examine eye for redness
• Test pupil response to direct light
• Assess movement, reflex and visual field
Hyphaema
• Exclude foreign body
• Dilation of pupil affected eye
• Antibiotic drops
• Use slit lamp to examine whole eye
• Whenever local anaesthetic used in Ed, pad eye
for protection for few hours
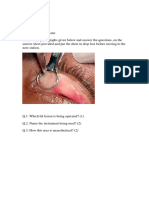
CORNEAL ABRASIONS
Corneal abrasions result from
scratch/injury to eye
Eye red, painful and watering
Blepharospasm
May have sensation to F.B.
CONTACT LENS
ABRASIONS
• Contact lense wearer has bilateral,
large shallow abrasions. Caused by
wearing hard lens in hot dry smoky
environment.
• Manage as for corneal abrasions
SUBTARSAL FOREIGN
BODY
• Foreign material lodge under conjunctival
sac
• Eye red, watering
• Pain and Blepharospasm
• Pain on blinking
• Linear scratches to superior cornea suggests
subtarsal foreign body
•Foreign Bodies in eye
• Red, painful watering eye
• Blepharospasm (local anaesthetic)
• Vision may be blurred
• Anaesthetized cornea r/o with
cotton bud/needle
•ARC EYE
• Welder, skier or ultraviolet bather has
inadequate eye protection
• Both eyes affected
• Eyes painful, red weeping.
• Blepharospasm resembles FB
• Instill local, dilate pupil, AB’s, eye pad
• Settles 48 hrs
CHEMICAL SPLASHES
• Chemicals cause inflammation conjunctiva,
or corneal burn
• Painful, red watery eye
• Alkalis may cause penetrating eye injury
• Irrigate eye 1Litre normal saline
• Antibiotics
PENETRATING EYE
INJURIES
• Deep penetrating injuries are difficult to identify and
not very painful.
• Caused by hammer, chisel, glass, machinery, high
pressure water jet
• Hyphaema, prolapse intra ocular contents, distortion of
pupil= poor outcomes.
• Use Fluorescein,xray, need surgery.
• Avoid pressure on eyeball, coughing, straining because
can dislodge intro ocular structures
SEVERE BLUNT TRAUMA
TO EYE
• Sport injury- football, golf and squash
• Surgery
• Avoid pressure, coughing and straining
Blunt trauma cont
• Hyphaema: Blood in anterior chamber.
• Traumatic mydriasis i.e fixed dilated pupil
• Dislocation of lens may cause cataract
• Posterior segment injuries-sudden reduction visual
acuity- tears, haemorrhage and detachment.
• SUBJUNCTIVAL HAEMORRHAGE
• Post trauma, common and
triviallook for conjunctival
lacerations, orbital and retro orbital
lacerations
CORNEAL ULCERS
• Dendritic Ulcers (herpes simplex)
• Eye red photophobic
• Branching ulcer stains fluorscein
• Treat acyclovir
• Bacterial Corneal Ulcers
• Chronic corneal disease
TIP
Develop transitions or
• Eye red painful and opaque bridges between key points.
UVEITIS IRITIS
• Idiopathic inflammation of ant.intro ocular structures
• Reoccurs in young with p/h anklosing spondylitis
• Painful red tender eye with photophobia
• Adhesions between lens and pupillary margin.
• Anaesthetic, surgery
GLAUCOMA
Overflow aqueous humor into ant chamber of eye
increases IOP.
Red painful tender eye
Visual loss
Semi dilated ovoid pupil non reacting
Corneal Haze from oedema N & v
MARGINAL KERATITIS
• Red injected eye with photophobia
• Small white patches with cornea
close to limbus not responsive to
fluorescein.
• Inflammatory infiltrates
• treat by bring to next eye clinic
RED EYE
• Infective conjunctivitis many
causes, bilateral, eye red and gritty
can be viral or bacterial
• Ocular conditions not improved
within 24 hours need specialist
opinion.
RED EYE cont.
• Allergic Conjunctivitis. Caused by exposure
to plants, eye drops, or other allergens
associated with atopy.
• Puffy red eye, lid swelling and conjunctival
oedema. Irritating not painful
• Treat by r/o cause. Vasoconstrictor and
antihistamines
Red Eye cont.
• Acute conjunctival oedema.
• Common in kids cause by allergy
• Balloon eye
• Treat by vasoconstrictor
ORBITAL CELLULITIS
• Common in kids caused by infection
eyelid or sinus.
• Eye red and puffy, swelling
• Treat by admit and iv ab
EYELIDS
• BLEPHAROSPASM- spasm of muscles
which close the eye indictative of
problem.use anaesthetic drops
• Blepharitis inflammation of eye lids
• Treat with ab and bath eyelids
• Lumps on eyelids (Meibomian cysts)
• Topical antibiotics
SUDDEN LOSS OF VISION
• Retinal detachment- vision loss like
a curtain, flashing lights. Detached
retina looks dark (black hole).
Associated severe short sightedness
• Retinal venous occlusion- loss of
vision bleed in retina in defined
area. Common in aged persons
SUDDEN LOSS VISION
(cont)
• Retinal arterial occlusion-acute
unilateral vision loss. Pale ischaemic
retine with cherry spot at macula and
swollen optic disc. Associated with
temporal arteritis. Blindness after hour.
• Migrane may cause distortion and vision
loss
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Visual Acuity: Presented By: Kartik Kumar Gupta G. Bhavani Reddy BV (Du) MC School of Optometry-2 YearDocumento61 pagineVisual Acuity: Presented By: Kartik Kumar Gupta G. Bhavani Reddy BV (Du) MC School of Optometry-2 Yearkartik GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Point Examination Translation Guide: Descriptive Name # Target CommentsDocumento1 pagina21 Point Examination Translation Guide: Descriptive Name # Target CommentsANDREW OMAKANessuna valutazione finora
- 2005 Clinical Importance of LOCS III in Phacoemulsification - Bencic PDFDocumento4 pagine2005 Clinical Importance of LOCS III in Phacoemulsification - Bencic PDFMauVeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Eyesight Naturally - FREE Eye Relaxation TechniquesDocumento4 pagineImproving Eyesight Naturally - FREE Eye Relaxation Techniquessnezha100% (16)
- Watery Eye: Magdy Fawzy $ Taha Sarhan Prof of OphthalmologyDocumento93 pagineWatery Eye: Magdy Fawzy $ Taha Sarhan Prof of OphthalmologymiemednoteNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxic Anterior Segment SyndromeDocumento13 pagineToxic Anterior Segment SyndromePrathibha M ChachadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Eyes and VisionDocumento8 pagineAssessment of The Eyes and Visionmary krisNessuna valutazione finora
- Case SheetDocumento5 pagineCase SheetvisweswarkcNessuna valutazione finora
- Pearls Nov Dec 2010Documento3 paginePearls Nov Dec 2010Nhật LongNessuna valutazione finora
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocumento5 pagineGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento6 pagineReferencesAndrew MakariosNessuna valutazione finora
- JFF..H, .R) : B.'FT-F ......................Documento1 paginaJFF..H, .R) : B.'FT-F ......................rehanNessuna valutazione finora
- STD NBHDocumento76 pagineSTD NBHerpNessuna valutazione finora
- The Red Eye Challenge: QuestionsDocumento5 pagineThe Red Eye Challenge: QuestionsDaniel CrookNessuna valutazione finora
- Rose K2 XL Special OptionsDocumento4 pagineRose K2 XL Special Optionsreza arlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Short & Long Question PhysiologyDocumento2 pagineFinal - Short & Long Question Physiologykikukiku728Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Nerve Examination OSCE GuideDocumento26 pagineCranial Nerve Examination OSCE GuideAbdullah Basheer AL-AnaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Myopia Control: A Review: Jeffrey J. WallineDocumento6 pagineMyopia Control: A Review: Jeffrey J. WallineChristine Yohana SianturiNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Ospe-1Documento68 pagineEye Ospe-1noorNessuna valutazione finora
- Capsular Tension Rings:: Current Indications and OutcomesDocumento12 pagineCapsular Tension Rings:: Current Indications and OutcomesShahid ManzoorNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Eye: BY Steffy Agnes .V.B Natural ScienceDocumento33 pagineThe Human Eye: BY Steffy Agnes .V.B Natural ScienceSteffy100% (1)
- 04 - Assessment of Eyes & EarsDocumento62 pagine04 - Assessment of Eyes & Earsisrar88990% (1)
- Measuring Contrast Sensitivity Using The M&S Smart System II Versus The Pelli-Robson ChartDocumento3 pagineMeasuring Contrast Sensitivity Using The M&S Smart System II Versus The Pelli-Robson ChartRaissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcon AcrySof IQ Lens ImplantDocumento2 pagineAlcon AcrySof IQ Lens ImplantAbdelmonem HamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Log Book Final Year B. Optometry: Maharishi Markandeshwar UniversityDocumento4 pagineClinical Log Book Final Year B. Optometry: Maharishi Markandeshwar UniversityHarshitNessuna valutazione finora
- Optic Disc Abnormalities - Cheat SheetDocumento6 pagineOptic Disc Abnormalities - Cheat SheetPaula EmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal ReadingDocumento4 pagineJurnal ReadingArum DiannitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Cataract Not FixedDocumento41 pagineCataract Not FixedDeasy MirayashiNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Announcement INAVRS Meeting 2023 INANOS IOASDocumento2 pagineSecond Announcement INAVRS Meeting 2023 INANOS IOASAndi Ayu LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Blindness in Indonesia: Farida SirlanDocumento41 pagineBlindness in Indonesia: Farida SirlannonawitaNessuna valutazione finora